Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter-1 Elementary Theory
Uploaded by
Dr.S.RamamurthyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter-1 Elementary Theory
Uploaded by
Dr.S.RamamurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEMENTARY PRINCIPLES
Units:
DIMENSION SI
Time Seconds (S)
Length meter(m)
Force Newton(N)
Mass Kilogram(kg)
Temperature Celsius(C)
FORCE: A one Newton force will give a one kilogram mass an acceleration of 1m/s
2
1N =1kg *1m/sec
2
DENSITY AND SPECIFIC VOLUME: Density r is mass per unit volume (kg/m
3
)
Specific volume (v) is volume per unit mass (m
3
/kg) r=1/v
Specific Weight: Weight per unit volume (n), n=rg (N/m
3
)
Pressure : Force per unit area (N/m
2
)
SI system 1Pascal (Pa)=1N/m
2
, 1bar =10
5
N/m
2
Gage Pressure Measured w.r.t surrounding (ambient) pressure
P
abs
=P
amb
+P
gage
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
If Pgage is Negative then the absolute pressure is below ambient. It is called
(positive) vacuum reading
AMBIENT PR.
P1 Gage
P2 Vacuum
P1 Absolute
P2abs
PERFECT VACUUM
1
2
ABSOLUTE AND GAGE PRESSURE
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
Temperature : K =
o
C+273.15
Viscosity:
Any substance that will continuously deform when subjected to shear stress
) / ( cos ,
2
m s N
tion lardeforma Rateofangu
s ShearStres
ity Vis = ) / ( cos
2
s m ity Vis Kinematic
=
Equation of state: P=rRT For ideal gas , P=ZrRT For Non-ideal gas
P=absolute pressure in N/m2, r =density in kg/m
3
,T is the absolute temperature in K
and R in N-m/kg-K(J /kg K), Z-Factor for non-ideal gas
Some Mathematical Concepts: y=f(x) ,y is dependent and x is independent
P=f(x,y,z)
Infinitesimal : A quantity which eventually is allowed to approach zero in the limit is called an
infinitesimal
dy/dx=lim Dx>0 Dy/Dx
Binomial Theorem
(a+x)
n
= a
n
+na
(n-1)
x+n(n-1)/2! a
(n-2)
x
2
+n(n-1)(n-2)/3!a
(n-3)
x
3
+..
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
Thermodynamic concepts
Microscopic approach: deals with molecules their motion and behavior
structure & behavior of matter
Macroscopic approach: deals directly with the average behavior like
temperature, pressure etc.
Control volume: A fixed quantity of mass which is being analyzed
closed system, Since no matter cross the boundary
Control Volume : A region in space which is being analyzed Open system
since matter or energy may cross
Properties: Characteristics which describe the state of a system Pressure,
temperature, entropy)
Intensive Property: Depends only on the state of the system and is independent
of its mass (ex: temperature,Pressure)
Extensive Property: Depends on mass of the system (eg: internal energy,
volume)
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
Types of properties
1. Observable-readily measurable, Pressure, temperature, velocity, mass
2. Mathematical: Defined from combination of other properties like density, specific heat, enthalpy
3. Derived :Obtained from analysis, internal energy Ist Law, Entropy 2
nd
Law
State Change: Comes about as the result of a change in any property
Path or Process: represent a series of adjacent states which define a unique path one to another
Types of process:
1. Adiabatic - No heat transfer
2. Isothermal - Temperature is constant
3. Isobaric - Pressure is constant
4. Isentropic - Entropy is constant
CYCLE: A sequence of process in which the system is returned to its original state
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
Laws of classical thermodynamics
O2 (OO) relation among properties
O Thermodynamic equilibrium
Conservation of energy
Degradation of energy (Irreversibility)
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
O2 (OO) Law assumes that a relationship exists among the properties of the system ie an
equation of state
For a single component substance only three independent properties are required to fix the state
of the system
O - Two system in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each
other (and thus have the same temperature)
Deals with conservation of energy, Heat and work are two types of energy
For closed system Q=W+DE
E=u+V
2
/2+gZ=Internal energy due to motion of molecules within system+KE+PE
For infinitesimal process dq =dW + de
Work done by pressure force dW =p dV
Combination of the terms u and PV enters into many equations and it is convenient to define
term called
Enthalpy, h as h=u + PV
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
Enthalpy is a property , dh=du+d(PV) =DU+P dV +V dP
C
p
=(jh/jT)
p
C
v
=(ju/jT)
v
C
p
=C
v
+d(PV)/dT , d(RT)/dT=C
p
-C
v
=R
Second Law : It is impossible for an engine operating in a cycle to produce net work output if exchanging
heat with only one temperature source - Entropy
Reversible Process: is one in which both the system and its surroundings can be restored to their
original states.
