Professional Documents
Culture Documents
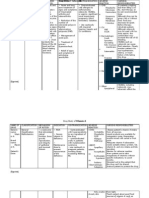
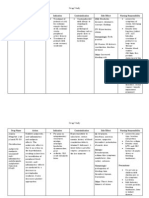
Drug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Uploaded by
TrojangBaboyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
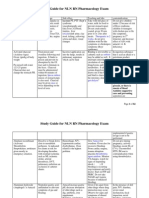
Drug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Uploaded by
TrojangBaboyCopyright:
Available Formats
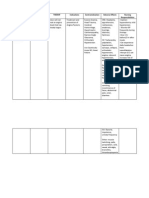
DRUG STUDY Generic Name/ Trade Name sodium chloride Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing
Responsibilities
1 Tab TID 8am 1pm 6pm
prophylaxis of heat prostration or muscle cramps; chloride deficiency due to dieresis or salt restrictions; prevention or treatment of extracellular volume depletion
congestive heart failure, severely impaired renal function, hypernatremia, fluid retention
hypernatremia, hypopotassemia, acidosis. Fluid and solute overload leading to dilution of serum electrolyte level, CHF, overhydration, acute pulmonary edema
a. Monitor electrolytes, ECG, liver and renal function studies b. Note level of consciousness c. Assess the heart and lung sounds d. Observe S&S of hypernatremia, flushed skin, elevated temperature, rough dry tongue, and edema e. Monitor VS and I&O f. Assess urine specific gravity and serum sodium levels
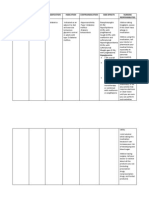
Enalapril Maleate
5 mg/ tab 1 tab OD
Treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other antihypertensives, especially thiazide-type diuretics Treatment of acute and chronic CHF Treatment of asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) Unlabeled use: Diabetic nephropathy
Contraindicated with allergy to enalapril. Use cautiously with impaired renal function; salt or volume depletion (hypotension may occur); lactation, pregnancy.
CNS: Headache, dizziness, fatigue, insomnia, paresthesias CV: Syncope, chest pain, palpitations, hypotension in salt- or volume-depleted patients GI: Gastric irritation, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, elevated liver enzymes GU: Proteinuria, renal insufficiency, renal failure, polyuria, oliguria, urinary frequency, impotence Hematologic: Decreased hematocrit and hemoglobin Other: Cough, muscle cramps, hyperhidrosis
Monitor patients on diuretic therapy for excessive hypotension after the first few doses of enalapril. Monitor patient carefully because peak effect may not be seen for 4 hr. Do not administer second dose until BP has been checked.
Aspirin
80 g 1 Tab OD 1PM
Mild to moderate pain Fever Inflammatory conditionsrheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Reduction of risk of recurrent TIAs or stroke in males with history of TIA due to fibrin platelet emboli Reduction of risk of death or nonfatal MI in patients with history of infarction or unstable angina pectoris MI prophylaxis Unlabeled use: Prophylaxis against cataract formation with long-term use
Allergy to salicylates or NSAIDs (more common with nasal polyps, asthma, chronic urticaria); allergy to tartrazine (cross-sensitivity to aspirin is common); hemophilia, bleeding ulcers, hemorrhagic states, blood coagulation defects, hypoprothrombinemia, vitamin K deficiency (increased risk of bleeding) Use cautiously with impaired renal function; chickenpox, influenza (risk of Reye's syndrome in children and teenagers); children with fever accompanied by dehydration; surgery scheduled within 1 wk; pregnancy (maternal anemia, antepartal and postpartal hemorrhage, prolonged gestation, and prolonged labor have been reported; readily crosses the placenta; possibly teratogenic; maternal ingestion of aspirin during late pregnancy has been associated with the following adverse fetal effects: low birth weight, increased intracranial hemorrhage, stillbirths, neonatal death); lactation.
