Professional Documents
Culture Documents
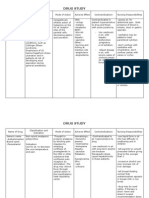
Drug Mechanism Use Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Implications
Uploaded by
hendra_darmawan_4Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Mechanism Use Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Implications
Uploaded by
hendra_darmawan_4Copyright:
Available Formats
Respiratory Drug Chart
Drug Mechanism
-competes for H1 receptors
Use
-prevent & treat allergic responses -hypnoticsafe, nonnarcotic -anticholinergic -anti-emetic
Side/Adverse Effects
-CNS: drowsiness, sedation, vertigo CV: hypotension, palpitations, arrhythmias -Resp: dryness of mouth, thickened bronchial secretions -GI: anorexia, N/V, diarrhea or constipation -GU: urinary retention, dysuria
Nursing Implications
-additive depression of CNS w/ alcohol, hypnotics, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety, narcotics -anticholinergiccaution w. glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, CV dx or hypertension -avoid pregnancy /lactation -take at bedtime to avoid sedation -caution about driving -caution w/ older persons -teach proper administration of nose drops & nose sprays -caution against misuse rebound congestion DDIs: Inderal antagonizes antihistamines
Antihistamines
diphenhydramine hydrochloride-BENADRYL
ALLEGRA, CLARITIN, ZYRTEC
Beta Agonists
Nonselective: Isoproterenol, Epinephrine, Ephedrine Selective: albuterol, metaproterenol, terbutaline, salmeterol
-stimulate beta-2 adrenoreceptors -bronchial smooth muscle relaxation -stimulate mucocillary clearance
-rescue therapy during acute asthma attacks -prophylaxis for exerciseinduced asthma -prophylaxis for exposure to known antigens
-Nonselective: stimulate cardiac beta receptors tachycardia, arrhythmias, angina -CNS effects: nervousness, anxiety, insomnia, irritability, dizziness & sweating -vasoconstriction: incr. BP -systemic side effects minimal especially CV -dryness of oropharynx -cough -exacerbation of symptoms -if plasma level >20 ug/ml -CNS: nervousness, insomnia, HA, dizziness, tremors late sign -Cardiac: tachycardia, angina, hypotension -GI: nausea (1st sign), vomiting, anorexia
-assess respiratory status -decr. environmental irritants -improve humidification -avoid OTC inhalers DDIs: potentiated by MOA inhibitors, tricylcic antidepressants and other sympathomimetic drugs
Bronchodilators
Muscarinic-receptor antagonists (anticholinergics)
-inhibits ACh mediated constriction of bronchial smooth muscle -decr. vagal-stimulated mucus secretion
-inhibits phosphodiesterase leads to incr. cAMP so bronchodilation -decr. histamine release -stimulates ciliary transport of mucus -improve contractility of diaphragm -incr. CO, produces diuresis & decr. PV
-treat chronic conditions; not for acute use
Methylxanthines
-prophylaxis & treatment of asthma -relieve SOB, wheezing & dyspnea -stimulate newborns who dont breath well
-Narrow TIincr. side effect w/ caffeine -Monitor blood levels10-20 ug/ml=therapeutic range -Give during day to prevent insomnia -Take w/ food if GI upset -smokers may require incr. dosing Know DDIs
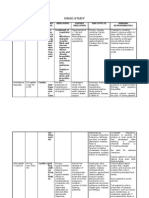
Drug Cromolyn Sodium
(non-steroidal) INTAL
Mechanism
-prevents influx of Ca into mast cells, therefore inhibiting degranulation and release of histamine & leukotrines -inhibits the recruitment of inflammatory cells into airway -inhibits late bronchoconstriction -blocks the formation of leukotrienes from arachiodonic acid -prevents bronchoconstriction & airway inflammation -incr. CHO, protein & fat metabolism -suppress inflammatory process -suppress normal immune system
Use
-prophlyaxis in asthma (esp for children or exercise induced asthma) -seasonal allergic rhinitis & opthalmic adm in allergic conjunctivitis
Side/Adverse Effects
-HA -bronchospasm -dry throat
Nursing Implications
-teach proper use of inhaler & nasal sprays -drug in powder form may cause bronchospasm -assess breath sounds pre & post tx -mouth care after use to minimize irritation to the throat & oral mucosa -incr. plasma concentrations of theophylline, warfarin, betaadrenergic blockers -not for pts w/ liver dx or alcoholism -teach proper use inhaler properly -gargle & rinse mouth after each use -notify care provider ifillness or feel worse, continued asthma attacks, incr. in stressful situations -wear medical alert -assessment VS, wt, monitor glucose -assess for signs of depression -do not abruptly withdraw, taper slowly -avoid injury to skinfragile -avoid risk of infection -take care w/ application of topical -instruct not to overuse; may be addictive -limit # of days (3-5) -NO w/ incr. BP, nsg mother, w/ MAO inhibitors -caution w/ elderly, glaucoma, BPH, DM & hyperthyroidism -limit caffeine intake maintain sitting position when takin nasal sprays -avoid taking w/ diet pills