It can be shown for a reversible process is independent of path. Therefore this integral represent
the change of a property which is called Entropy
DS=
}
T
dQ
}
T
dQ
R
R-Represent reversible
Property Relations: Combination of 1
st
and 2
nd
law, dQ=dW+du, dS=dQ/T=(dW+du)/T
T.dS= dW + du
= PdV + du
= P.dV + dh - V.dP - P.dV
dW = P.dV Work is done by the Pressure force during change in volume
H = u + PV , dh = du + P.dV + V.dP , du = dh V.dP P.dV
T.dS = P.dV + du and T.dS = dh-V.dP
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
t Cons P
P
dT
dh
C
tan =
|
.
|
\
|
=
dT C dh
P
=
V
P
C
C
=
Entropy Change:
T
dQ
dS =
Change in entropy between two points can be obtained by integrating above equation
}
= = A
2
1
1 2 2 1
T
dQ
S S S
1
2
1
2
ln ln
P
P
C
V
V
C
V P
+ =
1
2
1
2
ln ln
P
P
R
T
T
C
P
=
1
2
1
2
ln ln
V
V
R
T
T
C
V
+ =
Perfect Gas: Equation of state P=rRT
Internal energy and also the enthalpy are functions of temperature only
t Cons V
V
dT
du
C
tan =
|
.
|
\
|
=
dT C du
V
=
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
Process Diagrams: Many process in the gaseous region can be represented as a polytrophic process
,i.e. which follows PV
n
=Constant, where n is a polytrophic exponent (is a any positive number)
From equation of state t Cons TV
n
tan
1
=
t cons TP
n
n
tan
1
=
Cases: n=0 P=constant
n=1 T=constant
n=g S=constant
n=infinity V=constant
n=infinity
n=g
n=1
n=0
P
V
n=1
n=g
n=0
n=infinity
V=C
P=C
(S=C)
T=C
n increasing
n increasing
T
S
Prepared by Dr. S. Ramamurthy, ramamurthy302@gmail.com
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Getting Started with MATLAB GuideDocument252 pagesGetting Started with MATLAB GuideAnirban Chakraborty89% (18)
- Getting Started with MATLAB GuideDocument252 pagesGetting Started with MATLAB GuideAnirban Chakraborty89% (18)
- Quiz ElectricityDocument4 pagesQuiz ElectricityMaestro Pisika LptNo ratings yet
- Mock Electrical Engineer ExamDocument21 pagesMock Electrical Engineer ExamJohn MarianoNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis TMDocument8 pagesDimensional Analysis TMDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Introduction To TMDocument6 pagesChapter-2 Introduction To TMDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Diffusion in Ducts and DiffusersDocument9 pagesDiffusion in Ducts and DiffusersDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- SofcDocument35 pagesSofcDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- India's Own AMCA Fighter: by SP's Special CorrespondentDocument3 pagesIndia's Own AMCA Fighter: by SP's Special CorrespondentDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument8 pagesBatteryDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Low ASR Wing With FlapDocument40 pagesLow ASR Wing With FlapDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Aircraft Design 2 SummaryDocument14 pagesAdvanced Aircraft Design 2 SummaryJack AzadNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Predictions, Comparisons, and Validations Using Missile DATCOM (97) and Aeroprediction 98 (AP98)Document9 pagesAerodynamic Predictions, Comparisons, and Validations Using Missile DATCOM (97) and Aeroprediction 98 (AP98)sdgpass2585No ratings yet
- Design and Testing of Ejectors For High Temperature Fuel Cell Hybrid SystemsDocument8 pagesDesign and Testing of Ejectors For High Temperature Fuel Cell Hybrid SystemsDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- FCT 5 kW SOFC Power System SpecsDocument2 pagesFCT 5 kW SOFC Power System SpecsDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Eurofighter Vs Sukhoi 27Document14 pagesEurofighter Vs Sukhoi 27Dr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine BasicsDocument8 pagesGas Turbine BasicsZulmi_MiatNo ratings yet
- Iplf08 KimDocument12 pagesIplf08 KimDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- A Review of More-Electric AircraftDocument13 pagesA Review of More-Electric AircraftYang TaoNo ratings yet
- Sri Mad Bhagavat Am 015439 MBPDocument327 pagesSri Mad Bhagavat Am 015439 MBPDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- More Electric Aircraft 000Document24 pagesMore Electric Aircraft 000Dr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to MATLAB FundamentalsDocument34 pagesIntroduction to MATLAB FundamentalsHaseeb BalochNo ratings yet
