Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Business 16 BUS101: Chapter 21: Accounting Fundamentals
Uploaded by
nahidul202Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Business 16 BUS101: Chapter 21: Accounting Fundamentals
Uploaded by
nahidul202Copyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
CHAPTER 21: ACCOUNTING FUNDAMENTALS
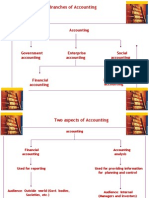
Layout of Chapter: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. What is Accounting Types of Accountants The Accounting Cycle The Accounting Equation Analyzing Financial Statements WHAT IS ACCOUNTING
The process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed decisions by users of the information. 2. TYPES OF ACCOUNTANT
Based on the type of Certification: CPA (Certified Public Accountant) (i.e. chartered accountant of Bd) CMA (Certified Management Accountant) also classified as: Public Accountant Private Accountant 3. ACCOUNTING CYCLE
The steps - analyzing, recording, posting and preparing records - by which the results of the business transactions are communicated. Journal Account General Ledger Financial Statement 4. THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity This indicates a companys financial position at any point in time.
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
East West University
INCOME STATEMENT
For the year ended December 31, 2003 Details Gross Sales Less: Sales discounts Sales returns Net Sales Less: Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Gross profit Less: Selling and Administrative expenses (Advertising, salary, rent, utility, insurance, depreciation, transportation) EBIT (Earning Before Interest and Tax) Less: Interest expense EBT (Earning Before Tax) Less: Tax Net Income/ (Loss) (165) 430 ( 85) 345 (100) 245 25 35 ( 60) 940 (345) 595 $ $ 1000
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
EAST WEST UNIVERSITY
BALANCE SHEET
As at December 31, 2003 Details ASSETS a) Currents Assets Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Total current Assets b) Fixed Assets Land Building Machinery and Equipment Furniture and Fixtures Total Fixed Assets TOTAL ASSETS LIABILITIES a) Current Liabilities Accounts Payable Short-term bank loan Total Current Liabilities b) Long-term Liabilities Notes Payable Long-term bank loan Total Long-term liabilities TOTAL LIABILITIES OWNERS EQUITY Capital Stock Retained Earnings Add Current Years Profit TOTAL OWNERS EQUITY TOTAL LIABILITIES + EQUITY 5. ANALYZING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS $ $
495 150 175 820 500 250 100 100 950 1770
125 175 300 425 225 650 950 325 250 245 820 1770
Ratio Analysis: Methods of analyzing financial information by comparing logical relationships between various financial statement items. 1. Liquidity Ratio: Measure of a firms ability to pay its short-term debts as they come due.
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
a) Current Ratio measures the firms ability to pay off current liabilities from its current assets.
Current Ratio = Current Current Assets Liabilitie s
b) Quick Ratio
Quick Ratio = Qucik Current Assets Liabilitie s
*Where quick asset = Total Current Assets Inventory {When Ratio is 1:1 then it is adequate} 2. Activity Ratio: Measure of how efficiently assets are being used to generate revenue. a) Accounts Receivable Turnover
Accounts Re ceivable Turnover = Net Net Sales Re ceivable
Accounts
b) Number of Days Sales in Receivable.
