Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Koleksi Soalan Topikal
Uploaded by
Kwai Ying Abdul AzizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Koleksi Soalan Topikal
Uploaded by
Kwai Ying Abdul AzizCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 2
P PA AN NE EL L M MO OD DU UL L P PE EC CU UT TA AN N A AK KA AD DE EM MI IK K 2 20 01 12 2
TN HJ BURHAN B RAMLI
SM SAINS MACHANG
PN AMINAH BT AB RAHMAN
SM SAINS TENGKU MUHAMMAD FARIS PETRA
PN CHE ROMAH BT JAYA
SM SAINS MACHANG
EN ISMAIL B MAHMOOD
SMK KOTA
EN SYAFIZAL B SAID
SMK KOK LANAS
PN NIK MAHANI BT NIK ZAID
SMK KUBANG BEMBAN
PN HASNAH BT DAUD
MAKTAB SULTAN ISMAIL
P P
H H
Y Y
S S
I I
C C
S S
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 3
CHAPTER 1: UNDERSTANDING PHYSICS
PAPER 1
1. The accuracy of a measurement can be increased by
Kejituan sesuatu ukuran boleh ditambah dengan
A ignoring zero error
mengabaikan ralat sifar
B ignoring parallax error
mengabaikan ralat paralaks
C calculating the average value
menghitung nilai purata
D calculating value to a more decimal places
menghitung nilai kepada tempat perpuluhan yang lebih
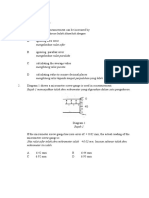
2. Diagram 1 shows a micrometer screw gauge is used in a measurement.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan tolok skru mikrometer yang digunakan dalam satu pengukuran.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
If the micrometer screw gauge has zero error of + 0.02 mm, the actual reading of the
micrometer screw gauge is
Jika ralat sifar tolok skru mikrometer ialah +0.02 mm, bacaan sebenar tolok skru
mikrometer itu ialah
A 6.42 mm B 6.44 mm
C 6.92 mm D 6.95 mm
45
0
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 4
3. Which of the following is the correct converted unit ?
Antara berikut yang manakah pertukaran unit yang betul?
A 1 000 mm
3
= 1.0 x 10
-4
m
3
B 100 mm
3
= 1.0 x 10
-2
m
3
C 450 mm
3
= 4.5 x 10
-7
m
3
D 45 mm
3
= 4.5 x 10
-6
m
3
4 . Which of the following values is equal to 30 mHz?
Antara nilai berikut,yang manakah sama dengan 30 mHz?
A 3 x 10
-5
Hz B 3 x 10
-4
Hz
C 3 x 10
-3
Hz D 3 x 10
-2
Hz
5. A,B,C, and D show the shooting marks on a target.
Which of the following show the highest precision?
A,B,C, dan D merupakan kesan tembakan pada papan sasar. Antara berikut yang
manakah menunjukkan kepersisan yang paling tinggi?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 5
6. Table 1 shows the results obtained from an experiment resistivity of a wire.
Jadual 1 menunjukkan keputusan yang diperolehi daripada ekperimen kerintangan
wayar.
Table 1
Jadual 1
Which of the following statements is true about the experiment?
Manakah antara pernyataan berikut adalah benar tentang eksperimen?
A The current is the manipulated variable
Arus elektrik adalah pembolehubah manipulasi
B The smallest scale on the ammeter is 0.02 A
Skala paling kecil pada ammeter adalah 0.02 A
C The smallest scale on the voltmeter is 0.01 V
Skala paling kecil pada voltmeter ialah 0.01 V
D The diameter of the wire is measured using micrometer screw gauge
Diamater wayar diukur dengan mengunakan tolok skru mikrometer
7. Which of the following base quantities has a correct SI unit?
Antara kuantiti-kuantiti asas berikut, yang manakah mempunyai unit SI yang betul?
