Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics - Unit 2 - Definitions
Uploaded by
ks010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views0 pagesPhysics – Unit 2 - Definitions
Original Title
Physics – Unit 2 - Definitions
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhysics – Unit 2 - Definitions
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views0 pagesPhysics - Unit 2 - Definitions
Uploaded by
ks01Physics – Unit 2 - Definitions
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 0
Physics
AS
-
Unit
2
-
Mechanics,
Materials
and
Waves
-
Definitions
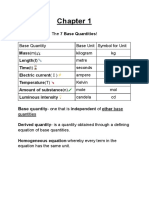
Moment Force multiplied by perpendicular distance between force and the
pivot
Principle of moments States that for an object to be in equilibrium the sun of
the anticlockwise moments equals the sum of the anticlockwise moments (no
turning moment)
An Object is in equilibrium if:
o Sum of anticlockwise moments = sum of clockwise moments
o All vertical forces cancel and all horizontal forces cancel
A Couple A pair of opposite and equal forces separated by distance d, acting
about point p, the turning effect at point p is equal to one of Forces multiplies by
the perpendicular distance between the forces
Centre of mass Where all of an objects mass appears to act about and
moments cancel
A Newton Force required to accelerate 1kg by 1ms-2
A Joule Work done 1N through a distance of 1m in direction of force
Law of conservation of energy energy is never created or destroyed just
converted between different types
Hookes Law The extension of a spring is proportional to the force applied to
it as long as the limit of proportionality is not exceeded
Stress Force per unit area
Strain Ratio of extension to original length
Youngs Modulus Stiffness constant of a material
A longitudinal Wave a propagating wave with oscillations in the same
direction as propagation/energy transfer
A transverse wave A propagating wave with oscillations perpendicular to the
direction of propagation
Transverse waves can be polarized but longitudinal waves cannot
Stationary wave Formed when 2 waves of similar frequency travelling in
opposite directions interfere and the resultant wave is the vector sum of each
waves displacements at that point by the principle of superposition
Diffraction Spreading out of a wave when passed through a slit of around an
obstacle
Coherent Sources Same frequency and constant phase relationship
Constructive Interference occurs 2 waves intersect and interfere through
principle of superposition and the resultant displacement I the vector sum of the
2 waves displacement at that point and the phase difference between the 2
waves at that point is a whole number of wavelengths (destructive when 180
degrees phase difference half number of wavelengths)
Differences between single and double slit diffraction
o Single Wide central maxima 2x width of others and reduction in
intensity going away
o Double Same intensity same width going out
You might also like
- Physical Quantities and Units DefinitionsDocument9 pagesPhysical Quantities and Units DefinitionsKoushiki MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- (Phys) Compiled Definitions and Principles For ASlevel Paper 1/paper 2Document10 pages(Phys) Compiled Definitions and Principles For ASlevel Paper 1/paper 2qidamadani100% (1)
- IB HL Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesIB HL Physics DefinitionsshinyrayquazaNo ratings yet
- Phys 100 SERIES Physics GuideDocument12 pagesPhys 100 SERIES Physics GuideimagemaniaNo ratings yet
- Definitions To LearnDocument4 pagesDefinitions To LearnGrace LuoNo ratings yet
- Physics Laws, Principles, Concepts and DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPhysics Laws, Principles, Concepts and DefinitionsTheLuckS; ラッキー矢印No ratings yet
- Physics DefinitionsDocument4 pagesPhysics DefinitionsRhichelle StraussNo ratings yet
- Mechanics & Materials Definitions for LearningDocument10 pagesMechanics & Materials Definitions for LearningRERORI GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument24 pagesFinals ReviewerAdrian SalvoNo ratings yet
- Key science definitions guideDocument3 pagesKey science definitions guidesamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MechDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Mechsubodya alahakoonNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument14 pagesPhysics Notesgreg frsNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and WavesDocument38 pagesVibrations and WavesKiara De LeonNo ratings yet
- OCR G484 Definitions (The Newtonian World)Document3 pagesOCR G484 Definitions (The Newtonian World)Ashish ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Science Yearly Notes: Physics Chemistry Biology Earth ScienceDocument30 pagesScience Yearly Notes: Physics Chemistry Biology Earth Sciencedavid tsaiNo ratings yet
