Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Fundamental Chapter 02
Uploaded by
Farhan Ishaq0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views0 pagesMy book
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMy book
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views0 pagesComputer Fundamental Chapter 02
Uploaded by
Farhan IshaqMy book
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 0
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K.
Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 1/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 2/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
In this chapter you will learn about:
Basic operations performed by all types of computer
systems
Basic organization of a computer system
Input unit and its functions
Output unit and its functions
Storage unit and its functions
Types of storage used in a computer system
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
(Continued on next slide)
15
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 3/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Control Unit (CU)
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Computer as a system
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
(Continued from previous slide..)
15
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 4/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Inputting. The process of entering data and instructions
into the computer system
Storing. Saving data and instructions to make them
readily available for initial or additional processing
whenever required
Processing. Performing arithmetic operations (add,
subtract, multiply, divide, etc.) or logical operations
(comparisons like equal to, less than, greater than, etc.)
on data to convert them into useful information
The Five Basic Operations of a Computer System
The Five Basic Operations of a Computer System
(Continued on next slide)
15
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 5/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Outputting. The process of producing useful information
or results for the user such as a printed report or visual
display
Controlling. Directing the manner and sequence in which
all of the above operations are performed
The Five Basic Operations of a Computer System
The Five Basic Operations of a Computer System
15
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 6/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
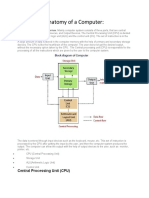
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Storage Unit
Secondary
Storage
Primary
Storage
Control
Unit
Arithmetic
Logic Unit
Input
Unit
Output
Unit
Program
and
Data
Information
(Results)
Indicates flow of
instructions and data
Indicates the control
exercised by the
control unit
Basic Organization of a Computer System
Basic Organization of a Computer System
16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 7/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
An input unit of a computer system performs the
following functions:
1. It accepts (or reads) instructions and data from outside
world
2. It converts these instructions and data in computer
acceptable form
3. It supplies the converted instructions and data to the
computer system for further processing
Input Unit
Input Unit
16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 8/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
An output unit of a computer system performs the
following functions:
1. It accepts the results produced by the computer, which
are in coded form and hence, cannot be easily
understood by us
2. It converts these coded results to human acceptable
(readable) form
3. It supplies the converted results to outside world
Output Unit
Output Unit
16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 9/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
The storage unit of a computer system holds (or stores)
the following :
1. Data and instructions required for processing (received
from input devices)
2. Intermediate results of processing
3. Final results of processing, before they are released to
an output device
Storage Unit
Storage Unit
17
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 10/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Primary storage
Used to hold running program instructions
Used to hold data, intermediate results, and
results of ongoing processing of job(s)
Fast in operation
Small Capacity
Expensive
Volatile (looses data on power dissipation)
Two Types of Storage
Two Types of Storage
(Continued on next slide)
17
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 11/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Secondary storage
Used to hold stored program instructions
Used to hold data and information of stored jobs
Slower than primary storage
Large Capacity
Lot cheaper that primary storage
Retains data even without power
Two Types of Storage
Two Types of Storage
(Continued from previous slide..)
17
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 12/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Arithmetic Logic Unit of a computer system is the place
where the actual executions of instructions takes place during
processing operation
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
18
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 13/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Control Unit of a computer system manages and coordinates
the operations of all other components of the computer
system
Control Unit (CU)
Control Unit (CU)
18
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 14/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Arithmetic
Logic Unit
(ALU)
Control Unit
(CU)
=
Central
Processing
Unit (CPU)
It is the brain of a computer system
It is responsible for controlling the operations of
all other units of a computer system
+
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
18
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 15/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
A system has following three characteristics:
1. A system has more than one element
2. All elements of a system are logically related
3. All elements of a system are controlled in a manner to
achieve the system goal
A computer is a system as it comprises of integrated
components (input unit, output unit, storage unit, and CPU)
that work together to perform the steps called for in the
executing program
The System Concept
The System Concept
18
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Slide 16/16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization
Ref. Page
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Auxiliary storage
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Computer system
Control Unit (CU)
Controlling
Input interface
Input unit
Inputting
Main memory
Output interface
Output unit
Outputting
Primate storage
Processing
Secondary storage
Storage unit
Storing
System
Key Words/Phrases
Key Words/Phrases
19
You might also like
- Chapter 2 BCO 2opDocument10 pagesChapter 2 BCO 2opBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalsDocument17 pagesComputer Fundamentalsdarmahnoor0% (1)
- Chapter 14-OS-2oP PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 14-OS-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-Internet 2opDocument8 pagesChapter 18-Internet 2opskitvikkyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19-Multimedia-1-2oP PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 19-Multimedia-1-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16-BDP-2oP PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 16-BDP-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Secondary Storage-2oP PDFDocument58 pagesChapter 8-Secondary Storage-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-IO Devices-2oP PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 9-IO Devices-2oP PDFBalkrishan Goswami0% (1)
- Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti SinhaDocument0 pagesComputer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti SinhaWamiq ReyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Computer Arithmetic-2oP PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 5-Computer Arithmetic-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03-Number SystemDocument40 pagesChapter 03-Number SystempoojamudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction-2oP PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1-Introduction-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Number System-2oP PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 3-Number System-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Hierarchy Definition - Human Resources (HR) Dictionary - MBA Skool-Study - Learn.shareDocument1 pageOrganizational Hierarchy Definition - Human Resources (HR) Dictionary - MBA Skool-Study - Learn.shareBilal AwanNo ratings yet
- The 8 Principles of FinanceDocument3 pagesThe 8 Principles of FinanceSaddam HossainNo ratings yet
- Short Term Sources of FinanceDocument13 pagesShort Term Sources of FinanceCharwi MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04-Computer CodesDocument30 pagesChapter 04-Computer CodesAlok PandaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Data Operations or Calculations ResultDocument7 pagesUnit-I: Data Operations or Calculations ResultSiva SankariNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesParts of A Computer With Their Functionsglenn0805No ratings yet
- Computer System ArchitectureDocument22 pagesComputer System ArchitectureParth ViraniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A ComputerDocument9 pagesAnatomy of A ComputerAnjuman AraaNo ratings yet
- ICT and SocietyDocument13 pagesICT and SocietyFirdaus AhmadNo ratings yet
- Role of Operating System PDF Computer ScienceDocument7 pagesRole of Operating System PDF Computer ScienceSayhan Fareedi Ahmed100% (1)
- Green HRM - Issues & Challenges: Mrs. Pallavi KumariDocument21 pagesGreen HRM - Issues & Challenges: Mrs. Pallavi KumariAbida SultanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Information SystemsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Computer Information SystemsMr. JahirNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1 PPT 1.1 (Introduction, Drawback of File Sysstem, View of Data)Document4 pagesDBMS Unit-1 PPT 1.1 (Introduction, Drawback of File Sysstem, View of Data)lightNo ratings yet
- What Is Gender EqualityDocument3 pagesWhat Is Gender EqualityAna Teresa MoyaNo ratings yet
- Review Questions PDocument7 pagesReview Questions PRomeo GongobNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument29 pagesCentral Processing Unitsaurav gautam singhNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument39 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsJamer AmpongNo ratings yet
- BBA 2nd SemesterDocument14 pagesBBA 2nd SemesterKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ict - Important Keyword To RememberDocument8 pagesIct - Important Keyword To Remembermal887No ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument16 pagesOperating System NotesSreedhar YellamNo ratings yet
- Prototyping in Systems AnalysisDocument9 pagesPrototyping in Systems AnalysisDenisho Dee100% (1)
- Introduction To Computer SystemsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Computer SystemsRoumen GuhaNo ratings yet
- Information Communication Technology: Chapter 2: Computers in Our Daily LifeDocument7 pagesInformation Communication Technology: Chapter 2: Computers in Our Daily Lifechenchen gabitanNo ratings yet
- Article FinalDocument31 pagesArticle FinalAbida SultanaNo ratings yet
- Five Pillars of Technology EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesFive Pillars of Technology EntrepreneurshipALL IN ONENo ratings yet
- Nestle TDDocument57 pagesNestle TDAbida SultanaNo ratings yet
- Data Resource ManagementDocument61 pagesData Resource Managementmotz100% (2)
- Computer MultitaskingDocument5 pagesComputer MultitaskingWhitney NewtonNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer NotesDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Computer NotesVijay Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Components of The Data ProcessingDocument4 pagesComponents of The Data ProcessingmuhororoNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ModelDocument30 pagesDecision Making ModelAzmatullah Khan Sherani100% (1)
- Introduction To HCIDocument21 pagesIntroduction To HCIjayson virtucio100% (1)
- Law of Variable ProportionsDocument6 pagesLaw of Variable ProportionsDeepashikhaNo ratings yet
- FOC Notes Unit 1 and Unit 2 PDFDocument46 pagesFOC Notes Unit 1 and Unit 2 PDFhill_rws407No ratings yet
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument19 pagesCustomer Relationship Managementrakesh_ballaNo ratings yet
- Ict Notes 4,5,6 Pre UpdateDocument19 pagesIct Notes 4,5,6 Pre UpdateAtif Mehmood100% (1)
- Economics of Industry PPT Lecture 1Document62 pagesEconomics of Industry PPT Lecture 1rog67558No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Modern Computer SystemsDocument44 pagesLecture 2 - Modern Computer SystemsKisarach PhilipsNo ratings yet
- 2.basic Computer OrganisationDocument16 pages2.basic Computer OrganisationkhankhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 BCODocument16 pagesChapter 02 BCOJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Basic Computer OrganizationDocument15 pagesTopic 3 Basic Computer OrganizationShwe Eain LinnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14-OS 3opDocument18 pagesChapter 14-OS 3opRenieNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals (ALL in ONE)Document818 pagesComputer Fundamentals (ALL in ONE)Arya BhattNo ratings yet
- PK Sinah - Computer FundamentalsDocument536 pagesPK Sinah - Computer FundamentalsAleeza KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document15 pagesLecture 2Priyam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemDocument5 pages5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemNuj Wehtam Inairam100% (7)
- Components CFDocument15 pagesComponents CFankudubeyNo ratings yet
- Professional Competences IDPDocument2 pagesProfessional Competences IDPUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Angomes DavidDocument1 pageAngomes DavidUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Professional Competences IDPDocument2 pagesProfessional Competences IDPUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Professional Competences IDPDocument2 pagesProfessional Competences IDPUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Building Worksheets: Designer SpreadsheetsDocument1 pageChapter 1: Building Worksheets: Designer SpreadsheetsUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Hadoop Summit Fair SchedulerDocument30 pagesHadoop Summit Fair SchedulerUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Notes On KB and MouseDocument17 pagesNotes On KB and Mousebans78No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Building Worksheets: Designer SpreadsheetsDocument1 pageChapter 1: Building Worksheets: Designer SpreadsheetsUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Feb 2014Document11 pagesFeb 2014Udita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Feb 2014Document11 pagesFeb 2014Udita BadolaNo ratings yet
- GK Capsule January 2014Document9 pagesGK Capsule January 2014shashankksandeepNo ratings yet