Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tree measurements, bird reproduction, species distributions
Uploaded by
mohammedhusseinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tree measurements, bird reproduction, species distributions
Uploaded by
mohammedhusseinCopyright:
Available Formats
Part one: Tree measurements
Tree measurements: 75 - 36.5 36 - 32.7 34 32 31 79 229 -69 91 80 127 54 -89 377 -219 216
316 Mean: 117.01 Variance: 1.0211 x 10^4 Range: 346 Median: 79 There were 27 herbaceous plants in the quadrat, and variance > mean, this population exerts clumped distribution.
Part two: Bird Reproduction vs. Rainfall
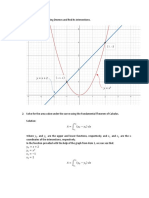
Graph one: X Y 5 1.5 10 2.5 15 1.8 50 1.2 180 0.7 275 0.5
Graph one shows a both a positive and negative correlation between bird reproduction and rainfall. Between rainfall= 5 and 10, bird reproduction increases from 1.5 to 2.5 showing a positive correlation. However, after rainfalls increase and keep increasing, bird reproduction decreases significantly with each increase indicating a negative correlation between rainfall and bird reproduction.
Graph two:
X y
28 4
33 14
35 9
43 17
44 25
44 40
49 44
56 46
57 47
This graph shows us a positive correlation between both rainfall and bird reproduction. Bird reproduction increases as rainfall increases with only a negligible drop when rainfall is between 33 and 35. This drop could be a source of error in measuring reproduction and not actually represent a negative correlation between rainfall and bird reproduction.
Part three:
Species A: 10 - 2 - 8 1 2 5 9 4 5 - 16 - 8 Species B: 5 - 6 - 6 - 5 - 5 - 5 -5 - 6 - 4 5 - 5 Species C: 20 - 1 - 2 - 1 - 15 - 3 - 1 - 1 - 10 - 2- 2
Species Mean Variance A 6.363636 17.68595 B 5.181818 0.330579 C 5.272727 40.380165 In species A, variance is significantly > mean, therefore species A exerts a clumped distribution. In species B, variance is significantly < mean, therefore species B exerts regular or even distribution. In species C, variance is significantly > mean, therefore species C exerts a clumped distribution.
Conclusion: We have seen that there are various ways to determine the distribution pattern of species. The Variance/Mean ratio method focuses mainly on determining whether a species fits a randomly spaced distribution, but can also be used as evidence for either an even or clumped distribution. To utilize the Variance/Mean ratio method, data is collected from several random samples of a given population. The number of individuals present in each sample is compared to the expected counts in the case of random distribution. If the variance/mean ratio is equal to 1, the population is found to be randomly distributed. If it is significantly greater than 1, the population is found to be clumped distribution. Finally, if the ratio is significantly less than 1, the population is found to be evenly distributed. We also learnt how to use other statistical calculations in ecology and each of those calculations helped us interpret different phenomena.
P.s: I would have loved to have attended this lab to give a greater content in the report. I drew the graphs but my phones camera is not taking good pictures to post them here and also I dont have a scanner, so I opted for making the graphs on the computer, and they turned out a lot more clear and elegant.
You might also like
- Introduction To Music Theory: Inversions of ChordsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Music Theory: Inversions of Chordsnaveenmanuel8879No ratings yet
- Modern Scoring BRASS Manual1Document25 pagesModern Scoring BRASS Manual1Pepe ChorrasNo ratings yet
- Well CompletionDocument26 pagesWell Completionnitesh kumarNo ratings yet
- FETs DatabookDocument189 pagesFETs DatabookTito Titon0% (1)
- Determining Sample Size: Glenn D. IsraelDocument5 pagesDetermining Sample Size: Glenn D. IsraelHandhi Montok SetiawanNo ratings yet
- ACL Injuries in The Female Athlete: Causes, Impacts, and Conditioning Programs Frank R. Noyes Sue Barber-WestinDocument658 pagesACL Injuries in The Female Athlete: Causes, Impacts, and Conditioning Programs Frank R. Noyes Sue Barber-WestinluizamgoNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument364 pagesNeurophysiologyTaimoor Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- MCQs in Developmental BiologyDocument6 pagesMCQs in Developmental BiologySundaralingam Raj62% (13)
- First Quarter - Curriculum Map - Science 8Document7 pagesFirst Quarter - Curriculum Map - Science 8Mich Hora100% (7)
- 9th-Implementing Lockout Function With IEC61850 PDFDocument11 pages9th-Implementing Lockout Function With IEC61850 PDFBharath SaiNo ratings yet
- Jennings 1978Document9 pagesJennings 1978Jacob Luttrell100% (1)
