Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Head Losses in Pipes: Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Audrey Patrick Kalla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pageschemical engineering
Original Title
fluid flow
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchemical engineering
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesHead Losses in Pipes: Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Audrey Patrick Kallachemical engineering
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
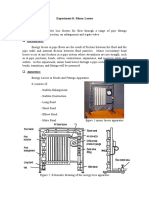
Head Losses in Pipes
Prepared by Professor J . M. Cimbala, Penn State University
Latest revision: 11 J anuary 2012
Nomenclature
d inside diameter of a pipe or device
f Darcy friction factor, as on the Moody chart or from the Colebrook equation
g gravitational constant (9.81 m/s
2
)
h head, i.e. elevation of a fluid column
h
major
major head loss (height of water column) due to friction in a pipe
h
minor
minor head loss (height of water column) due to a device in the pipe system
Ah
L, total
total irreversible head loss, including major and minor losses:
, total major minor L
h h h A = +
K nondimensional minor loss coefficient
L length of pipe section
L
e
Entrance length required for fully developed flow in a pipe
m
mass flow rate through the pipe
P static pressure
Re
d
Reynolds number based on length scale d: Re
d
=Vd/v
V mean velocity in a pipe
V volume
V
or Q
volume flow rate
pump
W
work done to the control volume by a pump
turbine
W
work done by the control volume on a turbine
viscous
W
viscous work done on the control volume by a moving wall
o kinetic energy correction factor in energy equation for a control volume
c average roughness height in a pipe
v kinematic viscosity of the fluid (for water, v ~ 1.0 10
-6
m
2
/s)
density of the fluid (for water, ~ 998 kg/m
3
at room temperature)
Educational Objectives
1. Learn how to measure the volume flow rate of water through a pipe.
2. Reinforce concepts of the Moody chart, and of major and minor head losses in pipes.
3. Measure the friction factor for pipes of various diameters and roughnesses.
4. Compare the experimental results to the published Moody chart (or Colebrook equation).
Equipment
1. pipe flow rig, consisting of a flow loop powered by a flow pump, a control valve, and various test specimens with
static pressure taps
2. tape measure
3. micrometer
4. stopwatch
5. graduated cylinders of various volumes and sizes
6. Validyne pressure transducer with display unit and analog DC voltage output to measure the head difference along a
length of pipe section
7. calibration stand with water manometer tubes to calibrate the pressure transducer
8. long sections of pipe, with static pressure taps:
- nominal 1/2-inch and nominal 3/4-inch copper pipes
- nominal 1/2-inch, nominal 1-inch, and nominal 1 1/2-inch PVC pipes (hydrodynamically smooth)
- nominal 3/4-inch galvanized iron pipe
9. personal computer with digital data acquisition software
10. magnetic resonance flow meter (Rosemount reads volume flow rate in liters per minute)
Background
When water (or any other fluid) flows through a pipe, the pressure continuously drops in the streamwise direction
because of friction along the walls of the pipe. It is common to express this pressure drop in terms of an irreversible head
loss. Head is defined as the vertical height of a column of fluid connected to the flow by a static pressure tap. A fluid column
that is at rest has a hydrostatic pressure difference from top to bottom of the column given by AP =g|Az| =gh, where h =
|Az| is the difference in head or elevation of the column from top to bottom. In flow through piping systems, there are two
types of irreversible head losses. Major losses, denoted by h
major
(sometimes h
f
), are those due to frictional losses through
sections of constant diameter pipe, in which the flow is fully developed. Major losses are expressed in reference books in
terms of a nondimensional friction factor, f, defined as
major
2
2
h
f
L V
d g
= (1)
The Moody chart, or its corresponding equation, the Colebrook equation, is useful for obtaining friction factor as a function
of Reynolds number and pipe roughness coefficient.
Minor losses, denoted by h
minor
, are those due to any other devices in the piping system other than constant-diameter
pipe sections. These include entrances, valves, couplings which change the diameter of the pipe, elbows, etc. Minor losses are
listed in reference books in terms of a nondimensional minor loss coefficient, K, defined as
minor
2
2
h
K
V
g
= (2)
In a system with both major and minor losses, it is important to recognize that a minor loss is defined as the additional loss
due to the presence of the valve, elbow, etc. For example, the minor loss through an elbow does not include the frictional
(Moody chart) loss through the length of the elbow. Thus, when measuring a minor loss coefficient, it is necessary to
measure the length of the elbow, and to incorporate this length into the total length, L, of the pipe system.
For a piping system where the pipe diameter remains constant, Equations (1) and (2) can be combined as follows:
2
, total major minor
2
L
V fL
h h h K
g d
| |
A = + = +
|
\ .
