Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GTPS Curriculum Science Grade 6
Uploaded by
Bullet RubiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GTPS Curriculum Science Grade 6
Uploaded by
Bullet RubiaCopyright:
Available Formats
GTPS Curriculum Science - Grade 6
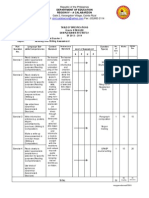
Suggest ed Blocks of Instruct ion
Grade 6 Science Objectives/CPIs/Standards
5.4.6.A.1 Generate and analyze evidence (through simulations) that the Suns apparent motion across the sky changes over the course of a year. 5.4.6.A.2 Construct and evaluate models demonstrating the rotation of Earth on its axis and the orbit of Earth around the Sun. 5.4.6.A.3 Predict what would happen to an orbiting object if gravity were increased, decreased, or taken away. 5.4.8.A.2 Use evidence of global variations in day length, temperature, and the amount of solar radiation striking Earths surface to create models that explain these phenomena and seasons. 5.4.6.A.4 Compare and contrast the major physical characteristics (including size and scale) of solar system objects using evidence in the form of data tables and photographs. 5.4.8.A.1 Analyze moon-phase, eclipse, and tidal data to construct models that explain how the relative positions and motions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon cause these three phenomena. 5.4.8.A.3 Predict how the gravitational force between two bodies would differ for bodies of different masses or bodies that are different distances apart. 5.4.8.A.4 Analyze data regarding the motion of comets, planets, and moons to find general patterns of orbital motion.
Topic: Astronomy Essential Questions/Enduring Understandings
Essential Questions What predictable, observable patterns occur as a result of the interaction between the Earth, Moon, and Sun? What causes these patterns? What predictable, observable patterns occur as a result of the interaction between the Earth, Moon, and Sun? What causes these patterns? Enduring Understandings Observable, predictable patterns of movement in the Sun, Earth, Moon system occur because of gravitational interaction and energy from the Sun Observable, predictable patterns of movement in the Sun, Earth, Moon system occur because of gravitational interaction and energy from the Sun.
Learning Activities Materials/Assessment
Learning Activities: Hands on explorations Inquirybased lessons Labs Reading Pearsons text Materials: Pearson Chapter 1: Earth, Moon, and Sun o Complete all Sections (1-4) Chapter 2: Exploring Space o Section 1 & 3/comp lab activity Chapter 3: The Solar System o Sections 2-5 Chapter 4: Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe o Section 5 Web Site Resources: United Streaming Videos o A Spin Around the Solar System video series Assessments: Formative Teacher observation Quizzes Projects Summative Labs Tests
29 days
GTPS Curriculum Science - Grade 6
Suggested Blocks of Instructio n
Grade 6 Science Objectives/CPIs/Standards
Topic: Inside Earth Essential Questions/Enduring Understandings
Essential Questions How do geologic events occurring today provide insight Earths past? How do changes in one part of an Earth system affect other parts of the system? To what extent does the exchange of energy within the Earth drive geologic events on the surface? What is the role of the sun in energy transfer in the atmosphere and in the oceans? To what extent does the exchange of energy within the Earth drive geologic events on the surface? Enduring Understandings Earths components form systems? These systems continually interact at different rates of time, affecting the shape of the Earths surface regionally and globally. How do changes in one part of an Earth system affect other parts of the system? Energy flow and movement of material from the Earths interior causes geologic events on the Earths surface. The energy from the sun is transferred throughout the oceans and atmosphere. Energy flow and movement of material from the Earths interior causes geologic events on the Earths surface.