Base Quantity SI Unit
Kuantiti asas Unit SI
A Mass g
Jisim
B Time h
Masa j
Diameter of wire /mm
Diameter wayar/mm
Current/A
Arus elektrik/A
Potential Diference/V
Beza keupayaan/V
0.20 0.34 3.4
0.60 0.39 3.6
1.00 0.53 4.3
1.40 0.70 4.8
1.80 0.86 5.0
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 6
C Electric Current mA
Arus Elektrik
D Temperature K
Suhu
8. In a shooting competition, Ali has won the competition because his shots were very
accurate and consistent. Which of the following target boards shows the shots made
by Ali?
Dalam sebuah pertandingan menembak, Ali telah memenangi pertandingan
tersebut kerana tembakannya yang sangat jitu dan persis. Antara papan-
papan sasaran berikut, yang manakah menunjukkan tembakan yang telah
dilakukan oleh Ali ?
A B
C D
9. Diagram 2 shows the reading of a micrometer screw gauge.
Rajah 12 menunjukkan bacaan satu tolok skru mikrometer.
What is the reading of the micrometer screw gauge?
Berapakah bacaan tolok skru micrometer itu ?
A 4.38 mm B 4.32 mm
C 4.78 mm D 4.82 mm
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 7
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 1.1 shows the reading of a measuring instrument when there is no object on it.
Diagram 1.2 shows the reading of the measuring instrument when an object is placed on
it.
Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan bacaan satu alat pengukur apabila tiada objek diletakkan
di atasnya.
Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan bacaan alat pengukur tersebut apabila satu objek diletakkan
di atasnya.
Diagram 1.1
Rajah 1.1
Diagram 1.2
Rajah 1.2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 8
(a) Name the physics quantity that can be measured by the measuring instrument
in Diagram 1.1.
Namakan kuantiti fizik yang boleh diukur oleh alat pengukur pada Rajah 1.1.
.
[1 mark]
(b) Name the type of error produced in Diagram 1.1
Namakan jenis ralat yang terhasil dalam rajah 1.1
..........
[1 mark]
(c) What is the value of error in Diagram 1.1 ?
Berapakah nilai ralat yang terhasil dalam rajah 1.1?
..
[1 mark]
(d) What is the actual reading of the physical quantity measured in Diagram 1.2?
Berapakah bacaan sebenar kuantiti fizik yang diukur dalam Rajah 1.2?
..
[1 mark]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 9
CHAPTER 1 : UNDERSTANDING PHYSICS
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 C 4 D 7 D
2 D 5 C 8 C
3 C 6 D 9 D
PAPER 2
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1. (a) mass 1
1
(b) Zero error 1
1
(c) 6 g 1
1
(d) 24 g 1
1
TOTAL MARK 4M
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 10
CHAPTER 2: FORCE AND MOTION
PAPER 1
1. Diagram 1 shows the journey of a bus from city A to reach city D.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan pergerakan bas dari bandar A ke bandar D.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
What is the displacement of the bus?
Berapakah sesaran bas ?
A 60 km B 100 km
C 128 km D 220 km
2. Which of the following ticker tapes describes a motion with a deceleration?
Antara pita-pita detik berikut, yang manakah menerangkan pergerakkan dengan
nyahpecutan?
A
B
C
D
Direction of motion
Arah gerakan
Direction of motion
Arah gerakan
Direction of motion
Arah gerakan
Direction of motion
Arah gerakan
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 11
3. Diagram 2 shows a velocity-time graph for the motion of an object.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu graf halaju-masa bagi suatu objek bergerak. .
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
Based on the graph which of the following statement is true?
Berdasarkan graf , pernyataan berikut yang manakah adalah benar?
A. The car moves with constant acceleration and then stop.
Kereta itu bergerak dengan pecutan tetap dan kemudian berhenti.
B. The car moves with constant velocity and then stop.
Kereta itu bergerak dengan halaju tetap dan kemudian berhenti.