(3)
where
, total L
h A is the sum of all the major and minor losses. In keeping with the above convention, length L represents the
total length of pipe, including the centerline length through each elbow or other minor loss device.
References
1. engel, Y. A. and Cimbala, J . M., Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Applications, McGraw-Hill, NY, 2006.
2. White, F. M., Fluid Mechanics, Ed. 5, McGraw-Hill, NY, 2003.
You might also like
- Head Loss in Pipe - Lab Report MannualDocument4 pagesHead Loss in Pipe - Lab Report MannualRampukar SahNo ratings yet
- Pipeline LosessDocument23 pagesPipeline Losessasl91No ratings yet
- Assignment LabDocument19 pagesAssignment LabHidayah HumairaNo ratings yet
- Major and Minor Losses in PipesDocument15 pagesMajor and Minor Losses in Pipesanjalid9176% (17)
- Conservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesConservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi Meterdist2235No ratings yet
- Flow in PipesDocument29 pagesFlow in PipesRafa MartínezNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 - Friction Loses in PipesDocument20 pagesExpt 1 - Friction Loses in PipesFauzi Helmi67% (6)
- Experiment 8: Minor LossesDocument8 pagesExperiment 8: Minor LossesTalha TirmiziNo ratings yet
- A3 (A) : Elements of Water Supply Network Design.: Pipe FlowDocument4 pagesA3 (A) : Elements of Water Supply Network Design.: Pipe Flowpradeep987No ratings yet
- Steady Incompressible Flow in Pressure Conduits: Lecture - 10Document34 pagesSteady Incompressible Flow in Pressure Conduits: Lecture - 10Nawaz441No ratings yet
- Open Ended Full Report CEWB121Document18 pagesOpen Ended Full Report CEWB121Nur FarehaNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Bends Lab Report Download Full VersionDocument2 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends Lab Report Download Full VersionOBO EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in Pipes-ReportDocument41 pagesExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in Pipes-ReportKhairil Ikram67% (3)
- Friction Factor ManualDocument4 pagesFriction Factor ManualM K TEHSEENNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in Pipes-ReportDocument41 pagesExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in Pipes-ReportKhairil Ikram68% (53)
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesDocument34 pagesExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesKhairil Ikram33% (3)
- Frictional Losses in Circular PipeDocument5 pagesFrictional Losses in Circular PipeVrushiket PatilNo ratings yet
- Energy Loss in Valves: E K U L D U GDocument6 pagesEnergy Loss in Valves: E K U L D U GashrafsaberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Flow in PipesDocument49 pagesChapter 6 Flow in PipesMamuye Busier YesufNo ratings yet
- Module 3-Part3-FM&FMC - Pipe FlowDocument42 pagesModule 3-Part3-FM&FMC - Pipe FlowASHITA K BNo ratings yet
- Friction Loss in PipesDocument15 pagesFriction Loss in PipesMohammed youssifNo ratings yet
- Jayam College of Engineering & Technology Fluid Mechanics & Machinery Me1202Document17 pagesJayam College of Engineering & Technology Fluid Mechanics & Machinery Me1202Muthuvel MNo ratings yet
- 3 Minor LossesDocument47 pages3 Minor LossesFatbardha MorinaNo ratings yet
- Total Head CalculationDocument16 pagesTotal Head CalculationZaid Al RayesNo ratings yet
- Fitting: Pressure Loss From Fittings - 2K MethodDocument10 pagesFitting: Pressure Loss From Fittings - 2K MethodNoor AiniNo ratings yet
- Losses in PipeDocument9 pagesLosses in PipeNiroexNo ratings yet
- Pipe Systems DesignDocument31 pagesPipe Systems DesignAvinash VasudeoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Loss in PipeDocument8 pagesPressure Loss in PipesaeidianNo ratings yet
- Steady Conduit FlowDocument13 pagesSteady Conduit FlowEyuelAdamNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in BendsDocument10 pagesEnergy Losses in BendsAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 2Document12 pagesExperiment 4 2ChongNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document6 pagesLab 5AimiWaniNo ratings yet
- Internal FlowDocument41 pagesInternal FlowTusanita MapuolaNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Abstract, Conclusion, ReferenceDocument4 pagesIntroduction, Abstract, Conclusion, ReferenceChiu Fong50% (2)
- Losses in Bends FittingsDocument26 pagesLosses in Bends FittingsKunalNo ratings yet
- T 2Document31 pagesT 2Vinay Gupta100% (1)
- Viscous Dissipation Term in Energy EquationsDocument14 pagesViscous Dissipation Term in Energy Equationsscience1990No ratings yet
- Mee 303 Lecture 3 AdamDocument46 pagesMee 303 Lecture 3 AdamTomisin EniolaNo ratings yet
- Practical 3 - Friction and Minor Losses in PipesDocument12 pagesPractical 3 - Friction and Minor Losses in PipesAisha Bint IdrisNo ratings yet
