Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NOVI KATALOG GASOVA MESSER - EnG Inert Gas Welding Indert Gas Welding Selected Reference Tables
Uploaded by
Ivan DulicOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NOVI KATALOG GASOVA MESSER - EnG Inert Gas Welding Indert Gas Welding Selected Reference Tables
Uploaded by
Ivan DulicCopyright:
Available Formats
Inert gas welding selected reference tables
Inert gas welding selected reference tables
At a glance This summarized compilation of reference tables is intended as an aid to orientation in shielding gas welding. It gives an overview of the wide range of welding inert gases and their areas of application. The tables can be helpful in the solution of welding problems but you should not miss out on the experience and advice of our welding experts. Special information on our shielding gases is contained in our detailed publications. For optimum control of profitability in inert gas welding, Messer has developed a welding cost calculation system with computer aided measured value processing. We are happy to place this facility at the disposal of users on request.
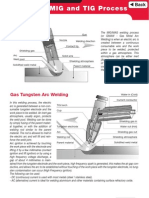
Inert gas welding
Tungsten inert gas welding
Metal inert gas welding
Non-consumable tungsten electrode
consumable wire electrode
Tungsten inert gas welding open arc
TIG
Plasma
Plasmawelding confined arc
Metal inert gas welding Inert gas atmosphere
MIG
Metal active gas welding CO2 or O2 in shielding gas
MAG
Shielding gases for welding at a glance
Product designation Welding-Argon 4.6 Argon Special 4.8 Helium 4.6 Alumix He90 Alumix He70 Alumix He50 Alumix He30 Alumix N* Alumix He15 N* Alumix He30 N* Alumix He50 N* Inoxmix H2 Inoxmix H5 Inoxmix H7 Inoxmix N1 Inoxmix N2 Inoxmix He15 N1 Inoxmix He3 H1 Inoxmix X2 Inoxmix C2 Inoxmix He15 C2 Inoxmix He30 H2 C Ferromix C8 Ferromix C18 Ferromix C25 Ferromix X4 Ferromix X8 Ferromix C5 X5 Ferromix C3 X1 Ferromix C6 X1 Ferromix C12 X2 Ferromix He20 C8 carbon dioxide (industrial grade) Forming gas (N2-H2-mixes)
Group according as ISO 14175 I1 I1 I2 I3 I3 I3 I3 Z Z Z Z R1 R1 R1 N2 N2 N2 R1 M13 M12 M12 Z M20 M21 M21 M22 M22 M23 M14 M24 M24 M20 C1 N5
Composition [%] Ar 100 100 100 10 30 50 70 balance balance balance balance 98 95 92,5 98,75 97,5 83,75 95,5 98 97,5 83 balance 92 82 75 96 92 90 96 93 86 72 20 4 8 5 1 1 2 5 3 6 12 8 100 5-25 95-75 15 30 15 3 2 2,5 2 0,12 8 18 25 2 1,5 15 30 50 2 5 7,5 1,25 2,5 1,25 90 70 50 30 0,015 0,015 0,015 0,015 He O2 CO2 H2 N2
Process according as DIN 1910 TIG/MIG TIG/M1G TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG/MIG TIG TIG TIG TIG TIG TIG TIG MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG M MAG C Root protection
* In Germany Alumix is distributed without nitrogen content
Areas of application
