Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Objectives
Uploaded by
Bunzay GelineOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Objectives
Uploaded by
Bunzay GelineCopyright:
Available Formats
General Objectives: This study aims to identify and determine the underlying factors that will lead to ischemic
stroke. This presentation also intends to promote health and put into practice the acquired knowledge in rendering effective nursing intervention in accordance to client condition. Specific Objectives: At the end of presentation, the student nurses will be able to: 1. Determine the underlying factors that cause Cerebrovascular Accident. 2. Identify the signs and symptoms of Cerebrovascular Accident. 3. Determine the anatomy and physiology affected by Cerebrovascular Accident as well as its pathophysiology. 4. Formulate a Realistic Nursing Care Plan based on priority needs to help patient recover. 5. Implement necessary interventions to our patient. 6. Identify the action, indication, contraindication of the drugs prescribed to the patient as well as the nursing responsibilities. 7. Look for suitable treatment for the patient. 8. Convey health teachings to the patient to address her condition. 9. Promote wellness to the patient.
INTRODUCTION Nursing is a distinct body of knowledge that provides nursing care to patients who are in need of nursing care in support of medical interventions, in collaboration with other members of the health team or exclusively or independently by the nurse herself. Our exposure at Lipa Medix Medical Center was another daring and momentous opportunity for us to develop our knowledge, skills and especially attitude. Eight (8) hours on duty was indeed a tough challenge in our physical capacity. During our morning shift we were blessed to handle different cases at the ward. There, we observed a familiar condition Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), which we decided to present as a case study because our group wants to relate preventive measures to the people and our significant others and how we can decimate or banish this kind of condition. In doing this study, we can widen our minds capacity as we explore on the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and control of this neurologic disorder. By studying this case, we can be able to understand more clearly and gain more useful knowledge that could benefit us as well as our future clients also. As we focus in this study, we include anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, drugs, health teachings, and nursing care plans for our patient. Cerebrovascular Accident, commonly known as stroke, is caused by a disruption in the normal blood supply to the brain. This disruption in blood supply may be in the form of an interruption in blood flow to the brain, which is called ischemic stroke, or it may also take the form of bleeding within or around the brain which is called hemorrhagic
stroke. General signs and symptoms include numbness of face, arm, and legs; confusion or change in mental status, trouble speaking or understanding speech; visual disturbances, loss of balance, dizziness, difficulty walking or sudden severe headache. Stroke is the second most common cause of death and major disability worldwide.
The causes of stroke may include the following: An artery to the brain may be blocked by a clot (thrombosis) which typically occurs in a blood vessel that has previously been narrowed due to atherosclerosis ("hardening of the artery"). When a blood clot or a piece of an atherosclerotic plaque (a cholesterol and calcium deposit on the wall of the artery) breaks loose, it can travel through the circulation and lodge in an artery of the brain, plugging it up and stopping the flow of blood; this is referred to as an embolic stroke. A blood clot can form in a chamber of the heart when the heart beats irregularly, as in atrial fibrillation; such clots usually stay attached to the inner lining of the heart but they may break off, travel through the blood stream, form a plug (embolus) in a brain artery and cause a stroke. A cerebral hemorrhage (bleeding in the brain), as from an aneurysm (a widening and weakening) of a blood vessel in the brain, also causes stroke.
The diagnosis of stroke involves a medical history and a physical examination. Tests are done to search for treatable causes of a stroke and help prevent further brain damage. A CT scan (a special X-ray study) of the brain is often done to show bleeding into the brain; this is treated differently than a stroke caused by lack of blood supply. A CT scan also can rule out some other conditions that may mimic a stroke. An echocardiogram may be done to look for a source of blood clots in the heart. Narrowing
of the carotid artery (the main artery that supplies blood to each side of the brain) in the neck can be seen with a soundwave test called a carotid ultrasound. Blood tests are done to look for signs of inflammation which can suggest inflamed arteries. Certain blood proteins are tested that can increase the chance of stroke by thickening the blood.
The incidence of strokes among people ages 30-60 years old is less than 1 %. This figure triples by the age of 80. Men are more prone to stroke due to physical needs and built. Persons with sedentary lifestyle are a higher risk for stroke than those with active life styles. The rate of occurrence for strokes in the United States fell by 15.52% but the number of deaths from stroke actually rose by 5%. Stroke is a medical emergency that strikes suddenly, and it should be treated immediately to prevent neurologic deficit and permanent disability.