- Authentic Ductwork CalculationDocument10 pagesAuthentic Ductwork CalculationbernardsilvanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21. Hydraulics: by Brian BomanDocument10 pagesChapter 21. Hydraulics: by Brian BomanLao ZhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Turbulent Flow in Circular PipesDocument29 pagesChapter 8 Turbulent Flow in Circular PipesSiti Nurshahira100% (1)
- Head LossDocument6 pagesHead LossAli AimranNo ratings yet
- Water System Manual EditedDocument43 pagesWater System Manual EditedFroilan Roman Vergara PineNo ratings yet
- Water SupplyDocument5 pagesWater SupplyZahid BasharNo ratings yet
- P IpesDocument15 pagesP IpesMelvin EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Diaz Bendo Lipana FinalDocument73 pagesDiaz Bendo Lipana FinalAries Villegas MontabonNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document9 pagesLab 5Cem UsmangilNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamic Analysis of Flow Coefficient For Pan Check ValveDocument4 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamic Analysis of Flow Coefficient For Pan Check ValveMax KocourNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Flow Through PipesDocument54 pagesUnit-6 Flow Through PipesS PrathebaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydraulics/Pipeline CalculationsDocument29 pagesEngineering Hydraulics/Pipeline Calculationsbasher rajabNo ratings yet
- PlumbingDocument16 pagesPlumbingMelvin EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Grade LineDocument0 pagesHydraulic Grade LinemuazeemKNo ratings yet
- Report Fluid Friction TestDocument12 pagesReport Fluid Friction TestAbdul Fatah Najmi60% (5)
- Lab Report 2Document16 pagesLab Report 2Limmy Yingran0% (1)
- THERMOFLUIDSDocument23 pagesTHERMOFLUIDSareejkhanNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionStripping PDFDocument25 pagesAbsorptionStripping PDFJuan Camilo HenaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Process DiagramsDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Process Diagramsmrajim93No ratings yet
- 5 StereoisomersDocument37 pages5 StereoisomersAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Ads or PtionDocument141 pagesAds or PtionAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia StorageDocument6 pagesAmmonia Storagemsathishkm3911No ratings yet
- Safety and Security Emergency Plan For EVENTDocument11 pagesSafety and Security Emergency Plan For EVENTAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Absorption ColumnsDocument55 pagesAbsorption ColumnsAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Paint Production Process DiagramDocument4 pagesPaint Production Process DiagramQasim SarwarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process DesignDocument93 pagesChemical Process DesignAudrey Patrick Kalla50% (2)
- .Cost EstimationDocument15 pages.Cost EstimationAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - QDocument32 pagesChapter 10 - Qmohammedakbar88No ratings yet
- Unit Operations and Processes in Environmental EngineeringDocument815 pagesUnit Operations and Processes in Environmental EngineeringAudrey Patrick Kalla89% (28)
- EiaDocument16 pagesEiaAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument16 pagesHeat ExchangerAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Paints Know How Plant Setting FormulationsDocument1 pageAerosol Paints Know How Plant Setting FormulationsAudrey Patrick Kalla67% (3)
- 09.electromagntic and Faraday Law - InductionDocument53 pages09.electromagntic and Faraday Law - InductionAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Paint Testing ChartDocument39 pagesPaint Testing ChartAudrey Patrick Kalla0% (1)
- Magnetic Fields: PHYS102 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument11 pagesMagnetic Fields: PHYS102 Previous Exam ProblemsAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Paint and Coating ProcessesDocument65 pagesPaint and Coating ProcessesAudrey Patrick Kalla100% (1)
- 84 enDocument6 pages84 enNomaan AsimNo ratings yet
- Operator'S Manual: E-Series Ultraviolet Hand LampsDocument9 pagesOperator'S Manual: E-Series Ultraviolet Hand LampsGuiss LemaNo ratings yet
- David Beard Composer CV ShortDocument2 pagesDavid Beard Composer CV ShortEhsan KarimyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Supercritical Flow in Rectangular ChannelDocument10 pagesCharacteristics of Supercritical Flow in Rectangular ChannelFatihNo ratings yet
- Template For Table of Contents of RPMS PortfolioDocument4 pagesTemplate For Table of Contents of RPMS PortfolioGener Toledo100% (4)
- JeeleDocument9 pagesJeeleAnonymous SZDGk7SvGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ada Solo Project: Robert Rostkowski CS 460 Computer Security Fall 2008Document20 pagesIntroduction To Ada Solo Project: Robert Rostkowski CS 460 Computer Security Fall 2008anilkumar18No ratings yet
- 20 and 21. Requirements For Licensure by Examination Nclex. Revised 06.20.19 1Document2 pages20 and 21. Requirements For Licensure by Examination Nclex. Revised 06.20.19 1Glennah Marie Avenido RamosNo ratings yet
- Times of India - Supply Chain Management of Newspapers and MagazinesDocument18 pagesTimes of India - Supply Chain Management of Newspapers and MagazinesPravakar Kumar33% (3)
- DH Xvr4b16Document3 pagesDH Xvr4b16Jumar JumadiaoNo ratings yet
- BS EN 12536-2000 Gas Welding Creep Resistant, Non-Alloy and Fine Grain PDFDocument11 pagesBS EN 12536-2000 Gas Welding Creep Resistant, Non-Alloy and Fine Grain PDFo_l_0No ratings yet
- IET Membership Guidance NotesDocument4 pagesIET Membership Guidance NotesKingsley InbasinghNo ratings yet
- ECSS E ST 50 03C (31july2008)Document43 pagesECSS E ST 50 03C (31july2008)jsadachiNo ratings yet
- Microsoft ISA Server 2006 - Certificate Troubleshooting - Part IIDocument7 pagesMicrosoft ISA Server 2006 - Certificate Troubleshooting - Part IIKhodor AkoumNo ratings yet
- The Miser'S T/R Loop Antenna: MiserlyDocument3 pagesThe Miser'S T/R Loop Antenna: MiserlyTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study On Drilling of Metals Through Microwave HeatingDocument6 pagesA Feasibility Study On Drilling of Metals Through Microwave HeatingT J GNo ratings yet
- Hyperion Essbase 6 - 5 Bootcamp - Basic TrainingDocument659 pagesHyperion Essbase 6 - 5 Bootcamp - Basic Trainingrams08No ratings yet
- PROSIS Part Information: Date: Image Id: Catalogue: ModelDocument2 pagesPROSIS Part Information: Date: Image Id: Catalogue: ModelAMIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- AAE 11.3.1 User Guide ClientDocument475 pagesAAE 11.3.1 User Guide Clientme4ias100% (2)
- Java Lang OutOfMemoryError Handbook - PlumbrDocument28 pagesJava Lang OutOfMemoryError Handbook - PlumbrcuonglunNo ratings yet
- AR Porta CabinDocument2 pagesAR Porta CabinVp SreejithNo ratings yet
- Tank TacticsDocument241 pagesTank TacticsSlobodan Petrovic100% (1)
- MDLink User Manual PDFDocument41 pagesMDLink User Manual PDFkulov1592No ratings yet
- The Impact of Internet Use For StudentsDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Internet Use For StudentsCharlesNo ratings yet
- DLS RSeriesManual PDFDocument9 pagesDLS RSeriesManual PDFdanysan2525No ratings yet
- D 5720-95Document9 pagesD 5720-95ipkm123No ratings yet
- RAC D Expansion DevicesDocument21 pagesRAC D Expansion DevicesSohaib IrfanNo ratings yet
- Fallout New OrleansDocument44 pagesFallout New Orleansender000No ratings yet
- Photometric Design White PaperDocument5 pagesPhotometric Design White PaperScott VokeyNo ratings yet
- NNH4-65C-R6-V2: Electrical SpecificationsDocument4 pagesNNH4-65C-R6-V2: Electrical SpecificationsAntony López GálvezNo ratings yet
- Sem 638 Manual de MantenimientoDocument12 pagesSem 638 Manual de MantenimientoJhon Simanca100% (1)
- The Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeFrom EverandThe Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (52)
- Waste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretFrom EverandWaste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionFrom EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionFrom EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CFrom EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CNo ratings yet
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthFrom EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (197)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseFrom EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersFrom EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fuels, Furnaces and Refractories: International Series on Materials Science and TechnologyFrom EverandFuels, Furnaces and Refractories: International Series on Materials Science and TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeFrom EverandProof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (165)
- Chasing the Demon: A Secret History of the Quest for the Sound Barrier, and the Band of American Aces Who Conquered ItFrom EverandChasing the Demon: A Secret History of the Quest for the Sound Barrier, and the Band of American Aces Who Conquered ItRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)From EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- Gas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsFrom EverandGas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsFrom EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Electrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeFrom EverandElectrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Mechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringFrom EverandMechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet