Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Model Question PDF
Uploaded by
John LeonsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Model Question PDF
Uploaded by
John LeonsCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 1
SUBJECT NAME : Transforms and Partial Diff. Eqn.
SUBJECT CODE : MA2211
MATERIAL NAME : Problem Material
MATERIAL CODE : JM08AM3006
(Scan the above Q.R code for the direct download of this material)
Name of the Student: Branch:
Unit I (Fourier Series)
1) Develop a Fourier series for the function ( ) ( ) f x x x t = in the interval (0, 2 ) t .
2) Find the Fourier series for the function
2
( ) ( ) f x x t = in the interval (0, 2 ) t and
deduce sum of series as
2 2 2
1 1 1
1 ...
2 3 4
+ + + + and also find
4 4 4
1 1 1
1 ...
2 3 4
+ + + +
3) Find the Fourier series of periodic 2 for
in (0, )
( )
2 in ( , 2 )
x
f x
x
t
t t t
and deduce that
2
2 2 2
1 1 1
...
1 3 5 8
t
+ + + = .
4) Obtain the Fourier expansion of periodicity 2 for ( ) f x x = when x t t < < .
Deduce that
2
2 2
1 1
1 ...
3 5 8
t
+ + + = and also find the value of
4 4
1 1
1 ...
3 5
+ + +
5) Find the Fourier series of
2
( ) f x x = in the interval ( , ) t t . Hence deduce that
2 2 2
1 1 1
...
1 2 3
+ + + also find the value of
4 4 4
1 1 1
...
1 2 3
+ + +
6) Find the Fourier series for the function
2
( ) f x x x = + in the interval ( , ) t t and also
deduce the value of
2
2
1
6 n
t
=
.
7) Show that when 0 x t < < ,
sin2 sin4 sin6
...
2 1 2 3
x x x
x
t
t = + + +
8) Develop a sine series of the function
0 / 2
( )
/ 2
x x
f x
x x
t
t t t
< <
=
< <
9) Find the Fourier series of ( ) cos f x x x = in the interval ( , ) t t .
10) Find the Fourier series of ( ) cos f x x = in the interval [-, ].
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 2
11) Obtain the Fourier series of ( ) f x period 2 and defined as follows
0
( )
0 2
x x
f x
x
< <
=
< <
and hence deduce the following
i)
1 1 1
1 ...
3 5 7 4
t
+ + =
ii)
2
2 2 2
1 1 1
...
1 3 5 8
t
+ + + =
12) Find the Fourier series of
2
( ) f x x = in the interval ( , ) . Hence deduce the sum of
series
2 2 2
1 1 1
...
1 2 3
+ + + .
13) Find the Fourier series of ( ) (2 ) f x x x = in 0 2 x < < . Deduce the sum of the
series
2 2 2 2
1 1 1 1
...
1 2 3 4
+ + + + .
14) Find the complex form of the Fourier series of the function ( )
ax
f x e = when
x t t < < and ( 2 ) ( ) f x f x t + = .
15) Find the complex form of the Fourier series of the periodic function ( ) sin f x x = when
0 x t < < .
16) Find the Fourier Series up to three harmonic for y = f(x)in (0,2) for the following data
x 0 /3 2/3 4/3 5/3 2
y 1.0 1.4 1.9 1.7 1.5 1.2 1.0
17) Find the Fourier Series up to two harmonic for y = f(x)in (0,2) for the following data
x 0 60 120 180 240 300 360
y 40.0 31.0 -13.7 20.0 3.7 -21.0 40.0
18) Find the Fourier Series up to two harmonic for y = f(x)in (0,2) for the following data
x 0 1 2 3 4 5
y 9 18 24 28 26 20
19) The values of x and the corresponding values of f(x) over a period T are given below
Show that ( ) 0.75 0.37cos 1.004sin f x u u = + + where
2 x
T
t
u = .
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 3
x 0 T/6 T/3 T/2 2T/3 5T/6 T
f(x) 1.98 1.30 1.05 1.30 -0.88 -0.25 1.98
Unit II (Fourier Transforms)
Part I
1) Show that the Fourier transform of
2 2
,
( )
0 ,
a x x a
f x
x a
<
=
>
is
3
2 sin cos
2
as as as
s t
| |
|
\ .
