Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology ARDS
Uploaded by
Roderick Agbuya100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pageFor research about the disease ARDS
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFor research about the disease ARDS
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pagePathophysiology ARDS
Uploaded by
Roderick AgbuyaFor research about the disease ARDS
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
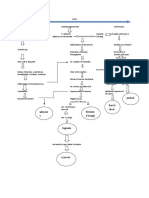
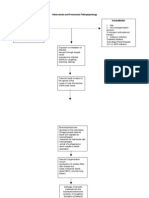
Pathophysiology of ARDS
Predisposing factors:
Aspiration of gastric contents Sepsis Burns Trauma Inhalation of toxic chemicals Type II pneumocyte damage
Clinical lung injury
Alveolar epithelial damage
Endothelial damage
Initiation of inflamm atoryimmune response
Comple ment (C5a) activati on
Increase capilliary membrane permiability Platelet aggregat ion Extravasation of fluid
Bacteri al endoto xin
Decrease surfactant production
Release of neutrophil chemotactic factors
Macroph age mobilizati on
Neutrophil aggregation & release of mediators: Alveolar collapse Oxygen radicals, proteolytic enzymes, Arachidonic acid metabolites, PAF
Release of cytokines
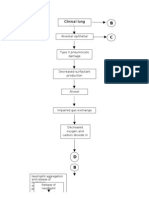
Dyspnea & tachypne a
Atelectasis & impaired lung compliance Alveolocapillary membrane permeability Right to left shunt, hyaline membrane formation, finally fibrosis
vasocons triction
Decrease flow Alveolar capilliary leak Impaired gas exchange
Acute respiratory failure
Exudation of fluid, protein, RBCs into interstitium
hypoxe mia Pulmonary edema & hemorrhage w/ severe impairment of alveolar ventilation
You might also like
- Contributing factors and risk of developing bacterial pneumoniaDocument2 pagesContributing factors and risk of developing bacterial pneumoniabilliam123No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Copd-ChfDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Copd-ChfZaira Batalo100% (2)
- ARDS With PathophysiologyDocument79 pagesARDS With Pathophysiologymabec pagaduan95% (19)
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument8 pagesCerebrovascular Accidentplethoraldork100% (10)
- Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPleural EffusionRafahiah HaronNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure Due to Myocardial DysfunctionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Heart Failure Due to Myocardial DysfunctionabbeeyyNo ratings yet
- DCM - Heart Failure Due to Dilated CardiomyopathyDocument13 pagesDCM - Heart Failure Due to Dilated CardiomyopathyPrincysuzine PintoNo ratings yet
- COPD PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCOPD PathophysiologyJustin Ahorro-Dionisio33% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Septic Shock Draft 1Document1 pagePathophysiology of Septic Shock Draft 1Ju Lie AnnNo ratings yet
- CAP - Patho DiagramDocument5 pagesCAP - Patho DiagramAzai Rhea Malate63% (8)
- pg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDocument2 pagespg36-37 of Pneumothorax Case Studyikemas100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Failure Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia TrueDocument56 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia TrueDominica Fuentes100% (1)
- Copd Pathophysiology DiagramDocument2 pagesCopd Pathophysiology DiagramVHyneh Basher100% (1)
- Respiratory Function TestDocument7 pagesRespiratory Function TestMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- Pathophysiology and Management of COPDDocument6 pagesPathophysiology and Management of COPDNeil Andro Marcelo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Malignant Pleural Effusion Due to Breast Cancer MetastasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Malignant Pleural Effusion Due to Breast Cancer Metastasisfaula rocamora80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaFirenze Fil100% (21)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyJoann67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. Sallan100% (4)
- Emphysema Case Study E3Document28 pagesEmphysema Case Study E3scarletsky1975% (8)
- Covid - 19 Concept Map: by Sidney Piñero, Aubrey Perojon, & Shania ReyesDocument1 pageCovid - 19 Concept Map: by Sidney Piñero, Aubrey Perojon, & Shania ReyesJoi Owen Yap TevesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaIrene Demegillo SalongaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure PathoDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure PathoGlenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Patho (Lung Cancer)Document1 pagePatho (Lung Cancer)k.n.e.d.No ratings yet
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERDocument1 pageGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePneumonia PathophysiologyDee Sarajan100% (3)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Justine Mae Loria0% (1)
