Professional Documents
Culture Documents
400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9
Uploaded by
thailander2011Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9
Uploaded by
thailander2011Copyright:
Available Formats
The Collapse of Soviet Union, 1989 - 1991 (Double-sided) Economic Collapse
-USSR focused industrial development on military production and NOT consumer or domestic goods -Following the death of Stalin, the economic growth of the USSR became very sluggish (diminished significantly) -1/3 of all USSR income went to supporting their ARMS RACE with the United States *Severe reduction in consumer good development *The central planning (central govt.) was very corrupt and spent USSR money on corrupt firms that did not produce needed materials -Mikhail Gorbachev (Soviet Premier / President) attempted reforms. Gorbachevs beliefs / goals: 1. He believed that the economy should tell producers what to make (supply & demand) not the central planning of the government 2. Wanted to allow for SOME private ownership and less central control of agriculture and industry Attempted reforms = PERESTROIKA (1987) which means restructuring *Restructured the Soviet economy to be competitive with global markets *Allowed some individual, private ownership in both agriculture and industry *Limited the influence of the central government to attempt to eliminate corruption *Wanted major reduction in military spending and force to allocate more funds to the general consumer production BUT this did not happen to the degree needed RESULTS: 1. Perestroika was NOT the answer Gorbachev was hoping that it would be BUT the restructuring plan did show the USSR and the world the magnitude of the problems in the USSR. 2. By 1990, a proposed economic restructuring package was given to the Soviet Government. It wouldve allowed for private ownership of property, allow individual USSR Republics (states) to decide their economic future AND allow for the breaking up of monopolies.
Social Collapse
-Due to the stagnation of the economy after the death of Stalin, citizens began to resent Communist Party officials because of their lavish lifestyles (this is against Communism and the ideals of Lenin). -Resentment against the Communist Party grows significantly under Premier Brezhnev in the 1970s. -Laborers were less motivated to work under Communism because there was no reward system (more work did NOT equal more privileges). Huge increase in alcoholism, death rates and suicides. -Citizens become aware of the environmental damage the military / industrial economy is doing to their country. DISEASES as a result of environmental abuse concerned citizens. -Introduction of Western tourism opened the eyes of Soviets as to the alternatives to their government/economy/way of life. -Riots begin to commence in Soviet occupied areas due to housing, land and food shortages (Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan are first to demonstrate their discontent). -NATIONALISM / SEPARATISM BEGAN TO ARISE IN SOVIET REPUBLICS 1. Warsaw Pact countries (Bulgaria, Hungary, Poland, Easy Germany, Czechoslovakia, Rumania, and Yugoslavia) wanted to separate from the USSR for econ., soc., and polt. Reasons 2. Non-Russian (Asian) Soviet Republics gain a strong sense of nationalism and have wanted to separate since being included in the USSR. Resentment over Russification becomes very strong. 3. Russians themselves feel a sense of social loss. Their culture and heritage had been manipulated by the Soviet government to suit the needs of central planning. It has been negatively altered to assist in central planning but not to assist the preservation of Russian culture. -The promises of Communism were not being honored. Instead, the doctrine is constantly revised and altered to suit the needs of the central government. -Sense of nationalism would give rise to national anxieties within the borders of the Non-Russian Soviet Republics and result in bloodshed in areas like Armenia & Ukraine where a homogenous culture/society had been forced on the people.