Acute aspirin toxicity: Respiratory alkalosis, hyperpnea, tachypnea, hemorrhage, excitement, confusion, asterixis, pulmonary edema, seizures, tetany, metabolic acidosis, fever, coma, CV collapse, renal and respiratory failure (dose related 2025 g in adults, 4 g in children) Aspirin intolerance: Exacerbation of bronchospasm, rhinitis (with nasal polyps, asthma, rhinitis) GI: Nausea, dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric discomfort, anorexia, hepatotoxicity Hematologic: Occult blood loss, hemostatic defects Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactoid reactions to anaphylactic shock Salicylism: Dizziness, tinnitus, difficulty hearing, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mental confusion, lassitude (dose related)
Give drug with food or after meals if GI upset occurs. Give drug with full glass of water to reduce risk of tablet or capsule lodging in the esophagus. Do not crush, and ensure that patient does not chew sustained-release preparations. Do not use aspirin that has a strong vinegar-like odor. Report ringing in the ears; dizziness, confusion; abdominal pain; rapid or difficult breathing; nausea, vomiting.
Isosorbide mononitrate
30 g OD 8AM
Isosorbide mononitrate is used to prevent chest pain in patients with a heart condition known as angina.
Immediate Release Tablets: Allergic reactions to organic nitrates are extremely rare, but they do occur. Isosorbide mononitrate is contraindicated in patients who are allergic to it. Extended Release Tablets: Isosorbide mononitrate extended release tablets are contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity or idiosyncratic reactions to other nitrates or nitrites.
This can cause dizziness and lightheadedness when standing quickly and during the first days of therapy. This medication can cause headache which also indicates the drug is working. These headaches are relieved with aspirin or acetaminophen. For this drug to be most effective it should be taken as prescribed, separating doses by 7 hours. Missed doses should not be doubled up.
Patients should be told that the antianginal efficacy of Isosorbide Mononitrate Extended-Release Tablets can be maintained by carefully following the prescribed schedule of dosing. For most patients, this can be accomplished by taking the dose on arising.
In patients who get these headaches, the headaches are a marker of the activity of the drug. Patients should resist the temptation to avoid headaches by altering the schedule of their treatment with Isosorbide Mononitrate,
You might also like
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Feu NRMF IcuDocument9 pagesDrug Study Feu NRMF IcuAnne Genesis V. PinedaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug General Action Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageName of Drug General Action Specific Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesNicole SooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Francisco Tampos JRDocument37 pagesDrug Study: Francisco Tampos JRCarlmeister Ambray JudillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Document9 pagesDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument4 pagesDrug Study ICUArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine BesylateDocument7 pagesAmlodipine BesylatebabuagoodboyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine Classifications: Therapeutic: Antiasthmatics, Bronchodilators, Vasopressors Pharmacologic: Adrenergics IndicationsDocument14 pagesEpinephrine Classifications: Therapeutic: Antiasthmatics, Bronchodilators, Vasopressors Pharmacologic: Adrenergics IndicationsLindy Shane BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument21 pagesIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Propranolol Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesPropranolol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Drug Study ArvinDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101No ratings yet
- Aspirin: Anticoagulants Antiplatelets & Fibronolytic (Thrombolytics) Nonsteroid Anti-Inflamatory Drugs (Nsaids)Document3 pagesAspirin: Anticoagulants Antiplatelets & Fibronolytic (Thrombolytics) Nonsteroid Anti-Inflamatory Drugs (Nsaids)Acuña MonalyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument64 pagesPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKynaWeeNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- CNS: GI: Assessment & Drug Effects: Generic Name Brand Name Indications Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesCNS: GI: Assessment & Drug Effects: Generic Name Brand Name Indications Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJon Adam Bermudez SamatraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- Fosinopril SodiumDocument3 pagesFosinopril Sodiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Index Updated2Document113 pagesDrug Index Updated2tam meiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Definitions OF DiagnosisDocument25 pagesDefinitions OF DiagnosisGlaire ZarateNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyrocketwapNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Amplodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmplodipine Drug StudyRai HanahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mnemonics for Medicine: Differential Diagnoses and Other PearlsFrom EverandMnemonics for Medicine: Differential Diagnoses and Other PearlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Oblefias, Kevin P.: Art AppreciationDocument1 pageOblefias, Kevin P.: Art AppreciationTrojangBaboyNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program of ImmunizationDocument3 pagesExpanded Program of ImmunizationTrojangBaboyNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentDocument42 pagesDevelopmentSheikh Muhammad ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Data Levels of MeasurementDocument2 pagesData Levels of MeasurementTrojangBaboy100% (1)
- CSR Final Exam CaseDocument1 pageCSR Final Exam CaseTrojangBaboyNo ratings yet
- RMK Akl 2 Bab 5Document2 pagesRMK Akl 2 Bab 5ElineNo ratings yet
- Tiny House 2020: Less House, More HomeDocument11 pagesTiny House 2020: Less House, More HomeVanshika SpeedyNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networks Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesData Communication and Networks Syllabus PDFgearlaluNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation IDocument21 pagesHeredity and Variation Ismbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Sample Information For Attempted MurderDocument3 pagesSample Information For Attempted MurderIrin200No ratings yet
- Student's Lab Pack: Preteens 02 11 Weeks CourseDocument30 pagesStudent's Lab Pack: Preteens 02 11 Weeks CourseMi KaNo ratings yet
- NHD Process Paper 1Document2 pagesNHD Process Paper 1api-544229559No ratings yet
- C Programming Bit Bank U-1, U-2Document17 pagesC Programming Bit Bank U-1, U-2HariahNo ratings yet
- Tle9cookery q1 m7 Presentingandstoringarangeofappetizer v2Document30 pagesTle9cookery q1 m7 Presentingandstoringarangeofappetizer v2Almaira SumpinganNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Unit-8Document4 pagesDigital Image Processing Unit-8Kpsteja TejaNo ratings yet
- BM - GoPro Case - Group 6Document4 pagesBM - GoPro Case - Group 6Sandeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Masters Thesis Oral Reading For Masters in Education ST Xavier ED386687Document238 pagesMasters Thesis Oral Reading For Masters in Education ST Xavier ED386687Bruce SpielbauerNo ratings yet
- Fume Cup BrochureDocument2 pagesFume Cup Brochuremfisol2000No ratings yet
- Danmachi Volume 15Document319 pagesDanmachi Volume 15Muhammad Fazrul Rahman100% (1)
- Joker Pattern PDF New PDFDocument7 pagesJoker Pattern PDF New PDFLorena CapogrossiNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools Design: InstructorsDocument31 pagesMachine Tools Design: InstructorsAladdin AdelNo ratings yet
- Eastwoods: College of Science and Technology, IncDocument2 pagesEastwoods: College of Science and Technology, IncMichael AustriaNo ratings yet
- Trabajos de InglésDocument6 pagesTrabajos de Inglésliztmmm35No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Design: Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.2.3Document6 pagesLesson Plan Design: Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.2.3api-323520361No ratings yet
- Fruit LeathersDocument4 pagesFruit LeathersAmmon FelixNo ratings yet
- MSPM Clark UniversityDocument27 pagesMSPM Clark Universitytushar gargNo ratings yet
- Savage Cyberpunk 2020Document14 pagesSavage Cyberpunk 2020dmage_uNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument3 pagesJournalJuvz BezzNo ratings yet
- The Fat Cat Called PatDocument12 pagesThe Fat Cat Called PatAlex ArroNo ratings yet
- Aporte Al IPSS Del Empleador Por TrabajadorDocument4 pagesAporte Al IPSS Del Empleador Por Trabajadorvagonet21No ratings yet
- Flex Design Guide - 2020 DigitalDocument15 pagesFlex Design Guide - 2020 Digitalzahi xddNo ratings yet
- Song FlowDocument4 pagesSong FlowEhij ZheyNo ratings yet
- Main Book LR X PDFDocument192 pagesMain Book LR X PDFjay danenjeyanNo ratings yet
- SH Case3 Informants enDocument1 pageSH Case3 Informants enHoLlamasNo ratings yet
- Articles On Philippine Obligation and ContractsDocument114 pagesArticles On Philippine Obligation and ContractsKriz Batoto100% (1)