Learning Activities Materials/Assessment
Learning Activities: Hands on explorations Inquirybased lessons Labs Reading Pearsons text Materials: Pearson Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics o Complete all Sections (1-5) Chapter 2: Earthquakes o Section 2,4 (earthquake safe building) Chapter 3: Volcanoes o Complete all sections Chapter 4: Minerals o Skip Chapter 5: Rocks o All Sections Media Resources: Video: Nova: The Day the Earth Shook Assessments: Formative Teacher observation Quizzes Projects Summative Labs Tests
32 days
5.4.6.B2 Examine Earths surface features and identify those created on a scale of human life or on a geologic time scale. 5.4.8.B.2 Evaluate the appropriateness of increasing the human population in a region (e.g., barrier islands, Pacific Northwest, Midwest United States) based on the regions history of catastrophic events, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and floods. 5.4.6.C.2 Distinguish physical properties of sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic rocks and explain how one kind of rock could eventually become a different kind of rock. 5.4.6.D.1 Apply understanding of the motion of lithospheric plates to explain why the Pacific Rim is referred to as the Ring of Fire. 5.4.8.D.2 Present evidence to support arguments for the theory of plate motion. 5.4.6.D.3 Apply knowledge of Earths magnetic fields to successfully complete an orienteering challenge. 5.4.6.E.1 Generate a conclusion about energy transfer and circulation by observing a model of convection currents. 5.4.8.D.1 Model the interactions between the layers of Earth.
GTPS Curriculum Science - Grade 6
Suggested Blocks of Instruction
Grade 6 Science
Topic: Human Biology and Health Learning Activities Materials/Assessment
Objectives/CPIs/Standards Essential Questions/Enduring Understandings
5.3.6.A.1 Model the interdependence of the human bodys major systems in regulating its internal environment. 5.3.6A2 Model and explain ways in which organelles work together to meet the cells needs. 5.3.8A1 All organisms are composed of cell(s). In multicellular organisms, specialized cells perform specialized functions. Tissues, organs, and organ systems are composed of cells and function to serve the needs of cells for food, air, and waste removal. 5.3.8.A.2 Relate the structures of cells, tissues, organs, and systems to their functions in supporting life. 5.3.8.B.1 Relate the energy and nutritional needs of organisms in a variety of life stages and situations, including stages of development and periods of maintenance. Essential Questions What do all living things have in common? How is matter transformed, and energy transferred/transformed in living systems? Enduring Understandings Systems of the human body are interrelated and regulate the bodys internal environment. Living organisms have a variety of observable features that enable them to obtain food and reproduce. All organisms transfer matter and convert energy from one form to another. Food is broken down to provide energy for the work that cells do, and is a source of the molecular building blocks from which needed materials are assembled.
91 days
Learning Activities: Hands on explorations Inquirybased lessons Labs Reading Pearsons text Materials: Pearson Human Biology & Health Chapter 1: Bones, Muscles, and Skin (1,2,3,4,5) Chapter 2: Food and Digestion (1-4) Chapter 3: Circulation (1,2,3,4) Chapter 4: Respiration and Excretion (1-3) Chapter 5: Fighting Disease (1-5) Chapter 6: The Nervous System (1-4) Chapter 7: The Endocrine & Reproduction Systems(2,3) Web Site Resources: Assessments: Formative Teacher observation Quizzes Projects Summative Labs Tests
You might also like
- HSC Physics The Cosmic EngineDocument35 pagesHSC Physics The Cosmic Engineninjaassassin103No ratings yet
- Solar System InquiryDocument4 pagesSolar System Inquiryapi-232002863No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan / Rancangan Pembelajaran (RP)Document10 pagesLesson Plan / Rancangan Pembelajaran (RP)Muhammad Amir Zaki Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Trees Forests Unit Plan - Szumlas KatrinaDocument12 pagesTrees Forests Unit Plan - Szumlas Katrinaapi-380333501No ratings yet