Oxymethazoline (AFRIN, DRISTAN) Phenylephrin (NEO-SYNEPHRINE) Pseudophederine + chlorpheniramine + dextromethorphan + acetaminophen (COMTREX) Pseudoephedrin hydrochloride (SINUTAB, SUDAFED)
Anti-Inflammatory
Leukotriene Inhibitors
ZYFLO, ACCOLATE
-Maintenance therapy in chronic asthma
-hepatitis w/ ZYFLO -drug allergy w/ ACCOLATE
-acute & maintenance asthma management
Inhalation: -fungal (Candida) infections -oral & nasal irritation Oral: -immunosuppressant effect -growth retardation, muscle wasting -hyperglycemia, hypertension -mood swings, physical changes
Glucocorticoids
Decongestants
-shrinks nasal membranes by a vasoconstrictive mechanism (alpha-1 adrenergic agonists)
-systemic relief of allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, colds & flu
-CNS: nervousness, restlessness, insomnia -GI: N/V -palpitations, hypertension -rebound engorgement
congestion worsens after incr. frequency of use
Drug
Mechanism
-incr. respiratory tract fluid -decr. viscosity of bronchial & tracheal secretions
Use
-persistent coughs -mucus plugs -common cold, bronchitis
Side/Adverse Effects
-allergies to the drug -GI: N/V, anorexia -pregnancy category C
Nursing Implications
-assess lung sounds & secretions -sufficient humidification -teach effective coughing -use no more than 1 wk -encourage fluid intake 2-3 L/day -drink full glass of water after each dose taken -avoid ETHOL or drugs w/ ETHOL -wait 15-20 min after taking syrup before drinking liquid -monitor use of controlled substance -take at bedtime -dryness of mouthrelieve w/ hard candy, ice chips, mouth care -caution w/ activities -pregnancy category C -not used for children< 6 yr -avoid use of ETHOL -OTC drugsread directions carefully -opiates more sedating -odor of rotten eggs may cause GI upset -administered through nebulizer -caution older adults bronchospasm -assess lung sounds & respiratory status -Oral: mix w/ iced liquid17 doses over 4 day period for overdose of acetaminophen
Expectorants
Guaifenesin (ROBITUSSIN)
-suppress cough reflex center in medulla
-suppresses nonproductive cough
-GI, sedation, anesthesia of mouth
Antitussives
Nonnarcotic
benzonatate (TESSALON) dextromethorphan (OTC cough syrups) diphenhydramine (BENYLIN)
Narcotic
codeine sulfate hydrocodone bitartrate (HYCODAN)
Mucolytic drugs
MUCOMYST
-reduce thickness of mucus -makes mucus secretions less tenacious -alters metabolism of acetaminophen
-Inhaledrespiratory conditions -Orallyacetaminophen overdose
-may irritate nasal passages
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument5 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsYvonne AgathaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDocument7 pagesNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Respiratory Medications ReviewerDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medications ReviewerKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PharmacologyDocument35 pagesChapter 13 PharmacologyEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyBea Andrea LarismaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesDrugs Acting On Respiratory SystemQusai BassamNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument3 pagesUntitled Document PDFdzmtz02No ratings yet
- (Brand Name) : Generic Name Classificati ON Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pages(Brand Name) : Generic Name Classificati ON Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GalaponDocument4 pagesDrug Study GalaponSheryl DiazNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mode of Action Indications Contra-Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mode of Action Indications Contra-Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesChristine AlavazoNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin & CiticolineDocument6 pagesAtorvastatin & CiticolineJames LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Review PharmacologyDocument137 pagesReview PharmacologyGeronimo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- First Generation: A. AntihistamineDocument32 pagesFirst Generation: A. AntihistamineAyumi StarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyLynel Joy JamotilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument43 pagesDrug Studyapi-3818438100% (2)