Standard shielding gases and their application in TIG welding Product Welding Argon Inoxmix H 2 % H2 5 % H2 7,5 % H2 1,25 % 2,5 % 15 % He,1,25 % N2 Typical Mixes Group acc. ISO 14175 l1 R1 R1 R1 N2 N2 N2 I2 I3 I3 I3 I3 Z Z Z Z I1 5 % H2 10 % H2 15 % H2 20 % H2 25 % H2 N5 N5 N5 N5 N5 Application High alloy and mild steels, aluminum alloys, other non ferrous metals Austenitic CrNi steels (5% and 7.5% preferably fully mechanical) Duplex, super-duplex fully austenitic CrNi steels Aluminum (negative polarity welding) Steels (orbital technique) Aluminum, copper (preferably 70% He) Nickel (preferably 30% He) Steels (orbital technique) TIG DC welding (preferably 90% He) Aluminum + Al - alloys Aluminum + Al - alloys
Inoxmix N
Helium 4.6 Alumix He 30 % He 50 % He 70 % He 90 % He 0,015 % N2 15 % He, 0,015 % N2 30 % He, 0,015 % N2 50 % He, 0,015 % N2
Alumix N* Alumix He N*
Argon 4.8 Forming gas (N2-H2 mixes)
Gas sensitive materials such as titanium, niobium, molybdenum, tantalum, as well as for root protection Root protection for high alloy and alloyed steels
Standard shielding gases and their application in MIG welding Group acc. ISO 14175 I3 I3 I3 Z Z Z Z Z I2
Product Alumix He
Typical Mixes 30 % He 50 % He 70 % He 0,015 % N2 15 % He, 0,015 % N2 30 % He, 0,015 % N2 50 % He, 0,015,% N2 30 % He, 2 % H, 0,12 %
Application Aluminum, nickel alloys CuNiFe alloys, copper Aluminum materials Aluminum + Al - alloys Aluminum + Al - alloys
Alumix N* Alumix He 15 N* Alumix He 30 N* Alumix He 50 N* Inoxmix He 30 H2 C Helium 4.6
Nickel-based materials Copper (if preheating not possible)
* In Germany Alumix is distributed without nitrogen content
Applications for MAG welding
Product families for MAG welding Product family Inoxmix Ferromix Application high alloy steels, conditionally mild steels mild steels, conditionally high alloy steels
Classification of shielding gases for joint welding and related processes according as DIN EN ISO 14175 short term
main sub group group
Components [%] oxidizing CO2 O2
Ar 100 inert
reductive He 100 H2
low reactive N2
M1
M2
1 2 3 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 1
Balance 0,5 He 95
0,5 CO2 5 0,5 CO2 5 0,5 CO2 5 < CO2 15 < CO2 0,5 5 5 15 15 25 < < < < < CO2 CO2 CO2 CO2 CO2 CO2 0,5 O2 5 0,5 O2 15 25 3 < O2 5 3 < O2 15 0,5 O2 15 3 < O2 25 0,5 O2 25 3 < O2 50 10 < O2 20 2 < O2 25 10 < O2 50 10 < O2
Balancea) Balancea)
0,5 H2 5
3 Balancea) 3 Balancea)
Balancea) Balancea)
10 10 3 10 3 10 15 10 15 15
Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea) Balancea)
M3
C R N
25 < CO2 5 < CO2 25 < CO2 100 Balance
0,5 O2 30
Balancea) Balance Balance
a)
0,5 H2 15 15 < H2 50 100 0,5 N2 5 5 < N2 50 0,5 H2 10 0,5 N2 5 0,5 H2 50 Balance
a)
Balancea) Balancea)
O Z
a) b)
100
Gas mixtures with components, which are not listed in the table or gas mixtures with a composition out of the specified range. b)
For this classification Argon may be replaced partially or completely with helium. Two gas mixtures with the same Z-classification must not be replaced against each other.
