Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pae Emp Poster
Uploaded by
shaksnafeeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pae Emp Poster
Uploaded by
shaksnafeeCopyright:
Available Formats
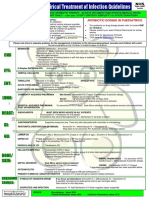
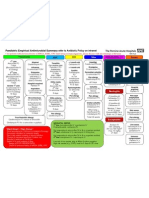
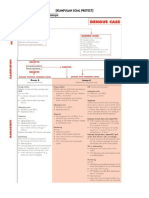
Guidance for initial antibiotic therapy in children in acute hospitals. Specialist units may have separate policies.
Infection Management Guidelines: Empirical Antibiotic Therapy for Children
STOP AND THINK BEFORE YOU GIVE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY! The initial treatment may need to be modified according to clinical response and results of microbiology and other investigations. The appropriate specimens of microbiology should be taken whenever possible before administering antibiotics; however this will depend upon the severity of the illness and the nature of the specimen. In patients who are stable and not septic, and in whom infection is only one of a number of possibilities, consideration should be given to deferring antibiotics until the results of cultures are known, as long as there is no change in the clinical condition in the interim. Upper Respiratory Tract Lower Respiratory Tract Skin/Soft Tissue Urinary Tract Gastrointestinal Bone/Joint Infection CNS Sepsis or Feverish Illness Unknown Source Neonates - community acquired Benzylpenicillin IV + Gentamicin ** IV. In Penicillin allergy, Cefotaxime IV + Gentamicin ** IV. Neonates nosocomial Gentamicin ** IV + Vancomycin ** IV. 1 3 months Cefotaxime IV + Amoxicillin IV. > 3 months Cefotaxime IV. After 48 hours, if child is > 3 months and unlikely to require HDU/ITU care then consider switching to Ceftriaxone* IV. If known MRSA carrier or in penicillin allergy give: > 1 month Vancomycin ** IV + Gentamicin ** IV +/- Metronidazole IV. Neutropenic Sepsis Piperacillin/tazobactam IV + Gentamicin ** IV. In mild Penicillin allergy: Ceftazidime IV + Gentamicin ** IV. Add Teicoplanin IV if fever and/or rigors after line flushed earlier in day or soon after new line inserted. Endocarditis
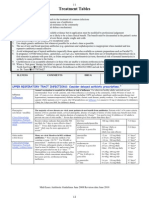
Tonsillitis Benzylpenicillin IV (if unable to swallow) Switch to oral Penicillin V. In Penicillin allergy, Clarithromycin IV (if unable to swallow) Switch to oral Clarithromycin. Duration: 10 days.
Pneumonia Young children (< 2 years) with mild symptoms do not need antibiotics.
Limited soft tissue infection Flucloxacillin oral + Penicillin V oral. In Penicillin allergy, Neonates Erythromycin oral. > 1 month Clarithromycin oral.
Non-severe community acquired pneumonia (CAP) Amoxicillin (IV or oral) or if true Penicillin allergy or atypical suspected Clarithromycin (IV or oral). Duration 3 - 5 days (10 days if atypical). Severe CAP Neonates Benzylpenicillin IV + Gentamicin IV > 1 month Co-amoxiclav IV If atypical pneumonia suspected + Clarithromycin IV/oral. Switch to oral Co-amoxiclav +/- Clarithromycin. If Penicillin allergy, > 1 month Cefuroxime IV +/- Clarithromycin oral. Switch to oral Cefpodoxime +/- Clarithromycin. Duration: 7 - 10 days. Aspiration Pneumonia Co-amoxiclav IV. Switch to oral Co-amoxiclav. If Penicillin allergy, Cefuroxime IV + Metronidazole IV. Switch to oral Cefpodoxime + Metronidazole. Duration: 7 days.
Acute Otitis Media Avoid or delay antibiotics in children without systemic features. Amoxicillin oral If severe, Co-amoxiclav IV. In Penicillin allergy, Clarithromycin oral. If severe, Cefuroxime IV. Duration: 5 days.