C. The car moves with constant acceleration and then constant velocity.
Kereta itu bergerak dengan pecutan tetap dan kemudian halaju tetap.
D. The car moves with constant acceleration and then constant deceleration.
Kereta itu bergerak dengan pecutn tetap dan kemudian nyahpecutan
tetap.
4. Which of the following graph shows the object moving with decreasing acceleration?
Antara graf berikut, yang manakah menunjukkan objek bergerak dengan pecutan
yang semakin berkurang?
A B
Time
masa
Velocity
Halaju
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 12
C D
5. Diagram 3 shows the velocity-time graph of the motion of an object.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan graf halaju-masa bagi gerakan suatu objek.
Which of the following acceleration-time graphs describes the motion of the object?
Yang manakah antara graf pecutan-masa berikut menerangkan gerakan objek itu?
A
B
v (ms
-1
)
t (s)
0
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
t (s)
a (ms
-2
)
t (s)
a (ms
-2
)
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 13
C
D
6. Diagram 4 shows two identical trolleys, P and Q with masses of 1 kg on a frictionless
plane. Trolley P is moving with a velocity of 10 ms
-1
and trolley Q is moving with a
velocity of 5 ms
-1
in an opposite direction.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan dua troli yang serupa, P dan Q dengan jisim 1 kg, di atas
suatu satah tanpa geseran. Troli P sedang bergerak dengan halaju 5 ms
-1
dan troli Q
sedang bergerak dengan halaju 10 ms
-1
dalam arah yang berlawanan.
Trolley P and trolley Q collide with each other and then move together with a
common velocity, v. What is the magnitude of v?
Troli P dan troli Q berlanggar dengan satu sama lain dan bergerak bersama-sama
dengan halaju sepunya, v. Berapakah magnitud v?
A 2.5 ms
-1
B 5.0 ms
-1
C 7.5 ms
-1
D 15.0 ms
-1
t (s)
a (ms
-2
)
t (s)
a (ms
-2
)
Trolley P
Troli P
Trolley Q
Troli Q
v = 5 ms
-1
v = 10 ms
-1
Frictionless plane
Satah tanpa geseran
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 14
7. Which of the following has the highest net force?
Antara berikut, yang manakah mempunyai daya bersih paling tinggi?
8. Diagram 5 shows a wooden block experiences an acceleration when it is pulled by a
force of F . The frictional force of 10 N acting on the wooden block.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan sebuah bongkah kayu mengalami pecutan bila ditarik dengan
daya F. Daya geseran sebanyak 10 N bertindak ke atas blok kayu itu.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
The pulling force, F is
A equals to 10 N.
sama dengan 10 N
B greater than 10 N.
lebih besar dari 10 N
C smaller than 10 N.
lebih kecil dari 10 N
9. Diagram 6 shows a method to determine the resultant force of the two forces, P and
Q.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan kaedah untuk menentukan paduan daya bagi dua daya, P dan
Q.
Friction force , 10 N
Daya geseran , 10 N
F
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 15
Which of the followings represents the magnitude of the resultant force?
Yang manakah antara yang berikut mewakili magnitud daya paduan tersebut?
A PR B RQ
C PQ D OR
10. Diagram 7 shows a car is moving at zero acceleration.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan sebuah kereta sedang bergerak dengan pecutan sifar.
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Which relationship of the forces is correct ?
Hubungan daya yang manakah benar ?
A T > F g B T = Fg
C T < Fg D W > R
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 16
11 Diagram 8 shows a high jumper is falling on a thick mattress.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan seorang peserta lompat tinggi sedang jatuh di atas tilam yang
tebal.
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
What is the function of the mattress?
Apakah fungsi tilam itu ?
A. To reduce the change in momentum of the high jumper.
Mengurangkan perubahan momentum ahli lompat tinggi
B. To reduce the time of impact between the high jumper and the mattress.
Mengurangkan masa tindakan antara ahli lompat tinggi dengan tilam
C. To reduce the impulsive force acting on the high jumper.
Mengurangkan daya impuls ke atas ahli lompat tinggi
12. Ali kicks a ball of mass 1.5 kg with a force of 50 N and the time of impact between
his boot and the ball is 0.2 s.