I. DEMOGRAPHIC PROFILE Name: Address: Age: Date of Birth: Gender: Civil status: Religion: Nationality: Date of Admission: Chief Complaint: Present Diagnosis: Patient XYY # 302 Brgy. Malabanan, Balete, Batangas 51 y/o July 16, 1950 Female Married Roman Catholic Filipino September 25, 2013 9:36 am
Fall secondary to dizziness, HPN CVA
Attending Physician: Dra. Andal
II. HISTORY A. HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS Few hours prior to admission, the patient experienced dizziness and the patient was rushed to the hospital because her son saw her that she fell down on the ground. The patient was conscious but not responsive. B. PAST MEDICAL HISTORY The client received 2 immunizations only (BCG and DPT) because the family is not aware of its importance. The client commonly had cough and fever. The childhood diseases that she acquired are mumps, measles, and chicken pox and sore eyes .There were no known food or medication allergy. Client has no history of accidents or injuries. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. C. FAMILY HISTORY OF ILLNESS The client has a history of hypertension, stroke and DM. D. HEALTH PERCEPTION PATTERN BEFORE HOSPITALIZATION The client experienced weakness on the left side of her body when she does some household task like gardening. She manages it by having a period of rest in bed. She is still uncomfortable with her state of health because it greatly affects her daily activities. She cannot perform the things she likes and usually do. Client believed that proper diet, exercises,
and adequate financial support are the things needed to maintain proper health diet and no vices are factors of having a healthy body. E. NUTRITIONAL AND METABOLIC PATTERN PRIOR TO HOSPITALIZATION The clients typical food intake is composed of rice, meat, and fish. Occasionally she eats vegetables and fruits. Shes fond of eating processed food like corned beef, anything with preservatives, tocino, chicharon and fried dish (porkchop, chicken). She used a lot fish sauce, MSG when cooking. Her appetite was good and drinks 6 glasses of water daily. Client wound heals well and she wears complete upper and lower dentures but this doesnt affect her food intake. DURING HOSPITALIZATION She developed difficulty in swallowing. F. ELIMINATION PATTERN BEFORE HOSPITALIZATION Client usually defecates at least 2-3 times of soft and watery stool consisting of small amounts. Client urinates 6x a day which is yellowishorange color w/out any discomfort.
DURING HOSPITALIZATION Client usually defecate at least 1-2x a day semi formed stool with the presence of blood which is light brown to brown. She has difficulty in defecation with excessive sweating. Client urinates 4x a day which is yellow in color w/out any discomfort. G. ACTIVITY-EXERCISE PATTERN BEFORE HOSPITALIZATION The clients relative said that her activities at home were limited because she has experience high blood pressure. She spends her days with minimal cleaning like gardening and watching TV. She also played with her granddaughter and grandsons. She walks short distances as form of her exercise. DURING HOSPITALIZATION Client shows tiredness and limited movement. A client d oesnt perform any routine exercise. In the hospital the client instructed to Perform ROM by the health care provider. 3-FEEDING 3-GENERAL MOBILITY 4-BATHING 3-GROOMING 4-COOKING 3-TOILETTING 3-BED MOBILITY 4-HOME MAINTENANCE
3-DRESSING
Level 0 - Full self care Level 1 - Requires use of equipment or device Level 2 - Requires assistance or supervision from another person Level 3 - Requires assistance or supervision from another person or device Level 4 - Is dependent and does not participate H. SLEEP-REST PATTERN BEFORE HOSPITALIZATION The client sleeps for 8-9 hours usually from 8pm-5am but not continuous because of prompt abdominal pain. She doesnt take any sleep medications. She also does take naps during afternoon. The client sleeps inadequately at night. Clients usually watch TV shows and played with her granddaughter and grandsons. DURING HOSPITALIZATION The client sleeps is lessen to 6 hours due to abdominal pain and interrupted when the health care provider give medication and monitor her vital signs during the night. She takes naps in the afternoon for about 1 hour.
I. COGNITIVE-PERCEPTUAL PATTERN The client does not have any hearing difficulty and cant remember past events. Abdominal pain is the one which alters her comfort and she manages it with taking prescribed medications. J. SELF PERCEPTION AND SELF CONCEPT PATTERN The client said that her condition was not improve, she still experience left sided body weakness and high blood pressure. Client feels that she lose some weight. Financial problems and health condition usually makes her worried. When these things are encountered the client diverts her attention through talking to a family member and praying. K. ROLE-RELATIONSHIP PATTERN The client lives in extended family. They live peacefully even there are hardship and difficulties that arrives to their lives. By means of good conversation they can easily fixed family problems. When family experienced difficulty of caring for the client they just take it as trials given by God. They have harmonious relationships with the family and their neighbors. L. SEXUALITY-REPRODUCTIVE PATTERN The client is done in stage of menopausal. There is no sexual activity. According to the client, decreased sexual activity is not a problem because they were already old. They spent most of their time by taking
care of each other and with that they are showing their love for one another. M. COPING STRESS TOLERANCE PATTERN The client was observed to be withdrawn but the behavior improved as evidenced by her socialization with other people. When things are not so well, she finds her husband to be the most helpful person in talking things over. When big problems encountered, she always prays and ask assistance with the Lord. Some of the time they failed to attain what they want and try other alternatives in solving it. N. VALUE-BELIEF PATTERN The client is a Roman Catholics usually go to the church to attend mass every Sundays, first Friday of the month and novena. She is very active in participating religious activities. She helps spread the word of god through catechism.
III. Physical Assessment The clients pulse rate is 98 beats per minute, his respiratory rate is 20 breaths per minute, temperature is 36.8c. BP-180/110.
Mental status
The client is conscious but not responsive. GCS of 8/15.
Skin The clients skin is of normal racial tone which is brown. It is dry and smooth. The skin turgor is wrinkled and loss of elasticity. The body hair is evenly distributed. She doesnt have any edema.
Nail The clients nail shape is convex clubbing, the nail is rough and the nail bed is pink. The capillary refill is within 3 seconds.
Head and Face The clients skull is proportionate to the body size; there were no tenderness in the scalp. Her hair is evenly distributed and the strands are thin and brittle. The color of his hair is a mixture of white and black.
Eyes
The condition of his eyes is straight normal; the eye brows are evenly distributed. Eyelids have effectively closure. The blink response is bilateral, eye balls are symmetrical, the palpebral conjunctiva is pink and the sclera is white. Pupils are equal in size. Pupils are equally round and reactive to light and accommodation. Ear The color of the ear is of normal racial tone which is brown, and is symmetrical. The alignment of the pinna is symmetrical. The pinnas are elastic and recoil when folded. The mastoid process is tender. The auditory canal contains some cerumen, the color is brown and there is an absent of discharges.
Nose The color of the clients nose is of racial tone which is brown. His septum is in the
midline. The mucosa is pink, nostrils are both patent, nasal flaring is absent. Landmarks visible. Sinuses are non-tender. There is an NGT in his right nostrils. are
Mouth and Oropharynx
The lips is symmetrical and pink, the consistency is smooth, buccal mucosa is pink, the gum is pink, the tongue is in the midline, the color is pink and it is smooth. The tongue movements are not that smooth. Its texture is rough. Neck The neck has involuntary movement and with resistance, the muscle strength 3/5. The trachea is in the midline, thyroid is in the midline and it is smooth. Maxillary lymph nodes are palpable.
Upper extremities
The client cannot resist force when asked to resist. Muscle strength is 2/5. The peripheral pulses are equal. The IV site is in his left arm.
Lower extremities
The client cannot resist force when asked to resist. Muscle strength is 1/5. She doesnt have any deformity. The peripheral pulses are equal.
IV. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
NERVOUS SYSTEM
The nervous system is a very complex system in the body. The nervous system is divided into two main systems, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system. The spinal cord and the brain make up the CNS. Its main job is to get the information from the body and send out instructions. The peripheral nervous system
is made up of all of the nerves and the wiring. This system sends the messages from the brain to the rest of the body.
One of the parts of the CNS is the brain. It keeps the body in order. It helps to control all of the body systems and organs, keeping them working like they should. The brain also allows us to think, feel, remember and imagine. In general, the brain is what makes us behave as human beings. The brain communicates with the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the nerves. They tell the brain what is going on in the body at all times. This system also gives instructions to all parts of the body about what to do and when to do it. There are five main senses - touch, smell, taste, hearing and sight. These are the external sensory system, because they tell you about the world outside your body. Your senses tell you what is happening in the outside world. Your body's sense organs constantly send signals about what is happening outside and inside it to your control center - the brain.
Cerebrum
The biggest part of the brain is the cerebrum. The cerebrum makes up 85% of the brain's weight. The cerebrum is the thinking part of the brain and it controls voluntary muscles.
