Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02-YT-05 Cable Testing
Uploaded by
Ary PutraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02-YT-05 Cable Testing
Uploaded by
Ary PutraCopyright:
Available Formats
High Potential Cable Testing
Why Test? Series
W H Y T EST?
What is High Potential Testing?
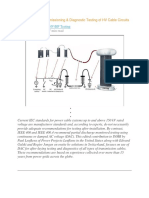
High potential (hipot) cable system testing can be performed using DC, AC or Very Low Frequency AC (also known as VLF) test voltage. Such testing can be conducted as an acceptance test for new installations or as a maintenance test for existing installations. Hipot testing involves applying an overvoltage to the cable system for a short duration to verify the dielectric integrity of the system (cable, splices, and terminations). In most cases hipot testing is applied as a pass/fail or go/no-go test. If the cable system does not fail during the test, it is considered to have passed the test and can be placed into or back into service.
What Test Voltages?
As previously stated, industry standards regarding DC hipot maintenance testing of cables with XLP and EPR insulation have been changing. Few standards provide for DC hipot testing after such cables have been in service 5 years. Recommended acceptance and maintenance DC hipot test information can be found in ICEA standards (S-97-682, S-93-639, and S-94-649), NETA standards (MTS and ATS), and in IEEE standard 400. IEEE standard 400.1 will also provide test voltage guidance when it is finalized. VLF hipot test voltages are provided by the IEEE 400.2 standard.
DC Hipot Testing
Methods for using DC hipot testing of cables were developed in the early 1900s, primarily for testing laminated cable systems such as paper insulated lead covered cable types. A DC hipot unit is relatively easy to control, provides accurate leakage current data, and is relatively small and light weight. Current standards provide for the use of DC hipot testing for acceptance testing of cables with extruded (e.g. cross-linked polyethylene [XLP] or ethylene propylene rubber [EPR] insulation or laminated construction (such as paper insulated lead covered [PILC]). But most industry standards, especially the IEEE 400 standard, no longer recommend DC hipot testing for maintenance testing of field aged XLP or EPR cables. This standard states that DC hipot testing of field aged XLP and EPR cables may not provide meaningful information, and in fact may cause damage. ICEA standards do not provide for testing XLP or EPR cables after they have been in service for 5 years. The IEEE 400 standard does provide for DC hipot testing of field aged PILC cable types.
VLF Hipot Testing
VLF hipot test has the same advantages as DC hipot testers they are relatively small and light weight. But unlike DC hipot testing, the IEEE standard does not caution that VLF hipot testing may not provide meaningful information. More importantly, it does not warn that VLF hipot testing is likely to cause damage to field aged XLP or EPR cables.
AC Hipot Testing
There are no widely accepted test standards for AC hipot testing of cables and power frequency AC hipot testing of cable systems is rarely performed. This is primarily due to the availability of other test methods and the high levels of power consumption and the large, heavy units required for AC hipot testing.
2010 Emerson Network Power 02-YT-05
Electrical Reliability Services 1 (877) 468-6384 www.electricalreliability.com
You might also like
- Electrical Codes, Standards, Recommended Practices and Regulations: An Examination of Relevant Safety ConsiderationsFrom EverandElectrical Codes, Standards, Recommended Practices and Regulations: An Examination of Relevant Safety ConsiderationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- No Nonsense General Class License Study Guide: for Tests Given Between July 2019 and June 2023From EverandNo Nonsense General Class License Study Guide: for Tests Given Between July 2019 and June 2023Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- The IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedFrom EverandThe IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- 01 Cable Testing Standards Overview of The IEEE 400 BundleDocument40 pages01 Cable Testing Standards Overview of The IEEE 400 BundleMuhammad Tanveer Satti50% (2)
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- VLF Testing GuidelinesDocument4 pagesVLF Testing Guidelinesnisteri100% (1)
- In-Film BrandingDocument27 pagesIn-Film BrandingSantosh Parachuri0% (1)
- 4026Document5 pages4026Ary Putra0% (3)
- IEEE 400.2 New Testing Req For Medium Voltage Cables Technical Paper Auth - Craig Goodwin NETA 2005Document18 pagesIEEE 400.2 New Testing Req For Medium Voltage Cables Technical Paper Auth - Craig Goodwin NETA 2005Giovanni Leras100% (4)
- Power Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewDocument22 pagesPower Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- 03 CTAL TM Sample ISTQB Questions - v2.04Document35 pages03 CTAL TM Sample ISTQB Questions - v2.04CorniciucOanaNo ratings yet
- Mv-105 Cable - Field Acceptance Testing - A Cable Manufacturer'S PerspectiveDocument7 pagesMv-105 Cable - Field Acceptance Testing - A Cable Manufacturer'S PerspectiveMarcelo Gomes PlanteirNo ratings yet
- What Is HIPOT Testing (Dielectric Strength Test) - EEPDocument7 pagesWhat Is HIPOT Testing (Dielectric Strength Test) - EEPmahmoud fawzyNo ratings yet
- MPeschel-VLF Cable TestingDocument93 pagesMPeschel-VLF Cable TestingNesarkiran Bagade100% (2)
- HipotDocument4 pagesHipotdayini roslizanNo ratings yet
- ITP Crane - Pertamina EPDocument14 pagesITP Crane - Pertamina EPAry Putra100% (4)
- Load Flow AnalysisDocument1 pageLoad Flow AnalysispvpavanNo ratings yet
- DC Field TestDocument5 pagesDC Field TestXavier.aq100% (1)
- Ieee Guide For Making High-Direct-Voltage Tests Power Cable Systems The FieldDocument10 pagesIeee Guide For Making High-Direct-Voltage Tests Power Cable Systems The FieldIsrael JosueNo ratings yet
- Partial Discharge 1 PDFDocument8 pagesPartial Discharge 1 PDFsamsungloverNo ratings yet
- Akta-332 Copyright Act 1987Document50 pagesAkta-332 Copyright Act 1987Kartigesan999No ratings yet
- k90mcc6 PDFDocument381 pagesk90mcc6 PDFTammy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Power Cable TestingDocument15 pagesPower Cable Testingbedasie2385100% (2)
- Protection Technologies of Ultra-High-Voltage AC Transmission SystemsFrom EverandProtection Technologies of Ultra-High-Voltage AC Transmission SystemsNo ratings yet
- InstruCalc8 QuickStart GuideDocument26 pagesInstruCalc8 QuickStart GuideBari Ipung Guntur100% (1)
- SP0407Document12 pagesSP0407isukuruNo ratings yet
- Being Digital Engaging The Organization To Accelerate Digital Transformation PDFDocument11 pagesBeing Digital Engaging The Organization To Accelerate Digital Transformation PDFAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Standards For On-Site Cable TestingDocument27 pagesStandards For On-Site Cable Testingasawinraja100% (4)
- Cable TestingDocument29 pagesCable TestingRakesh Kumar100% (4)
- Design of Transient Protection Systems: Including Supercapacitor Based Design Approaches for Surge ProtectorsFrom EverandDesign of Transient Protection Systems: Including Supercapacitor Based Design Approaches for Surge ProtectorsNo ratings yet
- XLPE Land Cable Systems 2GM5007GB Rev 5Document28 pagesXLPE Land Cable Systems 2GM5007GB Rev 5Alexander SanguinoNo ratings yet
- EDOC-Damped AC For CommissioningDocument19 pagesEDOC-Damped AC For CommissioningEl Comedor BenedictNo ratings yet
- Surge Arresters GuideDocument116 pagesSurge Arresters GuideSudharsan SD100% (1)
- FAQ - VLF TestingDocument4 pagesFAQ - VLF TestingrksubuNo ratings yet
- IEEE Guide For Field Testing and EvaluaDocument4 pagesIEEE Guide For Field Testing and EvaluavelisbarNo ratings yet
- 2659 8 VLF TD Epri High Voltage IncDocument68 pages2659 8 VLF TD Epri High Voltage IncJavier Valencia MurilloNo ratings yet
- Prime Time FeaturesDocument15 pagesPrime Time FeaturesPruthwish PatelNo ratings yet
- Cables - NETA Power Cable Diagnostics Field Application & Case StudiesDocument15 pagesCables - NETA Power Cable Diagnostics Field Application & Case StudiescadtilNo ratings yet
- HV CAble TestingDocument12 pagesHV CAble TestingM Kumar Marimuthu100% (2)
- Cigre Tf21-05id44ver24Document10 pagesCigre Tf21-05id44ver24salekojic5332No ratings yet
- Legislation Statutory Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesLegislation Statutory Inspection ChecklistAry PutraNo ratings yet
- FR4 Suitability of Different Test Voltages For On Site Cable Testing Rev00Document34 pagesFR4 Suitability of Different Test Voltages For On Site Cable Testing Rev00Ho Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Hipot TestingDocument1 pageHipot Testingbrijeshmaurya2No ratings yet