What is the change in momentum of the ball?
Ali menendang sebiji bola berjisim 1.5 kg dengan daya 50 N dan masa pelanggaran
di antara but dan bola ialah 0.2 s.
Berapakah perubahan momentum bola itu?
A 10 Ns B 15 Ns
C 250 Ns D 375 Ns
Mattres
tilam
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 17
13. Diagram 9 shows a brick falls from a high building.
Rajah 9 menunjukkan satu batu bata terjatuh dari sebuah bangunan yang tinggi.
Diagram 9
Rajah 9
Which of the following quantities remains unchanged?
Antara kuantiti-kuantiti berikut yang manakah tidak berubah?
A Acceleration B Velocity
Pecutan. Halaju.
C Kinetic energy D Momentum
Tenaga kinetik Momentum
14. Diagram 10 shows a coconut falling from a tree.
Rajah 10 menunjukkan sebiji buah kelapa sedang jatuh dari pokoknya.
Diagram 10
Rajah 10
What is the physical quantity of the coconut is constant?
Apakah kuantiti fizik yang malar bagi buah kelapa itu?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 18
A Potential energy B Kinetic energy
Tenaga keupayaan Tenaga kinetik
C Acceleration D Velocity
Pecutan Halaju
15. Diagram 11 shows two marbles A and B of different masses is being released at the
same time in a vacuum cylinder.
Rajah 11 menunjukkan dua biji guli A dan guli B yang berlainan jisim dijatuhkan
serentak dalam satu silinder vakum.
Diagram 11
Rajah 11
Which observation is correct?
Antara pernyataan berikut yang manakah benar ?
A Marble A and B float in the tube
Guli A dan B terapung dalam tiub
B Marble B will reach at the base earlier
Guli B sampai ke dasar tiub lebih awal
C Marble A will reach at the base earlier
Guli A sampai ke dasar tiub lebih awal
D Marble A and B will reach at the base at the same time
Guli A dan B sampai ke dasar tiub serentak
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 19
16. Diagram 12 shows two objects of different masses, P and Q is experiencing a state of
free fall.
Rajah 12 menunjukkan dua objek yang berlainan jisim, P dan Q sedang mengalami
keadaan jatuh bebas.
Which of the following statements is true?
Yang manakah antara pernyataan-pernyataan berikut adalah betul ?
A. Gravitational attraction force of P = Gravitational attraction force of Q
Daya tarikan graviti P = Daya tarikan graviti Q
B. Momentum of P = Momentum of Q
Momentum P = Momentum Q
C. Acceleration of P = Acceleration of Q
Pecutan P = Pecutan Q
D. Velocity of P = Velocity of Q
Halaju P = Halaju Q
17. Diagram 13 shows a metal ball is thrown vertically upwards.
Rajah 13 menunjukkan sebiji bola logam dilontar tegak ke atas.
Diagram 13
Rajah 13
Metal ball
Bola logam
Object Q
Objek Q
Object P
Objek P
ground
bumi
Diagram 12
Rajah 12
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 20
Which of the following statements is true about the momentum of the ball before it
reaches the maximum height?
Antara pernyataan berikut, yang manakah benar mengenai momentum bagi bola itu
sebelum ia mencapai tinggi maksima?
A Decrease B Increase C Constant
Berkurang Bertambah Malar
18. Which of the following graphs show the relationship between the acceleration and
height for an object that undergoes free fall to the ground?
Antara graf-graf berikut,yang manakah menunjukkan hubungan antara pecutan dan
ketinggian bagi suatu objek yang mengalami jatuh bebas ke arah permukaan bumi?
A B
C D
19. Diagram 14 shows an object which is in equilibrium of three forces P, Q and R.
Rajah 14 menunjukkan satu objek yang berada dalam keseimbangan tiga daya P,
Q dan R.