# Days Sales in Re ceivable = # of Days in Year Account Re ceivable Turnover
3. Profitability Ratio: Financial Performance a) Return on Sales Re turn on Sales = (Average is 5%) b) Return on Equity
Re turn on Equity = Net Income =% Equity
Net Income Net Sales
=%
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
This Ratio measures the return company earns on every taka of shareholders (owners) investments. 4. Debt Ratio: Ability to pay long-term debts. a)
Debt to Total Assets Ratio Equity =
b)
Time Interest Earned = EBIT
Total Liabilitie s Total Assets
Interest Expense
EBIT = Earnings before Interest & Tax
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
PRACTICE ACCOUNTING PROBLEM 1. Dhaka Ltd. exports CK shirts to USA. Use the following information to prepare a) b) An Income Statement for the year ended on 31 December 2001; A Balance Sheet as on 31 December 2001. (All figures are in Bangladeshi Taka) Advertising expense Utility Income Tax Accounts payable (A/P) Cost of goods sold Transportation Interest Expense Accounts receivable Land Machinery Long-term loan Answer: Net Income Total Assets Total Liabilities & Owners Equity Tk. 20,000 Tk.1,92,500 Tk.1,92,500 1,500 5,000 1,600 12,000 15,000 1,300 2,400 15,000 50,000 20,000 40,000 Building Capital stock Rent Salary Sales returns Insurance Wages Cash Inventory Notes payable Gross Sales Short-term loan 30,000 80,000 3,600 6,000 1,000 600 2,000 60,000 17,500 20,000 60,000 19,000
Retained Earnings (Dec. 31) 1,500
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
Not all the information is required for various calculations. One has to identify which bit of information is required for what calculation. For Income Statement, only the information which is directly related to Revenue, Expenses, Interest and Tax is needed. For Balance Sheet, you need to isolate the data regarding Assets (Current & Fixed), Liabilities (Short-term & Long-term), and Equity Capital & Retained Earnings. (Figures needed in Income Statement) Gross Sales Sales returns Cost of goods sold Advertising expense Utility Rent Salary Insurance Transportation Wages Interest Expense Income Tax (Figures needed in Balance Sheet) Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Land Machinery Building Accounts payable (A/P) Short-term loan 60,000 15,000 17,500 50,000 20,000 30,000 12,000 19,000 60,000 1,000 15,000 1,500 5,000 3,600 6,000 600 1,300 2,000 2,400 1,600
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
Notes payable Long-term loan Capital stock Retained Earnings (Dec. 31)
20,000 40,000 80,000 1,500
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
Dhaka Ltd.
INCOME STATEMENT
For the year ended Dec. 31, 2003 Gross Sales Less: Sales returns Net Sales Cost of goods sold Gross Profit Less: Selling & Administrative Expenses Advertising expense Utility Rent Salary Insurance Transportation Wages EBIT (Earnings before Interest & Tax) Less: Interest Expense EBT (Earnings before Tax) Less: Income Tax Net Profit 1,500 5,000 3,600 6,000 600 1,300 2,000 (20,000) 24,000 (2,400) 21,600 (1,600) 20,000 60,000 (1,000) 59,000 (15,000) 44,000
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
Dhaka Ltd.
BALANCE SHEET
At Dec. 31, 2003
ASSETS
Current Asset Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Total Current Asset Fixed Asset Land Machinery Building Total Fixed Asset Total Assets 50,000 20,000 30,000 100,000 192,500 60,000 15,000 17,500 92,500
LIABILITIES
Short-term Liability Accounts payable (A/P) Short-term loan Total Short-term Liability Long-term Liability Notes payable Long-term loan Total Long-term Liability Total Liabilities 20,000 40,000 60,000 91,000 12,000 19,000 31,000
OWNERS EQUITY
Capital stock Retained Earnings (Dec. 31) Add Net Profit Total Owners equity 1,500 20,000 21,500 101,500 80,000
Total Liabilities & Owners Equity
192,500
10
Introduction To Business BUS101
16
Analyzing Financial Statement of Dhaka Ltd. 1. Current Ratio
Current Ratio = Current Current Assets Liabilitie s = 92,5000 = 2.98 31,000
2. Quick Ratio
Quick Ratio = Qucik Current Assets Liabilitie s = 75,000 = 2.41 31,000
*Where quick asset = Total Current Assets Inventory {When Ratio is 1:1 then it is adequate} 3. Return on Sales Re turn on Sales = Net Income Net Sales 4. Return on Equity
Re turn on Equity = Net Income 20,000 = = .1970 or 19.70 % Equity 101,500
20,000 = .3389 or 33.89% 59,000
This Ratio measures the return company earns on every taka of shareholders (owners) investments. 5. Debt to Assets Ratio
Debt to Total Assets Ratio Equity = = 91,000 = .4727 or 47.27% 192,500
Total Liabilities Total Assets
6. Time Interest Earned
Time Interest Earned = EBIT Interest Expense = 24,000 = 10 times 2,400
11
You might also like
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies and Procedures Rev 030110Document50 pagesAccounting Policies and Procedures Rev 030110Soehermanto Dody100% (1)
- Finance For Non FinanceDocument56 pagesFinance For Non Financeamitiiit31100% (3)
- Final Answer Key Buad 280 Practice Exam Midterm 3Document7 pagesFinal Answer Key Buad 280 Practice Exam Midterm 3Connor JacksonNo ratings yet
- About Financial Accounting Volume 2 8th DoussyDocument503 pagesAbout Financial Accounting Volume 2 8th DoussyNomthandazo Sikhosana100% (8)
- Week 6 - Solutions (Some Revision Questions)Document13 pagesWeek 6 - Solutions (Some Revision Questions)Jason0% (1)
- (PDF) Practice Set OwnDocument19 pages(PDF) Practice Set OwnIronic Cloud100% (1)
- Financial Accounting11Document14 pagesFinancial Accounting11AleciafyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Financial StatementsDocument664 pagesChapter 2 Financial StatementsfarhansignsNo ratings yet
- ICMA Questions Dec 2012Document55 pagesICMA Questions Dec 2012Asadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Econ 3a Midterm 1 WorksheetDocument21 pagesEcon 3a Midterm 1 WorksheetZyania LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2 MBA Financial and Managerial AccountingDocument7 pagesAssignment # 2 MBA Financial and Managerial AccountingSelamawit MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Pas 1 - Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument27 pagesPas 1 - Presentation of Financial StatementsJomel Serra BrionesNo ratings yet
- Recruitment &45 Selection Hiring ProcessDocument20 pagesRecruitment &45 Selection Hiring Processnahidul202No ratings yet
- ACCA P2INT Notes J15 PDFDocument256 pagesACCA P2INT Notes J15 PDFopentuitionID100% (1)
- Cash Flow StatementDocument28 pagesCash Flow StatementJaan Sonu100% (2)
- HRM at Coca Cola CompanyDocument5 pagesHRM at Coca Cola Companynahidul20250% (2)
- IAS 12 - Bai TapDocument15 pagesIAS 12 - Bai TapHuỳnh Minh Gia HàoNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management of Apple - IncDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Management of Apple - Incnahidul202100% (2)
- CHAPTER13 Home Office and Branch - Special ProblemsDocument21 pagesCHAPTER13 Home Office and Branch - Special ProblemsAlgifariAdityaNo ratings yet
- FA Mod1 2013Document551 pagesFA Mod1 2013Anoop Singh100% (2)
- 2.0 Accounting Defined: The American Institute of Certified Public Accountant HasDocument31 pages2.0 Accounting Defined: The American Institute of Certified Public Accountant HashellenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1imamibrahim726No ratings yet
- Accounting ExamDocument2 pagesAccounting ExamMichelle JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Financial Statement and Analysis PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Financial Statement and Analysis PDFRagy SelimNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting Week 1-2Document5 pagesAdvanced Accounting Week 1-2rahmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ManagersDocument14 pagesAccounting For ManagersKabo Lucas67% (3)
