Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Basic Grammar Chart: Cinema Every Week Earth Goes Around The The Sun A Shower When The Telephone Rang
Uploaded by
Veeresh Savadi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views0 pageschart
Original Title
Grammar Chart
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchart
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views0 pagesEnglish Basic Grammar Chart: Cinema Every Week Earth Goes Around The The Sun A Shower When The Telephone Rang
Uploaded by
Veeresh Savadichart
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 0
IES LA RABIDA, 2010 (Antonia Domnguez)
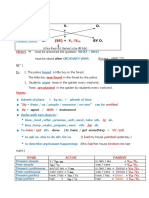
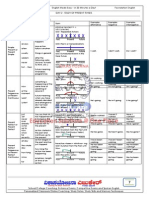
ENGLISH BASIC GRAMMAR CHART
PRESENT SIMPLE:
Affirmativa: S + V
(-s 3 p)
Negativa: S + Dont/Doesnt + V
Interrogativa: Do/Does + S + V
USE: * Acciones habituales que se repiten cada cierto tiempo: I go to the
cinema every week
* Horarios oficiales, verdades absolutas: The train leaves at 5/ The
earth goes around the the sun
PRESENT CONTINUOUS:
Affirmativa: S + is/are +V
-ing
Negativa: S + isnt/arent +V
-ing
Interrogativa: is/are + S +V
-ing
USE: * Acciones que se realizan en el momento de hablar: I am using the
computer now.
* Acciones temporales en el presente: They are building a new school
in this street.
* Planes de futuro: I am leaving to London tomorrow.
PAST SIMPLE:
Affirmativa: S + V
-ed (-2c. v. irreg)
.......
Negativa: S + Didnt + V ......
Interrogativa: Did + S + V ......?
USE: * Acciones empezadas y terminadas en el pasado: I went to Paris last
summer.
* Acciones puntuales en el pasado: I was cooking when he arrived
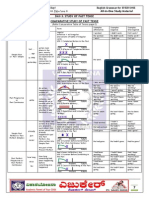
PAST CONTINOUS:
Affirmativa: S + was/were +V
-ing
Negativa: S + wasnt/werent +V
-ing
Interrogativa: was/were + S +V
-ing
USE: * Acciones que se estaban realizando en el pasado sin saber si se
terminaron o no: I was studying Maths yesterday at 4:30
* Acciones largas que se estaban realizando en el pasado: I was having
a shower when the telephone rang.
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE:
Affirmativa: S + have/has + V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
Negativa: S + havent/hasnt + V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
Interrogativa: Have/has + S + V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
USE: * Accin que empez en el pasado y continua hasta el presente: I have
lived in Huelva for 15 years
* Accin con consecuencia en el presente o que acaba de terminar justo
ahora: I have cut my finger!
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS:
Affirmativa: S + have has + been + V
-ing
Negativa: S + havent/hasnt + been + V
-ing
Interrogativa: Have/has + S + been + V
-ing
USE: * Accin que empez en el pasado y continua hasta el presente y no
sabemos si termin o no. Lo que nos importa es la accin en s misma,
lo que dur, etc.: I have been painting the room for three hours! /How
long have you been writing that book?
IES LA RABIDA, 2010 (Antonia Domnguez)
PAST PERFECT SIMPLE:
Affirmativa: S + had + V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
Negativa: S + hadnt + V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
Interrogativa: Had + S + V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
USE: * Accin que empez y acab en el pasado antes de que ocurriera otra
accin tambin el pasado: When I arrived at the party, Miguel had
gone home.
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS:
Affirmativa: S + had + been + V
-ing
Negativa: S + hadnt + been + V
-ing
Interrogativa: Had + S + been + V
-ing
USE: * Una accin que estaba en proceso antes de una segunda accin/tiempo
definido en el pasado: The grass was wet because it had been raining
all night long.
ORACIONES DE RELATIVO:
WHO Que, quien para personas The people who work there are my
friends, la gente que trabaja ah son mis
amigos
WHICH Que para cosas Madrid, which is in central Spain, is the
capital of the country. Madrid, que esta
en el centro de Espaa,.....
THAT Reemplaza a who o which en
las oraciones que no van
entre comas
Did you see the car that Juan bought?
Viste el conche que se compr J uan?
WHOM Uso muy formal, apenas se
usa y sustituye al objeto.
This is the boy whom/that I met on the
train. Este es el chico que conoc en el
tren.
WHERE Donde, sustituye a lugares, a
there, here
The school where I studied has been
closed. La escuela donde estudi est
cerrada.
WHOSE Se usa para el posesivo,
cuyo/a, de quien
The man whose car was stolen called
the police. El hombre cuyo coche
robaron llam a la polica
WHEN Se usa para el tiempo,
cuando
I remember when we first met.
Recuerdo cuando nos conocimos.
ORACIONES DE RELATIVO EXPLICATIVAS:
* Aaden informacin extra.
* Va entre comas
* Nunca se puede sustituir who, o which por that.
Janet Sullivan, who is the presidents wife, died yesterday.
J anet Sullivan, que es la mujer del presidente, muri ayer.
ORACIONES DE RELATIVO ESPECIFICATIVAS:
* Especifican DE quin se est hablando
* No van entre comas
* Who o which se puede sustituir por that.
* Who, which o that se puede omitir por completo cuando no son el sujeto de la
oracin de relativo.
The woman who/that lives next door is a widow
La mujer que vive al lado es viuda
This is the book (that) I bought yesterday.
Este es el libro que compr ayer
ORACIONES TEMPORALES:
* Son oraciones que acompaan a ideas de futuro
* Van introducidas por partculas como : before (antes de), after (despus de),
when (cuando), until (hasta que), as son as (tan pronto como), as long as (siempre
que).
* Estas partculas siempre van seguidas de presente o pasado simple nunca futuro.
When he comes home, I will tell him. Cuando llegue se lo dir
As soon as I pass the exam, I ll buy a car. Tan pronto como apurebe el exmen
me comprar un coche.
I wont talk to her until she apologizes for what she did. No le hablar hasta que
no me pida perdn por lo que hizo.
IES LA RABIDA, 2010 (Antonia Domnguez)
MODALES:
* Siempre van seguidos de infinitivo sin to
* No tienen s de la 3 persona singular
* Algunos no tienen pasado o futuro (must, can)
* No necesitan auxiliares para negar y preguntar.
CAN: * Expresa habilidad: I can play the piano
* Para pedir permiso: Can I go to the toilet?
* Para pedir algo: Can you open the door please?
* Negativa: imposibilidad: He cant be in Italy now. I just saw him (No puede
estar en Italia. Acabo de verle)
COULD: * Habilidad en el pasado: I could play the piano when I was 6.
* Peticin (ms formal que can): Could you open the door, please?
* Posibilidad: They could be in the disco (podran estar en la discoteca)
MAY: * Para pedir permiso: May I go to the toilet, please? (Puedo ir al servicio)
* Posibilidad escasa: He may come tomorrow. (El puede que venga maana)
MIGHT: * Posibilidad muy remota: It might rain tomorrow. (Pudiera ser que lloviera
maana)
MUST: * Oblicacin: You must be quiet here. (Debes estar en silencio aqu)
* Prohicin (negativa): You mustnt smoke here. (No debes/est prohibido fumar
aqu)
* Gran posibilidad: He must be home now. (El debe estar ya en casa)
HAVE TO: * Obligacin: We have to wear school uniforms. (Tenemos que llevar
uniforme en la escuela).
DONT HAVE TO: *Ausencia de obligacin: You dont have to pay until next month. (No
tienes que pagar hasta el mes que viene)
NEEDNT: *Ausencia De obligacin =dont have to: You neednt come to the meeting.
Its not necessary. (No tienes que venir a la reunin.No es necesario)
SHOULD: * Para dar consejo, deberas....: You should go to the doctor if you are ill.
(Deberas ir al mdico si ests enfermo)
* Sugerencia sobre hacer o no algo: Should I give you my passport now?
(Debera darle mi pasaporte?)
WILL: * Prediccin: He will arive at 6. (El llegar a las 6.)
* Decisin inmediata, espontnea: Ill answer the phone (Yo coger el telfono)
Peticin educada: Will you pass me the sugar, please? (Me pasas el azcar por
favor?
WOULD: * peticin educada: Would you move your car?
ORACIONES PASIVAS:
* Las oraciones pasivas siempre tienen un sujeto paciente que originariamente es
el objeto del verbo en activa:
John built that house That house was built by John
J ohn construy esa casa. Esa casa fue construida por J ohn
* El verbo en pasiva se forma con el verbo to be +el participio del verbo
principal. Al pasar de activa a pasiva el verbo be tiene que estar conjugado en el mismo
tiempo que el verbo activo.
Activa: S + V
T
+ O
Pasiva: O + BE
T
+ V
-ed (3 col.V. irreg.)
John built that house built=pasado simple
That house was built by John was=pasado simple
Ejemplos:
* They sell tickest here Tickets are sold here
Venden entradas aqu Las entradas son vendidas aqu
* They are building a new school A new school is being built here
Estn construyendo una escuela Una escuela est siendo construida
* We sent the letter in May The letter was sent in May
Enviamos la carta en Mayo La carta fue enviada en Mayo
* We were planning a trip to London yesterday. A trip to London was being
planned yesterday
Ayer estbamos planeando un viaje a Londres Un viaje a Londres estaba
siendo planeado ayer
IES LA RABIDA, 2010 (Antonia Domnguez)
FUTURO:
Afirmativa: S + WILL + V
Negativa: S + WON'T + V
Interrogativa: WILL + S + V ?
------------------------------------
Affirmativa: S + is/are GOING TO + V
Negativa: S + isn't/aren't GOING TO + V
Interrogativa: is/are + S + GOING TO + V
USO DE WILL:
* Para predicciones u opiniones personales: They will arrive tomorrow.
(Llegarn maana)
* Decisiones inmediatas, espontneas: I will answer the pone. (Yo
contestar el telfono)
USO DE BE GOING TO:
* Para predicciones que se pueden anticipar desde el presente: Look at
those black clouds. It is going to rain soon. (Mira esas nubes negras.
Va a llover pronto.)
* Para planes premeditados de antemano: We are going to travel to
Greece this summer. (Vamos a viajara Grecia este verano)
USO DEL PRESENT CONTINUOUS:
* Planes de futuro fijados de antemano con seguridad: I am leaving to
London tomorrow.
CONDICIONALES:
CONDICIONAL ZERO: (100% seguro)
IF + PRESENTE , ......... PRESENTE
If you water a plant, it grows
Si riegas una planta, crece.
PRIMERA CONDICIONAL: (posible)
IF + PRESENTE , .........WILL + V
If I win the lottery, I will buy a new house
Si gano la lotera, me comprar una casa nueva.
SEGUNDA CONDICIONAL: (probable)
IF + PASADO, ........ WOULD + V
If he studied more, he would pass the exam.
Si el estudiara ms, aprobara el examen
TERCERA CONDICIONAL: (imposible)
IF + PAST PERFECT, . WOULD HAVE + V-ed
If I had gone to the party, I would have met Bard Pitt.
Si hubiera ido a la fiesta, habra conocido a Brad Pitt.
You might also like
- Đề cương ôn tập kiểm tra học kỳ II tiếng Anh 8Document9 pagesĐề cương ôn tập kiểm tra học kỳ II tiếng Anh 8Nhi HoàngNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales & Sus UsosDocument5 pagesTiempos Verbales & Sus UsosAllan BertrandNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales - Tabla-UsosDocument4 pagesTiempos Verbales - Tabla-Usossb1111No ratings yet
- Interogativ:: Prezent Simple Mod de FormareDocument10 pagesInterogativ:: Prezent Simple Mod de Formarerenata louisNo ratings yet
- Present Simple TenseDocument7 pagesPresent Simple TenseAnonymous SIXJJVIMuNo ratings yet
- Tense: Passive Voice Active: PassiveDocument6 pagesTense: Passive Voice Active: PassiveĐình HiềnNo ratings yet
- Prepare For FinalDocument10 pagesPrepare For FinalHa MyNo ratings yet
- Tenses ExplainedDocument27 pagesTenses ExplainedMazhar aliNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses TeorieDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses TeorieAnca TatarNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument9 pagesPresent SimpleMitzi TurcituNo ratings yet
- EduardDocument187 pagesEduardLili LiliNo ratings yet
- StefanDocument154 pagesStefanLili LiliNo ratings yet
- IonutDocument200 pagesIonutLili LiliNo ratings yet
- Tense Overview: A. The Present Simple TenseDocument185 pagesTense Overview: A. The Present Simple TenseLili LiliNo ratings yet
- Andrei TDocument135 pagesAndrei TLili LiliNo ratings yet
- Tense Overview: A. The Present Simple TenseDocument126 pagesTense Overview: A. The Present Simple TenseLili LiliNo ratings yet
- AdrianDocument138 pagesAdrianLili LiliNo ratings yet
- Grammar I: Past TensesDocument9 pagesGrammar I: Past TensesdouaeNo ratings yet
- Grammar2: 5.past Perfect Continuous: S + Had + Been + V-IngDocument4 pagesGrammar2: 5.past Perfect Continuous: S + Had + Been + V-Ingtranbichngan90No ratings yet
- GramáticaDocument10 pagesGramáticaRebeca Ponce OchoaNo ratings yet
- Getting used to verbs and tensesDocument13 pagesGetting used to verbs and tensesMaria BigiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Time and TenseDocument30 pagesLecture 2 Time and TenseCosmin LemnaruNo ratings yet
- Final English ExamDocument8 pagesFinal English Examms94kh96g2No ratings yet
- English PresentationDocument31 pagesEnglish PresentationDonna Cr RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Ving or Vto InfinitiveDocument6 pagesVing or Vto InfinitivePhạm Ngọc HòaNo ratings yet
- Communicating by phone and telephoneDocument32 pagesCommunicating by phone and telephoneYban LaupNo ratings yet
- Dory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesDocument20 pagesDory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesHuyền Trinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BTS CG1 - 2022.11.22 - Anglais - English Tenses TheoryDocument12 pagesBTS CG1 - 2022.11.22 - Anglais - English Tenses TheoryDuong CamNo ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP HỌC KÌ 2 TIẾNG ANHDocument4 pagesÔN TẬP HỌC KÌ 2 TIẾNG ANHThanh NgaNo ratings yet
- Ly Thuyet Anh k12-17.4Document4 pagesLy Thuyet Anh k12-17.4baongantran2122002No ratings yet
- English Tenses: The Simple PresentDocument14 pagesEnglish Tenses: The Simple PresentadasalbatecuNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument6 pagesFuture Tensesdragos.spinuNo ratings yet
- Noi Dung On Tap Hoc Ky I Anh 9 - 1012202210235Document36 pagesNoi Dung On Tap Hoc Ky I Anh 9 - 1012202210235Duy HoangNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TenseDocument12 pagesUnit 1 TenseVăn Đại - BKHNNo ratings yet
- Chuyên đề 1- TensesDocument2 pagesChuyên đề 1- TensesTuyen LeNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap Hoc Ki 2 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 8Document51 pagesDe Cuong On Tap Hoc Ki 2 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 8Huyền Anh ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses and Modals Level 3Document19 pagesFuture Tenses and Modals Level 3paulNo ratings yet
- روس الانجليزية PDFDocument14 pagesروس الانجليزية PDFKhaoulaFaithfulNo ratings yet
- IS: He, She, It: Things, Places, Animals Are: You, We, They Am: IDocument7 pagesIS: He, She, It: Things, Places, Animals Are: You, We, They Am: INicoleta GordonNo ratings yet
- CHUYEN DE PASSIVE VOICE (4) Hoan ChinhDocument10 pagesCHUYEN DE PASSIVE VOICE (4) Hoan ChinhanhsangNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous: PositiveDocument6 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous: PositivePhạm Nguyễn Anh QuốcNo ratings yet
- ĐC ÔN THPTQG 2019 - TIẾNG ANH PDFDocument124 pagesĐC ÔN THPTQG 2019 - TIẾNG ANH PDFHatha NguyenNo ratings yet
- (BE) V /V: Passive VoiceDocument7 pages(BE) V /V: Passive VoiceLe Anh ThuNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Tense Signal Words USE Form Example: Affirmative EXAMPLE: Negative Example: InterrogativeDocument5 pagesPresent Simple: Tense Signal Words USE Form Example: Affirmative EXAMPLE: Negative Example: InterrogativeAnaNo ratings yet
- Temario Instrumental - OdtDocument12 pagesTemario Instrumental - OdtLeticia HerzogNo ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument9 pages16 TensesEmmil SalimNo ratings yet
- Timpuri VerbaleDocument2 pagesTimpuri VerbaleFlorin PîrîialăNo ratings yet
- Present Future Perf TenseDocument6 pagesPresent Future Perf Tensesumire shiny dartokNo ratings yet
- 4 Timpurile verbaleDocument6 pages4 Timpurile verbaleOzana IoanaNo ratings yet
- ABC-ul Limbii Engleze Pe GlobDocument34 pagesABC-ul Limbii Engleze Pe GlobLily HuzdupNo ratings yet
- English Grammar FileDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar FileAmmar MaddelNo ratings yet
- English Revision. Semester 2 - 8 - 2019Document11 pagesEnglish Revision. Semester 2 - 8 - 2019Thùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Caustive VerbsDocument5 pagesCaustive Verbscompullsy100% (1)
- Apuntes Ingles b2Document25 pagesApuntes Ingles b2Arancha ManeiroNo ratings yet
- How to Use the Word “Go” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Go”From EverandHow to Use the Word “Go” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Go”Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Exercises with Phrasal Verbs #1: For intermediate students of English: Exercises with Phrasal Verbs, #1From EverandExercises with Phrasal Verbs #1: For intermediate students of English: Exercises with Phrasal Verbs, #1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Abhi Is Studing in Adarasha School ManviDocument1 pageAbhi Is Studing in Adarasha School ManviVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Physical World: Genius Physics Class XIDocument2 pagesPhysical World: Genius Physics Class XIAryan MahajanNo ratings yet
- Physical World: Genius Physics Class XIDocument2 pagesPhysical World: Genius Physics Class XIAryan MahajanNo ratings yet
- Name of Your Newspaper: Main Story HeadlineDocument1 pageName of Your Newspaper: Main Story HeadlineBrylle B DadangNo ratings yet
- SSLC Question Bank TEXTBOOK ONLYDocument100 pagesSSLC Question Bank TEXTBOOK ONLYVeeresh Savadi63% (8)
- Gulbarga Teachers Transfer Guidelines 2016-17Document2 pagesGulbarga Teachers Transfer Guidelines 2016-17Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: V I Sin T RDocument8 pagesAlternating Current: V I Sin T RVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Tet English Wts Material1Document62 pagesTet English Wts Material1Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- 01 (T) - Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument13 pages01 (T) - Electric Charge and Electric Fieldp_k_soni_iit_physics50% (2)
- Qa PartnershipDocument3 pagesQa PartnershipThilagavathi MuthukumarNo ratings yet
- 10ef-1st Language English Mqp-1 RegularDocument7 pages10ef-1st Language English Mqp-1 RegularVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Government Orders on Civil Services Rules 1957-2005Document224 pagesKarnataka Government Orders on Civil Services Rules 1957-2005nrhmhealthNo ratings yet
- Complete The Following Using FTE As of Sept 30 .Document4 pagesComplete The Following Using FTE As of Sept 30 .Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Grant-VNSDocument33 pagesScheme of Grant-VNSVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Cca Rules 1966Document13 pagesCca Rules 1966Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day2 Present TenseDocument2 pagesDay2 Present TenseVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Functions.: Modal Verbs and Their Meaning What Are Modal Verbs?Document3 pagesFunctions.: Modal Verbs and Their Meaning What Are Modal Verbs?Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- 10e-Gr-Common Errors in EnglishDocument6 pages10e-Gr-Common Errors in EnglishVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day4 Future TenseDocument3 pagesDay4 Future TenseVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 VrsDocument4 pagesChap 12 VrsAnand MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Day2 PaintDocument5 pagesDay2 PaintVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- 10e GR ArticlesDocument4 pages10e GR ArticlesVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day1 PaintDocument4 pagesDay1 PaintVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day3 Past TenseDocument2 pagesDay3 Past TenseVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day9 Sentences in BriefDocument2 pagesDay9 Sentences in BriefVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- OutsourcingDocument2 pagesOutsourcingVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day5-Graphical Representation of TensesDocument1 pageDay5-Graphical Representation of TensesVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Techniques3Document12 pagesProblem Solving Techniques3Veeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Day-1: An Introduction To TensesDocument6 pagesDay-1: An Introduction To TensesVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Fe Book1 d3n Study of Past TensesDocument2 pagesFe Book1 d3n Study of Past TensesVeeresh SavadiNo ratings yet
- Helmholtz DecompositionDocument4 pagesHelmholtz DecompositionSebastián Felipe Mantilla SerranoNo ratings yet
- Bibliography PresocraticsDocument10 pagesBibliography Presocraticsalraun66No ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Pregnancy Shady' With YouDocument48 pagesI Am Sharing 'Pregnancy Shady' With YouNouran AlaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Empirical Beginnings and Basic Contents of Educational PsychologyDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - The Empirical Beginnings and Basic Contents of Educational PsychologyJoshua Almuete71% (7)
- Hmdu - EnglishDocument20 pagesHmdu - EnglishAbdulaziz SeikoNo ratings yet
- Pressing and Finishing (Latest)Document8 pagesPressing and Finishing (Latest)Imran TexNo ratings yet
- De HSG Lay Cau - Ban WordDocument124 pagesDe HSG Lay Cau - Ban WordNguyễn Hải YếnNo ratings yet
- Laboratory SafetyDocument4 pagesLaboratory SafetyLey DoydoraNo ratings yet
- New Microwave Lab ManualDocument35 pagesNew Microwave Lab ManualRadhikaNo ratings yet
- Tender Evaluation Template GuideDocument15 pagesTender Evaluation Template GuideKhalid NaeemNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument1 pageNetworkingSherly YuvitaNo ratings yet
- List of SQAC DQAC SISC DISC 2019 20Document39 pagesList of SQAC DQAC SISC DISC 2019 20Shweta jainNo ratings yet
- Differentiation SS2Document88 pagesDifferentiation SS2merezemenike272No ratings yet
- Title Page Title: Carbamazepine Versus Levetiracetam in Epilepsy Due To Neurocysticercosis Authors: Akhil P SanthoshDocument16 pagesTitle Page Title: Carbamazepine Versus Levetiracetam in Epilepsy Due To Neurocysticercosis Authors: Akhil P SanthoshPrateek Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- VANSINA, Jan. Art History in AfricaDocument250 pagesVANSINA, Jan. Art History in AfricaRaphaelTim100% (1)
- Why Leaders Should Look in the “MirrorDocument4 pagesWhy Leaders Should Look in the “MirrorCaryl Baylon EstreraNo ratings yet
- MAN 2 Model Medan Introduction to School Environment ReportDocument45 pagesMAN 2 Model Medan Introduction to School Environment ReportdindaNo ratings yet
- Argenti, P. Corporate Communication. Cap. 8-9Document28 pagesArgenti, P. Corporate Communication. Cap. 8-9juan100% (1)
- Johnson 1999Document20 pagesJohnson 1999Linh Hoàng PhươngNo ratings yet
- Inclusive E-Service or Risk of Digital Divide The Case of National ICT Policy 2018 of BangladeshDocument11 pagesInclusive E-Service or Risk of Digital Divide The Case of National ICT Policy 2018 of BangladeshInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDiego S. FreitasNo ratings yet
- Motor Electrico Bojin J4103 - B User ManualDocument6 pagesMotor Electrico Bojin J4103 - B User ManualJordan BonnettNo ratings yet
- Resume Android Developer Format1Document3 pagesResume Android Developer Format1Shah MizanNo ratings yet
- Ragavendhar Seeks Entry Software JobDocument2 pagesRagavendhar Seeks Entry Software JobfferferfNo ratings yet
- GEd 105 Midterm ReviewerDocument17 pagesGEd 105 Midterm ReviewerAndryl MedallionNo ratings yet
- SLU Missalette 2016 Capping (Not-Final)Document18 pagesSLU Missalette 2016 Capping (Not-Final)Teanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- British and American Culture Marking RubricDocument5 pagesBritish and American Culture Marking RubricAn Ho LongNo ratings yet
- IntegrityDocument5 pagesIntegrityPritam Kumar100% (1)
- The Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsDocument28 pagesThe Power of Networking for Entrepreneurs and Founding TeamsAngela FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Painter CardDocument1 pagePainter CardPraveen RANANo ratings yet