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Ards Cmap FinalDocument4 pagesArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Understanding Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJSDocument53 pagesUnderstanding Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJSKathrina CraveNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- Asthma PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAsthma PathophysiologyCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ARDSDocument2 pagesPathophysiology ARDSKim AmboyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurePaolo Luis MontenegroNo ratings yet
- ArdsDocument53 pagesArdsSophy Sony100% (3)
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocument3 pagesFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- ARDS Pathophysiology and EtiologyDocument3 pagesARDS Pathophysiology and EtiologyJorie Roco100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AtherosclerosisAzrul Hakim100% (2)
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of COPD - The BasicsDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of COPD - The BasicstiaranindyNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchiectasis PathophysiologyRayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraNo ratings yet
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesPathophysiologyElbert Hermogino ﭢNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument4 pagesLung CancerKrizia TepootNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument6 pagesMyocardial InfarctionMaicie Rose Bautista VallesterosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniamatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Acs Nstemi Vs Ua - PathoDocument2 pagesAcs Nstemi Vs Ua - PathoJerom YamatNo ratings yet
- Factors That Damage the Stomach LiningDocument8 pagesFactors That Damage the Stomach LiningTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureAnnie Grace PoliranNo ratings yet
- Acute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument15 pagesAcute Post-Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisJeanne Marie ValesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffieNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of ThrombophlebitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of ThrombophlebitisJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel YacasNo ratings yet
- Respi. DistressDocument2 pagesRespi. DistressDorothy Joy CumigadNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi PneumoniaDocument3 pagesPatofisiologi PneumoniainggridNo ratings yet
- ARDS Patho PortraitDocument3 pagesARDS Patho PortraitLouise RojoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Values Case PressDocument3 pagesLaboratory Values Case PressRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Fix Skyrim SKSE ErrorsDocument4 pagesFix Skyrim SKSE ErrorsRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- VanityDocument3 pagesVanityRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Renderer InfosdfDocument1 pageRenderer Infosdfagulfam5542No ratings yet
- VanityDocument3 pagesVanityRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- There Are No ModBuddy Extensions YetDocument1 pageThere Are No ModBuddy Extensions YetRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument10 pagesCare of Patient With Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument1 pageAssessmentRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Psych QuizDocument3 pagesPsych QuizRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Revised Disaster NursingDocument25 pagesRevised Disaster NursingLlana Pauline JacintoNo ratings yet
- Alloren Grace P (1) ThesisDocument20 pagesAlloren Grace P (1) ThesisRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Edited JeffDocument20 pagesChapter II Edited JeffRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory and Self-EfficacyDocument30 pagesBandura's Social Cognitive Theory and Self-EfficacyRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Case Format HahaDocument5 pagesCase Format HahaRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- EAB Breastfeeding Final VersionDocument73 pagesEAB Breastfeeding Final VersionRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Edited JeffDocument20 pagesChapter II Edited JeffRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Count of Monte Cristo ReationDocument2 pagesCount of Monte Cristo ReationRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy ReportDocument25 pagesBell's Palsy ReportRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing HistoryDocument1 pageNursing HistoryRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocument1 pageAssessment of Respiratory FunctionRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)Document4 pagesEsomeprazole (Nexium)Roderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NeurologiaDocument45 pagesTrigeminal NeurologiaRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument13 pagesHiatal HerniaRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Typhoid FeverDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Typhoid FeverRoderick Agbuya63% (8)
- Mindanao's Epic Poetries Like Homer's Iliad and OdysseyDocument1 pageMindanao's Epic Poetries Like Homer's Iliad and OdysseyRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Mindanao's Epic Poetries Like Homer's Iliad and OdysseyDocument1 pageMindanao's Epic Poetries Like Homer's Iliad and OdysseyRoderick AgbuyaNo ratings yet