- Chapter 3 Lecture Hand-Outs - Problem SolvingDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Lecture Hand-Outs - Problem SolvingLuzz LandichoNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting & Analysis Session Provides InsightsDocument41 pagesFinancial Reporting & Analysis Session Provides InsightspremoshinNo ratings yet
- October 21, 2020 Financial AssetDocument12 pagesOctober 21, 2020 Financial AssetareebNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis: 15.511 Corporate AccountingDocument31 pagesCash Flow Analysis: 15.511 Corporate AccountingAnanda RamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Mai PhurepongNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Lecture EssentialsDocument105 pagesFinancial Accounting Lecture Essentialsmukesh697No ratings yet
- ACCT 504 Midterm Exam 2Document7 pagesACCT 504 Midterm Exam 2DeVryHelpNo ratings yet
- Analytical Techniques Used Horizontal Analysis Trend Analysis Common Size Statement RatiosDocument35 pagesAnalytical Techniques Used Horizontal Analysis Trend Analysis Common Size Statement RatiosAparna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Final Upload Buad 280 Practice Exam Midterm 3Document7 pagesFinal Upload Buad 280 Practice Exam Midterm 3Connor JacksonNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries Justin Park CASEDocument20 pagesAdjusting Entries Justin Park CASEDKzNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument11 pagesAccounting EquationNacelle SayaNo ratings yet
- Cashflowstatement IMPDocument30 pagesCashflowstatement IMPAshish SinghalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document8 pagesLesson 1Amangeldi SalimzhanovNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement (C.F.S.)Document6 pagesCash Flow Statement (C.F.S.)Kopal ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- 1 Basics of Financial Accounting - 220926 - 163000Document23 pages1 Basics of Financial Accounting - 220926 - 163000Health AlertnessNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Part 1Document41 pagesCH 1 Part 1hstptr8wdwNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment Financial Accounting and Report 1Document7 pagesIndividual Assignment Financial Accounting and Report 1Sahal Cabdi AxmedNo ratings yet
- Ac550 FinalDocument4 pagesAc550 FinalGil SuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document43 pagesChapter 1Shah NidaNo ratings yet
- ACC121 FinalExamDocument13 pagesACC121 FinalExamTia1977No ratings yet
- Completion of The Accounting CycleDocument4 pagesCompletion of The Accounting Cycleapi-202886197No ratings yet
- BIS SheetDocument24 pagesBIS Sheetmagdy kamelNo ratings yet
- Acct 504 Week 8 Final Exam All 4 Sets - DevryDocument17 pagesAcct 504 Week 8 Final Exam All 4 Sets - Devrycoursehomework0% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Financial AnalysisDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Financial AnalysisMinh Anh NgNo ratings yet
- MBA Basics: The Essentials Taught in America's Top Business SchoolsDocument59 pagesMBA Basics: The Essentials Taught in America's Top Business SchoolsNishanth PillaiNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Review and Discussion Problems SolutionsDocument11 pagesCH 01 Review and Discussion Problems SolutionsArman BeiramiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Solutions T1 2014Document78 pagesWorkshop Solutions T1 2014sarah1379No ratings yet
- CA IPCC Nov 2010 Accounts Solved AnswersDocument13 pagesCA IPCC Nov 2010 Accounts Solved AnswersprateekfreezerNo ratings yet
- Accounting Quiz YP 51 BDocument4 pagesAccounting Quiz YP 51 Bnicasavio2725No ratings yet
- f3 Financial AccountingDocument11 pagesf3 Financial AccountingSam KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Investments in Stocks and Bonds: Aggregate Securities (E.g. One For Trading and One ForDocument16 pagesChapter 17 Investments in Stocks and Bonds: Aggregate Securities (E.g. One For Trading and One ForBrian BlackNo ratings yet