Cost comparison Shielding gas 70 % Helium / 30 % Argon Shielding gas 100 % Argon
1.00
0.50
0.75
2.50
2.25
0.50
0.50
Labor cost
Wire 2,25 / unit
Gas
Labor cost
Wire
Gas
Edge preparatio
5,75 / unit
Penetration intensification 20 mm
100 % Argon
70 % Argon 30 % Helium AI Mg 4,5 Mn 240 A 20 mm
50 % Argon 50 % Helium
30 % Argon 70 % Helium
100 % Helium
Base material: Welding current: Sheet thickness:
Messer Group GmbH Gahlingspfad 31 47803 Krefeld Tel. +49 2151 7811-0 Fax +49 2151 7811-503 welding-technology@messergroup.com www.messergroup.com
10/08 / 1.EN1.205
You might also like
- Inert Gas Welding Indert Gas Welding Selected Reference TablesDocument6 pagesInert Gas Welding Indert Gas Welding Selected Reference Tableshooky1No ratings yet
- Mag Welding of Mild Steel FerrolineDocument1 pageMag Welding of Mild Steel FerrolinecanakyuzNo ratings yet
- Gases For Welding and Cutting - OverviewDocument1 pageGases For Welding and Cutting - OverviewtomasinkaNo ratings yet
- International Standard for Welding & Cutting GasesDocument4 pagesInternational Standard for Welding & Cutting GasesZoran DanilovNo ratings yet
- International - Standard ISO 14175Document3 pagesInternational - Standard ISO 14175Geom_MengoliNo ratings yet
- Gases for welding and cutting guideDocument1 pageGases for welding and cutting guideVladan TimotijevicNo ratings yet
- Gases de Proteccion MIG-MAG-GMAW. Standard ISO 14175 Vs en 439Document3 pagesGases de Proteccion MIG-MAG-GMAW. Standard ISO 14175 Vs en 439xevi00No ratings yet
- FSH TigDocument105 pagesFSH TigChee WeiNo ratings yet
- GM Aw and GT Aw ConsumablesDocument118 pagesGM Aw and GT Aw Consumablessepe00No ratings yet
- (AIR PRODUCTS) Inomaxx TIG - T1 ArH2 PDFDocument2 pages(AIR PRODUCTS) Inomaxx TIG - T1 ArH2 PDFaauriscNo ratings yet
- 1 0 Next: ExamplesDocument2 pages1 0 Next: ExamplesSatish MehtaNo ratings yet
- Hensley SpecBook Ch07Document92 pagesHensley SpecBook Ch07RENE ACEBEYNo ratings yet
- EN 10025 Grade S355J2C Normalized or Normalized Formed (+N)Document3 pagesEN 10025 Grade S355J2C Normalized or Normalized Formed (+N)melvin ekboteNo ratings yet
- Mild steel solid rod classification and propertiesDocument1 pageMild steel solid rod classification and propertiessoft4gsmNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Welding by Weld RealityDocument50 pagesStainless Steel Welding by Weld RealitylightwinterdayNo ratings yet
- Copper-Coated Solid Wire for Universal Welding ApplicationsDocument1 pageCopper-Coated Solid Wire for Universal Welding ApplicationsInaamNo ratings yet
- Aluminium SpecificationDocument2 pagesAluminium SpecificationklhlNo ratings yet
- AGA Aluminum Welding BrochureDocument16 pagesAGA Aluminum Welding Brochureaghosh704No ratings yet
- Shielding Gases for Welding & CuttingDocument12 pagesShielding Gases for Welding & CuttingJuan Carlos100% (3)
- EN 1706 Grade AC-42100 T6: Matmatch Is Trusted by 2 Million+ Engineers and Product Developers Each YearDocument4 pagesEN 1706 Grade AC-42100 T6: Matmatch Is Trusted by 2 Million+ Engineers and Product Developers Each Yearmelvin ekboteNo ratings yet
- Gandhi Special Tubes ISO 9001 2008Document6 pagesGandhi Special Tubes ISO 9001 2008mukeshkumarjNo ratings yet
- This documentDocument44 pagesThis documentTran Thanh HaoNo ratings yet
- High Temp. Alloy UNS N02200 N07080: Uns No Description Brand/Trp ASTM EquivalentDocument36 pagesHigh Temp. Alloy UNS N02200 N07080: Uns No Description Brand/Trp ASTM Equivalent윤병택No ratings yet
- Din 1732-3-2007Document5 pagesDin 1732-3-2007Luis PaletoNo ratings yet
- WPSAmerica Shielding Gases and Mechanical PropertiesDocument44 pagesWPSAmerica Shielding Gases and Mechanical PropertiesRameshBaskaranNo ratings yet