- Iroquois Confederacy Unit PlanDocument7 pagesIroquois Confederacy Unit Planapi-283598007No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Innocent Until Proven GuiltyDocument4 pagesLesson 3 - Innocent Until Proven Guiltyapi-265442361No ratings yet
- Ancient Athens Social StructureDocument3 pagesAncient Athens Social Structureapi-341952960No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Aerodynamics UnitDocument78 pagesGrade 6 Aerodynamics Unitsavikar aroraNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Social StudiesDocument2 pagesGrade 6 Social Studiesapi-241511669No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Science Long-Range PlanDocument6 pagesGrade 6 Science Long-Range PlanelizabethahansenNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan - Evidence InvestigationDocument5 pagesUnit Plan - Evidence Investigationapi-438996430No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Science Art LessonDocument3 pagesGrade 6 Science Art Lessonapi-533139236No ratings yet
- DDT BiomagnificationDocument2 pagesDDT BiomagnificationZe Rong Yin100% (1)
- Grade 6 Air and Aerodynamics March 27Document2 pagesGrade 6 Air and Aerodynamics March 27api-266874931No ratings yet
- Dec 1 LessonDocument2 pagesDec 1 Lessonapi-241511669No ratings yet
- EDPS 410 Midterm PrepDocument12 pagesEDPS 410 Midterm PrepAnthony KhaNo ratings yet
- Art Lesson Plan For WeeblyDocument3 pagesArt Lesson Plan For Weeblyapi-237240293No ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan - Building Arches DecDocument3 pagesScience Lesson Plan - Building Arches Decapi-534505202No ratings yet
- Unit Plan: Unit D: Structures and Forces Grade 7Document19 pagesUnit Plan: Unit D: Structures and Forces Grade 7api-275750758100% (1)
- UNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesUNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan Templateapi-383717086No ratings yet
- Population Introduction Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesPopulation Introduction Lesson Planapi-253204315No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Seasonal ChangeDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Seasonal Changeapi-298370521No ratings yet
- Local Government Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLocal Government Lesson Planapi-574265327No ratings yet
- Edso3200 MappingunitplanDocument8 pagesEdso3200 Mappingunitplanapi-252533855No ratings yet
- Lunar Phases Science Lesson TiersDocument2 pagesLunar Phases Science Lesson Tiershoneydew008No ratings yet
- Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesTest Questionsapi-405140973No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Curriculum ConnectionsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Curriculum Connectionsapi-311700306No ratings yet
- Siop LessonDocument3 pagesSiop Lessonapi-522660891No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1 (Seasons)Document3 pagesLesson Plan 1 (Seasons)api-283961148100% (1)
- Lesson 5 PbaDocument5 pagesLesson 5 Pbaapi-242493709No ratings yet
- Ancient Greece Unit Plan: Standard: Cognitive LevelDocument6 pagesAncient Greece Unit Plan: Standard: Cognitive Levelapi-266136729100% (1)
- Science - Nov 25Document2 pagesScience - Nov 25api-267007426No ratings yet
- Drawing Unit Plan Grade 7Document28 pagesDrawing Unit Plan Grade 7api-265991000100% (2)
- 3rd Grade ScienceDocument4 pages3rd Grade Scienceapi-304589758No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide: Unit/Chapter Objective/Generalization/Big IdeaDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Guide: Unit/Chapter Objective/Generalization/Big Ideaapi-333209073No ratings yet
- Moon Surface Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMoon Surface Lesson Planapi-382263458No ratings yet
- Unit Plan 1 Earth ScienceDocument9 pagesUnit Plan 1 Earth SciencejessaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 PbaDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Pbaapi-242493709100% (1)
- Understanding Physics ConceptsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Physics Conceptsjacylin_a_663291230No ratings yet
- Inquiry MapsDocument4 pagesInquiry Mapsapi-397334707No ratings yet
- Daftar Buku GeofisikaDocument26 pagesDaftar Buku GeofisikaMasri Razak0% (1)