Political Collapse
-Stagnation of the political system (no positive change) grows during the 1970s under Brezhnevs regime. -Gorbachev is reform-minded and barely gains support of the Politburo (the main Communist political organization in USSR) 1. Many of the conservative Politburo members are scared of the reforms that Gorbachev will propose (it threatens the security of the jobs/lifestyles of the Politburo members) 2. Implementation of GLASTNOST (which means openness in Russian) to allow for the critique of the government by the people. Loosening of restrictions on political speech and action on the people (still in place, but loosened). 3. Perestroika (restructuring) was implemented later in an attempt to restructure the economy but it was a failure (too little, too late). 4. Gorbachev continually wavered between complete reform and the conservative nature of the strict Politburo. His wavering did not lead to effective reform. 5. Warsaw Pact countries begin to disengage from the Soviet Union and create their own political and economic systems. The dissent in these nations spreads to the Soviet Republics and allows for the power needed to break away from the Soviet government. -New Constitution of 1988: New parliament formed. Introduction of democratic reforms. BORIS YELTSIN gains prestige and power as a democratic reformer. -Gorbachev tries to gain power (1990) by having himself popularly elected (by the people). He is elected, but his power dwindles quickly. -Failed coup to recapture power by loyal, conservative followers of Gorbachev in 1991. 1. Coup attempts take-over while Gorbachev is away on vacation (they dont even have their leader around) 2. Failure of coup is a reaction by the general population against Communism 3. Gorbachev understands the loss of his power base and the growing discontent. 4. Yeltsin elected AND Commonwealth of Independent States (temporary organization of old Soviet States) is formed - but fails soon thereafter. 5. Dec. 8, 1991 - Gorbachev resigns and disbands the Soviet/Communist Central Committee. USSR = done.
3. TOO LITTLE, TOO LATE. The Soviet economy is ruined and beyond repair.
Significance of the collapse of the USSR 1. This is the official end of the Cold War order. No longer is their a BI-POLAR world of USA vs. USSR. 2. 25,000,000 (+) Russians are displaced from the former Soviet states where they were living. The rise in nationalism in the newly-free countries leads to the forcing out of Russians who were living there (they were often FORCED to live there by the Soviet government). 3. Eastern Europe begins integration into the western European political (NATO) and economic spheres (European Economic Union). 4. Increased destabilization of Russian government and economy during the period of transition. 5. Ethnic republics battle with minority populations within their borders (ex. Ukraine). 6. Ex-Soviet and former Russian republics suffer economically as they attempt capitalism. Once dependent upon one another, now they cannot rely on each others failing economies. There is no a. Economic growth b. Economic coordination / sharing or production or responsibility c. THERE IS ethnic conflict that causes economic problems 7. China becomes the only major Communist country that is also a viable economic and military contender (Cuba is a non-issue). 8. UNSAFE DIFFUSION OF SOVIET TECHNOLOGY a. Nuclear power plants are not maintained or governed properly. They stay in the newly freed countries, but continue to run without funding or maintenance. This leads to severe environmental disasters (Chernobyl disaster is one example). b. Nuclear weaponry becomes the property of the freed Soviet states. Unable to maintain safety OR funding, these new governments are tempted (and often do) to sell their weapons. c. Nuclear proliferation. Countries that did not have the financial or technological resources during the Cold War to develop their own nuclear power can now BUY IT from the struggling countries that were once part of the USSR. 9. United States becomes a hegemonic (solo) world power by default. 10. Economic / Social void created in USSR as the upstart democracies attempt to provide for their people without the resources of the former command economy. New, staggering levels of poverty, alcoholism, homelessness, starvation, drug use and spreading of disease are seen across the former Soviet Union. (becomes a WORLD ISSUE, the HEALTH of world citizens).
You might also like
- Political System of USSRDocument24 pagesPolitical System of USSRasadNo ratings yet
- Disintegration of USSR 1991 Reasons and ImpactDocument4 pagesDisintegration of USSR 1991 Reasons and ImpactBhawna RanaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument22 pagesIntroductionKhushiNo ratings yet
- Class12 Political Science 2 World Politics Unit02 NCERT TextBook English EditionDocument14 pagesClass12 Political Science 2 World Politics Unit02 NCERT TextBook English EditionAbhilash KhajuriaNo ratings yet
- 7.soviet Union DisintegrationDocument5 pages7.soviet Union DisintegrationUsamahNo ratings yet
- Humanities ArticleDocument3 pagesHumanities Articleapi-361658127No ratings yet
- Disintegration of The USSR 1991 Reasons and ImpactDocument4 pagesDisintegration of The USSR 1991 Reasons and ImpactMunna SinghNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts about the Collapse of the Soviet Union - History Book with Pictures | Children's Military BooksFrom EverandInteresting Facts about the Collapse of the Soviet Union - History Book with Pictures | Children's Military BooksNo ratings yet
- The Fall of The Soviet Union and The End of The Cold WarDocument6 pagesThe Fall of The Soviet Union and The End of The Cold WarNatalia Castillejo AriasNo ratings yet
- 12 Political Science The End of Bipolarity Notes & Mind MapDocument7 pages12 Political Science The End of Bipolarity Notes & Mind Mapsayooj tv88% (17)
- The Collapse of The Soviet UnionDocument36 pagesThe Collapse of The Soviet UnionSoma DamNo ratings yet
- Ch-2The End of BipolarityDocument11 pagesCh-2The End of BipolarityMuskan DhankherNo ratings yet
- XVI. The Collapse of The USSRDocument18 pagesXVI. The Collapse of The USSREce DinçNo ratings yet
- End of Cold War PHB9Document31 pagesEnd of Cold War PHB9poNo ratings yet
- CH-2 The End of Bipolarity Notes:: Soviet SystemDocument10 pagesCH-2 The End of Bipolarity Notes:: Soviet SystemDeepika ITNo ratings yet
- Units 8 and 10.: The Interwar Years and The Second World WarDocument4 pagesUnits 8 and 10.: The Interwar Years and The Second World WarJuan Pablo Angarita DuqueNo ratings yet
- Leps 102Document14 pagesLeps 102Santanu SahaNo ratings yet
- Fall of Communism PowerpointDocument29 pagesFall of Communism PowerpointSanjana Gupta50% (2)
- Mikhail Gorbachev's Dual Policies: Gorbachev Introduced Two Sets of Policies That He Hoped Would HelpDocument3 pagesMikhail Gorbachev's Dual Policies: Gorbachev Introduced Two Sets of Policies That He Hoped Would HelpJimmy ReeceNo ratings yet
- Factors Responsible For The Disintegration of The Soviet UnionDocument10 pagesFactors Responsible For The Disintegration of The Soviet UnionAlizain AmiraliNo ratings yet
- End of BipolarityDocument3 pagesEnd of Bipolarityi change my mind, you're all ugly0% (1)
- Ch-2 End of BipolarityDocument9 pagesCh-2 End of Bipolarity1630 Gursimran Saluja ANo ratings yet
- 2.end of BipolarityDocument8 pages2.end of Bipolaritygunjan sahota100% (1)
- CHP 2 - B1 END OF BIPOLARITYDocument12 pagesCHP 2 - B1 END OF BIPOLARITYPrabhjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Bipolarity (World Politics)Document7 pagesBipolarity (World Politics)Amazing Aditi SingalNo ratings yet
- The Collapse of Soviet Control and The End of Communist Regimes in Eastern EuropeDocument12 pagesThe Collapse of Soviet Control and The End of Communist Regimes in Eastern EuropeBrian DeanNo ratings yet
- CH-2 End of Bipolarity (PS1)Document25 pagesCH-2 End of Bipolarity (PS1)loneferooz83No ratings yet
- Summary Of "New Social Movements: WWII Ending To 1970s" By Florencio Núñez: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "New Social Movements: WWII Ending To 1970s" By Florencio Núñez: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- A Glance On Soviet Union Its DisintegartionDocument2 pagesA Glance On Soviet Union Its DisintegartionBakhtiar Azeem SoomroNo ratings yet
- XII Political Science Ch-2 End of BipolarityDocument8 pagesXII Political Science Ch-2 End of BipolaritysunshineNo ratings yet
- The Crisis of Socialist Modernity: The Soviet Union and Yugoslavia in the 1970sFrom EverandThe Crisis of Socialist Modernity: The Soviet Union and Yugoslavia in the 1970sNo ratings yet
- Do Publicly Owned, Planned Economies WorkDocument20 pagesDo Publicly Owned, Planned Economies WorkRichard BalducciNo ratings yet
- An Unexpected CollapseDocument8 pagesAn Unexpected Collapsethailander2011No ratings yet
- Political Science NotesDocument8 pagesPolitical Science NotesAayushi JhaNo ratings yet
- 12th Chapter 2Document6 pages12th Chapter 2reyaz loneNo ratings yet
- Comparative EconomicsDocument13 pagesComparative EconomicsHaidee BellaNo ratings yet
- Commanding Heights IIDocument12 pagesCommanding Heights IINadean Kate PalmesNo ratings yet
- The End of BipolarityDocument9 pagesThe End of BipolarityAayushi JhaNo ratings yet
- The Collapse of The Soviet UnionDocument29 pagesThe Collapse of The Soviet UnionSumitpal SinghNo ratings yet
- End of BipolarityDocument9 pagesEnd of Bipolarityekagrata100% (1)
- Units 7 and 8 HistoryDocument8 pagesUnits 7 and 8 HistoryMaría GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Twilight of the Gods - Götterdämmerung over the "New World Order"From EverandTwilight of the Gods - Götterdämmerung over the "New World Order"No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentKunsh WadheraNo ratings yet
- Disintegration of The Ussr: Western History M.A., Semester - IV, Paper-I, International Relations Since 1989Document5 pagesDisintegration of The Ussr: Western History M.A., Semester - IV, Paper-I, International Relations Since 1989Supriya KhajuriaNo ratings yet
- Russia Group 4Document5 pagesRussia Group 4gressylmaepainagan17No ratings yet
- ss30-1 Ri2 ch5 Communism As A Rejection of Liberalism 2014Document22 pagesss30-1 Ri2 ch5 Communism As A Rejection of Liberalism 2014api-263969748No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (The End of Bipolarity)Document6 pagesChapter 2 (The End of Bipolarity)poojaarora_10_juneNo ratings yet
- End of Bipolarity NotesDocument8 pagesEnd of Bipolarity NotesAsaduddin OwaisiNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers On Stalin RussiaDocument52 pagesQuestions and Answers On Stalin RussiaHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- HISTORY NOTES Part 1Document13 pagesHISTORY NOTES Part 1Laura MontagutNo ratings yet
- Conversations with Gorbachev: On Perestroika, the Prague Spring, and the Crossroads of SocialismFrom EverandConversations with Gorbachev: On Perestroika, the Prague Spring, and the Crossroads of SocialismNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of The Communist Group. The USSR and The Evolution Og The Non-Aligned Countries.Document4 pagesThe Evolution of The Communist Group. The USSR and The Evolution Og The Non-Aligned Countries.orionnidkNo ratings yet
- გამლეტ ხანDocument37 pagesგამლეტ ხანZviad MiminoshviliNo ratings yet
- Russian Government:: ExecutiveDocument3 pagesRussian Government:: ExecutiveNeculai ZotaNo ratings yet
- 2 5 NotesDocument11 pages2 5 Notesapi-3831398No ratings yet
- Ussr PaperDocument5 pagesUssr Paperapi-346838508No ratings yet
- Causes of The Collapse of The Soviet Union PDFDocument12 pagesCauses of The Collapse of The Soviet Union PDFparamjit100% (1)
- Myth of The Authoritarian ModelDocument17 pagesMyth of The Authoritarian Modelthailander2011No ratings yet
- FinalThesis July 15 2011Document47 pagesFinalThesis July 15 2011thailander2011No ratings yet
- The Fall of Soviet UniionDocument19 pagesThe Fall of Soviet Uniionthailander2011No ratings yet
- An Unexpected CollapseDocument8 pagesAn Unexpected Collapsethailander2011No ratings yet
- Lenin ArticleDocument6 pagesLenin ArticlelolmemNo ratings yet
- Meyerhold and StanislavskyDocument47 pagesMeyerhold and StanislavskyDavid Herman100% (1)
- The October Revolution RevisedDocument5 pagesThe October Revolution RevisedDMC3444No ratings yet
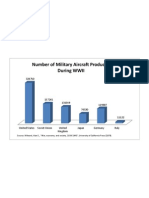
- Aircraft Production Graph WWIIDocument1 pageAircraft Production Graph WWIIsteven_e_kleinNo ratings yet
- Career Counselling HistoryDocument15 pagesCareer Counselling HistoryZain Ul AbidenNo ratings yet
- FDR & UnDocument8 pagesFDR & UnDebajit KarNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement Examples Cold WarDocument6 pagesThesis Statement Examples Cold Waraflpbpcnhjpwkd100% (2)
- Sarah Hamblin's 2012 PHD Dissertation "Screening The Impossible: The Politics of Form and Feeling in Second Wave Revolutionary Cinema".Document310 pagesSarah Hamblin's 2012 PHD Dissertation "Screening The Impossible: The Politics of Form and Feeling in Second Wave Revolutionary Cinema".Benjamin RosenzweigNo ratings yet
- Origins of The CW Tci ReadingDocument8 pagesOrigins of The CW Tci Readingapi-235209117No ratings yet
- MOONSPIRACY - Real or FakeDocument65 pagesMOONSPIRACY - Real or FakeFrank AbrignaniNo ratings yet
- Kennedy Assassination: Oswald As Manchurian CandidateDocument55 pagesKennedy Assassination: Oswald As Manchurian CandidateTom Slattery100% (8)
- National History Day PaperworkDocument36 pagesNational History Day PaperworkthebenkaplanNo ratings yet
- Indian Foreign Policy Unit 1-QuestionsDocument14 pagesIndian Foreign Policy Unit 1-QuestionsMahi Sanjay PanchalNo ratings yet
- Theories of CommunicationDocument31 pagesTheories of CommunicationRehmia ArshadNo ratings yet
- Plekhanov, Selected Philosophical Works, Vol. I (OCRed)Document809 pagesPlekhanov, Selected Philosophical Works, Vol. I (OCRed)danielgaid100% (1)
- Mearsheimer - Nato1Document2 pagesMearsheimer - Nato1Jane DoeNo ratings yet
- By Robert Henry GoldsboroughDocument30 pagesBy Robert Henry GoldsboroughJelani FletcherNo ratings yet
- Fritz FischerDocument212 pagesFritz FischerAnonymous vnTWqRDmLNo ratings yet
- Artinian - Communist Eudaemonia - Evald Ilyenkov and The Good Life - V7Document16 pagesArtinian - Communist Eudaemonia - Evald Ilyenkov and The Good Life - V7Keti ChukhrovNo ratings yet
- Korean War Research Paper ThesisDocument4 pagesKorean War Research Paper Thesisfc2b5myj100% (3)
- Chapter 1 The Cold War EraDocument6 pagesChapter 1 The Cold War EraMuskaan SinghNo ratings yet
- The German Question: The Stalin Note of 1952 and The Problem of ReunificationDocument208 pagesThe German Question: The Stalin Note of 1952 and The Problem of ReunificationvellyvNo ratings yet
- 70 Years of Pakistans Foreign PolicyDocument6 pages70 Years of Pakistans Foreign Policymuhammad ihsanNo ratings yet
- John Prados - Presidents' Secret Wars - CIA & Pentagon Covert Operations Since World War II-William Morrow & Co. (1986) PDFDocument480 pagesJohn Prados - Presidents' Secret Wars - CIA & Pentagon Covert Operations Since World War II-William Morrow & Co. (1986) PDFmackandall sinisNo ratings yet
- Pakistan-Russian Relations: A Glance Over History by Zeeshan FidaDocument46 pagesPakistan-Russian Relations: A Glance Over History by Zeeshan FidaYassir ButtNo ratings yet
- Studies in Eastern European Cinema 1.1Document132 pagesStudies in Eastern European Cinema 1.1Intellect BooksNo ratings yet
- Aleksandre Zibzibadze - International Business Confirmation PaperDocument81 pagesAleksandre Zibzibadze - International Business Confirmation PaperAlexander ZibzibadzeNo ratings yet
- Woman in Bulgarian SocietyDocument11 pagesWoman in Bulgarian SocietyLakiLakicNo ratings yet
- Cold War SourcesDocument90 pagesCold War Sourcesbdw39No ratings yet
- Globalism in The Schools: Education or Indoctrination?Document11 pagesGlobalism in The Schools: Education or Indoctrination?Independence InstituteNo ratings yet