.
Hence deduce that
3
0
sin cos
4
t t t
dt
t
t
=
}
. Using
Parsevals identity show that
2
3
0
sin cos
15
t t t
dt
t
t
| |
=
|
\ .
}
.
2) Find the Fourier transform of
2
1 , 1
( )
0 , 1
x x
f x
x
<
=
>
. Hence prove that
3
0
sin cos 3
cos
2 16
s s s s
ds
s
t
=
}
.
3) Find the Fourier transform of ( ) f x if
1 ,
( )
0 , 0
x a
f x
x a
<
=
> >
. Hence deduce that
i)
0
sin
2
t
dt
t
t
=
}
ii)
2
0
sin
2
t
dt
t
t
| |
=
|
\ .
}
4) Find the Fourier transform of ( ) f x if
1 , 1
( )
0 , 1
x x
f x
x
<
=
>
. Hence deduce that
2
0
sin
2
t
dt
t
t
| |
=
|
\ .
}
and
4
0
sin
3
t
dt
t
t
| |
=
|
\ .
}
.
Note: The same problem they may ask
,
( )
0 ,
a x x a
f x
x a
<
=
>
with same
deduction.
Part II
5) Find the Fourier cosine and sine transform of the function ( ) , 0
ax
f x e a
= > .
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 4
6) Evaluate
( )
2
2 2
0
, 0
dx
if a
a x
>
+
}
using Parsevals identity.
7) Evaluate
( )
2
2
2 2
0
, 0
x
dx a
a x
>
+
}
using Parsevals identity.
8) Evaluate
( ) ( )
2 2 2 2
0
, , 0
dx
if a b
x a x b
>
+ +
}
using Parsevals identity.
9) Evaluate
( ) ( )
2
2 2 2 2
0
, , 0
x
dx if a b
x a x b
>
+ +
}
using Parsevals identity.
10) Evaluate
( ) ( )
2 2
0
1 4
dx
x x
+ +
}
using transforms method.
Part III
1) Find the Fourier sine transform of
, 0 1
( ) 2 , 1 2
0, 2
x x
f x x x
x
< <
= < <
>
.
2) Find the Fourier sine and cosine transform of
sin , 0
( )
0,
x x a
f x
x a
< <
=
>
.
3) Find the Fourier integral representation of ( ) f x defined as
0 for 0
1
( ) for 0
2
for 0
x
x
f x x
e x
<
= =
>
.
Part IV
1) Find the Fourier cosine and sine transform of ( )
ax
f x xe
=
.
2) Find the Fourier cosine transform of ( )
ax
e
f x
x
=
.
3) Find the Fourier sine transform of ( )
ax
e
f x
x
=
.
4) Find the Fourier cosine transform of
2
( )
x
f x e
=
.
5) Find the Fourier cosine transform of
2 2
, 0
a x
e a
> and hence deduce that sine transform
of
2 2
a x
xe
.
6) Show that the Fourier sine transform of
2
2
x
xe
is self reciprocal.
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 5
7) Find the Fourier sine and cosine transform of
x
e
also find the Fourier sine transform of
2
1
x
x +
and Fourier cosine transform of
2
1
1 x +
.
8) State and Prove Convolution theorem in Fourier transform.
Unit III (Partial Differential Equations)
- Higher Order Homogeneous and Non Homogeneous PDE
1) Solve
( )
2 2
6 5 sinh
x
D DD D z e y xy ' ' + = + .
Ans.:
3 4
1 2
1
( ) ( 5 )
8 24 6 4
x y x y
x x y x
z f y x f y x e e
+
= + + + + + .
2) Solve
( ) ( )
2 2
3 4 cos 2 D DD D z x y xy ' ' + = + + .
3) Solve
( )
3 2 2
4 4 6sin(3 6 ) D D D DD z x y ' ' + = + .
Ans.:
1 2 3
2
( ) ( 2 ) ( 2 ) cos(3 6 )
81
z f y f y x xf y x x y = + + + + + + .
4) Solve
( )
2
sin sin2 D DD z x y ' = .
