Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LPI Exam 101
Uploaded by
Caslav ProkopijevicOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LPI Exam 101
Uploaded by
Caslav ProkopijevicCopyright:
Available Formats
Exam 101: Detailed Objectives
This is a required exam for LPIC-1 or LPI certification Level 1. It covers basic skills for the Linux professional that are common to major distributions of Linux.. IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These are the current 101 objectives, which are valid effective 2009-0401. Each objective is assigned a weighting value. The weights range roughly from 1 to 10 and indicate the relative importance of each objective. Objectives with higher weights will be covered in the exam with more questions.
Objectives: Exam 101
Topic 101: System Architecture 101.1 Determine and configure hardware settings Description Candidates should be able to determine and configure fundamental system hardware.
Key Knowledge Areas
Enable and disable integrated peripherals. Configure systems with or without external peripherals such as keyboards. Differentiate between the various types of mass storage devices. Set the correct hardware ID for different devices, especially the boot device. Know the differences between coldplug and hotplug devices. Determine hardware resources for devices. Tools and utilities to list various hardware information (e.g. lsusb, lspci, etc.) Tools and utilities to manipulate USB devices Conceptual understanding of sysfs, udev, hald, dbus
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/sys /proc /dev modprobe lsmod lspci lsusb
101.2 Boot the system Description Candidates should be able to guide the system through the booting process.
Key Knowledge Areas
Provide common commands to the boot loader and options to the kernel at boot time. Demonstrate knowledge of the boot sequence from BIOS to boot completion. Check boot events in the log files.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/var/log/messages dmesg BIOS bootloader kernel init
101.3 Change runlevels and shutdown or reboot system Description Candidates should be able to manage the runlevel of the system. This objective includes changing to single user mode, shutdown or rebooting the system. Candidates should be able to alert users before switching runlevel and properly terminate processes. This objective also includes setting the default runlevel.
Key Knowledge Areas
Set the default runlevel. Change between run levels including single user mode. Shutdown and reboot from the command line. Alert users before switching runlevels or other major system event. Properly terminate processes.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/etc/inittab shutdown init /etc/init.d telinit
Topic 102: Linux Installation and Package Management 102.1 Design hard disk layout Description Candidates should be able to design a disk partitioning scheme for a Linux system.
Key Knowledge Areas
Allocate filesystems and swap space to separate partitions or disks. Tailor the design to the intended use of the system. Ensure the /boot partition conforms to the hardware architecture requirements for booting.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/ (root) filesystem /var filesystem /home filesystem swap space mount points partitions
102.2 Install a boot manager Description Candidates should be able to select, install and configure a boot manager.
Key Knowledge Areas
Providing alternative boot locations and backup boot options. Install and configure a boot loader such as GRUB. Interact with the boot loader.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/boot/grub/menu.lst grub-install MBR superblock /etc/lilo.conf lilo
102.3 Manage shared libraries Description Candidates should be able to determine the shared libraries that executable programs depend on and install them when necessary.
Key Knowledge Areas
Identify shared libraries. Identify the typical locations of system libraries. Load shared libraries.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
ldd ldconfig /etc/ld.so.conf LD_LIBRARY_PATH
102.4 Use Debian package management Description Candidates should be able to perform package management using the Debian package tools.
Key Knowledge Areas
Install, upgrade and uninstall Debian binary packages. Find packages containing specific files or libraries which may or may not be installed. Obtain package information like version, content, dependencies, package integrity and installation status (whether or not the package is installed).
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/etc/apt/sources.list dpkg dpkg-reconfigure apt-get apt-cache aptitude
102.5 Use RPM and YUM package management Description Candidates should be able to perform package management using RPM and YUM tools.
Key Knowledge Areas
Install, re-install, upgrade and remove packages using RPM and YUM. Obtain information on RPM packages such as version, status, dependencies, integrity and signatures. Determine what files a package provides, as well as find which package a specific file comes from.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
rpm rpm2cpio /etc/yum.conf /etc/yum.repos.d/ yum yumdownloader
Topic 103: GNU and Unix Commands 103.1 Work on the command line Description Candidates should be able to interact with shells and commands using the command line. The objective assumes the bash shell.
Key Knowledge Areas
Use single shell commands and one line command sequences to perform basic tasks on the command line. Use and modify the shell environment including defining, referencing and exporting environment variables. Use and edit command history. Invoke commands inside and outside the defined path.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
. bash echo env exec export pwd set unset man uname history
103.2 Process text streams using filters Description Candidates should should be able to apply filters to text streams.
Key Knowledge Areas
Send text files and output streams through text utility filters to modify the output using standard UNIX commands found in the GNU textutils package.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
cat cut expand fmt head od join nl paste pr sed sort split tail tr unexpand uniq wc
103.3 Perform basic file management Description Candidates should be able to use the basic Linux commands to manage files and directories.