- Drug File SupriyaDocument36 pagesDrug File SupriyaSalim MinjNo ratings yet
- OB Med SheetDocument12 pagesOB Med SheetSam DanaNo ratings yet
- Adults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YDocument2 pagesAdults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YFildehl Janice Bomediano Catipay100% (1)
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Symph A To Mimetic SDocument27 pagesSymph A To Mimetic Sjl frusaNo ratings yet
- HyosDocument8 pagesHyosAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Sept23Document23 pagesPharmacology - Sept23Jek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol Drug StudyClaire Go Tajarros82% (11)
- Dimenhydrinate Med CardDocument2 pagesDimenhydrinate Med CardAnja de VriesNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument6 pagesDRUG StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMaye HerbitoNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Drug Classification: Drug:: MedicationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Drug Classification: Drug:: MedicationsCharmaigne Aurdane PajeNo ratings yet
- PARACETAMOLDocument2 pagesPARACETAMOLMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyjohnclement_dcNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ArvinDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsdeepika kushwah100% (1)
- DrugsDocument13 pagesDrugsJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Fluimucil 300mg / 3mlDocument3 pagesFluimucil 300mg / 3mlRezti PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetylcyst e I N eDocument12 pagesDrug Study: Acetylcyst e I N eMarvin V ParahinogNo ratings yet
- PHARMA BulletsDocument6 pagesPHARMA BulletsRhea Anne VeraNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsElisa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities To:: Magnesium SulfateDocument13 pagesNursing Responsibilities To:: Magnesium SulfateabrokenheartedgirlNo ratings yet
- Respi DrugsDocument36 pagesRespi DrugsLady Mae RamosNo ratings yet
- DRUg StudyDocument11 pagesDRUg StudyKathNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedsDocument36 pagesRespiratory MedsJan-Jan PandanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Pedia)Document7 pagesDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Drugs of MineDocument16 pagesDrugs of MineJoan GungobNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Review For FinalsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Review For FinalsJaya ReyesNo ratings yet
- 06 2014 Anticholinergic Agents - AtropineDocument6 pages06 2014 Anticholinergic Agents - AtropinemodayearNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsDocument9 pagesNursing Pharmacology HandoutsVince LeonidaNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Blood Pressure Epilepsy Pregnancy Breast: Dry Mouth HeadachemclubertNo ratings yet
- Methotrexate MTX: Antineoplastic Agents Antibetabolites Drug Mechanism Clinical Use ToxicityDocument2 pagesMethotrexate MTX: Antineoplastic Agents Antibetabolites Drug Mechanism Clinical Use Toxicityhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Complementary & Alternative Medicine Source Book 2010Document655 pagesComplementary & Alternative Medicine Source Book 2010Angel Celestial100% (4)
- Common Cold EducationDocument2 pagesCommon Cold Educationhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminshendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Type2 Diabetes HandoutDocument1 pageType2 Diabetes Handouthendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Sub Arachnoid BlockDocument32 pagesSub Arachnoid Blockhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Patient Management in Family PracticeDocument21 pagesProblem Solving and Patient Management in Family Practicehendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Lecture Presentation - Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base BalanceDocument16 pagesLecture Presentation - Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base Balancehendra_darmawan_4100% (2)
