Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biostat - Normal Distribution
Uploaded by
Anna Dominique JimenezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biostat - Normal Distribution
Uploaded by
Anna Dominique JimenezCopyright:
Available Formats
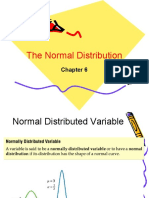
THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
Normal Curve
- also called the Normal Probability Curve
or Gaussian Curve
- figure representing a normal distribution
of data.
Properties of the Normal Curve
- for continuous-type of random variable
- bell shaped
- M =Md =Mo
- central around the mean
- asymptotic to the x-axis on both sides
and extends in both directions toward
infinity
- total area =100%
The Standard Score (the z- score)
- determines how many standard deviations a score is from the mean.
Examples:
1. The score of all the students taking up a Statistics class has an average of 24.30, with a standard deviation of 5.45. Determine the standard score
(or z-score) of the following:
a) a score of 35
b) a score of 16
c) a score of 10
2. Two equivalent tests were given to a similar group. The tests are designed with different scales. The statistics of the tests are given below. Which
is better, a score of 145 on Test I, or a score of 60 onTest II?
On Test I: Mean =100 On Test II: Mean =40
St.Dev. =15 St.Dev.=5
3. Kristine got 141 in Chemistry and 112 in Math. If the average of the scores in Chemistry is 148, with a standard deviation of 3.2, while the average
of the scores in Math is 115, with a standard deviation of 2.3, in what course did she perform better?
Areas Under the Normal Curve
- determines the area (in percentage) that a standard score occupies from the mean.
- use Table A of your textbook (page 386)
Find the following:
1. Area from z =0 to z =.83 2. Area from z =0 to z =1.75
2o 1o 0o 1o 2o
M
Md
Mo
68.26%
13.59% 13.59%
2.18% 2.18%
x
or
s
x x
z
=
3. Area from z =0 to z = 1.26
4. Area from z =.87 to the right.
5. Area from z =1.04 to the left.
6. Area from z =- 1.40 to the right.
7. Area from z =.5 to z =1.3
8. Area from z 1.5 to 1.0
9. Area from z =.40 to z =.80
10. Area from z =1.3 to z =-2.85
Find the z- score
of the following:
Word Problems Leading to Normal Distribution (taken from the textbook):
Exercise 6.6. If the heights of male youngsters are normally distributed with a mean of 60 inches
and a standard deviation of 10, what percentage of the boys heights (in inches) would expect to be
a) between 45 and 75 b) between 30 and 90
c) less than 50
d) 45 or more
e) 75 or more
f) between 50 and 75
Exercise 6.8. Assume that the age at onset of disease X is distributed normally with a mean of
50 years and a standard deviation of 12 years. What is the probability that an individual afflicted with
disease X developed it
a) before age 35?
b) between ages 34 and 70?
c) beyond age 54?
Exercise 6.7. An instructor is administering a final examination. She tells her class that she will give an A to the
10% of students who earn the highest grades. Past experience with the same examination has shown
that the mean grade is 75 and the standard deviation is 8. If the present class runs true to form, what
grade would a student need to earn an A? Assume a normally distributed scores.
Exercise 6.13. The weights of 18 to 24-year old women are normally distributed with a mean of 132 pounds and
a variance of 750.76 sq. pounds. If one randomly selected 150 of these women ages 18-24, how many of
them would expect to weight 100-150 pounds?
Exercise 6.20. Serum cholesterol levels were taken from a population of college students. Males had a mean of
195 and a standard deviation of 10. Females had a mean of 185 and a standard deviation of 12.
a) What were the cholesterol levels of the highest 5% of the males?
b) What percentage of females would have a cholesterol level of less than 180?
c) What percentage of males would have a cholesterol level between 180 and 200?
d) What assumption do you have to make in (a) to (c) to obtain a valid answer?
CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM: ( ) 1 0, ~
lim
N
n
x
n
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
EXCEL: =NORMDIST(x, , , true) 0.5
=NORMSDIST(z)-0.5
}
|
.
|
\
|
=
x
x
2
1
e
2
1
You might also like
- MARSHALLESE Language.Document96 pagesMARSHALLESE Language.Sándor Tóth100% (2)
- Understanding P-Values and Statistical SignificanceDocument6 pagesUnderstanding P-Values and Statistical Significancevk0% (1)
- Cards Against MGCDocument44 pagesCards Against MGCAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Medical MneumonicsDocument139 pagesMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNo ratings yet
- Medical MneumonicsDocument139 pagesMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Non-Parametric StatisticsDocument21 pagesModule 6 - Non-Parametric StatisticsGabrielle Marie RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Normal Probability Distribution PDFDocument6 pagesLecture6 Normal Probability Distribution PDFnauliNo ratings yet
- Socio AnthroDocument17 pagesSocio AnthroMary Rose Sefulan SivaNo ratings yet
- Random and Systematic ErrorDocument1 pageRandom and Systematic ErrorGGNo ratings yet
- Statistic Frequency DistributionDocument66 pagesStatistic Frequency DistributionEllina James100% (3)
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution Curve ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Normal Distribution Curve ExplainedAlyssa Marie L. Palamiano100% (1)
- Z-Score Practice WorksheetDocument3 pagesZ-Score Practice WorksheetAgeng Kastawaningtyas100% (2)
- Analyze Variance with One-Way and Two-Way ANOVADocument19 pagesAnalyze Variance with One-Way and Two-Way ANOVALabiz Saroni Zida0% (1)
- NORMAL CURVE GUIDEDocument32 pagesNORMAL CURVE GUIDEElmer Salamanca Hernando Jr.No ratings yet
- 01a Using Anatomical LanguageDocument6 pages01a Using Anatomical Languageapi-3067625270% (1)
- NMAT Practice Set Part IIDocument32 pagesNMAT Practice Set Part IIAlfred Benjamin Cajita93% (107)
- GraphicalDocument26 pagesGraphicalMary Joy DesaletNo ratings yet
- MD Internal MedicineDocument99 pagesMD Internal MedicineAamir HamaadNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Measures of DispersionDocument11 pagesChapter4 Measures of DispersionRoshan KCNo ratings yet
- STATISTICAL MEASURES FOR ANALYZING INFECTIOUS DISEASESDocument17 pagesSTATISTICAL MEASURES FOR ANALYZING INFECTIOUS DISEASESNash ShantolNo ratings yet
- Snell's Clinical Anatomy 1 - IntroductionDocument3 pagesSnell's Clinical Anatomy 1 - IntroductionAnna Dominique Jimenez40% (5)
- Notes For CHEDocument10 pagesNotes For CHEJoshua ClimacoNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Syllabus 2015 2016Document4 pagesPre Calculus Syllabus 2015 2016Madison CrockerNo ratings yet
- Parts of The ThesisDocument9 pagesParts of The ThesisCharlotteAnnePatNo ratings yet
- 2 Components of ResearchDocument46 pages2 Components of ResearchTiba AlaniNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument24 pagesCorrelation and Regressionkaushalsingh2080% (5)
- Binomial DistributionDocument22 pagesBinomial DistributionNix SantosNo ratings yet
- Academic Supervision in The Improvement of Teachers' Professional Competencies: Effective Practices On The EmergenceDocument9 pagesAcademic Supervision in The Improvement of Teachers' Professional Competencies: Effective Practices On The EmergenceLorensius Amon100% (1)
- Normal DistributionDocument41 pagesNormal DistributionRenee Jezz Lopez100% (1)
- Hypothesis Testing With One SampleDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing With One SampleRika MitsuiNo ratings yet
- KP Teaching PortfolioDocument14 pagesKP Teaching PortfolioKrisciaPortilloNo ratings yet
- 13-Methods of RandomisationDocument4 pages13-Methods of Randomisationhalagur75No ratings yet
- The Normal DistributionDocument2 pagesThe Normal DistributionColleen Bautista100% (1)
- Binomial DistributionsDocument78 pagesBinomial DistributionssyahmiNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion and T-TestDocument12 pagesMeasures of Dispersion and T-TestKeennan L. CuyosNo ratings yet
- HMB323H1S Global Health Research Syllabus Dimaras2016 17Document3 pagesHMB323H1S Global Health Research Syllabus Dimaras2016 17Santosh MiryalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document40 pagesChapter 3Jiah Mohd DaudNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument25 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyASClabISB0% (1)
- Binomial DistributionDocument5 pagesBinomial DistributionK.Prasanth Kumar50% (2)