Ans.:
1 2
1 1
( ) ( ) cos( 2 ) cos( 2 )
6 2
z f y f y x x y x y = + + + .
5) Solve
3 3 3
3
3 2 3
7 6 sin( 2 )
x y
z z z
z x y e
x x y y
+
| | c c c
= + +
|
c c c c
\ .
.
Ans.:
3
1 2 3
1
( ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) cos( 2 )
75 20
x y
x
z f y x f y x f y x x y e
+
= + + + + + .
6) Solve
( )
2 2
6 cos D DD D z y x ' ' + = .
Ans.:
1 2
( 2 ) ( 3 ) cos sin z f y x f y x y x x = + + + .
7) Solve
( )
2 2
2 2 2 sin( 2 ) D DD D D D z x y ' ' ' + + = + .
8) Solve
( )
2 2 2
3 3 7
x y
D D D D z e xy
+
' ' + = + + .
9) Solve
( )
2 2
2 3 3 2 cosh(2 ) D DD D D D z x y ' ' ' + + + = + .
10) Solve
( )
2 2
2 2 2 cos 2 cos D DD D D D z x y ' ' ' + + =
11) Solve
2 2
2 6 3
y
D DD D D D z xe ' ' ' ( + + =
.
- Standard Types
1) Form the PDE by eliminating the arbitrary function | from
( )
2 2 2
, 0 x y z ax by cz | + + + + = .
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 6
2) Solve z px qy pq = + + . Ans.: 0 z xy + =
3) Solve
2 2
z px qy p q = + + . Ans.:
2 2
4z y x =
4) Solve
2 2
1 z px qy p q = + + + + . Ans.:
2 2 2
1 x y z + + = .
5) Solve
2 2
z px qy p pq q = + + + + .
6) Solve
z x y
pq
pq q p
= + + . Ans.:
Hint: Multiply pqon both side, we get ( )
3/ 2
z px qy pq = + +
7) Solve
( )
2 2 2
1 p y x qx + = .
Hint: Rearrange the above equation, we get
( )
2 2
2
1
(says)
p x
q
k
x y
+
= = .
This is of the form
1 2
( , ) ( , ) f x p f y q = .
8) Solve
( )
2 2
9 4 p z q + = . Ans.:
( ) ( )
3
2
2
z a x ay b + = + + .
Hint: This is of the form ( , , ) 0 f z p q = .
9) Solve
2 2 2
1 z p q = + + . Ans.: ( )
1
2
1
cosh
1
z x ay b
a
= + +
+
.
Hint: This is of the form ( , , ) 0 f z p q = .
10) Solve ( ) 1 p q qz + = . Ans.: ( ) log 1 x ay c az ( + =
.
Hint: This is of the form ( , , ) 0 f z p q = .
11) Solve ( ) ( ) ( ) x y z p y z x q z x y + = . Ans.: ( ) , 0 x y z xyz | + + =
12) Solve
( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2 2 2 2
x y z p y z x q z x y + = . Ans.:
( )
2 2 2
, 0 x y z xyz | + + =
13) Solve the partial differential equation ( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2
x y z p y z x q z x y + = .
14) Solve( ) ( ) ( ) m n n m z y p x z q y x + = .
Ans.:
( )
2 2 2
, m n 0 x y z x y z | + + + + =
15) Solve( ) ( ) ( ) 3 4 4 2 2 3 z y p x z q y x + = .
Ans.:
( )
2 2 2
, 2 3 4 0 x y z x y z | + + + + =
16) Solve
( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2
x yz p y zx q z xy + = .
Ans.: , 0
x y
xy yz zx
y z
|
| |
+ + =
|
\ .
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 7
Unit IV (Application of PDE)
- One dimensional Wave equation.
1) Problems on Zero initial velocity (Pre work: 1).
For the following ( ) f x
a) ( ) sin
x
f x a
t
= (another name Sinusoid of length a)
b)
3
0
( ) sin
x
f x y
t
=
c) ( ) ( ) f x x x =
d) The midpoint of the string is displaced to a small height h or b is given.
e) Any problems with string of length 2.
2) Problems on Non Zero initial velocity (Pre work: 2).
For the following ( ) f x
f) ( ) sin
x
f x a
t
= (another name Sinusoid of length a)
g)
3
0
( ) sin
x
f x v
t
=
h) ( ) ( ) f x x x =
i)
, 0 / 2
( ), / 2
cx x
v
c x x
s s
=
s s
j) Any problems with string of length 2.
- One dimensional Heat flow equation.
3) Problems on zero boundary conditions. (Pre work: 3)
4) Problems on One end zero and another end non zero boundary condition
andreduced to 0C. (Pre work: 4)
5) Problems on both ends non zero boundary condition and reduced to 0C.
6) Problems on both ends non zero boundary condition and reduced to non zero
temperature.
Unit V (Z Transform)
- Problems on Z transform
1) Find the Z transform of the functioncos , sin , cos , sin ,
n n
n n a n a n u u u u
cos / 2, sin / 2, cos / 2, sin / 2,
n n
n n a n a n t t t t sin , cos
n n
na n na n u u .
2) State and Prove final value theorem in Z transform.
3) State and Prove Initial value theorem in Z transform.
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 8
4) Find the Z transform of the following functions (i)
{ }
n
a (ii)
{ }
n
na (iii)
1
n
`
)
(iv)
1
! n
`
)
(v)
!
n
a
n
`
)
(vi)
1
1 n
`
+
)
(vii) { } n (viii)
1
n
`
)
(ix) ( ) ( ) 1 2 n n + + (x)
( ) ( )
1
1 2 n n n + +
5) Find the Z transform of the function
( ) ( )
2 3
( )
1 2
n
f n
n n
+
=
+ +
.
- Problems on Inverse Z transform using Partial fraction
method
1) Find the inverse Z transform of
( ) ( ) ( )
2
3
2 1 5
z z
z z z
+
+ +
using partial fraction
method.
2) Find
( )
( ) ( )
2
1
2
2
1 1
z z z
Z
z z
(
+
(
( +
by using partial fraction method.
3) Find the inverse Z transform of
( ) ( )
2
2
2 4
z
z z + +
using partial fraction method.
4) Find
1
2
7 10
z
Z
z z
(
(
+ +
by using partial fraction method.
5) Find the inverse Z transform of
2
3 2
3
3 4
z z
z z
+
+
using partial fraction method.
6) Find
( )
( )
1
3
1
1
z z
Z
z
(
+
(
(
by using residues method.
- Problems on Convolution Theorem
1) State Convolution theorem and use it to evaluate
( )
2
1
( )
z
Z
z a z b
(
(
.
2) Find
2
1
2
( )
z
Z
z a
(
(
+
using convolution theorem.
3) Find
2
1
8
(2 1)(4 1)
z
Z
z z
(
(
+
using convolution theorem.
Engineering Mathematics 2013
Prepared by C.Ganesan, M.Sc., M.Phil., (Ph: 9841168917) Page 9
4) Using Convolution theorem, find
( ) ( )
2
1
1 3
z
Z
z z
(
(
.
5) Find the inverse Z transform of
2
z
z a
| |
|
\ .
, using Convolution theorem.
6) Use Convolution theorem to find the inverse Z transform
( ) ( )
1 1
12
3 4 z z
.
- Solving Difference Equation
1) Form the difference equation from the relation .3
n
n
y a b = + .
2) Using Z transform, solve
2 1
6 9 2
k
k k k
y y y
+ +
+ + = given
0 1
0 y y = = .
3) Solve
2 1
3 2 0
n n n
u u u
+ +
+ + = given
0 1
1, 2 u u = = , using Z transform.
4) Solve ( 3) 3 ( 1) 2 ( ) 0 y n y n y n + + + = given that (0) 4, (1) 0 y y = = and
(2) 8. y =
5) Solve the system
2 1
5 6 ,
n n n n
y y y u
+ +
+ = with
0 1
0, 1 y y = = and 1
n
u = for
0,1, 2, ... n= by Z transform method.
Hint: Substitute 1
n
u = in given equation, we get
2 1
5 6 1
n n n
y y y
+ +
+ = and do as
usual method.
6) Using Z transform solve ( ) 3 ( 1) 4 ( 2) 0, y n y n y n + = 2 n> given that
(0) 3 y = and (1) 2. y =
----All the Best----
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Class 12 Computer Science Notes and Questions.Document135 pagesClass 12 Computer Science Notes and Questions.Vipul Arora82% (11)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Projectile MotionDocument11 pagesProjectile Motionbastard100% (1)
- TIL-I 2024-2025 - 1 - Test SummaryDocument17 pagesTIL-I 2024-2025 - 1 - Test SummaryDeniz Kizilkaya100% (1)
- Signals Lab 1 and 2Document40 pagesSignals Lab 1 and 2Mohamad NabihNo ratings yet
- R. A. Rosenbaum, G. P. Johnson - Calculus - Basic Concepts and Applications-Cambridge University Press (1984)Document439 pagesR. A. Rosenbaum, G. P. Johnson - Calculus - Basic Concepts and Applications-Cambridge University Press (1984)Junk HitmanNo ratings yet
- A High Performance Binary To BCD Converter For Decimal PDFDocument4 pagesA High Performance Binary To BCD Converter For Decimal PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- %Uhqw:5Relqvrq0Hpehu, ( ( ('Dylg+Huqdqgh) Dugxqr0Hpehu, ( ( (Dqg0Rkdppdg6Dtxle6Hqlru0Hpehu, ( ( (Document4 pages%Uhqw:5Relqvrq0Hpehu, ( ( ('Dylg+Huqdqgh) Dugxqr0Hpehu, ( ( (Dqg0Rkdppdg6Dtxle6Hqlru0Hpehu, ( ( (John LeonsNo ratings yet
- Implementing Decimal Floating-Point Arithmetic Through Binary Some Suggestions PDFDocument4 pagesImplementing Decimal Floating-Point Arithmetic Through Binary Some Suggestions PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Parallel Decimal Multipliers Using Binary Multipliers PDFDocument6 pagesParallel Decimal Multipliers Using Binary Multipliers PDFJohn Leons100% (1)
- Newton-Raphson Algorithms For Floating-Point Division PDFDocument8 pagesNewton-Raphson Algorithms For Floating-Point Division PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- A Radix-10 Digit Recurrence Division Unit With A Constant Digit PDFDocument6 pagesA Radix-10 Digit Recurrence Division Unit With A Constant Digit PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Fixed and Floating-Point Implementations of Linear PDFDocument9 pagesFixed and Floating-Point Implementations of Linear PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- One Two Marks Public Volume (i&II) .DecryptedDocument133 pagesOne Two Marks Public Volume (i&II) .DecryptedRavi ShankerdNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Cs em Volume - I&II Important - Onemark - CSDocument46 pagesPlus Two Cs em Volume - I&II Important - Onemark - CSUniq ManjuNo ratings yet
- Star Office 2marksDocument4 pagesStar Office 2markssree7krishNo ratings yet
- Study - Material - XII - CS 2014 - 15 PDFDocument149 pagesStudy - Material - XII - CS 2014 - 15 PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- 11th STD Computer Science Book - English Medium - Volume 1Document200 pages11th STD Computer Science Book - English Medium - Volume 1JeganOnlyNo ratings yet
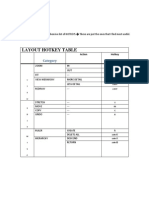
- Layout HotkeysDocument1 pageLayout HotkeysJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial 3Document17 pagesCadence Tutorial 3John LeonsNo ratings yet
- 12th Computer Science Import 2 & 5 Marks PDFDocument4 pages12th Computer Science Import 2 & 5 Marks PDFJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial7Document15 pagesCadence Tutorial7John LeonsNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial 6: - cdscdk2003 - CDSCDK - CD CadenceDocument24 pagesCadence Tutorial 6: - cdscdk2003 - CDSCDK - CD CadenceJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
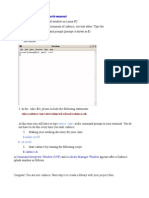
- Setting Up Your Linux Environment: $ Gedit .CSHRCDocument1 pageSetting Up Your Linux Environment: $ Gedit .CSHRCJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With AhdlDocument9 pagesGetting Started With AhdlJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial5Document21 pagesCadence Tutorial5John LeonsNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial 2Document12 pagesCadence Tutorial 2John LeonsNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial 4Document14 pagesCadence Tutorial 4bk249No ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial 1Document29 pagesCadence Tutorial 1John LeonsNo ratings yet