- Kul Perdana Anasthesiology DR - HariBDocument23 pagesKul Perdana Anasthesiology DR - HariBhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Urine Case 2010-2Document9 pagesUrine Case 2010-2hendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Fluid & Electrolyte TherapyDocument33 pagesFluid & Electrolyte Therapyhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument28 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysishendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Kurva Disosiasi HB OksigenDocument6 pagesKurva Disosiasi HB Oksigenhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Malarial NephropathyDocument68 pagesMalarial Nephropathyhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- OrganophosphateDocument21 pagesOrganophosphatehendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Leptospirosis Smt7Document34 pagesLeptospirosis Smt7hendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Male InfertilityDocument19 pagesMale Infertilityhendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- B. Geoinformatics PDFDocument77 pagesB. Geoinformatics PDFmchakra720% (1)
- in Strategic Management What Are The Problems With Maintaining A High Inventory As Experienced Previously With Apple?Document5 pagesin Strategic Management What Are The Problems With Maintaining A High Inventory As Experienced Previously With Apple?Priyanka MurthyNo ratings yet
- Jesus Prayer-JoinerDocument13 pagesJesus Prayer-Joinersleepknot_maggotNo ratings yet
- E0 UoE Unit 7Document16 pagesE0 UoE Unit 7Patrick GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Computing of Test Statistic On Population MeanDocument36 pagesComputing of Test Statistic On Population MeanKristoffer RañolaNo ratings yet
- CT SizingDocument62 pagesCT SizingMohamed TalebNo ratings yet
- Rule 113 114Document7 pagesRule 113 114Shaila GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Presentation 11Document14 pagesPresentation 11stellabrown535No ratings yet
- Oracle Forms & Reports 12.2.1.2.0 - Create and Configure On The OEL 7Document50 pagesOracle Forms & Reports 12.2.1.2.0 - Create and Configure On The OEL 7Mario Vilchis Esquivel100% (1)
- IMS Objectives Targets 2Document2 pagesIMS Objectives Targets 2FaridUddin Ahmed100% (3)
- Homework 1 W13 SolutionDocument5 pagesHomework 1 W13 SolutionSuzuhara EmiriNo ratings yet
- Objective & Scope of ProjectDocument8 pagesObjective & Scope of ProjectPraveen SehgalNo ratings yet
- The Construction of Optimal Portfolio Using Sharpe's Single Index Model - An Empirical Study On Nifty Metal IndexDocument9 pagesThe Construction of Optimal Portfolio Using Sharpe's Single Index Model - An Empirical Study On Nifty Metal IndexRevanKumarBattuNo ratings yet
- Leigh Shawntel J. Nitro Bsmt-1A Biostatistics Quiz No. 3Document6 pagesLeigh Shawntel J. Nitro Bsmt-1A Biostatistics Quiz No. 3Lue SolesNo ratings yet
- Pavement Design1Document57 pagesPavement Design1Mobin AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2009 2011 DS Manual - Club Car (001-061)Document61 pages2009 2011 DS Manual - Club Car (001-061)misaNo ratings yet
- How Drugs Work - Basic Pharmacology For Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument19 pagesHow Drugs Work - Basic Pharmacology For Healthcare ProfessionalsSebastián Pérez GuerraNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument1 pageElements of Artsamson8cindy8louNo ratings yet
- Mastertop 1230 Plus PDFDocument3 pagesMastertop 1230 Plus PDFFrancois-No ratings yet
- Richardson Heidegger PDFDocument18 pagesRichardson Heidegger PDFweltfremdheitNo ratings yet
- CX Programmer Operation ManualDocument536 pagesCX Programmer Operation ManualVefik KaraegeNo ratings yet
- School of Mathematics 2021 Semester 1 MAT1841 Continuous Mathematics For Computer Science Assignment 1Document2 pagesSchool of Mathematics 2021 Semester 1 MAT1841 Continuous Mathematics For Computer Science Assignment 1STEM Education Vung TauNo ratings yet
- BNF Pos - StockmockDocument14 pagesBNF Pos - StockmockSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- DPSD ProjectDocument30 pagesDPSD ProjectSri NidhiNo ratings yet
- Huawei R4815N1 DatasheetDocument2 pagesHuawei R4815N1 DatasheetBysNo ratings yet
- Opc PPT FinalDocument22 pagesOpc PPT FinalnischalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 1Document2 pagesChemistry Test 1shashankNo ratings yet
- Modulo EminicDocument13 pagesModulo EminicAndreaNo ratings yet
- Broken BondsDocument20 pagesBroken Bondsapi-316744816No ratings yet
- WebLMT HelpDocument12 pagesWebLMT HelpJoão LopesNo ratings yet