Cerebellum The cerebellum is at the back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It's smaller than the cerebrum at only 1/8 of its size. It controls balance, movement, and coordination.
Brain Stem The brain stem sits beneath the cerebrum and in front of the cerebellum. It connects the rest of the brain to the spinal cord, which runs down the neck and back. The brain stem is in charge of all the functions the body. Midbrain It is part of the brain stem, which includes the tectum and
tegmentum. Functions include vision, hearing, eye movement, and body movement. The anterior part has the cerebral peduncle, which is a huge bundle of axons traveling from the cerebral cortex through the brain stem and these fibers (along with other structures) are important for voluntary motor function. Pons It is involved in motor control and sensory analysis... for example, information from the ear first enters the brain in the pons. It has parts that are important for the level of consciousness and for sleep. Some structures within the pons are linked to the cerebellum, thus are involved in movement and posture. Medulla oblongata is the lower portion of the brainstem. It deals with autonomic functions, such as breathing and blood pressure. The cardiac center is the part of the medulla oblongata responsible for controlling the heart rate. Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is like your brain's inner thermostat. It is responsible for the regulation of temperature.
The second main part of the nervous system is the peripheral nervous system. The nervous system is made up of nerve cells or neurons that are "wired" together throughout the body, somewhat like communication system. Neurons carry messages in the form of electrical impulses. The messages move from one neuron to another to keep the body functioning. Neurons have a limited ability to repair themselves.
The Circle of Willis
The Circle of Willis is a vital formation of arteries at the base of the brain which supplies all thought processes with the necessary fuel. There is a grouping of arteries near the base of the brain which is called the Arterial Circle of Willis. It is named after a very influential English physician named Thomas Willis, who discovered it and then published his findings in his 1664 work.
The Circle of Willis is truly one of the most important, yet overlooked areas in the brain, and one of the most efficiently designed systems in the human body. It does not specifically help one to think or react but the more glamorous portions of the brain could not possibly function without the Circle.
The key element which makes the Circle of Willis so spectacularly effective in doing its job and so very remarkable in its design is the fact that the arteries contained therein (the Anterior Cerebral and the Posterior Cerebral Arteries being two of the main ones) are arranged in a looping pattern which allows for a complex system of redundancy built into the flow of the blood. This is important because if for some reason one of the arteries is having problems, the others can do their best to pick up the slack
and maintain cerebral profusion, wherein the pressure of blood flowing through the various parts of the brain is kept at normal levels.
While the ingenious design of the Circle helps significantly to prevent certain conditions from developing within the brain related to blood flow, it is not entirely perfect. There is always the possibility of several conditions occurring, such as arterial blockage (usually due to a blood clot) or cerebral hemorrhage, either of which can cause devastating strokes and other cerebral abnormalities.
V. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Tissue injury Causing compression of tissue Expanding hematoma or hematomas Distort and injure tissue The pressure may lead to a loss of blood supply to affected tissue with resulting infarction The blood released by brain hemorrhage appears to have direct toxic effects on brain tissue and vasculature
Cerebrovascular accident or stroke (also called brain attack) results from sudden interruption of blood supply to the brain, which precipitates neurologic dysfunction lasting longer than 24 hours. Stroke are either ischemic, caused by partial or complete occlusions of a cerebral blood vessel by cerebral thrombosis or embolism or hemorrhage (leakage of blood from a vessel causes compression of brain tissue and spasm of adjacent vessels). Hemorrhage may occur outside the dura (extradural),
beneath the dura mater (subdural), in the subarachnoid space (subarachnoid), or within the brain substance itself (intracerebral). Risk factors for stroke include transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) warning sign of impending stroke hypertension, arteriosclerosis, heart disease, elevated cholesterol, diabetes mellitus, obesity, carotid stenosis, polycythemia, hormonal use, I.V., drug use, arrhythmias, and cigarette smoking. Complications of stroke include aspiration pneumonia, dysphagia, constractures, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, depression and brain stem herniation.
VI. DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
Name of Diagnostic Procedure 1. Hematology Indication: - this is used to evaluate anemia, leukemia, reaction to inflammation and infections, peripheral blood cellular characters, state of hydration and dehydration, polycythemia, hemolytic disease of the newborn, to manage chemotherapy decisions.2. Name of Diagnostic Procedure
Name of Date Procedure Ordered
Normal Values Hct: mo. 40-0,56
Values Obtained 0.45
Interpretation Normal Normal Normal Above normal: values obtained is higher than the normal values Normal Above normal: values obtained is higher than the normal values Normal
Hgb: M 135-180 g/L 152 RBC: g/L September Hematology 25, 2013 5.0-6.5x10 4.86 4.5- 15.2
WBC: 11.00x10g/L
Platelet adequate Neutrophils: 0.70
count: Adequate 0.50- 0.82
Lymphocytes 0.20- 0.18 0.40
2 .Radiology Result: - No acute parenchymal infiltrates seen - Atherosclerotic Aorta Date of Examination: September 26, 2013 3. CT Scan Indication: CT Scanning of the head is typically used to detect: 1. 2. 3. 4. Results: Technique: Plan axial CT Images of the head Findings: There is widening of the sulci and narrowing of the gyri in both cerebral hemisphere. Impression: - Age related to cerebral atrophy with ex-vasodilatation at the ventricles The Cerebral vessels are calcified There are low alterations noted in the left temporo-parietal lobes. Bleeding, brain injury and skin fractures Brain Tumors A blood clot or Bleeding Enlarged brain cavities ,etc..
- Atheromatous cerebral vessels - Acute to subacute infarcts in the distribution area of the left middle cerebral artery Date of examination: September 27, 2013
VI. TREATMENT INTRAVENOUS FLUID PNSS 1000mL/12 hours (27.28 gtts/min.) IVF is an essential when patient are unable to take enough food and fluids orally. It is effective and efficient method of supplying liquids directly into the IVF compartment and replacing electrolyte losses. MEDICATIONS Amlodipine 1tab, PRN Clonidine 1tab, PRN Mannitol 75 mg, q6 Coversyl PRN NTG Patch PRN DIET The patient was advised to have low salt. Low fat diet and she was feed through NGT. ACTIVITY The patient was ordered to have complete bedrest because the patient is weak and he needs to conserve energy changing of position is required and advisable for proper blood circulation.
VIII. NURSING MANAGEMENT Obtain vital sign and pulse oximetry measurements every 2 -4 hours or as ordered for 24 hours on all patients with diagnosis of stroke. Asses level of consciousness, random movements, response to stimuli, eye contact and speech. Document. Patient should have at least one IV access site in the non-paralytic side. Monitor blood pressure every 30 minutes. Check for urinary retention. Initiate physical therapy. Activity needs to be advanced as tolerated. Avoid immobility. Apply high knee ted hose for patients with impaired mobility. Initiate the pressure ulcer prevention, general skin care, immobility management and fall prevention management.
IX. COURSE IN THE WARD CLIENTS DAILY PROGRESS CHART Diagnostic Procedure Admission Hematology Low Salt Low Fat Diet Amlodipine NGT 2000 Kcal / feeding. IV: PNSS 1L 27 gtts to run for 8 hours Diet Medication Treatment
Day 2
Radiology
Low Salt Low Fat Diet
Amlodipine Clonidine Mannitol Coversyl NTG Patch
NGT 2000 Kcal / feeding. IV: PNSS 1L 27 gtts to run for 8 hours
Day 3
CT scan
Low Salt Low Fat Diet
Amlodipine Clonidine Mannitol Coversyl NTG Patch
NGT 2000 Kcal / feeding. IV: PNSS 1L 27 gtts to run for 8 hours
XII. DISCHARGE PLAN MEDICATIONS Avoid over the counter medications without checking the physician. Emphasize the importance of not stopping medications unless instructed by the physician. EXERCISE Encourage patient to have a daily exercise but no heavy exercise is permitted. It will increase blood pressure. TREATMENT Follow doctors order for taking medications. Avoid eating high cholesterol rich foods. Control blood pressure by eating a healthful diet and have a regular exercise. Adequate intake of vitamins. HYGIENE Stress the importance of hand washing Follow proper hygiene. Maintain cleanliness on surroundings. OUTPATIENT Avoid stress because it is capable of increasing blood pressure.
Advise patient to take the prescribed medication at right time and right dosage. Stress the importance of regular follow-up visits after discharge. Check blood pressure regularly to detect any increase and if it is found to be consistently elevated, a physician should be consulted. Keep your weight under control. DIET Proper nutrition and fluid intake should be observed. Educate patient the importance of diet. Increase fiber in the diet. Eat a healthy diet that is low in saturated fat, transfat and maintain a low cholesterol and sodium diet. SPIRITUALITY Provide patient support, advice, and comfort. Encourage the patient to accept and cope up with current situation. Acceptance is the first thing in healing. Create a trusting relationship with the client so that any religious concerns or practices can be openly discussed and addressed.