Moderate to severe Cellulitis Flucloxacillin IV + Benzylpenicillin IV. Switch to oral Flucloxacillin +/- Penicillin V. In Penicillin allergy, Vancomycin ** IV. Switch to oral erythromycin for neonates or clarithromycin if > 1 month. Duration: 7 - 14 days. Orbital Cellulitis Seek ENT/Ophthalmology advice. Co-amoxiclav IV then oral. Duration: 7 10 days. Animal bite Co-amoxiclav oral. In Penicillin allergy, > 6 months and < 12 years Co-trimoxazole oral + Metronidazole oral. > 12 years Doxycycline oral + Metronidazole oral. Duration: 5 days. Human Bite Co-amoxiclav oral. In penicillin allergy, Clarithromycin oral. + (if severe) Metronidazole oral. Duration: 7 days.
Lower UTI/cystitis If child is receiving prophylactic medication and develops an infection, treatment should be with a different antibiotic. > 1month - 12 years Trimethoprim oral 4mg/kg (max 200mg) twice daily. 12 - 18 years Trimethoprim oral 200mg twice daily. Or > 1month - 12 years Cefalexin oral 12.5mg/kg twice daily (max 1g 4 times daily). 12 - 18 years Cefalexin oral 500mg 2 or 3 times daily. Duration: 3 days. Prophylaxis of recurrent symptomatic UTIs > 1 month - 12 years Trimethoprim 2mg/kg (max 100mg) at night. 12 - 18 years Trimethoprim 50 - 100mg at night. Or > 1 month - 18 years Cefalexin 12.5mg/kg (max 125mg) at night. Review once investigations completed.
Gastroenteritis No antibiotic usually required.
Acute Osteomyelitis/Septic arthritis/Acute discitis/ Deep muscle sepsis If < 2 years and no sensitivities: Flucloxacillin IV + Cefuroxime IV. If > 2 years or if Staphylococcus aureus confirmed: Flucloxacillin IV + Sodium Fusidate oral. IV therapy is usually required for 14 days but a switch to oral therapy can be considered once the patient is apyrexial for 48 hours. In Penicillin allergy or MRSA likely, Vancomycin ** IV. If < 2 years Add Gentamicin ** IV. If pseudomonas likely use Ceftazidime IV. Duration: 4 - 6 weeks, guided by inflammatory markers and clinical response.
IV therapy to be administered URGENTLY on arrival at hospital and after blood cultures. Always refer to senior staff. Seek ID/microbiology advice. Meningitis or Meningococcal Septicaemia < 3 months Cefotaxime IV + Amoxicillin IV. > 3 months Cefotaxime IV. Add Vancomycin ** IV if recently overseas, or prolonged multiple antibiotic exposure within last 3 months. After 48 hours if child is > 3 months and unlikely to require HDU/ITU care then consider switching to Ceftriaxone * IV. Refer to BNFC for course lengths for appropriate organisms.
Possible infective endocarditis Consult a cardiologist immediately. Acute: Flucloxacillin IV + Gentamicin ** V. Indolent: Benzylpenicillin IV (or Amoxicillin IV) + Gentamicin ** IV. or if true Penicillin allergy/ intra-cardiac prosthesis/ suspected MRSA: Vancomycin ** IV + Rifampicin oral + Gentamicin ** IV.
Appendicitis/Peritonitis/ Penetrating abdominal trauma < 3 months Cefotaxime IV + Metronidazole IV. > 3 months Ceftriaxone * IV + Metronidazole IV. If not responding, change to Amoxicillin IV + Metronidazole IV + Gentamicin ** IV. Switch to oral Co-amoxiclav. If beta-lactam allergy, Clindamycin IV then oral. Duration: 3 - 7 days.
* Ceftriaxone - refer to BNFC for contraindications. ** Gentamicin / Vancomycin - see IV monograph. The IV route for Clarithromycin is not licensed in children.
Pyelonephritis < 6 months Cefotaxime or Ceftriaxone* IV. > 6 months Co-amoxiclav IV. Add Gentamicin ** IV if severe infection or unresponsive after 48 hours. Switch to oral trimethoprim if sensitive. Duration: 7 - 10 days. Severe Penicillin allergy > 1 month Ciprofloxacin IV/ oral for 7 days.