- Oxyfuel Gas WeldingDocument19 pagesOxyfuel Gas WeldingHAZEL BELLONo ratings yet
- Material AlSiDocument2 pagesMaterial AlSidoanthanh88No ratings yet
- Raffmetal: UNI EN 1676 and 1706Document2 pagesRaffmetal: UNI EN 1676 and 1706Anshuman RoyNo ratings yet
- Technical Catalogue: Pipes Tubes Fittings FlangesDocument121 pagesTechnical Catalogue: Pipes Tubes Fittings FlangesDANIELVENZUELAANo ratings yet
- Analyses of Permanent GasesDocument2 pagesAnalyses of Permanent GaseshutamiNo ratings yet
- Carboxen 1000 Permanent Gases PDFDocument2 pagesCarboxen 1000 Permanent Gases PDFSichem Guerrero100% (2)
- Data SAF2205 04Document8 pagesData SAF2205 04il_yoo_1No ratings yet
- Simplifying Shielding Gas Selection: Kevin A Lyttle Reprinted From Practical Welding Today January/February 2005Document4 pagesSimplifying Shielding Gas Selection: Kevin A Lyttle Reprinted From Practical Welding Today January/February 2005essnelsonNo ratings yet
- Varian TOGADocument3 pagesVarian TOGAKiran ChokshiNo ratings yet
- SAE J403 Grade 1055: Matmatch Is Trusted by 2 Million+ Engineers and Product Developers Each YearDocument4 pagesSAE J403 Grade 1055: Matmatch Is Trusted by 2 Million+ Engineers and Product Developers Each YearALEX MURPHYNo ratings yet
- Av Catalogo Completo 2005Document20 pagesAv Catalogo Completo 2005Marin LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- MaterialData - Aço 1045Document2 pagesMaterialData - Aço 1045Victhor AraujoNo ratings yet
- URB25Document4 pagesURB25malika_00No ratings yet
- S355G10 GBDocument4 pagesS355G10 GBH41GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Pipes, Tubes, Fittings, FlangesDocument121 pagesPipes, Tubes, Fittings, FlangesCarl Jones100% (2)
- Specialty Materials Hastelloy C-276 ALLOY: Certified To Iso 9001Document3 pagesSpecialty Materials Hastelloy C-276 ALLOY: Certified To Iso 9001Jarbas MoraesNo ratings yet
- Flux Cored WireDocument38 pagesFlux Cored WireKentDemeterioNo ratings yet
- Technical Handbook Stainless Steel WeldingDocument92 pagesTechnical Handbook Stainless Steel WeldingRamesh sivanNo ratings yet
- En 43400Document2 pagesEn 43400shivendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Classifications: For 560mpa Low Temperature Service Steel (1.5% Ni)Document1 pageClassifications: For 560mpa Low Temperature Service Steel (1.5% Ni)BHARANINo ratings yet
- O2 Analyser,,YokoDocument13 pagesO2 Analyser,,YokoNogeshwar Kumar DewanganNo ratings yet
- Datasheet-Sandvik-Saf-2205-En-V2020-01-17 14 - 15 Version 1 PDFDocument15 pagesDatasheet-Sandvik-Saf-2205-En-V2020-01-17 14 - 15 Version 1 PDFDaniel GomezNo ratings yet
- Esab DublexDocument8 pagesEsab DublexSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Ultramag Sg3: Mild Steel Solid WireDocument1 pageUltramag Sg3: Mild Steel Solid Wireabidaliabid1No ratings yet
- Riello 40 Gs Series Package Gas BurnerDocument6 pagesRiello 40 Gs Series Package Gas BurnerIonutCiobanuNo ratings yet
- Gas CuttingDocument24 pagesGas CuttingashishghadiyaNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Spectra of Organometallics: Theoretical and Experimental DataFrom EverandVibrational Spectra of Organometallics: Theoretical and Experimental DataNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Metal Valves & Pipe Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandMetal Valves & Pipe Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy and Corrosion Control in Oil and Gas ProductionFrom EverandMetallurgy and Corrosion Control in Oil and Gas ProductionNo ratings yet
- BACKUP - Putanje Windows - ACAD - SWDocument1 pageBACKUP - Putanje Windows - ACAD - SWIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- (Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Document1 page(Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Ivan Briscoe100% (7)
- Uporedno15614 288 3Document11 pagesUporedno15614 288 3Ivan DulicNo ratings yet
- Welded Steel Pipe American Iron and Steel InstituteDocument80 pagesWelded Steel Pipe American Iron and Steel Institutemaminu1100% (1)
- KOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Document28 pagesKOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Ivan DulicNo ratings yet
- EM 6815 EN - Solutions For Traction MotorsDocument20 pagesEM 6815 EN - Solutions For Traction MotorsIvan Dulic100% (1)
- (Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Document1 page(Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Ivan Briscoe100% (7)
- KOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Document28 pagesKOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Ivan DulicNo ratings yet
- KOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Document28 pagesKOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Ivan DulicNo ratings yet
- Uporedno15614 288 3 PDFDocument11 pagesUporedno15614 288 3 PDFIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Material and WeldingDocument226 pagesMaterial and WeldingIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Rolling Bearings in Electrical Motors & GeneratorsDocument122 pagesRolling Bearings in Electrical Motors & GeneratorsJurun_Bidanshi100% (1)
- KOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Document28 pagesKOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Ivan DulicNo ratings yet
- Welding-Standards 23-03-2014Document1 pageWelding-Standards 23-03-2014givali100% (7)
- KOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Document28 pagesKOORDINATOR-doc 135 Ewf 1090 Workshop 2013 Part 2Ivan DulicNo ratings yet
- Preciznost Sečenja Limova LaseromDocument1 pagePreciznost Sečenja Limova LaseromIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Welding-Standards 23-03-2014Document1 pageWelding-Standards 23-03-2014givali100% (7)
- RENK Slide Bearings Couplings PDFDocument4 pagesRENK Slide Bearings Couplings PDFIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- ZM - Instructions For Installation, Operation, Maintenance and Inspection PDFDocument40 pagesZM - Instructions For Installation, Operation, Maintenance and Inspection PDFIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- NDT-ispitivanja SVA PDFDocument366 pagesNDT-ispitivanja SVA PDFIvan Dulic100% (1)
- DUZINA GIBLJIVOG CREVA - Stainless - Steel - Catalogue PDFDocument14 pagesDUZINA GIBLJIVOG CREVA - Stainless - Steel - Catalogue PDFIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Manganese SteelDocument2 pagesManganese SteelIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- BMS Snap door lockDocument2 pagesBMS Snap door lockIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- DriveWorksXpressMobileGantryTutorial PDFDocument22 pagesDriveWorksXpressMobileGantryTutorial PDFIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Migtig 2514 NcsiDocument1 pageMigtig 2514 NcsiIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Bohler EAS 2-IG TDSDocument1 pageBohler EAS 2-IG TDSIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- Hydroweld HGVDocument2 pagesHydroweld HGVIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- VRTP P Eg Eng Web PDFDocument4 pagesVRTP P Eg Eng Web PDFIvan DulicNo ratings yet
- ESAB OK Autrod 12.51Document2 pagesESAB OK Autrod 12.51hooky1No ratings yet
- Exhaust ManifoldDocument5 pagesExhaust ManifoldDeepak Chachra100% (1)
- Electrical Machines DC MotorDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines DC MotorKitkay NivramNo ratings yet
- 9.6MVA - Technical Specifications For Inverter Duty TransformerDocument7 pages9.6MVA - Technical Specifications For Inverter Duty Transformerarunghandwal100% (2)
- Pipe Sizes and Flow Rates for Air Flush DrillingDocument14 pagesPipe Sizes and Flow Rates for Air Flush DrillingzapspazNo ratings yet
- LHCb Seminar on New Physics SearchesDocument32 pagesLHCb Seminar on New Physics SearchesdedeNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy PracticeDocument1 pageKinetic and Potential Energy Practicealchemist2000No ratings yet
- Evaluating The Effectiveness of Retrofitting An Existing Hospitality Buildingsia in 2010-2014Document8 pagesEvaluating The Effectiveness of Retrofitting An Existing Hospitality Buildingsia in 2010-2014International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 10 MW Unit 214.00 709 55.83 1972Document1 page10 MW Unit 214.00 709 55.83 1972Gangadhara P.K.No ratings yet
- Week 6 - Sample Final TestDocument4 pagesWeek 6 - Sample Final TestMai Thúy VyNo ratings yet
- Rectification ProcessDocument5 pagesRectification ProcessDilnaz TegispayNo ratings yet
- Numatics Series 342Document6 pagesNumatics Series 342Jebran FarazNo ratings yet
- Cause Effect Analysis of Oil Loss in Edible Oil IndustryDocument60 pagesCause Effect Analysis of Oil Loss in Edible Oil IndustrySaurabh RaiNo ratings yet
- Solar Refrigerator SpecsDocument4 pagesSolar Refrigerator SpecsFaisal Bin FaheemNo ratings yet
- Flamanville France Nuclear Power Plant WallchartDocument1 pageFlamanville France Nuclear Power Plant WallchartArzu AkarNo ratings yet
- Teco s310 User ManualDocument10 pagesTeco s310 User ManualEhsan GhanbarzadehNo ratings yet
- Fundamix Brochure EN WebDocument9 pagesFundamix Brochure EN Webjgjb4csrj7No ratings yet
- Fluid MechDocument10 pagesFluid MechPrasant KumarNo ratings yet
- ChE 525: Physical & Chemical Principles Mock Board 3Document6 pagesChE 525: Physical & Chemical Principles Mock Board 3Kuo Garol SarongNo ratings yet
- PG Parts Catalog1Document179 pagesPG Parts Catalog1Olivier ORMANNo ratings yet
- Screw Compressor Units: For Sodium Carbonate Production (Soda Ash)Document2 pagesScrew Compressor Units: For Sodium Carbonate Production (Soda Ash)Jaswindersingh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Foster Wheeler Process Engineering Practices IndexDocument86 pagesFoster Wheeler Process Engineering Practices Indexchemiesm94% (16)
- Enclosed Control Product Guide: April 2008Document456 pagesEnclosed Control Product Guide: April 2008MED-ROBIN2000No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Achieve For Interactive General Chemistry, 1e by Macmillan Learning Test BankDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Achieve For Interactive General Chemistry, 1e by Macmillan Learning Test BankNail BaskoNo ratings yet
- Energy Consumption Benchmark Guide: Cement Clinker ProductionDocument14 pagesEnergy Consumption Benchmark Guide: Cement Clinker ProductionVisnu SankarNo ratings yet
- All Terrain Vehicle Wiring PDFDocument3 pagesAll Terrain Vehicle Wiring PDFVINAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument19 pagesPressure MeasurementShadmanSakiefHridoyNo ratings yet
- Amcor 2016Document69 pagesAmcor 2016Romulo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Test RDCDocument88 pagesTest RDCWan SahNo ratings yet
- DVC6200Document4 pagesDVC6200Jesus BolivarNo ratings yet
- Edited Economics AsDocument476 pagesEdited Economics AsShakeela ShanmuganathanNo ratings yet