RECOMMENDATION As a group, we recommend Patient XYY to strictly follow the discharge instructions of the physician as well as the nurse. Have a follow up check up to monitor health status. Adherence to the medications especially anti-hypertensive drugs, thrombolytic is strongly recommended. Ensure a healthy nutritious meal that is low in fats, salt to avoid or decrease the risk of having the same complications. Regular exercise but not heavy is encouraged to promote good blood flow to the bodys system, thus, providing more oxygen to the body. Maintenance of adequate oral fluid intake atleast 2-3 L per day is advised to promote wellness. Check blood pressure regularly to detect any increase and if it is found to be consistently elevated, a physician should be consulted. It is further recommended that the patients significant others should be aware of signs and symptoms of cerebrovascular accident and its complications and should immediately report it to the physician.
You might also like
- Atrial Fibrillation Explained: Understanding The Next Cardiac EpidemicFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation Explained: Understanding The Next Cardiac EpidemicNo ratings yet
- A Case Study ON Cerebrovascular Accident With Left HemiparesisDocument57 pagesA Case Study ON Cerebrovascular Accident With Left Hemiparesisdonheyzz_020% (1)
- Cva Case StudyDocument16 pagesCva Case StudyEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Stroke, (Cerebrovascular Infarction) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Stroke, (Cerebrovascular Infarction) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Case Study On CVADocument34 pagesCase Study On CVAGimcy Dela Fuente50% (2)
- Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms, RisksDocument12 pagesStroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms, RisksSuzette Rae TateNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CVADocument27 pagesCVAMafe Campo100% (3)
- Peripheral Vascular Disease Demystified: Doctor's Secret GuideFrom EverandPeripheral Vascular Disease Demystified: Doctor's Secret GuideNo ratings yet
- CVA Case PresentationDocument8 pagesCVA Case Presentationrichie_chan_2100% (3)
- Recovering from Stroke - Overcoming the Challenges of StrokeFrom EverandRecovering from Stroke - Overcoming the Challenges of StrokeNo ratings yet
- Miyat PresentationDocument73 pagesMiyat Presentationmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Explained: A Guide for Patients and FamiliesFrom EverandIdiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Explained: A Guide for Patients and FamiliesNo ratings yet
- ICU CVD GroupCaseStudyDocument43 pagesICU CVD GroupCaseStudyKrizziaNo ratings yet
- When Lightning Strikes: An Illustrated Guide To Stroke Prevention And Re coveryFrom EverandWhen Lightning Strikes: An Illustrated Guide To Stroke Prevention And Re coveryNo ratings yet
- Case Study CVDDocument49 pagesCase Study CVDzerpthederpNo ratings yet
- TIA Case StudyDocument44 pagesTIA Case Studyyer tagalajNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Treating a Stroke PatientDocument10 pagesDiagnosing and Treating a Stroke PatientMary Therese Joy BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On CVADocument22 pagesCase Study On CVAAgronaSlaughter100% (3)
- Case Study Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument11 pagesCase Study Acute Myocardial InfarctionChristine Elaine Batusin Ilagan91% (23)
- Case Study PaperDocument6 pagesCase Study Paperapi-434982019No ratings yet
- Case Pres MIDocument122 pagesCase Pres MIRanul Juntilla BacusmoNo ratings yet
- Mini Par G10 PDFDocument45 pagesMini Par G10 PDFKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Case Study Post Stroke SeizuresDocument12 pagesCase Study Post Stroke SeizuresVecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- CVA Infarct Case StudyDocument35 pagesCVA Infarct Case StudyArvic Fritz CastañasNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument43 pagesCase PresentationAmy Rose abuevaNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Congestive Heart CHFDocument31 pagesCase Study in Congestive Heart CHFJm RomancapNo ratings yet
- CVDDocument58 pagesCVDNeil Sabijon67% (6)
- Heart Disease Story Empowers PatientsDocument24 pagesHeart Disease Story Empowers PatientsDaisy Ree MojicaNo ratings yet
- Aspergilloma Case StudyDocument70 pagesAspergilloma Case StudyGilian DacanayNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 1Document21 pagesCase Study 1 1Melody DoriaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument19 pagesHirschsprung DiseaseJudith PurificacionNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 058 - Stroke Elseivier Powerpoint For My Class LectureDocument52 pagesChapter - 058 - Stroke Elseivier Powerpoint For My Class LectureSuraj Mukatira100% (2)
- Case Study On CVADocument19 pagesCase Study On CVAmolukas10190% (42)