FURTHER ADVICE can be obtained from the Consultant Paediatrician, Duty Microbiologist or Clinical Pharmacist or the ID Unit Aberdeen Royal Infirmary. Infection Control advice may be given by the duty microbiologist. The full antibiotic guidelines and policies can be found on the intranet at www.nhsgrampian.org/gjf - Chapter 5 Infections. Produced by the NHS Grampian Antimicrobial Management Team October 2011. Review October 2012.
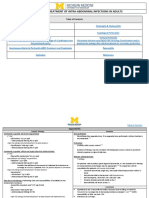
Catheter-related UTI Remove/replace catheter and culture urine. Antibiotics are not indicated unless the patient has evidence of systemic infection eg pyrexia, loin pain, raised WCC or acute confusion. If systemic infection likely treat as for pyelonephritis. Prophylaxis of UTI and bacteraemia Patients with clinical evidence of a UTI should be treated with appropriate antibiotics before or at the time of catheter insertion. Antibiotic prophylaxis at catheter insertion is only indicated in patients for whom bacteriuria is associated with a high risk of sepsis or those at particular risk of infective endocarditis. See full guidance for high risk conditions and treatment options.
REVIEW ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY DAILY STOP? SIMPLIFY? SWITCH?
RATIONALISE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY when microbiology results become available or clinical condition changes. Review IV therapy daily and remember IV - ORAL SWITCH - see IVOST policy on intranet
You might also like
- Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in Children: Clinical GuidelineDocument2 pagesEmpirical Antibiotic Therapy in Children: Clinical GuidelineAna-Mihaela BalanuțaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Antibiotic TeddyDocument1 pagePaediatric Antibiotic Teddyayu fitrianiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Empirical Antimicrobial SummaryDocument1 pagePaediatric Empirical Antimicrobial SummarywardahkhattakNo ratings yet
- Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in Children v7 Exp 31 Dec 2020Document2 pagesEmpirical Antibiotic Therapy in Children v7 Exp 31 Dec 2020Mohamad MostafaNo ratings yet
- Enteral InfectionsDocument6 pagesEnteral InfectionsAshley CheungNo ratings yet
- Antibiotka PicuDocument4 pagesAntibiotka Picusunu rachmat100% (1)
- 02 Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument28 pages02 Treatment of Urinary Tract Infectionbellatania yuda100% (1)
- Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument28 pagesTreatment of Urinary Tract InfectionHumza RasheedNo ratings yet
- Drug of Treatment For Meningitis: Penicillin Cefotaxime ResistantDocument5 pagesDrug of Treatment For Meningitis: Penicillin Cefotaxime ResistantNama BestNo ratings yet
- 2012 Aug IMG Poster 165760a SepsisDocument1 page2012 Aug IMG Poster 165760a SepsisTeng Huei LeeNo ratings yet
- Modul PneumoniaDocument16 pagesModul Pneumoniaandamar0290No ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Infections: Streptococcus PneumoniaeDocument9 pagesAcute Respiratory Infections: Streptococcus Pneumoniaesunma09082001No ratings yet
- Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. 1Document20 pagesAcute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. 1Joana Carolina QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- CAP Guidance 2020 Revision Final UpdatedDocument11 pagesCAP Guidance 2020 Revision Final UpdatedNeerajaNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument18 pagesDiphtheriaShishir ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Guideline For The Management of Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument11 pagesGuideline For The Management of Community-Acquired PneumoniaCarlos VSNo ratings yet
- What Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisVonn Bryan CalumiaNo ratings yet
- Management of Pneumonia in The Child 2 To 59 Months of AgeDocument5 pagesManagement of Pneumonia in The Child 2 To 59 Months of AgeOlive IrawadiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic RespirDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Respirlaur_rbNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Pneumonia Case StudyDocument2 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia Case StudyAngel Villamor0% (1)