- Iagnostics Field Testing of Medium-Voltage Cables: Special FeatureDocument4 pagesIagnostics Field Testing of Medium-Voltage Cables: Special FeatureShredder WardatNo ratings yet
- Prueba de VLF - GuíaDocument4 pagesPrueba de VLF - GuíaDaniel DíazNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Tests To Assure MV Power Cable Systems MeetDocument6 pagesCommissioning Tests To Assure MV Power Cable Systems MeetelcarmoNo ratings yet
- 2012 Xlpe Users Guide - UsaDocument28 pages2012 Xlpe Users Guide - UsaPablo ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- IEEE 400.2 Parte 6Document2 pagesIEEE 400.2 Parte 6FabianNo ratings yet
- IEC 61000-4-4: Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Immunity TestDocument5 pagesIEC 61000-4-4: Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Immunity TestJomaargNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Cable DischargeDocument8 pagesExperimental and Theoretical Analysis of Cable DischargeJINEETH JJOSEPHNo ratings yet
- VLF FaqDocument4 pagesVLF FaqsofyanshahNo ratings yet
- Xlpe .I HZ VLFDocument3 pagesXlpe .I HZ VLFeddisonfhNo ratings yet
- Testing of Distribution CablesDocument11 pagesTesting of Distribution CablesHashimi JuniNo ratings yet
- New Water Tree Retardant TR-XLPE Development For Improved Reliability of Medium Voltage Power Cables - WirecableDocument8 pagesNew Water Tree Retardant TR-XLPE Development For Improved Reliability of Medium Voltage Power Cables - Wirecablesubhashrathore2012No ratings yet
- Electrical Power Transmission 4Document7 pagesElectrical Power Transmission 4FaisalSoNo ratings yet
- Tran95-Sub Field TestDocument9 pagesTran95-Sub Field Testnellai_guna2008No ratings yet
- Rm-07 Ac DC Hipot PF DuarteDocument9 pagesRm-07 Ac DC Hipot PF DuarteEngr Irfan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of IS 1255 - 1983 Reaffirmed 1996Document5 pagesCritical Analysis of IS 1255 - 1983 Reaffirmed 1996Binod Kumar BhagatNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENTOHENDRIXDocument40 pagesDOCUMENTOHENDRIXConstanza Bernaldez0% (1)
- The Use of After-Installation Commissioning Tests To Assure MV Power Cable Systems Meet Manufacturers' StandardsDocument5 pagesThe Use of After-Installation Commissioning Tests To Assure MV Power Cable Systems Meet Manufacturers' StandardszeljkoNo ratings yet
- XLPE Land Cable Systems - User S GuideDocument28 pagesXLPE Land Cable Systems - User S GuideJeremy Mcfadden100% (1)
- Coaxial Cables and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesCoaxial Cables and ApplicationsgopinathsubbarayanNo ratings yet
- Trillion Dollar Cable QuestionDocument6 pagesTrillion Dollar Cable QuestionGualadrakeNo ratings yet
- The Impact of High Potential (Hipot) Testing OnDocument4 pagesThe Impact of High Potential (Hipot) Testing OnGonzalo GómezNo ratings yet
- 635091384224950000-Power & Control Cable CatalogueDocument33 pages635091384224950000-Power & Control Cable Catalogue400KVNo ratings yet
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- 40-Article Text-327-1-10-20211130Document9 pages40-Article Text-327-1-10-20211130Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- Kertas Pembatas GAB - 1Document12 pagesKertas Pembatas GAB - 1Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- CV Example4 PDFDocument4 pagesCV Example4 PDFAry PutraNo ratings yet
- 1-Day MV School Customer Site Flyer Feb2016Document2 pages1-Day MV School Customer Site Flyer Feb2016Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- GA Product Catalog V1Document7 pagesGA Product Catalog V1Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- ANNEX 3 Site Location and Preparation Study Rev1Document10 pagesANNEX 3 Site Location and Preparation Study Rev1Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- Field Engineering Limited: Ogabiri Gas Gathering ProjectDocument27 pagesField Engineering Limited: Ogabiri Gas Gathering ProjectAry PutraNo ratings yet
- CV Example4 PDFDocument4 pagesCV Example4 PDFAry PutraNo ratings yet
- 547Document4 pages547Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- M Tech-PSDocument24 pagesM Tech-PSRajesh PenumutchuNo ratings yet
- Genset BRIDocument28 pagesGenset BRIAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic Traction TranformerDocument7 pagesPower Electronic Traction TranformerAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Model Guidelines EERE Into State Energy Emergency Plan 2002-Sept99Document12 pagesModel Guidelines EERE Into State Energy Emergency Plan 2002-Sept99Ary PutraNo ratings yet
- 05 Toyota - 5FG 5 8Document8 pages05 Toyota - 5FG 5 8Edwin NgNo ratings yet
- PSV JambiDocument1 pagePSV JambiAry PutraNo ratings yet
- S.10.01.a Dynamic Optimization Model For Smart Microgrid Integration of A Mix of Renewable Resources For A Green Building - MICHELA ROBBADocument8 pagesS.10.01.a Dynamic Optimization Model For Smart Microgrid Integration of A Mix of Renewable Resources For A Green Building - MICHELA ROBBAAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Sarah Carter Talentoday Self Coaching Guide enDocument24 pagesSarah Carter Talentoday Self Coaching Guide enAry PutraNo ratings yet
- ATEX RulesDocument66 pagesATEX Rulesmarius_brkt6284No ratings yet
- MPPT Control Methods in Wind Energy Conversion Systems PDFDocument23 pagesMPPT Control Methods in Wind Energy Conversion Systems PDFHani M. El-TouniNo ratings yet
- Spec Cable 24P #16AWGDocument6 pagesSpec Cable 24P #16AWGAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Modeling ToolsDocument5 pagesRenewable Energy Modeling ToolsAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Distributor Form Afghan SolarDocument2 pagesDistributor Form Afghan SolarAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Apply For A U.SDocument1 pageApply For A U.SAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Techno-Commerical Offer - Part I: Sl. No. Description Page No. 1Document52 pagesTechno-Commerical Offer - Part I: Sl. No. Description Page No. 1aishah2209No ratings yet
- Report On PesoDocument10 pagesReport On PesoAerish RioverosNo ratings yet
- Java 9 Real - TimeDocument57 pagesJava 9 Real - TimeDiego AmayaNo ratings yet
- MEMORIAL ON BEHALF OF APPELLANTS DocsDocument29 pagesMEMORIAL ON BEHALF OF APPELLANTS DocsPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- March 2023 Complete Month Dawn Opinion With Urdu TranslationDocument361 pagesMarch 2023 Complete Month Dawn Opinion With Urdu Translationsidra shabbirNo ratings yet
- 17 0000362296Document1 page17 0000362296Ekansh BarsiwalNo ratings yet
- 4-Sided Planer & Moulder Operation Manual: For Spares and Service ContactDocument48 pages4-Sided Planer & Moulder Operation Manual: For Spares and Service ContactAlfred TsuiNo ratings yet
- Penn State: The Dickinson School of LawDocument88 pagesPenn State: The Dickinson School of LawHafiz UmmarNo ratings yet
- Transport ADRDocument3 pagesTransport ADRZbinca CristianNo ratings yet
- Environmental Life Cycle AssessmentDocument1 pageEnvironmental Life Cycle Assessmentkayyappan1957No ratings yet
- Fax Cross ReferenceDocument32 pagesFax Cross ReferenceBranga CorneliuNo ratings yet
- Murugan Temple of North America: Ahkpuf F Gankd - FZGJP JizDocument8 pagesMurugan Temple of North America: Ahkpuf F Gankd - FZGJP JizOurMuruganTempleNo ratings yet
- Boat, Time Speed and DistanceDocument5 pagesBoat, Time Speed and DistanceAnmol AswalNo ratings yet
- Cima E1 2019 Notes Managing Finance in A Digital WorldDocument91 pagesCima E1 2019 Notes Managing Finance in A Digital Worldumarfarooque869No ratings yet
- Utah State Hospital Policies and Procedures RadiologyDocument9 pagesUtah State Hospital Policies and Procedures RadiologysultanarahmanNo ratings yet
- CH03 HKM Law Investigation and EthicsDocument32 pagesCH03 HKM Law Investigation and Ethicsmilkikoo shiferaNo ratings yet
- RTP Cap III GR I June 2022Document92 pagesRTP Cap III GR I June 2022मदन कुमार बिस्टNo ratings yet
- GX Deloitte 2017 TMT PredictionsDocument60 pagesGX Deloitte 2017 TMT PredictionsMontevideo PortalNo ratings yet
- Macaw Recovery Network - Výroční Zpráva 2022Document20 pagesMacaw Recovery Network - Výroční Zpráva 2022Jan.PotucekNo ratings yet
- Indian - Origin Girls Bag Google Science Honour - Yahoo! India EducationDocument3 pagesIndian - Origin Girls Bag Google Science Honour - Yahoo! India EducationRiyaz RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Group5 - CHE11 - Midterm Essay - Seminar (CH4516E)Document28 pagesGroup5 - CHE11 - Midterm Essay - Seminar (CH4516E)Bình LêNo ratings yet
- Relevé: Partie 6: Vidéo "Le Blues en Jazz"Document1 pageRelevé: Partie 6: Vidéo "Le Blues en Jazz"santiagoNo ratings yet
- CS8792 CNS Unit5Document17 pagesCS8792 CNS Unit5024CSE DHARSHINI.ANo ratings yet
- Economic History of The PhilippinesDocument21 pagesEconomic History of The PhilippinesBench AndayaNo ratings yet
- 54 Sale1Document6 pages54 Sale1vakilarunNo ratings yet
- Woodworking SyllabusDocument3 pagesWoodworking SyllabusLeonard Andrew ManuevoNo ratings yet