- MMW 6 Data Management Part 3 Central Location Variability PDFDocument5 pagesMMW 6 Data Management Part 3 Central Location Variability PDFJhuliane RalphNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument70 pagesMCQJerry OktovaNo ratings yet
- Research: Introductory: Prof. Dr. Md. Ghulam Murtaza Khulna University Khulna, Bangladesh 23 February 2012Document23 pagesResearch: Introductory: Prof. Dr. Md. Ghulam Murtaza Khulna University Khulna, Bangladesh 23 February 2012abhi_sek200No ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Department of Natural Science University of Cebu - Main Senior High SchoolDocument41 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Department of Natural Science University of Cebu - Main Senior High SchoolJay GeeNo ratings yet
- Sample SizeDocument6 pagesSample SizeClaudio Garretón VénderNo ratings yet
- CH 5 PDocument4 pagesCH 5 PBrandon TulsiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Z-Scores, Measuring Performance: Learning OutcomeDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Z-Scores, Measuring Performance: Learning OutcomeCheska AtienzaNo ratings yet
- MAT240Document54 pagesMAT240Hiền Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Standard Score and Normal distMEdDocument12 pagesStandard Score and Normal distMEdRizalyn GepilanoNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics One-Variable Data Analysis Multiple-Choice PracticeDocument6 pagesAP Statistics One-Variable Data Analysis Multiple-Choice PracticeSunny LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Normal DistributionDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Normal DistributionJustin BorjaNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Properties & ApplicationsDocument33 pagesNormal Distribution Properties & ApplicationskekadiegoNo ratings yet
- STAT100 Fall19 Test 2 ANSWERS Practice Problems PDFDocument23 pagesSTAT100 Fall19 Test 2 ANSWERS Practice Problems PDFabutiNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution HomeworkDocument7 pagesNormal Distribution HomeworkInam Ullah JoharNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution MeansDocument2 pagesSampling Distribution MeansChristina TranNo ratings yet
- Normal Curve Standard Normal CurveDocument33 pagesNormal Curve Standard Normal CurveJahanvi AundhiyaNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurveDocument5 pagesCoefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurvemochiNo ratings yet
- NORMAL PROBABILITY CURVE APPLICATIONSDocument37 pagesNORMAL PROBABILITY CURVE APPLICATIONSK M TripathiNo ratings yet
- PPT Statistics New Syllabus - Part 2Document70 pagesPPT Statistics New Syllabus - Part 2Shubham TambeNo ratings yet
- Handout-B-Standard-Score-And-Normal-Dist Advance StatisticsDocument13 pagesHandout-B-Standard-Score-And-Normal-Dist Advance StatisticsRichard HisanzaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Normal Probability CurveDocument36 pagesUnderstanding the Normal Probability CurveKanchan ManhasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document30 pagesChapter 6Mohd Nazri OthmanNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Math in The Modern World Correlation: ST RDDocument19 pagesWeek 7. Math in The Modern World Correlation: ST RDRyan wilfred LazadasNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution 2012Document29 pagesNormal Distribution 2012Gabriel LloydNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Normal Probability DistributionsDocument13 pagesStudy Guide - Normal Probability DistributionsLamessa GaromaNo ratings yet
- Stat 151 Practice Final 1 - Mike KowalskiDocument11 pagesStat 151 Practice Final 1 - Mike Kowalskimys_genius_007No ratings yet
- Normal Distribution StanfordDocument43 pagesNormal Distribution Stanfordapi-204699162100% (1)
- 1 Normal DistributionDocument34 pages1 Normal DistributionDANELYN PINGKIANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical MedicineDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Clinical MedicineAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Dermot P. Kellher: Immunology, Nature Methods and Nature GeneticsDocument1 pageDermot P. Kellher: Immunology, Nature Methods and Nature GeneticsAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Motivational and Learning Strategies of UST Medical Tech StudentsDocument4 pagesMotivational and Learning Strategies of UST Medical Tech StudentsAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Biostat - Inference For Single