- Guidelines Treatment Adults Complicated Intra-abdominal InfectionsDocument2 pagesGuidelines Treatment Adults Complicated Intra-abdominal InfectionsluckevNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Treatment of Intra-Abdominal Infections in AdultsDocument10 pagesGuidelines For Treatment of Intra-Abdominal Infections in AdultsPratama InsaniNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument23 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illnessirwan junNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Infection GuidelinesDocument16 pagesPulmonary Infection GuidelinesFawad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Management of Infection Guidance For Primary Care in IrelandDocument29 pagesManagement of Infection Guidance For Primary Care in IrelandLouise GleesonNo ratings yet
- Malaria Treatment Protocol: Third EditionDocument32 pagesMalaria Treatment Protocol: Third Editionrizqi_cepiNo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTIC POLICY FOR Sassoon Hospital & BJGMC, PuneDocument32 pagesANTIBIOTIC POLICY FOR Sassoon Hospital & BJGMC, Puneshah007zaadNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis GuideDocument6 pagesNeonatal Sepsis GuideSirish ShresthaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticGuidelines PrimaryDocument12 pagesAntibioticGuidelines PrimaryHandriyato SukmaNo ratings yet
- Habits Are Some of The Strategies RecommendedDocument30 pagesHabits Are Some of The Strategies Recommendedmd.dascalescu2486No ratings yet
- Typhoid GuidelinesDocument3 pagesTyphoid GuidelinesMuthia Rahma AninditaNo ratings yet
- Manage Child Cough, Breathing IssuesDocument18 pagesManage Child Cough, Breathing IssuesNithu NithuNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuidDocument11 pagesAntibiotic Guidlaur_rbNo ratings yet
- 4_5780761539279587778Document2 pages4_5780761539279587778ጉራማይሌ TubeNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Policy - Final GovtMP - 211215 - 121049Document40 pagesAntibiotic Policy - Final GovtMP - 211215 - 121049Charchit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guideline On Neonatal Sepsis: Summarized by Dr. Catherine Chua October 2012Document3 pagesClinical Practice Guideline On Neonatal Sepsis: Summarized by Dr. Catherine Chua October 2012Joey CuayoNo ratings yet
- Splenectomy - Factsheet - For - Health - Professionals 2022 FinalDocument4 pagesSplenectomy - Factsheet - For - Health - Professionals 2022 Finalalpha.blocker11No ratings yet
- PCAP Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument33 pagesPCAP Diagnosis and TreatmentRenette UyNo ratings yet
- Child Infection 3Document22 pagesChild Infection 3Bishnoi MaheshNo ratings yet
- Internal-Abdominal-infection-Treatment-ProtocolDocument9 pagesInternal-Abdominal-infection-Treatment-Protocolhatem newishyNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever: Pua, Christian Franz A. Quilala, Gian MailoDocument24 pagesTyphoid Fever: Pua, Christian Franz A. Quilala, Gian MailoGNCDWNo ratings yet
- ZegenDocument9 pagesZegenJefferson ManasanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Choices For Common InfectionsDocument30 pagesAntibiotics: Choices For Common InfectionsAlfeus GradyNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection, Complicated (UTI) - Johns Hopkins ABX GuideDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract Infection, Complicated (UTI) - Johns Hopkins ABX GuideLaoMed plusNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Pembahasan Pretest IRDocument16 pagesSoal Dan Pembahasan Pretest IRSummer SnowNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Alina CommunityDocument29 pagesPresentation of Alina CommunitySmita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Case Management of Ari at PHC LevelDocument29 pagesCase Management of Ari at PHC Levelapi-3823785No ratings yet
- Imci UpdatesDocument37 pagesImci UpdateskristiandiorcapiliNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Drugs FormularyDocument95 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs FormularymahamoudNo ratings yet
- Anti Infective DrugsDocument77 pagesAnti Infective DrugsAginaya ReinNo ratings yet
- Immunologic ManagementDocument6 pagesImmunologic ManagementAlyssa MontimorNo ratings yet
- Tata Laksana PneumoniaDocument29 pagesTata Laksana PneumoniaSRI WIDOWATINo ratings yet
- Punemonia CaseDocument15 pagesPunemonia Caseshamaamo19No ratings yet
- Hospital Antibiotic PolicyDocument5 pagesHospital Antibiotic PolicyNaveen ArichwalNo ratings yet
- Meningitis ReviewDocument2 pagesMeningitis ReviewBolbol hayranNo ratings yet
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Essential Guide to Cephalexin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.From EverandThe Essential Guide to Cephalexin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.No ratings yet
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsFrom EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- FACTS WWSM 280110 Final Complete CorrectedDocument143 pagesFACTS WWSM 280110 Final Complete Correctedjustsomeguyyouknow83% (6)
- Evaluative Commentary Essay PartnershipDocument2 pagesEvaluative Commentary Essay Partnershipnoorlela jaafarNo ratings yet
- Basic Emergency Obstetric CareDocument5 pagesBasic Emergency Obstetric Caregabriel_marapaoNo ratings yet
- 2014 Solaf Science SPM Chapter 1 Paper 2 Answer SchemeDocument12 pages2014 Solaf Science SPM Chapter 1 Paper 2 Answer SchemeIvan Hoo Chean YiengNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocument2 pagesKawasaki DiseasejaehankimNo ratings yet
- Part4 Evidence1 CozineDocument2 pagesPart4 Evidence1 Cozineapi-286143658No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Zone Interpretation GuideDocument2 pagesAntimicrobial Zone Interpretation Guideabed wicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Jason Mercer Vaccinia Virus MethodsDocument318 pagesJason Mercer Vaccinia Virus MethodsCristina EneNo ratings yet
- UC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Feline - Panleukopenia - 2012-05-01Document5 pagesUC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Feline - Panleukopenia - 2012-05-01Kitt KaosNo ratings yet
- Definition of Medical TreatmentDocument2 pagesDefinition of Medical Treatmentfikadu100% (1)
- Copar ProgramsDocument19 pagesCopar ProgramsMitch LucenaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward HXDocument4 pagesPedia Ward HXMalshika JayatissaNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument39 pagesMalariaOlgaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Prevention and ControlDocument19 pagesHepatitis B Prevention and Controlcolltfrank100% (1)
- Cot Deaths Linked To Vaccinations: by DR Viera Scheibner (PHD) & Leif KarlssonDocument4 pagesCot Deaths Linked To Vaccinations: by DR Viera Scheibner (PHD) & Leif KarlssonboninhNo ratings yet
- Ao 99 S 1990Document2 pagesAo 99 S 1990taengoo2180% (1)
- Csr-Case Study Research Study 1Document4 pagesCsr-Case Study Research Study 1api-300476144No ratings yet
- Antiprotozoa MedicineDocument10 pagesAntiprotozoa MedicineWaldian IsmailNo ratings yet
- Printable Version of - "Instructions For Submitting SamplesDocument7 pagesPrintable Version of - "Instructions For Submitting SamplesRay Anthony RilveriaNo ratings yet
- CD 004407Document163 pagesCD 004407Astri Faluna SheylavontiaNo ratings yet
- Complete Vaccine ListingDocument5 pagesComplete Vaccine ListingSyed Esa MushranNo ratings yet
- The Poisoned Needle PDFDocument220 pagesThe Poisoned Needle PDFJulianna Ferrero75% (4)
- HTP FeverDocument8 pagesHTP FeverAina AngoluanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Research Public HealthDocument12 pagesImportance of Research Public HealthConcepcion MpsNo ratings yet
- List of Diseases Caused by Virus, Bacteria, Protozoa and WormDocument5 pagesList of Diseases Caused by Virus, Bacteria, Protozoa and WormShaik JainuddinNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Health - National Welfareville CMPD, Barangay Road Block 6, Barangay Addition Hills, Mandaluyong City, 1550Document3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Health - National Welfareville CMPD, Barangay Road Block 6, Barangay Addition Hills, Mandaluyong City, 1550אֲחִינוֹעַם אַחְלָמָה אֲחִיעֶזֶרNo ratings yet
- Immunisation Form - Greece 0Document0 pagesImmunisation Form - Greece 0Diego_Vitor92No ratings yet
- Health Assessment NotesDocument58 pagesHealth Assessment NotesNathalie kate petallar100% (1)
- MR FaqDocument35 pagesMR FaqbryfarNo ratings yet
- 2301 Peds Exam #2Document72 pages2301 Peds Exam #2JenniNo ratings yet