Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adjustable Speed Drives Save Energy & Provide Smoother Operation
Uploaded by
Aditya MahajanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adjustable Speed Drives Save Energy & Provide Smoother Operation
Uploaded by
Aditya MahajanCopyright:
Available Formats
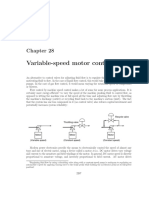
Adjustable speed drive (ASD) or variable-speed drive (VSD) describes equipment used to control the speed of machinery.
Many industrial processes such as assembly lines must operate at different speeds for different products. Where process conditions demand adjustment of flow from a pump or fan, varying the speed of the drive may save energy compared with other techniques for flow control. Where speeds may be selected from several different pre-set ranges, usually the drive is said to be adjustable speed. If the output speed can be changed without steps over a range, the drive is usually referred to as variable speed. Adjustable and variable speed drives may be purely mechanical (termed variators), electromechanical, hydraulic, or electronic The following are process control benefits that might be provided by an adjustable speed drive:
Smoother operation Acceleration control Different operating speed for each process recipe Compensate for changing process variables Allow slow operation for setup purposes Adjust the rate of production Allow accurate positioning Control torque or tension
[edit] Example
An adjustable speed drive can often provide smoother operation compared to an alternative fixed speed mode of operation. For example, in a sewage lift station sewage usually flows through sewer pipes under the force of gravity to a wet well location. From there it is pumped up to a treatment process. When fixed speed pumps are used, the pumps are set to start when the level of the liquid in the wet well reaches some high point and stop when the level has been reduced to a low point. Cycling the pumps on and off results in frequent high surges of electric current to start
the motors resulting in electromagnetic and thermal stresses in the motors and power control equipment, the pumps and pipes are subjected to mechanical and hydraulic stresses, and the sewage treatment process is forced to accommodate surges in the flow of sewage through the process. When adjustable speed drives are used, the pumps operate continuously at a speed that increases as the wet well level increases. This matches the outflow to the average inflow and provides a much smoother operation of the process.
[edit] Saving energy by using adjustable speed drives
An adjustable speed drive often uses less energy than an alternative fixed speed mode of operation. Fans and pumps are the most common energy saving applications. When a fan is driven by a fixed speed motor, the airflow may sometimes be higher than it needs to be. Airflow can be regulated by using a damper to restrict the flow, but it is more efficient to regulate the airflow by regulating the speed of the motor. It follows from the affinity laws that reducing fan speed to 50% results in a power consumption drop to 12.5%.[2]
[edit] Types of adjustable speed drives
Speed adjustment techniques have been used in transmitting mechanical power to machinery since the earliest use of powered machinery. Before electric motors were invented, mechanical speed changers were used to control the mechanical power provided by water wheels and steam engines. When electric motors came into use, means of controlling their speed were developed almost immediately. Today, various types of mechanical drives, hydraulic drives and electric drives compete with one another in the industrial drives market.
[edit] Mechanical adjustable speed drives
There are two types of mechanical drives, variable pitch drives and traction drives. Variable pitch drives are pulley and belt drives in which the pitch diameter of one or both pulleys can be adjusted. Traction drives transmit power through metal rollers running against mating metal rollers. The input/output speed ratio is adjusted by moving the rollers to change the diameters of the contact path. Many different roller shapes and mechanical designs have been used.
[edit] Hydraulic adjustable speed drives
There are three types of hydraulic drives, those are : hydrostatic drives, hydrodynamic drives and hydroviscous drives. A hydrostatic drive consists of a hydraulic pump and a hydraulic motor. Since positive displacement pumps and motors are used, one revolution of the pump or motor corresponds to a set volume of fluid flow that is determined by the displacement regardless of speed or torque. Speed is regulated by regulating the fluid flow with a valve or by changing the displacement of
the pump or motor. Many different design variations have been used. A swash plate drive employs an axial piston pump and/or motor in which the swash plate angle can be changed to adjust the displacement and thus adjust the speed. Hydrodynamic drives or fluid couplings use oil to transmit torque between an impeller on the constant-speed input shaft and a rotor on the adjustable-speed output shaft. The torque converter in the automatic transmission of a car is a hydrodynamic drive. A hydroviscous drive consists of one or more discs or connected to the input shaft pressed against a similar disc or discs connected to the output shaft. Torque is transmitted from the input shaft to the output shaft through an oil film between the discs. The transmitted torque is proportional to the pressure exerted by a hydraulic cylinder that presses the discs together.
You might also like
- Key Words:: Motion Control Is Required in Large No of Industrial and Domestic Applications LikeDocument11 pagesKey Words:: Motion Control Is Required in Large No of Industrial and Domestic Applications LikeVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- VFD SDocument25 pagesVFD Svasanth11kvNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Drives Lect8Document5 pagesHydrostatic Drives Lect8Rehan RashidNo ratings yet
- 074 Hydro Static TransmissionsDocument4 pages074 Hydro Static TransmissionsPrakash Chandrasekaran100% (1)
- Variable Frequency DriveDocument2 pagesVariable Frequency DriveDrazan GalusicNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machine PPTTDocument28 pagesHydraulic Machine PPTTFaisal SaifNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DrivesDocument11 pagesVariable Frequency DrivesLavanya VallbhareddyNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drives IntroductionDocument11 pagesVariable Frequency Drives Introductionvigneshwaranj87No ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drives Purchasing TipsDocument7 pagesVariable Frequency Drives Purchasing TipsMaintenance CircleNo ratings yet
- Improving industrial productivity through energy efficient VSDsDocument4 pagesImproving industrial productivity through energy efficient VSDssayed2846No ratings yet
- What Is A Variable Speed DriveDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Variable Speed DriveTerdy MNNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DriveDocument4 pagesVariable Frequency Drivearavind_k104No ratings yet
- Introduction About VFDDocument3 pagesIntroduction About VFDHuzaifa WasimNo ratings yet
- Designing optimal electro-hydraulic systemsDocument6 pagesDesigning optimal electro-hydraulic systemsJigar M. UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Industrial Drives: Types, Components, Control & ApplicationsDocument10 pagesIndustrial Drives: Types, Components, Control & ApplicationskicchasandeepNo ratings yet
- Speed DrivesDocument6 pagesSpeed DrivesMazen MohamedNo ratings yet
- DC and AC Motor ControlDocument6 pagesDC and AC Motor Controldes tosNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed Motor ControlsDocument1 pageVariable Speed Motor ControlsGohar Muhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 +Hydraulic+Actuators+-+BookDocument27 pages2 +Hydraulic+Actuators+-+BookmennatallahnoureldinNo ratings yet
- POE Lp3.2a Fluid Power IntroDocument32 pagesPOE Lp3.2a Fluid Power IntroPavitra AjagolNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Treatment Plants Are Used To Supply Purely Fresh Water To The EnvironmentDocument10 pagesFreshwater Treatment Plants Are Used To Supply Purely Fresh Water To The EnvironmentNguyen Huynh Tan Nguyen B2004405No ratings yet
- Variable Speed TechnologyDocument10 pagesVariable Speed Technologyashumishra007No ratings yet
- Pump Control With Variable Frequency Drives - Case Study: Hitachi America, Ltd.Document4 pagesPump Control With Variable Frequency Drives - Case Study: Hitachi America, Ltd.Hitachi America, Ltd., Industrial Components and Equipment DivisionNo ratings yet
- TM Unit 6Document5 pagesTM Unit 6eyobNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic and Electric DriveDocument25 pagesHydrostatic and Electric DriveJennsonFernandez50% (2)
- Closed Loop Hydraulic CircuitsDocument1 pageClosed Loop Hydraulic Circuitsandrija_ganzbergerNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors and Adjustable-Speed Drive Systems: 7.1 Energy ConservationDocument82 pagesInduction Motors and Adjustable-Speed Drive Systems: 7.1 Energy ConservationFer LopezNo ratings yet
- What Is A Variable Frequency Drive?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Variable Frequency Drive?Vinod GnanasekaranNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservationi N Pumps: M.V.Pande Dy - Director NPTI, NagpurDocument37 pagesEnergy Conservationi N Pumps: M.V.Pande Dy - Director NPTI, NagpurmvpngpNo ratings yet
- Variables PpedDocument24 pagesVariables PpedLuis LopezNo ratings yet
- Report PDFDocument14 pagesReport PDFNikhilVoodaNo ratings yet
- Variable TorqueDocument2 pagesVariable TorqueKrrishNo ratings yet
- Actuation SystemDocument11 pagesActuation SystemNavendu GuptaNo ratings yet
- VSD Benefits for Car Wash DryersDocument2 pagesVSD Benefits for Car Wash DryersMohamed Ayman Hefny MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Controls: Transmission Fluid Oil PumpDocument2 pagesHydraulic Controls: Transmission Fluid Oil PumpGary M TrajanoNo ratings yet
- ISA AW 2012 Control Valve Vs Variable Speed Drive PDFDocument10 pagesISA AW 2012 Control Valve Vs Variable Speed Drive PDFDavid Omar Torres GutierrezNo ratings yet
- V S DDocument17 pagesV S DveguruprasadNo ratings yet
- Guru Gobind Singh Polytechnic Nashik.: A Presentation OnDocument16 pagesGuru Gobind Singh Polytechnic Nashik.: A Presentation OnAmar Khandve100% (1)
- AC Adjustable Speed DriveDocument5 pagesAC Adjustable Speed DriveVENKATESAN RNo ratings yet
- Benefits of VSD SystemsDocument7 pagesBenefits of VSD Systemsalx 100No ratings yet
- Electromechanical ActuatorsDocument4 pagesElectromechanical ActuatorsMohammed Asif NNo ratings yet
- Danfoss HST Public Documents Web Content c022873Document8 pagesDanfoss HST Public Documents Web Content c022873Timon2005100% (1)
- Industrial Drives and ControlDocument10 pagesIndustrial Drives and ControlMohit SanandiyaNo ratings yet
- Vane Motor PresentationDocument16 pagesVane Motor PresentationJayesh BholeNo ratings yet
- B.E Mech - Regulations 2010 Fluid Power Systems Smex1022Document18 pagesB.E Mech - Regulations 2010 Fluid Power Systems Smex1022yuvaraja sNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power DME 6TH SEMDocument58 pagesFluid Power DME 6TH SEMAman Ahmed MokamiNo ratings yet
- 08 - Gvernor - 01Document7 pages08 - Gvernor - 01Aisha Zaheer100% (2)
- AC Adjustable Speed Drive ASD An OverviewDocument4 pagesAC Adjustable Speed Drive ASD An OverviewArnel Pascual LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Disk BrakeDocument8 pagesDisk Brakevivek sharmaNo ratings yet
- Study of Dynamometers: Lab Session No 12Document8 pagesStudy of Dynamometers: Lab Session No 12Faisal NaeemNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument41 pagesHydraulicsHoussam AssafNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorDocument27 pagesClosed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorRajesh kumar yadavNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics vs Hydraulics: A ComparisonDocument19 pagesPneumatics vs Hydraulics: A ComparisonGebBerheNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4actuation System For MechatronicsDocument62 pagesPresentation 4actuation System For MechatronicswabdushukurNo ratings yet
- A Second Look at ElectroDocument7 pagesA Second Look at ElectroPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology-Synchronous Motor ApplicationsDocument2 pagesElectrical Technology-Synchronous Motor ApplicationsAnoop MathewNo ratings yet
- Misc. Fluid MachinesDocument17 pagesMisc. Fluid MachinesJyotikrishna Gautam0% (1)
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideFrom EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Chemical Engineer CVDocument2 pagesChemical Engineer CVAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- CHWDocument1 pageCHWAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps: Training Program at Petronet LNGDocument30 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: Training Program at Petronet LNGAditya Mahajan100% (1)
- Mobile Phone Purchase InvoiceDocument1 pageMobile Phone Purchase InvoiceAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- Kirloskar Pneumatic Co. Ltd. Specification Sheet: PUNE 411 013Document1 pageKirloskar Pneumatic Co. Ltd. Specification Sheet: PUNE 411 013Aditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- 3-Tp-18 Ln2 Tie inDocument13 pages3-Tp-18 Ln2 Tie inAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- 05 - PumpsDocument80 pages05 - PumpsAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- Avoid Cavitation in Centrifugal PumpsDocument8 pagesAvoid Cavitation in Centrifugal PumpsAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- VaporizersDocument21 pagesVaporizersAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- AbcDocument3 pagesAbcAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- AbcDocument3 pagesAbcAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- Know His Plan", That Is The First Step in Accepting Our Destiny. Maharaj Said, "Once WeDocument4 pagesKnow His Plan", That Is The First Step in Accepting Our Destiny. Maharaj Said, "Once WeAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- BP's Big Green Train:: Benchmarking Next Generation LNG Plant DesignsDocument9 pagesBP's Big Green Train:: Benchmarking Next Generation LNG Plant DesignsAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument38 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Design of Plant For Sulphur Recovery Unit Using Super Claus ProcessDocument3 pagesProject Report On Design of Plant For Sulphur Recovery Unit Using Super Claus ProcessAditya Mahajan0% (1)
- MethaneDocument10 pagesMethaneAditya MahajanNo ratings yet
- HA472742 Iss6 AC-DC CatalogDocument118 pagesHA472742 Iss6 AC-DC CatalogUmesh ChandavathNo ratings yet
- Accessories For Frequency Inverter 1dd65Document7 pagesAccessories For Frequency Inverter 1dd65appinassociatesNo ratings yet
- Grundfos CR 15 6 A F A e HqqeDocument11 pagesGrundfos CR 15 6 A F A e HqqeRoat MechNo ratings yet
- Atv 61Document62 pagesAtv 61Сања БанковићNo ratings yet
- Edwards EDC Dry Claw Pumps Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesEdwards EDC Dry Claw Pumps Brochure PDFPete PompesNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Energy Efficiency SolutionsDocument12 pagesSchneider Electric Energy Efficiency SolutionsSargurusivaNo ratings yet
- FBC BOILER BIOMASS FUELSDocument2 pagesFBC BOILER BIOMASS FUELSsvprabhu123No ratings yet
- R5410202 Power Semiconductor DrivesDocument1 pageR5410202 Power Semiconductor DrivessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Vorecon Applications PDFDocument46 pagesVorecon Applications PDFlancasaNo ratings yet
- Actom DTRDocument8 pagesActom DTRVikram BorawakeNo ratings yet
- PE Presentation-Corporate - Low ResDocument66 pagesPE Presentation-Corporate - Low Resshashank715No ratings yet
- 3 Phase Induction Motor StarterDocument28 pages3 Phase Induction Motor StarterDivanshu GargNo ratings yet
- Mentor IIDocument114 pagesMentor IIHòa Trịnh0% (1)
- Efficiency Solutions For Motor-Driven SystemsDocument12 pagesEfficiency Solutions For Motor-Driven SystemsAMER MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- Flow Control August 2012 PDFDocument53 pagesFlow Control August 2012 PDFRichard YentumiNo ratings yet
- Catalogue ATV11 EN PDFDocument25 pagesCatalogue ATV11 EN PDFfdez_aNo ratings yet
- VariadoresDocument412 pagesVariadoresDannyNo ratings yet
- WEG Cfw11 System Drive EngDocument28 pagesWEG Cfw11 System Drive EngRICHARDNo ratings yet
- Max - E2: Low Voltage 3-Phase Induction Motors 0.18kW To 185kWDocument36 pagesMax - E2: Low Voltage 3-Phase Induction Motors 0.18kW To 185kWOmprakash_janaNo ratings yet
- Pump EffDocument15 pagesPump Effawhk2006No ratings yet
- GR Compact RDocument4 pagesGR Compact RHeri SulasionoNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument103 pagesPumpsKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - 1 AimDocument19 pagesExperiment No - 1 Aimvishwas agarwalNo ratings yet
- AC Motors, Motor Control and Motor ProtectionDocument25 pagesAC Motors, Motor Control and Motor Protectionwira eka0% (1)
- What's The Difference Between DOL Start, Star-Delta, Soft Starter and A Variable Speed Drive?Document1 pageWhat's The Difference Between DOL Start, Star-Delta, Soft Starter and A Variable Speed Drive?asdthuNo ratings yet
- Success QpsDocument15 pagesSuccess QpsLim ChsNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Plant (Engineering Plant Technology) 2014Document11 pagesCompressed Air Plant (Engineering Plant Technology) 2014Nadhyyra ZainolNo ratings yet
- Atv32 PDFDocument40 pagesAtv32 PDFRavi NegiNo ratings yet
- VSDDocument16 pagesVSDRICHARDNo ratings yet
- ABB Motors - General Purpose 3Document45 pagesABB Motors - General Purpose 3Vilius BukysNo ratings yet