- Stat 101 Sample Final ExamDocument6 pagesStat 101 Sample Final ExamMirko Alessandro ClementeNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Nature of StatisticsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding The Nature of StatisticsDenisse Nicole SerutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Multiple Comparisons and Trends Among Treatment MeansDocument21 pagesChapter 9. Multiple Comparisons and Trends Among Treatment MeanskassuNo ratings yet
- What's The Relative Risk?Document0 pagesWhat's The Relative Risk?Tika Dwi TamaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.1: Chapter 1: Statistical Analysis - Fifteen Summary FactsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.1: Chapter 1: Statistical Analysis - Fifteen Summary Factswendy_intriagoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Classification & ConservationDocument33 pagesBiodiversity, Classification & ConservationNeeti SinghNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis of a Quantitative TraitDocument8 pagesStatistical Analysis of a Quantitative Traitmaithili joshiNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: This Assignment Is A Final Assessment Tool For The Department and Will Count Toward Your Final GradeDocument9 pagesInstructions:: This Assignment Is A Final Assessment Tool For The Department and Will Count Toward Your Final Gradebay nguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapt 4 AssociationDocument6 pagesChapt 4 AssociationUtomo BudidarmoNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representations of Data, Mean, Median and Standard DeviationDocument23 pagesGraphical Representations of Data, Mean, Median and Standard Deviationarpit000No ratings yet
- Quantitative GeneticsDocument34 pagesQuantitative GeneticsSouraj DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and Statistics 13th Edition: de Mendenhall, Beaver Et Beaver. STT1700 (Automne 2008)Document47 pagesIntroduction To Probability and Statistics 13th Edition: de Mendenhall, Beaver Et Beaver. STT1700 (Automne 2008)Francisco JavierNo ratings yet
- ANOVA1 Weight-UnweightDocument5 pagesANOVA1 Weight-UnweightERIC DE LUNANo ratings yet
- Calculating Biodiversity: Species Richness, Species DiversityDocument3 pagesCalculating Biodiversity: Species Richness, Species DiversityDeepak Singha100% (1)
- GENETICS Chapter 13-14 - Quatitative Genetics 1-2Document58 pagesGENETICS Chapter 13-14 - Quatitative Genetics 1-2Ca Thy HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Regression: Predicting The UnknownDocument5 pagesCorrelation and Regression: Predicting The Unknownzahoor80No ratings yet
- Term ProjectDocument6 pagesTerm Projectapi-258539141No ratings yet
- SRM Assignement: 1. T-TestDocument5 pagesSRM Assignement: 1. T-TestGurjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Ecology Prac-1Document9 pagesEcology Prac-1tariNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions I: Jozef HvoreckyDocument6 pagesProbability Distributions I: Jozef HvoreckyMichaelZambranaNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics inDocument75 pagesBiostatistics inSarwar BaigNo ratings yet
- Repeated MeasuresDocument22 pagesRepeated MeasuresGeorge MSenoirNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 2000Document111 pagesUnit 3 2000MansiNo ratings yet
- STATISTICAL METHODS FOR ASSESSING AGREEMENT BETWEEN CLINICAL MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUESDocument9 pagesSTATISTICAL METHODS FOR ASSESSING AGREEMENT BETWEEN CLINICAL MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUESribesnigrum82No ratings yet
- CHYS 3P15 Final Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesCHYS 3P15 Final Exam ReviewAmanda ScottNo ratings yet
- Øving BA 2Document12 pagesØving BA 2Erik CarlströmNo ratings yet
- Materi Chapter 6Document11 pagesMateri Chapter 6cindy khairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions and Statistical InferenceDocument14 pagesSampling Distributions and Statistical InferenceParth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Data OrganizationDocument30 pagesData OrganizationJasmin GogdaNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument3 pagesMidtermJohn D SubosaNo ratings yet
- SPSS Regression Spring 2010Document9 pagesSPSS Regression Spring 2010fuad_h05No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document24 pagesUnit 3swetamakka1026No ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods VocabularyDocument5 pagesQuantitative Methods VocabularyRuxandra MănicaNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics Chapter SummaryDocument9 pagesApplied Statistics Chapter SummaryRutger WentzelNo ratings yet
- A Statistical Analysis of Color Distribution in CandyDocument8 pagesA Statistical Analysis of Color Distribution in Candy91dextert100% (1)
- Lec Set 1 Data AnalysisDocument55 pagesLec Set 1 Data AnalysisSmarika KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Maths Folio BiqDocument21 pagesMaths Folio Biqapi-349814923No ratings yet
- ExamView - Chapter 3 ReviewDocument6 pagesExamView - Chapter 3 Reviewjfinster1987100% (2)
- Stratified SamplingDocument4 pagesStratified Samplingisabella343No ratings yet
- Calculate Inbreeding Coefficient Using Path Coefficient MethodDocument4 pagesCalculate Inbreeding Coefficient Using Path Coefficient MethodMorchoNo ratings yet
- ReMA Quantitative Foundations Homework 4 (40/40Document9 pagesReMA Quantitative Foundations Homework 4 (40/40Lily WuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Text PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 13 Text PDFJames FengNo ratings yet
- SRMDocument6 pagesSRMsidharthNo ratings yet
- Inference For Two Population Means: Case StudyDocument33 pagesInference For Two Population Means: Case StudyZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- PEFR measured with Wright peak flow metersDocument4 pagesPEFR measured with Wright peak flow metersEthan XuNo ratings yet
- Species Richness, 9-15-11, Intro To Lab For WebDocument27 pagesSpecies Richness, 9-15-11, Intro To Lab For Webone kilometerNo ratings yet
- Comparing Two Person-Time RatesDocument10 pagesComparing Two Person-Time RatesClaudio SacchettiniNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution & CLTDocument3 pagesNormal Distribution & CLTAasim Bin BakrNo ratings yet
- Meta-analysis effect size measureDocument6 pagesMeta-analysis effect size measureFernando TerryNo ratings yet
- Concentrationindex Handout PDFDocument6 pagesConcentrationindex Handout PDFAremy TestarossaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Non Sampling ErrorsDocument296 pagesSampling and Non Sampling ErrorsNaman LadhaNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Introduction To Statistics: Eneral TerminologyDocument15 pagesAppendix B: Introduction To Statistics: Eneral TerminologyXingjian LiuNo ratings yet
- Mating. Iv.: Bureau D. CDocument5 pagesMating. Iv.: Bureau D. CHugo SobreiraNo ratings yet
- APS U10 10.1 Two Proportions Practice KEYDocument3 pagesAPS U10 10.1 Two Proportions Practice KEYM KNo ratings yet
- 4.1analysis of Varianc Eand CovarianceDocument41 pages4.1analysis of Varianc Eand CovarianceminalNo ratings yet
- Correlation Analysis-Students NotesMAR 2023Document24 pagesCorrelation Analysis-Students NotesMAR 2023halilmohamed830No ratings yet
- Exam2 04Document5 pagesExam2 04mohammedhusseinNo ratings yet
- Dev BankDocument1 pageDev BankmohammedhusseinNo ratings yet
- Dev Bank TableDocument1 pageDev Bank TablemohammedhusseinNo ratings yet
- God Names The TreesDocument2 pagesGod Names The TreesmohammedhusseinNo ratings yet
- Two-, Three-, and Four-Atom Exchange Effects in bcc3 HeDocument3 pagesTwo-, Three-, and Four-Atom Exchange Effects in bcc3 HezittoxNo ratings yet
- Vector Integration - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Integration - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook BlogNo ratings yet
- Discussion QuestionsDocument45 pagesDiscussion QuestionsSriRahayuNo ratings yet
- CH3 SolutionsDocument40 pagesCH3 SolutionsRonelNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Compressed Air Manual: 8 EditionDocument25 pagesAtlas Copco Compressed Air Manual: 8 EditionRajNo ratings yet
- Redirection & PipingDocument16 pagesRedirection & PipingPraveen PatelNo ratings yet
- Size Reduction LectureDocument28 pagesSize Reduction Lectureapsara karkiNo ratings yet
- Cargotec Side-Rolling Hatch Covers PDFDocument2 pagesCargotec Side-Rolling Hatch Covers PDFYin ThoNo ratings yet
- Area Under The CurveDocument3 pagesArea Under The CurveReyland DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Network Approach To Root Cause DiagnosisDocument17 pagesBayesian Network Approach To Root Cause DiagnosisDhinesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- IgE Level Effect of Phyllanthus Acidus Leaf ExtractDocument5 pagesIgE Level Effect of Phyllanthus Acidus Leaf Extractkhatami muhammadNo ratings yet
- GR/KWH, KG/HR or Tons/Month.: ScopeDocument5 pagesGR/KWH, KG/HR or Tons/Month.: ScopeThaigroup CementNo ratings yet
- Uniform ForceDocument11 pagesUniform ForcearnoldistunoNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.No ratings yet
- Explorer - Help RESCODocument18 pagesExplorer - Help RESCOTomás Oteros OrdóñezNo ratings yet
- Signal and Telecommunication - 1Document83 pagesSignal and Telecommunication - 1srinathNo ratings yet
- Vasu Chourasia Sde-01 ResumeDocument1 pageVasu Chourasia Sde-01 ResumeDhaval MailNo ratings yet
- Product Guide (English 140702)Document11 pagesProduct Guide (English 140702)Dineshkumar MahedranNo ratings yet
- The Use and Misuse of SEMDocument30 pagesThe Use and Misuse of SEMPPDTBM renNo ratings yet
- Indicate The Answer Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument10 pagesIndicate The Answer Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionHasan EserNo ratings yet
- Installation and Setup Guide For The Cisco Active Directory Agent, Release 1.0Document62 pagesInstallation and Setup Guide For The Cisco Active Directory Agent, Release 1.0Madelaine Velasquez Blacutt100% (1)