- Physics SummaryDocument12 pagesPhysics SummaryChen He LimNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Engineering SystemsDocument47 pagesDynamic Engineering SystemsGia BeNo ratings yet
- Physic Form 4/5 DefinitionDocument6 pagesPhysic Form 4/5 DefinitionKa Mun LeongNo ratings yet
- DAS Physics Glossary of TermsDocument6 pagesDAS Physics Glossary of TermsOabile 14kNo ratings yet
- Errors, Motion, Forces, Gravity ConceptsDocument3 pagesErrors, Motion, Forces, Gravity ConceptsCong FengNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Mechanical WaveDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Mechanical WaveJam JungNo ratings yet
- Definitions IG PhysicsDocument4 pagesDefinitions IG Physicsa.D.a.M aBdUlLaHNo ratings yet
- Revision GuideDocument10 pagesRevision GuideMohammed MazenNo ratings yet
- Definitions AS PhysicsDocument4 pagesDefinitions AS PhysicsFazelah YakubNo ratings yet
- OCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 4.4: WavesDocument7 pagesOCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 4.4: WavesjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Reviewer (Physics) : A. Forces and MotionDocument5 pagesScience 8 Reviewer (Physics) : A. Forces and Motionp r i n c e s s i t a86% (7)
- Chapter 12: Vibrations and Waves: 12.1 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument5 pagesChapter 12: Vibrations and Waves: 12.1 Simple Harmonic MotionSteven SuNo ratings yet
- Prelim Physics NotesDocument15 pagesPrelim Physics NotesrandomneNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam ReivewDocument12 pagesPhysics Exam ReivewemilygoldneyNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 4 Study GuideDocument8 pagesPhysics Topic 4 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- SPM Physics List of DefinitionDocument12 pagesSPM Physics List of DefinitionCrazyElfNo ratings yet
- Physics Waves NotesDocument20 pagesPhysics Waves Notesjhon isaac corimanya paccoNo ratings yet
- DEFINITIONS FOR PHYSICS UNITSDocument4 pagesDEFINITIONS FOR PHYSICS UNITSanonlukeNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Forces: 1. Forces and Their Effects 2. Simple Machines 3. Types of Forces 4. Common ForcesDocument31 pagesUnit 5. Forces: 1. Forces and Their Effects 2. Simple Machines 3. Types of Forces 4. Common ForcesgenusxyzNo ratings yet
- Definitions As PhysicsDocument7 pagesDefinitions As Physicsshaizamudassir13No ratings yet
- IB Physics Core Definitions ListDocument7 pagesIB Physics Core Definitions ListLaurus NagNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and Waves ExplainedDocument15 pagesVibrations and Waves ExplainedDesy SafitriNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Before Newton: - GalileoDocument24 pagesForce and Motion Before Newton: - GalileotommyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - WavesDocument26 pagesTopic 4 - WaveseisnNo ratings yet
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- Physics A Level DefinitionsDocument12 pagesPhysics A Level DefinitionsNaillah Saba100% (1)
- Physics Unit 4 Summary: Momentum, Circular Motion, GravitationDocument8 pagesPhysics Unit 4 Summary: Momentum, Circular Motion, GravitationTravisJohn-JohnsonReadNo ratings yet
- Physics Ion ListDocument11 pagesPhysics Ion ListkejimariaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1Document11 pagesGeneral Physics 1Aizeldy GuiribaNo ratings yet
- AS Physics DefinitionsDocument6 pagesAS Physics DefinitionshamzaNo ratings yet
- Cape Unit I RevisionDocument56 pagesCape Unit I Revisionsarcasticb15No ratings yet
- 11 Physics Cbse WavesDocument9 pages11 Physics Cbse Wavesvickyvicky0022okNo ratings yet
- Important Physics Definitions (AS)Document3 pagesImportant Physics Definitions (AS)Yan Xin LuNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mohsin EM Lecture 1,2Document41 pages1 - Mohsin EM Lecture 1,2UsamaNo ratings yet
- All About Waves NotesDocument1 pageAll About Waves NotesRusherNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Type of WavesDocument4 pages6.1 Type of WavesNirmal MohanNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 4Document12 pagesPhysics Unit 4Ibbz ChaabanNo ratings yet
- Physics Part Two Dictionary - Natural Science: Grow Your Vocabulary, #37From EverandPhysics Part Two Dictionary - Natural Science: Grow Your Vocabulary, #37No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and the Principles of Electromagnetic PhenomenaFrom EverandMaxwell's Equations and the Principles of Electromagnetic PhenomenaNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 4: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #4From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 4: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #4No ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3No ratings yet