- Mat Lab TourDocument16 pagesMat Lab TourDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Interpolating Gridded DataDocument24 pagesInterpolating Gridded DataDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Rotor BbladeDocument11 pagesSteam Turbine Rotor BbladeSajjad Ahmed100% (1)
- Introduction To TurbomachineryDocument66 pagesIntroduction To TurbomachineryJeff SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Interpolating Gridded DataDocument24 pagesInterpolating Gridded DataDr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Contrarotating PropfanDocument11 pagesContrarotating PropfanDr.S.Ramamurthy100% (1)
- 088Document7 pages088Dr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- 088Document7 pages088Dr.S.RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- 15EEE401 - II Ass - Aug 2018Document2 pages15EEE401 - II Ass - Aug 2018sriharshitha vegesnaNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler ExperimentDocument13 pagesMarcet Boiler ExperimentSatiah WahabNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Physics Investigatory ProjectAziyaNo ratings yet
- HV DC PrysmianDocument32 pagesHV DC PrysmianFiras AtwanNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet: Boyang Qin Date Created: Jan 2013Document3 pagesEquation Sheet: Boyang Qin Date Created: Jan 2013Boyang QinNo ratings yet
- 2910 Enthusiast Phase-TEAS (Pre-Score) Paper-2 (E) JADocument24 pages2910 Enthusiast Phase-TEAS (Pre-Score) Paper-2 (E) JAarushrigangjiNo ratings yet
- 2017 HKDSE Physics Paper 1A SolDocument32 pages2017 HKDSE Physics Paper 1A SolAlex KongNo ratings yet
- Residential DaDocument14 pagesResidential DaSasquatchCornNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Kirchhoffs LawDocument6 pagesWeek 10 - Kirchhoffs LawRowen PratherNo ratings yet
- Hfe Kenwood Kmf-x9000 Mx-5000 Service enDocument10 pagesHfe Kenwood Kmf-x9000 Mx-5000 Service enAnonymous iLQZpnK5No ratings yet
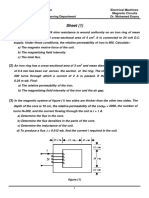
- Sheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMDocument2 pagesSheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMKhalifa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Singati Hydro Energy Ltd.Document47 pagesSingati Hydro Energy Ltd.kumarNo ratings yet
- API MPMS Chapter 11.1 2004 Uncertainty Worksheet: +44-1397-773190 LandlineDocument3 pagesAPI MPMS Chapter 11.1 2004 Uncertainty Worksheet: +44-1397-773190 LandlineMarcos CornelioNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes ExerciseDocument127 pagesPhysics Notes ExerciseNaeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fix eBike Error CodesDocument21 pagesFix eBike Error CodesFlorinNo ratings yet
- SDOFDocument107 pagesSDOFMohammed B TuseNo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document16 pagesPaper 4Sayan Kumar KhanNo ratings yet
- All About Fundamental Physical QuantitiesDocument18 pagesAll About Fundamental Physical Quantitiessreekanthreddy peramNo ratings yet
- Li-Ion Polymer Rechargeable Battery Specification Sheet: Customer's Model Number: HCP744560ZCDocument17 pagesLi-Ion Polymer Rechargeable Battery Specification Sheet: Customer's Model Number: HCP744560ZCJhoanie Marie Cauan100% (1)
- UNIT 2 - PhysicsDocument38 pagesUNIT 2 - PhysicsPpx XdNo ratings yet
- Students Dream Box Academy: Guduvanchery / Tambaram / Chrompet / SpkoilDocument8 pagesStudents Dream Box Academy: Guduvanchery / Tambaram / Chrompet / SpkoilSTUDENTS DREAM BOX - CBSENo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry for EngineersDocument58 pagesThermochemistry for EngineersPaul Jhon Eugenio100% (1)
- Daily Life Uses of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument15 pagesDaily Life Uses of Differentiation and IntegrationMohd Nasha Hafizulhilmi87% (15)
- D 4470 - 97 - Rdq0nzatotc - PDFDocument10 pagesD 4470 - 97 - Rdq0nzatotc - PDFislamakthamNo ratings yet
- Questions Bank Electronic BasicDocument96 pagesQuestions Bank Electronic Basiccsar_pc0% (1)
- Pneumatic Ball On-Off Valve/150LB (Fail Close) Tag Number: ESDV 201 A/B NO: 1Document12 pagesPneumatic Ball On-Off Valve/150LB (Fail Close) Tag Number: ESDV 201 A/B NO: 1mohsalehi1391No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentMohit YaduwanshiNo ratings yet