Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Labels
Uploaded by
pringle89Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Food Labels
Uploaded by
pringle89Copyright:
Available Formats
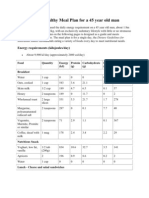
U N D E R S TA N D I N G
Foo Label
SERVING SIZE
Servings will vary from item to item. The best way to compare different products is by looking at the quantity per 100g or the percentage of your Recommended Daily Intake. That way youre comparing a consistent value across all labels and products.
CALORIES/KJ/ENERGY
Quick Guide to calories/KJ per serving: 40 calories/168 KJ= Low 100 calories/420 KJ = Moderate 400+ calories/1680 KJ = High
T E E EAOR ES M TH F O
IT M SE LI HE T
PROTEIN
NUTRITION INFORMATION
Servings per Package: 5 Serving Size: 3 cookies (32g/1.1oz) Average Quantity per Serving Energy Protein Fat Total Saturated Trans Cholesterol Total Carbohydrate Sugars Dietary Fibre Sodium 130 calories 2g 5g 2g 0g 0mg 20g 12g Less than 2g 170mg
Approximately 50g per day5. Protein is an important nutrient needed for the growth and repair of cells and for supplying essential amino acids (the bodys building blocks). Meat, chicken, fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, dried beans, lentils, dairy and soy products are all great sources.
Less than 20g per day1. Fats that are solid at room temperature increase risk of heart disease and cholesterol levels2.
SATURATED FAT
IT M SE LI HE T
IT E M S LI HE T
TRANS FAT
CHOLESTEROL
Less than 300mg per day1. Bad cholesterol (LDL) contributes to blocked arteries and risk of heart disease2.
Less than 2g per day (or as little as possible). Trans fats increase the levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) and decrease the levels of good cholesterol (HDL)3.
Example: Pack of cookies
IT E M S LI HE T
T E E EAOR ES M TH F O
SUGARS AS CARBOHYDRATE
Less than 50g per day4. Labels show total carbohydrate value and also how much of that value is made up of sugar. Sugar significantly increases energy content of food, too much energy in, and not enough out ends in weight gain and/or obesity.
SODIUM
FIBRE
No more than 2,400 mg per day1. Too much salt may increase the risk of developing high blood pressure - a risk factor for heart disease.
*Daily value recommendations are based on a 2000 Calorie/8360KJ diet. Your daily values may be higher or lower depending on your energy needs.
References: 1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2013). Labelling & Nutrition. Access: www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/LabelingNutrition/ucm266853.htm 2. National Heart Foundation of Australia. (2010). Understanding Fats and Cholesterol. Access: www.heartfoundation.org.au/sites/HealthyEating/ understandingfatsandcholesterol/Pages/default.aspx 3. Mozaffarian, D et al. (2006). Trans fatty acids and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 13;354(15):1601-13 4. World Health Organization. (2003). Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases. WHO Technical Report Series 916.Geneva. Access: www.whqlibdoc.who.int/trs/WHO_TRS_916.pdf 5. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (2002/2005). Food and Nutrition Board. Institute of Medicine. National Academies. Access: www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=10490
IT M SE LI HE T
25-30g per day5. Not only does it keep you feeling fuller longer, it is critical to keeping your digestive system healthy.
You might also like
- What Is The Food Guide Pyramid?: Hunt Buying Guide: Five Food Groups Were Milk and Meat CerealsDocument28 pagesWhat Is The Food Guide Pyramid?: Hunt Buying Guide: Five Food Groups Were Milk and Meat CerealsLanz PasaolNo ratings yet
- Module - TLEHE 10 - Unit 1Document10 pagesModule - TLEHE 10 - Unit 1Celina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Foods To AvoidDocument5 pagesFoods To AvoidTrisha HNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Facts LabelDocument2 pagesNutrition Facts LabelHayudini, Ashrina J.No ratings yet
- Energy and Energy and Nutrients NutrientsDocument12 pagesEnergy and Energy and Nutrients NutrientsNuno EspadaNo ratings yet
- Sample Food LabelDocument3 pagesSample Food LabelJaqueline Kaye Tivoli KalawNo ratings yet
- Sugar Counter for Health: The Smart Person's Guide to Hidden SugarsFrom EverandSugar Counter for Health: The Smart Person's Guide to Hidden SugarsNo ratings yet
- Dietary Advice For Polycystic Ovary Syndrome A4 2019Document10 pagesDietary Advice For Polycystic Ovary Syndrome A4 2019Linda gunawanNo ratings yet
- PBL CVDDocument8 pagesPBL CVDapi-704100991No ratings yet
- HASS Avocado Nutrition FactsDocument3 pagesHASS Avocado Nutrition FactspilisantaNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition MarikaDocument21 pagesFood and Nutrition Marikammeemz360No ratings yet
- Parker Kennedy Nutrition Tool-KitDocument11 pagesParker Kennedy Nutrition Tool-Kitapi-541137581No ratings yet
- 8 Tips For Healthy Eating - NHSDocument4 pages8 Tips For Healthy Eating - NHSp100% (1)
- Nutrition and Bodybuilding Greatness of The Mind, Strength of The BodyDocument59 pagesNutrition and Bodybuilding Greatness of The Mind, Strength of The BodyahmarmansoorNo ratings yet
- Food Guide PyramidDocument6 pagesFood Guide Pyramidknazareta100% (2)
- Is Breakfast Always A Good Idea?: by Philippa RoxbyDocument28 pagesIs Breakfast Always A Good Idea?: by Philippa RoxbyBapaknya BudiNo ratings yet
- Pink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 11Document18 pagesPink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 11jennmoyerNo ratings yet
- Erin Rentch Health Literacy PamphletDocument2 pagesErin Rentch Health Literacy Pamphletapi-273033291No ratings yet
- Food Labelling: For Healthy EatingDocument14 pagesFood Labelling: For Healthy Eatingmiroslav_miljenovicNo ratings yet
- Using The Nutrition Facts Label For Older AdultsDocument8 pagesUsing The Nutrition Facts Label For Older Adultsapi-660325689No ratings yet
- A Teenager's Nutritional Needs (14 To 17 Years Old)Document4 pagesA Teenager's Nutritional Needs (14 To 17 Years Old)SeharNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 2004 PDFDocument75 pagesNutrition 2004 PDFshaqtimNo ratings yet
- (ENG) The General Dietary Guidelines For Koreans PDFDocument12 pages(ENG) The General Dietary Guidelines For Koreans PDFSophia AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- Nutrional ProfileDocument117 pagesNutrional ProfileYash SuriNo ratings yet
- Diet Design Tools and GuidelinesDocument68 pagesDiet Design Tools and GuidelinescheriemooreNo ratings yet
- Sport Nutrition PowerpointDocument91 pagesSport Nutrition Powerpointapi-234854471No ratings yet
- Want To Learn More?: USE Nutrition Labels To Choose "3 Low" FoodDocument6 pagesWant To Learn More?: USE Nutrition Labels To Choose "3 Low" FoodalbertbhluiNo ratings yet
- Diet in Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiet in Cardiovascular Diseasepratyusha201No ratings yet
- Example of A Healthy Meal Plan For A 45 Year Old ManDocument12 pagesExample of A Healthy Meal Plan For A 45 Year Old ManzyloexNo ratings yet
- Nutrition OverviewDocument4 pagesNutrition Overviewapi-3749611No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 Food LabelDocument33 pagesLesson Plan 2 Food LabelDirgantaraAliifUtamaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Modified DietDocument20 pagesDefinition of Modified Dietmisbah67% (3)
- Carbohydrates, Fats and ProteinDocument22 pagesCarbohydrates, Fats and ProteinJena Mae Monsale FataganiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Balanced Diet and Why Is It ImportantDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Balanced Diet and Why Is It ImportantTESL2-0620 Jocelyn Marianne Anak JunnyNo ratings yet
- Meal Planning 3Document17 pagesMeal Planning 3Ming Dacayanan0% (1)
- Fuel Like A Champion Sports Nutrition HandoutsDocument49 pagesFuel Like A Champion Sports Nutrition HandoutsDanCurtisNo ratings yet
- Basic ToolsDocument47 pagesBasic ToolsCesca Medina100% (1)
- Kathleen Jane C. Ocay, BSN, RNDocument55 pagesKathleen Jane C. Ocay, BSN, RNKathleen Jane OcayNo ratings yet
- Food Calorie ChartsDocument124 pagesFood Calorie ChartsAkshay Poddar100% (1)
- People Look at Food Labels For Different ReasonsDocument12 pagesPeople Look at Food Labels For Different ReasonsyogikNo ratings yet
- These 8 Practical Tips Cover The Basics of Healthy EatingDocument5 pagesThese 8 Practical Tips Cover The Basics of Healthy Eatingprofessor SamNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument11 pagesBROCHUREManuela NaderaNo ratings yet
- Meal PlanDocument20 pagesMeal Plandowntown23No ratings yet
- j1188 Fiji1 Khana Kakana CookbookDocument48 pagesj1188 Fiji1 Khana Kakana Cookbookapi-295418392100% (2)
- 36 - Low Cholesterol DietDocument9 pages36 - Low Cholesterol DietfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Art of Eating SmartDocument4 pagesArt of Eating Smartsavvy_as_98100% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument37 pagesCarbohydratessamia tariqNo ratings yet
- Gout DietDocument2 pagesGout DietsamratkadamNo ratings yet
- CALORIEDocument13 pagesCALORIEharshika tembhurneNo ratings yet
- What Is Junk FoodDocument8 pagesWhat Is Junk FoodMuhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and Diabetic DietDocument4 pagesDiabetes and Diabetic DietSereneOne50% (2)
- High Cholesterol Eating Plan 2010Document6 pagesHigh Cholesterol Eating Plan 2010Navin ChandarNo ratings yet
- Hand Out For Grade 10Document6 pagesHand Out For Grade 10Brige SimeonNo ratings yet
- Healthy FactsDocument2 pagesHealthy FactsAsutosh SahooNo ratings yet
- Just Add Water: For Optimum PerformanceDocument1 pageJust Add Water: For Optimum Performancepringle89No ratings yet
- Processed Pyramid EngDocument1 pageProcessed Pyramid Engpringle89No ratings yet
- Acrylic Painting Step by StepDocument66 pagesAcrylic Painting Step by StepCarlo Di Domenico95% (21)
- Maths QuestionsDocument8 pagesMaths Questionspringle89No ratings yet
- 2015 Bull Mock CAT 31.pdfDocument60 pages2015 Bull Mock CAT 31.pdfPrateek Sarin50% (2)
- Regional Workshop On Regulating The Marketing and Sale of Foods and Non-Alcoholic Beverages at SchoolsDocument34 pagesRegional Workshop On Regulating The Marketing and Sale of Foods and Non-Alcoholic Beverages at SchoolsTrice DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cookery Modules Basic To PackageDocument140 pagesCookery Modules Basic To PackageRlon Franco BayocNo ratings yet
- Low Water Permeability Through Hydrophobicity: COIN Project Report 1 - 2008Document36 pagesLow Water Permeability Through Hydrophobicity: COIN Project Report 1 - 2008Alejandro Camargo SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Personal Diet Analysis Project FinalDocument27 pagesPersonal Diet Analysis Project Finalapi-302383239100% (2)
- Jurnal Studi Ekologi Bahasa Inggris PDFDocument6 pagesJurnal Studi Ekologi Bahasa Inggris PDFpinashty aulianaNo ratings yet
- Food Synergy Nutrients That Work Better TogetherDocument6 pagesFood Synergy Nutrients That Work Better TogetherGiyihfNo ratings yet
- Who European Action Plan For Food and Nutrition Policy 2015-2020Document24 pagesWho European Action Plan For Food and Nutrition Policy 2015-2020beatriz.21.941877No ratings yet
- Fats, Lipids DefinitionDocument4 pagesFats, Lipids DefinitionG AlionaNo ratings yet
- A Consumer's Guide To FatsDocument8 pagesA Consumer's Guide To FatschotrainNo ratings yet
- Hosc Intern ReportDocument39 pagesHosc Intern Reportnahom100% (1)
- Bbi2424 SCL Worksheet ComboDocument15 pagesBbi2424 SCL Worksheet ComboJIEHASMART100% (2)
- Reading 2 Test - Dong NaiDocument8 pagesReading 2 Test - Dong Naivinny4everNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document9 pagesScience 10GeminiNo ratings yet
- Processing Manual VCO PICT - Chap 7-Annex PDFDocument78 pagesProcessing Manual VCO PICT - Chap 7-Annex PDFjosephine mataNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE EXERCISE 3.3 KeyDocument4 pagesPRACTICE EXERCISE 3.3 KeyLê Minh QuangNo ratings yet
- Diet and FoodDocument2 pagesDiet and Foodneon333100% (2)
- NHI Assessment Report PDFDocument31 pagesNHI Assessment Report PDFAnonymous 1EHbXw100% (2)
- Nutrient BasicsDocument33 pagesNutrient Basicsapi-344976556No ratings yet
- Exp 8 Lipids PDFDocument7 pagesExp 8 Lipids PDFIsabel Joice EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Scavenger HuntDocument3 pagesScavenger Huntapi-405719582No ratings yet
- Classification of LipidsDocument18 pagesClassification of LipidsD Kaur100% (1)
- B. BiochemistryDocument22 pagesB. BiochemistryRadhika SarawagiNo ratings yet
- Mula Sa Puso: Chinese Community Health Care AssociationDocument23 pagesMula Sa Puso: Chinese Community Health Care Association2131443No ratings yet
- Salted Vs Unsalted ButterDocument6 pagesSalted Vs Unsalted ButterNur Izzah AnisNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument39 pagesPhysical ScienceRemar Jhon Paine67% (3)
- 1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Document112 pages1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Clàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Lyle McDonald - Applied Nutrition For Mixed SportsDocument77 pagesLyle McDonald - Applied Nutrition For Mixed SportsCatalin Dobre100% (11)
- 12 Biology Projects PDFDocument30 pages12 Biology Projects PDFAnurag PMNo ratings yet
- Dietary Guidelines For Americans 2020-2025-5Document10 pagesDietary Guidelines For Americans 2020-2025-5Guillermo ValdèsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainFrom EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellFrom EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietFrom EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsFrom EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (49)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)From EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- The Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayFrom EverandThe Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayNo ratings yet
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonFrom EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarFrom EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (352)
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthFrom EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomFrom EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookFrom EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeFrom EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Rapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: Deep Sleep Your Way to Rapid Weight Loss, Healing Your Body and Self Esteem with Guided Meditations and Positive AffirmationsFrom EverandRapid Weight Loss Hypnosis: Deep Sleep Your Way to Rapid Weight Loss, Healing Your Body and Self Esteem with Guided Meditations and Positive AffirmationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- The Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthFrom EverandThe Candida Cure: The 90-Day Program to Balance Your Gut, Beat Candida, and Restore Vibrant HealthNo ratings yet
- Foods That Cause You to Lose Weight: The Negative Calorie EffectFrom EverandFoods That Cause You to Lose Weight: The Negative Calorie EffectRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeFrom EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNo ratings yet
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingFrom EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Eat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthFrom EverandEat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (83)
- The Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodFrom EverandThe Diet Trap Solution: Train Your Brain to Lose Weight and Keep It Off for GoodNo ratings yet
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleFrom EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyFrom EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNo ratings yet
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouFrom EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNo ratings yet
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeFrom EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)