- Wetland Final Project - Lesson Plan Grade 5 ScienceDocument16 pagesWetland Final Project - Lesson Plan Grade 5 Scienceapi-310182964No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Interactions and EcosystemsDocument10 pagesUnit Plan Interactions and Ecosystemsapi-377430670No ratings yet
- GP1 - Q1 - Module 7Document32 pagesGP1 - Q1 - Module 7Juren TabunoNo ratings yet
- NewlessonplanDocument3 pagesNewlessonplanapi-316500203No ratings yet
- Boats and Buoyancy Mini Unit PlanDocument12 pagesBoats and Buoyancy Mini Unit Planapi-280000855100% (3)
- Lesson Plan #6: Unit Inquiry Question: Lesson Guiding QuestionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan #6: Unit Inquiry Question: Lesson Guiding Questionsapi-354444855No ratings yet
- Ubd Fractions PlanDocument9 pagesUbd Fractions Planapi-437407548100% (1)
- 3rd Grade Unit 2 Light and Sound - Color and Heat Absorption Teacher VersionDocument3 pages3rd Grade Unit 2 Light and Sound - Color and Heat Absorption Teacher VersionRoberth Alegre SeguilNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument5 pagesDesignapi-418711725100% (1)
- Weather UnitDocument22 pagesWeather Unitapi-357354808No ratings yet
- Light and Shadows Unit EdDocument20 pagesLight and Shadows Unit Edapi-490788696100% (1)
- Grade 6 Flight LessonDocument7 pagesGrade 6 Flight Lessonapi-451306299No ratings yet
- Ed3601 - Grade 6 Trees Forests Unit Plan UpdatedDocument24 pagesEd3601 - Grade 6 Trees Forests Unit Plan Updatedapi-227912716100% (1)
- Lesson Plans - World Geography UnitDocument28 pagesLesson Plans - World Geography Unitapi-367833271No ratings yet
- Egg Drop Lab: Understanding Force and GravityDocument1 pageEgg Drop Lab: Understanding Force and GravityhyperstalkerNo ratings yet
- Learning As ProfessionalDocument14 pagesLearning As Professionalsudhanshujain1993No ratings yet
- Lunar Phase UbdDocument3 pagesLunar Phase Ubdapi-279510418No ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: 6th Grade ScienceDocument2 pagesCourse Syllabus: 6th Grade ScienceJeambern Borja PondalesNo ratings yet
- Practice Test in MSEP 6Document1 pagePractice Test in MSEP 6melanie moradoNo ratings yet
- I4U58V 29oct2013Document6 pagesI4U58V 29oct2013Bullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- The EcosystemDocument10 pagesThe EcosystemBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science I - Teachers' GuideDocument432 pagesIntegrated Science I - Teachers' GuideMLSBU11100% (5)
- ANA 2012 GRADE 3 MATHS EXEMPLARDocument27 pagesANA 2012 GRADE 3 MATHS EXEMPLARBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- G 6 Scintbk 2Document275 pagesG 6 Scintbk 2Bullet Rubia100% (1)
- English GR 8-ToS Reading, Writing, Speaking, Viewing & ListeningDocument4 pagesEnglish GR 8-ToS Reading, Writing, Speaking, Viewing & ListeningBullet Rubia93% (27)
- Summative Test in Science 6circulatoryDocument3 pagesSummative Test in Science 6circulatoryBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Grade6SSspecificationsfinalrev 10 21 13Document50 pagesGrade6SSspecificationsfinalrev 10 21 13Bullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Cur Math Comcore Day3 Presentation Making It Your OwnDocument21 pagesCur Math Comcore Day3 Presentation Making It Your OwnBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Test Construction The Power of ADocument7 pagesClassroom Test Construction The Power of Ajasmina2869No ratings yet
- G 6 Scintbk 2Document275 pagesG 6 Scintbk 2Bullet Rubia100% (1)
- Math Content SpecificationsDocument120 pagesMath Content SpecificationsBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Grade6SSspecificationsfinalrev 10 21 13Document50 pagesGrade6SSspecificationsfinalrev 10 21 13Bullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- English GR 8-ToS Reading, Writing, Speaking, Viewing & ListeningDocument4 pagesEnglish GR 8-ToS Reading, Writing, Speaking, Viewing & ListeningBullet Rubia93% (27)
- Cur Math Comcore Day3 Presentation Making It Your OwnDocument21 pagesCur Math Comcore Day3 Presentation Making It Your OwnBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Summative Science 6Document3 pagesSummative Science 6Bullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- G 6 Scintbk 2Document275 pagesG 6 Scintbk 2Bullet Rubia100% (1)
- SMK Science Form 4 Mid Year Examination Objective QuestionsDocument7 pagesSMK Science Form 4 Mid Year Examination Objective QuestionsWindy WayneNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Science 6circulatoryDocument3 pagesSummative Test in Science 6circulatoryBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Test Construction The Power of ADocument7 pagesClassroom Test Construction The Power of Ajasmina2869No ratings yet
- Classroom Test Construction The Power of ADocument7 pagesClassroom Test Construction The Power of Ajasmina2869No ratings yet
- Grade6-PhysicalScience 000Document5 pagesGrade6-PhysicalScience 000Bullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Exam W Table of SpecificationDocument4 pagesScience 6 Exam W Table of SpecificationBullet Rubia67% (3)
- Science Explorer Guided Reading Workbook Gr6Document209 pagesScience Explorer Guided Reading Workbook Gr6Bullet Rubia75% (8)
- First Periodic Test Science ViDocument2 pagesFirst Periodic Test Science ViNick Bantolo67% (9)
- Science Workbook 1st GradingDocument52 pagesScience Workbook 1st GradingBullet RubiaNo ratings yet
- DepEd-Form-137-E BlanklDocument2 pagesDepEd-Form-137-E BlanklRonnie Gado87% (101)
- Science Explorer Guided Reading Workbook Gr6Document209 pagesScience Explorer Guided Reading Workbook Gr6Bullet Rubia75% (8)
- Annex-A (PMD Report)Document1 pageAnnex-A (PMD Report)zain iqbalNo ratings yet
- O ADocument581 pagesO ACristianCamiloNo ratings yet
- Future Scope of Dual Axis Solar Tracking SystemDocument1 pageFuture Scope of Dual Axis Solar Tracking SystemArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Setting Goals For SuccessDocument89 pagesSetting Goals For SuccessMichole chin MallariNo ratings yet
- Offering Help-Ppt Bahasa Inggris Kelompok 4Document14 pagesOffering Help-Ppt Bahasa Inggris Kelompok 4Nada NisrinaNo ratings yet
- 11.guide Mineduc 2BGUDocument2 pages11.guide Mineduc 2BGULuis CobaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Quarter 4 - Module 5 Solar EclipseDocument6 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 4 - Module 5 Solar Eclipsevincent baltazarNo ratings yet
- Parallel Universes PDFDocument17 pagesParallel Universes PDFالعشابالعصريNo ratings yet
- Released 2010 Achievement Test Science9Document36 pagesReleased 2010 Achievement Test Science9yukiNo ratings yet
- Tap Water As A Hydraulic Pressure Medium (2001)Document223 pagesTap Water As A Hydraulic Pressure Medium (2001)Florian_AngererNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Grade 11 Week 1 2Document26 pagesEarth and Life Science Grade 11 Week 1 2Kirk TyroneNo ratings yet
- International Olympiad in Astronomy and AstrophysicsDocument254 pagesInternational Olympiad in Astronomy and Astrophysicsธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- Science ExperimentDocument2 pagesScience Experimentapi-302323439No ratings yet
- My Favorite PlanetDocument4 pagesMy Favorite PlanetmaryebennettNo ratings yet
- Day 1 (Questions)Document21 pagesDay 1 (Questions)Pocholo BustosNo ratings yet
- Reading Report 5 - Observing Learning and TeachingDocument54 pagesReading Report 5 - Observing Learning and TeachingNINDI ASSABILA TAWROFIENo ratings yet
- Core - Week 1 - Gr11 - Earth ScienceDocument20 pagesCore - Week 1 - Gr11 - Earth ScienceSeputeraNo ratings yet
- Reforestation Project Proposal - by SlidesgoDocument50 pagesReforestation Project Proposal - by SlidesgoBPDASHL WAMPU SEI ULARNo ratings yet
- AlveolektomiDocument98 pagesAlveolektomiazkaziyan14No ratings yet
- UNIT 7 The UniverseDocument24 pagesUNIT 7 The UniverseCggNo ratings yet
- INFLUENCE OF SOLAR ENERGY by Peter DeunovDocument3 pagesINFLUENCE OF SOLAR ENERGY by Peter DeunovJahel RatkaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ TIẾNG ANH - ÔN TUYỂN SINH 10 SỐ 10Document5 pagesĐỀ TIẾNG ANH - ÔN TUYỂN SINH 10 SỐ 10Minh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Key Answer: Irst Ourse NdalucíaDocument44 pagesKey Answer: Irst Ourse NdalucíaCecilia VENo ratings yet
- The Venus Cycle, Morning StarDocument6 pagesThe Venus Cycle, Morning StarInanna Ninani100% (1)
- Take The Plunge: by Gloria EmersonDocument21 pagesTake The Plunge: by Gloria Emersonayesha ambreen100% (1)
- Solar Tracking System: Abstract-The Solar Photovoltaic Panels Are Used To GenerateDocument4 pagesSolar Tracking System: Abstract-The Solar Photovoltaic Panels Are Used To GenerateAdrian Ebero NunezNo ratings yet
- A Hanslmeier Habitability and Cosmic CatastrophesDocument258 pagesA Hanslmeier Habitability and Cosmic CatastrophesНиколија Цуцкић100% (1)
- Latihan Soal Bedah Kisi UsbnDocument11 pagesLatihan Soal Bedah Kisi UsbnFAJARNo ratings yet
- Solar Balance-Of-System - To Track or Not To Track, Part IDocument4 pagesSolar Balance-Of-System - To Track or Not To Track, Part IJose MustafhaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Checkpoint Science P2 Specimen 2012Document16 pagesCambridge Checkpoint Science P2 Specimen 2012Nafiur Rahman83% (12)
- The Accelerating Universe: Infinite Expansion, the Cosmological Constant, and the Beauty of the CosmosFrom EverandThe Accelerating Universe: Infinite Expansion, the Cosmological Constant, and the Beauty of the CosmosRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Universal One: An exact science of the One visible and invisible universe of Mind and the registration of all idea of thinking Mind in light, which is matter and also energyFrom EverandThe Universal One: An exact science of the One visible and invisible universe of Mind and the registration of all idea of thinking Mind in light, which is matter and also energyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Across the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsFrom EverandAcross the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsNo ratings yet
- Beginning and the End of Everything: From the Big Bang to the End of the UniverseFrom EverandBeginning and the End of Everything: From the Big Bang to the End of the UniverseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (61)
- Believing Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithFrom EverandBelieving Is Seeing: A Physicist Explains How Science Shattered His Atheism and Revealed the Necessity of FaithRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (32)
- When the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyFrom EverandWhen the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (7)
- You Are Here: A Portable History of the UniverseFrom EverandYou Are Here: A Portable History of the UniverseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1104)
- The Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodFrom EverandThe Creator and the Cosmos: How the Latest Scientific Discoveries Reveal GodRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Extraterrestrial Species Almanac: The Ultimate Guide to Greys, Reptilians, Hybrids, and NordicsFrom EverandThe Extraterrestrial Species Almanac: The Ultimate Guide to Greys, Reptilians, Hybrids, and NordicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- The Varieties of Scientific Experience: A Personal View of the Search for GodFrom EverandThe Varieties of Scientific Experience: A Personal View of the Search for GodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (272)
- The Book of the Moon: A Guide to Our Closest NeighborFrom EverandThe Book of the Moon: A Guide to Our Closest NeighborRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- Under Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseFrom EverandUnder Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Mercury in Retrograde: And Other Ways the Stars Can Teach You to Live Your Truth, Find Your Power, and Hear the Call of the UniverseFrom EverandMercury in Retrograde: And Other Ways the Stars Can Teach You to Live Your Truth, Find Your Power, and Hear the Call of the UniverseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- American Eclipse: A Nation's Epic Race to Catch the Shadow of the Moon and Win the Glory of the WorldFrom EverandAmerican Eclipse: A Nation's Epic Race to Catch the Shadow of the Moon and Win the Glory of the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (63)
- The Zodiac by Degrees: Second Edition, Extensively RevisedFrom EverandThe Zodiac by Degrees: Second Edition, Extensively RevisedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)