MeanDocument3 pagesBiostat - Inference For Single MeanAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Biostat Thesis PosterDocument2 pagesBiostat Thesis PosterAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument3 pagesCulture MediaMicNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument5 pagesCulture MediaAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Biostat Thesis PosterDocument2 pagesBiostat Thesis PosterAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology - Tables (Unfinished)Document2 pagesBacteriology - Tables (Unfinished)Anna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Philo Paper - Saint ThomasDocument6 pagesPhilo Paper - Saint ThomasAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Praying for Peace Through Our Lady of All NationsDocument5 pagesPraying for Peace Through Our Lady of All NationsAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- AnimalDocument2 pagesAnimalAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Complex at Ion To SpectrosDocument1 pageComplex at Ion To SpectrosAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemAnna Dominique JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document3 pagesLesson 7api-265451874100% (2)
- Virginia Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesVirginia Lesson Planapi-269387842No ratings yet
- Reflective Log: ELC081 Foundation of Engineering IIDocument2 pagesReflective Log: ELC081 Foundation of Engineering IIfahnacircleNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Significant Figures and Standard FormDocument15 pagesTopic 1 Significant Figures and Standard FormNoorazleenawazi HasanNo ratings yet
- Professional Development Plan 2017-2018Document2 pagesProfessional Development Plan 2017-2018api-353929409No ratings yet
- CV - of BKDocument3 pagesCV - of BKBadsha miaNo ratings yet
- CTEE Report Fall 2019. Source: National Student Clearinghouse Research CenterDocument23 pagesCTEE Report Fall 2019. Source: National Student Clearinghouse Research CenterHelen BennettNo ratings yet
- Unified Theory of Language LearningDocument5 pagesUnified Theory of Language LearningjamesramilNo ratings yet
- Coaching Teachers Week 2 ReadingDocument11 pagesCoaching Teachers Week 2 ReadinglearnerivanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Experience Report ResultsDocument10 pagesAssessment Experience Report Resultsapi-434489645No ratings yet
- Steam SyllabusDocument3 pagesSteam Syllabusapi-262391786No ratings yet
- Lesson Observation Form (Day 1: Observing English Language Classes)Document10 pagesLesson Observation Form (Day 1: Observing English Language Classes)Jimmy JaneNo ratings yet
- Syllabus East 560 Coms 646Document6 pagesSyllabus East 560 Coms 646Valdis SilsNo ratings yet
- Long 1988Document4 pagesLong 1988Ovirus OviNo ratings yet
- Comal ISD ReportDocument26 pagesComal ISD ReportMariah MedinaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Management - Ahmedabad - Louis KahnDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Management - Ahmedabad - Louis Kahntwinkle4545No ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M1NS-Ib-3 (Week Two-Day 2)Document4 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG OF M1NS-Ib-3 (Week Two-Day 2)Anonymous GLXj9kKp2No ratings yet
- The New Department of Labor Guidelines On InternshipsDocument37 pagesThe New Department of Labor Guidelines On InternshipsTintin Absalon YapNo ratings yet
- CET e Brochure 2Document35 pagesCET e Brochure 2trade_123No ratings yet
- KayCataylolesson PlanDocument9 pagesKayCataylolesson Planalex montemayoresNo ratings yet
- 14 Things Every Successful Person Has in CommonDocument2 pages14 Things Every Successful Person Has in Commonkeat_leong_yeeNo ratings yet
- PG Prospectus 2019 20 PDFDocument276 pagesPG Prospectus 2019 20 PDFSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- PR 2 6-15-2018Document2 pagesPR 2 6-15-2018Charline A. Radislao100% (2)
- Degree: Master of Science in Civil Engineering - Megastructure Engineering With Sustainable Resources (Academic)Document2 pagesDegree: Master of Science in Civil Engineering - Megastructure Engineering With Sustainable Resources (Academic)GenNo ratings yet
- TCS Application FormDocument73 pagesTCS Application FormAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- Using Checklists To Support Student LearningDocument7 pagesUsing Checklists To Support Student Learningvvk1991100% (1)
- SF 2 Emerald 9 2014-2015 BernabeDocument112 pagesSF 2 Emerald 9 2014-2015 BernabeRosendo BernabeNo ratings yet