- 15yo With Lethargy and FeverDocument7 pages15yo With Lethargy and FeverdakewtwontonNo ratings yet
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument26 pagesAplastic AnemiaMark Anthony S. Castillo100% (1)
- MICU Case Study PresentationDocument55 pagesMICU Case Study Presentationjmarc_21100% (4)
- MYOCARDIAL-INFARCTION-1 Copy FinalDocument4 pagesMYOCARDIAL-INFARCTION-1 Copy FinalReizel GaasNo ratings yet
- Case Study.... Group-BDocument33 pagesCase Study.... Group-BNazmul HossainNo ratings yet
- CHF Case Study on Congestive Heart FailureDocument40 pagesCHF Case Study on Congestive Heart Failurelyndzy100% (1)
- Final Paper Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument16 pagesFinal Paper Rheumatic Heart DiseasePrincess TumambingNo ratings yet
- Elderly FallsDocument7 pagesElderly FallsIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Stress Insomnia OutputDocument18 pagesStress Insomnia OutputReyes PaulNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY NEURO Group 1 2020Document13 pagesCASE STUDY NEURO Group 1 2020GenoMacaraanNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument34 pagesCase Pres Cerebrovascular DiseaseADRIATICO JAROSLUVNo ratings yet
- CvaDocument170 pagesCvaApril Jumawan ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Case Study On CVADocument54 pagesCase Study On CVAmolukas10186% (7)
- HypertensionDocument8 pagesHypertensiongilma100% (3)
- What Is A StrokeDocument5 pagesWhat Is A StrokeLintsuNo ratings yet
- Ebook Cardiovaskuler Disease StrokeDocument9 pagesEbook Cardiovaskuler Disease StrokearisNo ratings yet
- Ate Joya File Until LabsDocument36 pagesAte Joya File Until LabsMoneto CasaganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management 103 Related Learning Experience Health TeachingDocument10 pagesNursing Care Management 103 Related Learning Experience Health Teachingkarenfaye00No ratings yet
- Subject:: Emergencies and Critical SituationsDocument10 pagesSubject:: Emergencies and Critical SituationsHapipa HarwnNo ratings yet
- GRAND TotalDocument35 pagesGRAND TotalNoveeNo ratings yet
- Case Congenital AV BlockDocument27 pagesCase Congenital AV BlockPrima Hari NastitiNo ratings yet
- Case Study NSTEMIDocument26 pagesCase Study NSTEMIHomework Ping100% (1)
- ICU Case PresentationDocument51 pagesICU Case Presentationdeliejoyce0% (1)
- A. Discussion of The Health ConditionDocument5 pagesA. Discussion of The Health ConditionPeter AbellNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Discharge Summary Medications Compliance Exercise Treatment Health Teachings Follow Up DietDocument1 pageDischarge Summary Medications Compliance Exercise Treatment Health Teachings Follow Up DietBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Cho Rio CarcinomaDocument3 pagesCho Rio CarcinomaBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- VIII. Nursing ManagementDocument1 pageVIII. Nursing ManagementBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument22 pagesCommunity Health NursingBunzay Geline100% (9)
- Febrile SeizureDocument9 pagesFebrile SeizureBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Indication Dosage / Route Action Contra-Indication Adverse ReactionDocument3 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Indication Dosage / Route Action Contra-Indication Adverse ReactionBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument12 pagesCourse in The WardBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PresentationDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PresentationBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic Brand Dosage/ Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction NursingDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Generic Brand Dosage/ Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction NursingBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Child Breathing Difficulty Nursing CareDocument3 pagesChild Breathing Difficulty Nursing CareBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Chronic Illness and Self-Esteem IssuesDocument1 pageChronic Illness and Self-Esteem IssuesBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PneumoniaDocument4 pagesDrug Study PneumoniaBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Drugs One by OneDocument6 pagesDrugs One by OneBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Generic Brand Dosage/ Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction NursingDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Generic Brand Dosage/ Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction NursingBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PresentationDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PresentationBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PresentationDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PresentationBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument22 pagesCommunity Health NursingBunzay Geline100% (9)
- 4 Freud - S Psychosexual StagesDocument10 pages4 Freud - S Psychosexual StagesBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument10 pagesCommunity Health NursingBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Discharge Summary Medications Compliance Exercise Treatment Health Teachings Follow Up DietDocument1 pageDischarge Summary Medications Compliance Exercise Treatment Health Teachings Follow Up DietBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Cognitive DevelopmentDocument13 pagesPiaget's Cognitive DevelopmentBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication ReportDocument8 pagesTherapeutic Communication ReportBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- RizalDocument4 pagesRizalBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Behavior Patterns' SymptomsDocument33 pagesDynamics of Behavior Patterns' SymptomsBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document71 pagesGroup 3Bunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- 4 Freud - S Psychosexual StagesDocument10 pages4 Freud - S Psychosexual StagesBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Casestudy in OrthoDocument8 pagesCasestudy in OrthoBunzay GelineNo ratings yet
- Amphioxus LabDocument1 pageAmphioxus LabHenie PiogNo ratings yet
- 2014 Helsinki Workshop Material ShacklockDocument43 pages2014 Helsinki Workshop Material ShacklockAl100% (1)
- #Cartography 2 - Centers - RaDocument53 pages#Cartography 2 - Centers - RaDorabella100% (1)
- Lott 1966Document20 pagesLott 1966Shraddha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues (Anatomy) PDFDocument17 pagesBody Tissues (Anatomy) PDFNixonr RamsaranNo ratings yet
- PPT Bedah DigestifDocument28 pagesPPT Bedah DigestifFatima Rima AndiniNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 1Document43 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 1Tifanny Shaine Tomas100% (2)
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaNizarul HizomiNo ratings yet
- Renal Excretion of Drugs 3Document36 pagesRenal Excretion of Drugs 3Noorulhuda AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Lab Report for Mrs. Karamjeet KaurDocument2 pagesHealthcare Lab Report for Mrs. Karamjeet KaurMunishNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology Lesson on Menstrual CycleDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Biology Lesson on Menstrual CycleCheskaTelanNo ratings yet
- The Boxing Debate by The British Medical AssociationDocument132 pagesThe Boxing Debate by The British Medical AssociationTheRealBarrettNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - AgungDocument40 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - AgungalgutNo ratings yet
- Description of Reproductive System of Indian Water Scorpion, Laccotrephes Maculatus Fabr. (Hemiptera, Heteroptera: Nepidae)Document13 pagesDescription of Reproductive System of Indian Water Scorpion, Laccotrephes Maculatus Fabr. (Hemiptera, Heteroptera: Nepidae)Kanhiya MahourNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Quiz ADocument6 pagesCh.4 Quiz ASultan AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Encoding-Retrieval Similarity and MemoryDocument48 pagesEncoding-Retrieval Similarity and Memorydsekulic_1No ratings yet
- Complete Blood Picture: Test Name Value Units Reference Range 3.44 7.4 76 22 28.5Document107 pagesComplete Blood Picture: Test Name Value Units Reference Range 3.44 7.4 76 22 28.5anil tanankiNo ratings yet
- W.G. Igcse Transport in HumansDocument20 pagesW.G. Igcse Transport in Humansbloodshooter1996No ratings yet
- Mader Biology Chapter 40 OutlineDocument8 pagesMader Biology Chapter 40 OutlineEllen LiNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization QuizDocument41 pagesLevels of Organization QuizFritzie Anne Figura SamonteNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1571800842460Document27 pagesOrca Share Media1571800842460Reniel De MesaNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- Organ System ReviewerDocument31 pagesOrgan System ReviewerDronio Arao L-saNo ratings yet
- Kidney Functions and AnatomyDocument17 pagesKidney Functions and AnatomyAmy Lalringhluani100% (1)
- Ang Tunay Na Excretory SystemDocument17 pagesAng Tunay Na Excretory SystemcjNo ratings yet
- Digestive System CnaDocument6 pagesDigestive System CnayatanacoNo ratings yet
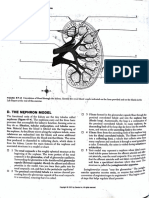
- D. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresDocument6 pagesD. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresCatherine BelonioNo ratings yet
- Assessing Ankylosed Deciduous MolarsDocument5 pagesAssessing Ankylosed Deciduous MolarsDeasy FaraditaNo ratings yet
- Modern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionsDocument11 pagesModern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionscdoskarNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeFrom EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (16)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)