Key Knowledge Areas
Copy, move and remove files and directories individually. Copy multiple files and directories recursively. Remove files and directories recursively. Use simple and advanced wildcard specifications in commands. Using find to locate and act on files based on type, size, or time. Usage of tar, cpio and dd.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
cp find mkdir mv ls rm rmdir touch tar cpio dd file gzip gunzip bzip2 file globbing
103.4 Use streams, pipes and redirects Description Candidates should be able to redirect streams and connect them in order to efficiently process textual data. Tasks include redirecting standard input, standard output and standard error, piping the output of one command to the input of another command, using the output of one command as arguments to another command and sending output to both stdout and a file.
Key Knowledge Areas
Redirecting standard input, standard output and standard error. Pipe the output of one command to the input of another command. Use the output of one command as arguments to another command. Send output to both stdout and a file.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
tee xargs
103.5 Create, monitor and kill processes Description Candidates should be able to perform basic process management.
Key Knowledge Areas
Run jobs in the foreground and background. Signal a program to continue running after logout. Monitor active processes. Select and sort processes for display. Send signals to processes.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
& bg fg jobs kill nohup ps top free uptime killall
103.6 Modify process execution priorities Description Candidates should should be able to manage process execution priorities.
Key Knowledge Areas
Know the default priority of a job that is created. Run a program with higher or lower priority than the default.. Change the priority of a running process.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
nice ps renice top
103.7 Search text files using regular expressions Description Candidates should be able to manipulate files and text data using regular expressions. This objective includes creating simple regular expressions containing several notational elements. It also includes using regular expression tools to perform searches through a filesystem or file content.
Key Knowledge Areas
Create simple regular expressions containing several notational elements. Use regular expression tools to perform searches through a filesystem or file content.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
grep egrep fgrep sed regex(7)
103.8 Perform basic file editing operations using vi Description Candidates should be able to edit text files using vi. This objective includes vi navigation, basic vi modes, inserting, editing, deleting, copying and finding text.
Key Knowledge Areas
Navigate a document using vi. Use basic vi modes. Insert, edit, delete, copy and find text.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
vi /, ? h,j,k,l i, o, a c, d, p, y, dd, yy ZZ, :w!, :q!, :e!
Topic 104: Devices, Linux Filesystems, Filesystem Hierarchy Standard 104.1 Create partitions and filesystems Description Candidates should be able to configure disk partitions and then create filesystems on media such as hard disks. This includes the handling of swap partitions.
Key Knowledge Areas
Use various mkfs commands to set up partitions and create various filesystems such as: o ext2 o ext3 o xfs o reiserfs v3 o vfat
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
fdisk mkfs mkswap
104.2 Maintain the integrity of filesystems Description Candidates should be able to maintain a standard filesystem, as well as the extra data associated with a journaling filesystem.
Key Knowledge Areas
Verify the integrity of filesystems. Monitor free space and inodes. Repair simple filesystem problems.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
du df fsck e2fsck mke2fs debugfs dumpe2fs tune2fs xfs tools (such as xfs_metadump and xfs_info)
104.3 Control mounting and unmounting of filesystems Description Candidates should be able to configure the mounting of a filesystem.
Key Knowledge Areas
Manually mount and unmount filesystems. Configure filesystem mounting on bootup. Configure user mountable removeable filesystems.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
/etc/fstab /media mount umount
104.4 Manage disk quotas Description Candidates should be able to manage disk quotas for users.
Key Knowledge Areas
Set up a disk quota for a filesystem. Edit, check and generate user quota reports.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
quota edquota repquota quotaon
104.5 Manage file permissions and ownership Description Candidates should be able to control file access through the proper use of permissions and ownerships.
Key Knowledge Areas
Manage access permissions on regular and special files as well as directories. Use access modes such as suid, sgid and the sticky bit to maintain security. Know how to change the file creation mask. Use the group field to grant file access to group members.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
chmod umask chown chgrp
104.6 Create and change hard and symbolic links Description Candidates should be able to create and manage hard and symbolic links to a file.
Key Knowledge Areas
Create links. Identify hard and/or softlinks. Copying versus linking files. Use links to support system administration tasks.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
ln
104.7 Find system files and place files in the correct location Description Candidates should be thouroughly familiar with the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS), including typical file locations and directory classifications.
Key Knowledge Areas
Understand the correct locations of files under the FHS. Find files and commands on a Linux system. Know the location and propose of impotant file and directories as defind in the FHS.
The following is a partial list of the used files, terms and utilities:
find locate updatedb whereis which type /etc/updatedb.conf
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Internet Adresiranje IPv4Document39 pagesInternet Adresiranje IPv4Caslav ProkopijevicNo ratings yet
- Analiza Kosinusne SlicnostiDocument4 pagesAnaliza Kosinusne SlicnostiCaslav ProkopijevicNo ratings yet
- Juniper CareersDocument2 pagesJuniper CareersCaslav ProkopijevicNo ratings yet
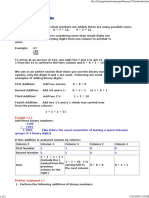
- 05.binarna AritmetikaDocument2 pages05.binarna AritmetikaCaslav ProkopijevicNo ratings yet
- Programiranje TurboPascalDocument210 pagesProgramiranje TurboPascalMilos Cune StojanovicNo ratings yet
- Word For BeginnersDocument23 pagesWord For BeginnersCaslav ProkopijevicNo ratings yet
- TelekomDocument14 pagesTelekom12345678987654321aNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CSC Project Report FinalDocument12 pagesCSC Project Report FinalHarsha KyleNo ratings yet
- MC 0067Document60 pagesMC 0067クマー ヴィーンNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: How To Install, Setup and Use SmartrootDocument13 pagesQuick Start Guide: How To Install, Setup and Use SmartrootManuellaNo ratings yet
- Gltools CrashlogDocument51 pagesGltools CrashlogAlan Douglas CordeiroNo ratings yet
- (ETL) Processes in Data Warehouse Environments (PDFDrive)Document202 pages(ETL) Processes in Data Warehouse Environments (PDFDrive)thanhdinhNo ratings yet
- CST Diag R12Document36 pagesCST Diag R12Arc Angel MNo ratings yet
- Virtual Private DatabasesDocument7 pagesVirtual Private DatabasesJawad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Distributed DatabasesDocument17 pagesDistributed DatabasesEhsanullah LodinNo ratings yet
- Full LDM TemplateDocument32 pagesFull LDM TemplateMarìa Puga CastroNo ratings yet
- Performance Point Services 2010Document16 pagesPerformance Point Services 2010reddysureshNo ratings yet
- CENG 351 Introduction To Data Management and File StructuresDocument29 pagesCENG 351 Introduction To Data Management and File StructuresMustafa GiNo ratings yet
- AD - Delegate Permissions To Add - Delete - Move - Modify Computer Objects - I Just Do ITDocument4 pagesAD - Delegate Permissions To Add - Delete - Move - Modify Computer Objects - I Just Do ITTESTNo ratings yet
- Components of DBMSDocument13 pagesComponents of DBMSsenthilNo ratings yet
- Displaying Data in Chart in VBDocument6 pagesDisplaying Data in Chart in VBMara TanamalNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions 123 PDFDocument94 pagesInterview Questions 123 PDFARJUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Fusion Middleware: Installing and Configuring Oracle Goldengate For Db2 LuwDocument54 pagesOracle® Fusion Middleware: Installing and Configuring Oracle Goldengate For Db2 Luwpush5No ratings yet
- Forcepoint DLP Admin GuideDocument494 pagesForcepoint DLP Admin GuideramankinNo ratings yet
- Joins in RDBMSDocument24 pagesJoins in RDBMSAnbusaba ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Excel: What'S So Great About Pivottable Reports?Document26 pagesExcel: What'S So Great About Pivottable Reports?Zudha HerlambangNo ratings yet
- TIB - Js Jrs Ce - 8.1.0 - Platform Support Community EditionDocument11 pagesTIB - Js Jrs Ce - 8.1.0 - Platform Support Community EditionRafael OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CIS552 Indexing and Hashing 1Document56 pagesCIS552 Indexing and Hashing 1Vinay VarmaNo ratings yet
- Veritas Netbackup Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesVeritas Netbackup Interview Questionsark308100% (1)
- AssignmentsDocument11 pagesAssignmentsRaghul RaviNo ratings yet
- DATASTAGE TS012708292 - Historic Job in Running State - IBM SupportDocument5 pagesDATASTAGE TS012708292 - Historic Job in Running State - IBM SupportLuis YoshihiraNo ratings yet
- DB BKPDocument14 pagesDB BKPM1No ratings yet
- Cm-Help enDocument140 pagesCm-Help enJithanth VainatheyaNo ratings yet
- Networking Concepts - Key Concepts of Domain Name System (DNS)Document14 pagesNetworking Concepts - Key Concepts of Domain Name System (DNS)api-378091350% (2)
- IS 4420 Database Fundamentals Introduction To SQL Leon ChenDocument42 pagesIS 4420 Database Fundamentals Introduction To SQL Leon Chennew_rajaNo ratings yet
- MerakiDuoGliph ReportDocument9 pagesMerakiDuoGliph ReportDaniel SilveiraNo ratings yet
- 04 02 2023 Hibernate Class NotesDocument5 pages04 02 2023 Hibernate Class NotesHarshith reddy BandamNo ratings yet