- Post Layout SimulationDocument2 pagesPost Layout SimulationJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Design Rule Check (DRC)Document2 pagesDesign Rule Check (DRC)John LeonsNo ratings yet
- Simulation With SpectreDocument2 pagesSimulation With SpectreJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Simulation With Verilog-XLDocument3 pagesSimulation With Verilog-XLJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- ExtractionDocument3 pagesExtractionJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Create Symbols: 1. Create Cell View - From Cell ViewDocument1 pageCreate Symbols: 1. Create Cell View - From Cell ViewJohn LeonsNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Section A: Straight Objective TypeDocument20 pagesTrigonometry: Section A: Straight Objective TypeRishabhNo ratings yet
- 0606 s15 QP 13Document16 pages0606 s15 QP 13tarius_1000No ratings yet
- Computer Science With Pyhton Practical FileDocument43 pagesComputer Science With Pyhton Practical FilenubaidNo ratings yet
- 1.4.3 Practice - Intro To TrigDocument3 pages1.4.3 Practice - Intro To TrigCorrelanderNo ratings yet
- Solved SSC CHSL 2 July 2019 Shift-2 Paper With Solutions PDFDocument37 pagesSolved SSC CHSL 2 July 2019 Shift-2 Paper With Solutions PDFTanuNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Sol PDFDocument34 pagesTrigonometry Sol PDFchirag aroraNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their Rates of ChangeDocument234 pagesFunctions and Their Rates of ChangePeter JonesNo ratings yet
- Measurement of The Elements of Spur Gear 6Document8 pagesMeasurement of The Elements of Spur Gear 6sen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- Periodic Functions, The Unit Step Function and The Second Shifting TheoremDocument21 pagesPeriodic Functions, The Unit Step Function and The Second Shifting TheoremChristian SarmientoNo ratings yet
- How To Do Trigonometry Step by StepDocument4 pagesHow To Do Trigonometry Step by Stepnishagoyal100% (1)
- Trigonometry in A NutshellDocument5 pagesTrigonometry in A NutshellRakesh S IndiaNo ratings yet
- Further Applications of TrigonometryDocument70 pagesFurther Applications of TrigonometryJayson IsidroNo ratings yet
- Reference For Unit 'Math': Procedures and FunctionsDocument2 pagesReference For Unit 'Math': Procedures and FunctionsLinndowwsNo ratings yet
- Double Angle and Half Angle IdentitiesDocument10 pagesDouble Angle and Half Angle IdentitiesKim TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Programming Pi-Bot With Minibloq: Stem Center UsaDocument33 pagesProgramming Pi-Bot With Minibloq: Stem Center UsaJerry Yaguar MorenoNo ratings yet
- IITians PaceDocument9 pagesIITians PaceAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2Document8 pagesCaie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2ballersNo ratings yet
- Pre - Board - 2 STD XII MathematicsDocument7 pagesPre - Board - 2 STD XII MathematicsPradip MohiteNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Control of A Rotary CraneDocument6 pagesModelling and Control of A Rotary CraneAliJunkoNo ratings yet
- Ch11 PDFDocument17 pagesCh11 PDFMasita RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ExercisesDocument8 pagesTrigonometry ExercisesSOFI ULLISKYNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents For Principles of Mathematics AllendoerferDocument3 pagesTable of Contents For Principles of Mathematics AllendoerferstreetbaNo ratings yet
- Cellphonetriagngulation Assignement 1Document2 pagesCellphonetriagngulation Assignement 1Chloe ClarkNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Inverse Trigo Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersDocument4 pagesCH 2 Inverse Trigo Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersNaresh bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Simple CurvesDocument21 pagesSimple CurvesHarsh RajNo ratings yet
- COMPETENCIES MATH Grades 7 - 9Document19 pagesCOMPETENCIES MATH Grades 7 - 9Unime PlazaNo ratings yet