- As - Sources of FinanceDocument34 pagesAs - Sources of Financeks01100% (1)
- Cash Flow Forecasting NotesDocument1 pageCash Flow Forecasting Notesks01No ratings yet
- English LiteratureDocument160 pagesEnglish LiteratureMaria GiannisiNo ratings yet
- Aqa Comp1Document53 pagesAqa Comp1ks01No ratings yet
- English LiteratureDocument160 pagesEnglish LiteratureMaria GiannisiNo ratings yet
- Aqa Phya1 W MS Jan09Document9 pagesAqa Phya1 W MS Jan09superpoohNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme For The Units June 2009: Biology B J643Document51 pagesMark Scheme For The Units June 2009: Biology B J643ks01No ratings yet
- Eneria Product List: Design Conditions Fuel Gas DataDocument1 pageEneria Product List: Design Conditions Fuel Gas DataPocola AdrianNo ratings yet
- Plant Utilities - Instrument Air Systems PDFDocument5 pagesPlant Utilities - Instrument Air Systems PDFAnurag TripathiNo ratings yet
- API 5CT Coupling Stock2Document10 pagesAPI 5CT Coupling Stock2tarno12No ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Polymer/particle Composites at Low TemperaturesDocument4 pagesThermal Properties of Polymer/particle Composites at Low TemperaturesSiva BhaskarNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Q3 - Module 3 - Week 5 - April 26-April 30 With InstructionDocument22 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Q3 - Module 3 - Week 5 - April 26-April 30 With InstructionRona Mae BetitaNo ratings yet
- Air-Cooled Chiller With Variable-Speed Screw Compressor: Performance InformationDocument2 pagesAir-Cooled Chiller With Variable-Speed Screw Compressor: Performance InformationVu Manh ThangNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions PDFDocument50 pagesLiquid Solutions PDFAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- 2018 Physical Metallurgy Principles and Design - Haidemenopoulos, Gregory N PDFDocument490 pages2018 Physical Metallurgy Principles and Design - Haidemenopoulos, Gregory N PDFPhạm Thịnh100% (1)
- SJPO 2016 General Round - Answer GuideDocument50 pagesSJPO 2016 General Round - Answer GuideZleep100% (1)
- Hermetic CAN&CNFDocument20 pagesHermetic CAN&CNFkikechuNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Prof. Dr. Ali KodalDocument116 pagesThermodynamics: Prof. Dr. Ali KodalThomas VerdugoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Hess Law 90 - From MR - TonoDocument14 pagesLesson Plan Hess Law 90 - From MR - TonoSiti Aminah Al-Hadi100% (2)
- A5 Catalog CG 091214 Unnop V10Document10 pagesA5 Catalog CG 091214 Unnop V10Tanjim FakirNo ratings yet
- Best Medical & Engineering Coaching Institute OnlineDocument51 pagesBest Medical & Engineering Coaching Institute OnlineajsdoNo ratings yet
- 420 Stainless Steel DS 201406 PDFDocument3 pages420 Stainless Steel DS 201406 PDFAlexander Saavedra MambuscayNo ratings yet
- 1 StsumDocument2 pages1 StsumElleiram ArellanoNo ratings yet
- ANSI Z97.1 SummaryDocument4 pagesANSI Z97.1 SummaryAli YalazNo ratings yet
- Dictionary April 2017 - Teflon CoatingsDocument2 pagesDictionary April 2017 - Teflon CoatingsCoatresa Recubrimientos TecnicosNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Additives - A Practical GuideDocument17 pagesLubricant Additives - A Practical GuideNeeraj Raushan KanthNo ratings yet
- Shear Connection - Beam - Steel Column - Fin PlateDocument30 pagesShear Connection - Beam - Steel Column - Fin Platekalpanaadhi100% (3)
- Methods Used For Curing of ConcreteDocument3 pagesMethods Used For Curing of ConcreteAjayNo ratings yet
- Iso 14224 2016 187 192Document6 pagesIso 14224 2016 187 192Ostap SepykNo ratings yet
- Cold Forming and Heat Treatment Requirement of Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubes.Document5 pagesCold Forming and Heat Treatment Requirement of Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubes.R kumarNo ratings yet
- The Secret of Physics: U U V V U U V VDocument5 pagesThe Secret of Physics: U U V V U U V VVIPscholarNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document9 pagesExp 1zackwanNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument103 pages7 PDFmuhammad izzulNo ratings yet
- Q4 LP7 GenPysics2Document11 pagesQ4 LP7 GenPysics2ROMELYN GRACE BORBENo ratings yet
- Quality Meets Efficiency: DR6000 UV-VIS SpectrophotometerDocument8 pagesQuality Meets Efficiency: DR6000 UV-VIS SpectrophotometerOudah AliNo ratings yet
- WPS - 006Document13 pagesWPS - 006MAT-LIONNo ratings yet
- Understanding Chemical EquilibriumDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Chemical EquilibriumYuvrajNo ratings yet