- Financial Plan: Maranatha University College: Entrepreneurship Remy Puoru LecturerDocument22 pagesFinancial Plan: Maranatha University College: Entrepreneurship Remy Puoru LecturerGodwin QuarcooNo ratings yet
- Income Statement: Results of Operating Performance: 15.501/516 Accounting Spring 2004Document59 pagesIncome Statement: Results of Operating Performance: 15.501/516 Accounting Spring 2004Ashish ChiraniaNo ratings yet
- SIMSR MMS Accounting Standards OverviewDocument36 pagesSIMSR MMS Accounting Standards OverviewRahul GiddeNo ratings yet
- Information Processing and Accounting CycleDocument60 pagesInformation Processing and Accounting Cyclemiadjafar463No ratings yet
- Manual For Finance QuestionsDocument55 pagesManual For Finance QuestionsMShoaibUsmani100% (1)
- ENGINEERING ECONOMY AND FINANCE DEPARTMENTDocument94 pagesENGINEERING ECONOMY AND FINANCE DEPARTMENTAbhishek PilliNo ratings yet
- Due Date: Tuesday September 30 (By 1:50 PM) : Intermediate Financial Accounting I - ADMN 3221H Accounting Assignment #2Document7 pagesDue Date: Tuesday September 30 (By 1:50 PM) : Intermediate Financial Accounting I - ADMN 3221H Accounting Assignment #2kaomsheartNo ratings yet
- ACT 501 - AssignmentDocument6 pagesACT 501 - AssignmentShariful Islam ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Aat P7 Hkas 1Document13 pagesAat P7 Hkas 1Edvan HervianNo ratings yet
- Commerce and Accountancy Mcqs-3: Ans. (B) ExplanationDocument4 pagesCommerce and Accountancy Mcqs-3: Ans. (B) ExplanationGaurav Chandra DasNo ratings yet
- Quotation T8 Tube Light 28wattDocument2 pagesQuotation T8 Tube Light 28wattnahidul202No ratings yet
- Price Quotation Non-Contact Infrared ThermometerDocument1 pagePrice Quotation Non-Contact Infrared Thermometernahidul202No ratings yet
- FormalbdDocument1 pageFormalbdnahidul202No ratings yet
- I Will Fix Google Merchant Center Errors and Disapproved Products Fix GMC Misrepresentation Issues Reactive Suspended Merchant Account GMC SuspensionDocument1 pageI Will Fix Google Merchant Center Errors and Disapproved Products Fix GMC Misrepresentation Issues Reactive Suspended Merchant Account GMC Suspensionnahidul202No ratings yet
- Order Confirmation:: Payment SystemDocument6 pagesOrder Confirmation:: Payment Systemnahidul202No ratings yet
- A Report On Dream CakeDocument27 pagesA Report On Dream Cakenahidul202No ratings yet
- Type of FabricsDocument11 pagesType of Fabricsnahidul202No ratings yet
- Alter Quality PolicyDocument2 pagesAlter Quality Policynahidul202No ratings yet
- Provident Fund: 1 - 2 Year: Nil 3 Year: 25% 4 Year: 50% 5 Year: 75%Document2 pagesProvident Fund: 1 - 2 Year: Nil 3 Year: 25% 4 Year: 50% 5 Year: 75%nahidul202No ratings yet
- Management of AIBL (Updated)Document57 pagesManagement of AIBL (Updated)RifatNo ratings yet
- Job Category: Garments/Textile/Fashion Job Title: Assistant Merchandizer Company/Organization: Ehsan and Moonlight Garments No. of Vacancies: 02Document1 pageJob Category: Garments/Textile/Fashion Job Title: Assistant Merchandizer Company/Organization: Ehsan and Moonlight Garments No. of Vacancies: 02nahidul202No ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument27 pagesFinal Reportnahidul202No ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument1 pageFinancial Institutionsnahidul202No ratings yet
- Simply: Tuesday, February 15, 2011Document29 pagesSimply: Tuesday, February 15, 2011nahidul202No ratings yet
- 1991Document5 pages1991nahidul202No ratings yet
- Avbwwqvj ZJ Gû K JR: K Yx T Câg Welq T MGVRDocument7 pagesAvbwwqvj ZJ Gû K JR: K Yx T Câg Welq T MGVRnahidul202No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentnahidul202No ratings yet
- HiDocument1 pageHinahidul202No ratings yet
- Underrating Procedures of Mortgage Loan in Real Estate SectorDocument19 pagesUnderrating Procedures of Mortgage Loan in Real Estate Sectornahidul202No ratings yet
- Mvrxcyiv Avdwwqvj ZJ Gû K JR: MV Rký 3Q Mwgói Cix V Ñ 2013Bs Welq T Mwyz, K Yx T Cö - GDocument2 pagesMvrxcyiv Avdwwqvj ZJ Gû K JR: MV Rký 3Q Mwgói Cix V Ñ 2013Bs Welq T Mwyz, K Yx T Cö - Gnahidul202No ratings yet
- A Study On Employees Motivation in Textile Mills in Coimbatore DistrictDocument1 pageA Study On Employees Motivation in Textile Mills in Coimbatore Districtnahidul202No ratings yet
- Assignment FormatDocument2 pagesAssignment Formatnahidul202No ratings yet
- Stay With Us Brand For All We Are For All Look Forward & Step Forward Raise Your MoralityDocument1 pageStay With Us Brand For All We Are For All Look Forward & Step Forward Raise Your Moralitynahidul202No ratings yet
- Long-Term finance policy factors housing finance developmentDocument13 pagesLong-Term finance policy factors housing finance developmentnahidul202No ratings yet
- Wf. Avb. Wc. Qvîvevm: Avevwmk K VK IæwubDocument2 pagesWf. Avb. Wc. Qvîvevm: Avevwmk K VK Iæwubnahidul202No ratings yet
- English Grammer Rules: ConditionalDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammer Rules: Conditionalnahidul202No ratings yet
- Stay With Us Brand For All We Are For All Look Forward & Step Forward Raise Your MoralityDocument1 pageStay With Us Brand For All We Are For All Look Forward & Step Forward Raise Your Moralitynahidul202No ratings yet
- Understanding Financial StatementsDocument103 pagesUnderstanding Financial StatementsLawa LopezNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Income Recognition GuideDocument44 pagesCPA Review Income Recognition GuideMarjorie PalmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Portfolio Activity Review of Key Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Portfolio Activity Review of Key Financial StatementsSimran PannuNo ratings yet
- Sawit-Sumbermas-Sarana TBK Billingual 30 Sep 22 - Released1667285054Document135 pagesSawit-Sumbermas-Sarana TBK Billingual 30 Sep 22 - Released1667285054Kon tTNo ratings yet
- Dog Concierges, LLC: Transaction Analysis and Statement of Cash Flows PreparationDocument9 pagesDog Concierges, LLC: Transaction Analysis and Statement of Cash Flows PreparationCristina Elizabeth Portilla BravoNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition and Profitability Analysis PDFDocument92 pagesRevenue Recognition and Profitability Analysis PDFElaine YapNo ratings yet
- IAS 1 - Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument13 pagesIAS 1 - Presentation of Financial StatementsPhillipa ChihlanguNo ratings yet
- Basics of AccountingDocument37 pagesBasics of Accountingbhallamudisravya02No ratings yet
- q3. Fs QuizzerDocument13 pagesq3. Fs QuizzerClaudine DuhapaNo ratings yet
- Module V Adjusting EntriesDocument16 pagesModule V Adjusting EntriesInfinity KingNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries PDFDocument16 pagesAdjusting Entries PDFabdul majid khawajaNo ratings yet
- ICBP Financial Results Summary 1Q20Document8 pagesICBP Financial Results Summary 1Q20ayun fauziah16No ratings yet
- LaporantahunanDocument231 pagesLaporantahunanelisa christianaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Financial StatementDocument11 pagesAssignment On Financial StatementHamza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard (PAS 1)Document13 pagesAccounting Standard (PAS 1)Raphael GalitNo ratings yet
- Activity #4Document8 pagesActivity #4Belleza AndreaNo ratings yet
- Annual Financial Report For The Local Government Volume IDocument373 pagesAnnual Financial Report For The Local Government Volume ISean Arvy SamsonNo ratings yet
- 1082 Muhasibat Aqil E.Document12 pages1082 Muhasibat Aqil E.DanielNo ratings yet
- Ümmüşnur Özcan-Proforma Questions Part2Document9 pagesÜmmüşnur Özcan-Proforma Questions Part2UMMUSNUR OZCANNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping MaterialDocument16 pagesBookkeeping MaterialPrincess Alyssa BarawidNo ratings yet
- Bharti Airtel Ltd. (India) : SourceDocument6 pagesBharti Airtel Ltd. (India) : SourceDivyagarapatiNo ratings yet
- Ias 38Document36 pagesIas 38Hr RuanNo ratings yet
- Sollutions To Chapter 5Document128 pagesSollutions To Chapter 5rudy100% (1)