Diagram 14
Rajah 14
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 21
Which of the following vector diagrams represents the three forces?
Antara rajah-rajah vektor berikut, yang manakah mewakili ketiga-tiga daya itu?
D
20. Diagram 15 shows a wooden block being pulled by a horizontal force, F and tension,
T.
Rajah 15 menunjukkan sebuah blok kayu ditarik oleh satu daya, F dan tegangan, T.
Diagram 15
Rajah 15
Which of the following vector diagrams represents the three forces?
Antara rajah-rajah vektor berikut, yang manakah mewakili ketiga-tiga daya itu?
A B
D C
B A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 22
C D
21. Diagram 16 shows three arrangement of springs K, L and M. All the springs used are
identical.
Rajah 16 menunjukkan tiga jenis susunan spring K, L dan M. Semua spring yang
digunakan adalah serupa.
Diagram 16
Rajah 16
Which of the following shows the correct graph of force, F against extension, x
for K, L and M ?
Antara berikut yang manakah menunjukkan graf yang betul bagi daya, F
melawan, x untuk K, L and M ?
A B
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 23
C D
22. Diagram 17 shows a system consists of three identical springs. The original length of
each spring is 10 cm. With a load of 50 g, each spring is stretched to 14 cm.
Rajah 17 menunjukkan satu sistem yang terdiri daripada tiga spring yang serupa.
Panjang asal bagi setiap spring adalah 10 cm. Dengan beban 50 g, setiap spring itu
akan meregang kepada 14 cm.
What is the total length, X of the springs ?
Berapakah jumlah panjang X bagi spring-spring ?
A 21 cm B 24 cm
C 26 cm D 28 cm
Load 50 g
Beban 50 g
spring
X
Diagram 17
Rajah 17
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 24
23. Diagram 18 shows a weightlifter is lifting a load of 60 kg to a height, h.
If the energy used to lift the load is 1020 J, what is h?
Rajah 18 menunjukkan seorang ahli angkat berat sedang mengangkat beban 60 kg
pada suatu ketinggian h.
Jika tenaga yang digunakan untuk mengangkat beban itu adalah 1020 J, berapakah
h?
A 1.7 m B 1.8 m
C 2.0 m D 2.3 m
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 1 shows an aeroplane flying horizontally with a constant velocity.
P and Q are two forces which maintain the aeroplane at constant altitude.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan sebuah kapalterbang sedang terbang dengan halaju malar.
P dan Q adalah dua daya yang menetapkan kapalterbang tersebut pada ketinggian
tetap.
(a). Name the forces P and Q.
Namakan daya-daya P dan Q.
Diagram 18
Rajah 18
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 25
P: ...
Q: ..
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(b). Write equation to show the relationship between P and Q.
Tuliskan persamaan yang menunjukkan hubungan antara P dan Q.
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
(c). Which of the forces is caused by the Bernoulli's effect?
Antara daya-daya tersebut yang manakah disebabkan oleh kesan Prinsip
Bernoulli?
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
2. Diagram 5.1 and 5.2 show two watermelons fall off a table and drop on to surface A
and surface B respectively.
Rajah 5.1 dan 5.2 menunjukkan dua biji tembikai jatuh dari sebuah meja ke atas
permukaan A dan permukaan B masing-masing.
Diagtam 5.1 Diagram 5.2
Rajah 5.1 Rajah 5.2
(a) What is meant by impulse?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan impuls?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) With reference to Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2,
Merujuk kepada Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2,
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 26
(i) Compare the force on the watermelons that strike on Surface A and
Surface B.
Bandingkan daya pada tembikai yang menghentam ke atas Permukaan
A dan Permukaan B.
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Compare the time of impact of the watermelons on Surface A and
Surface B.
Bandingkan masa hentaman tembikai itu pada Permukaan A dan
Permukaan B.
.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii). State the relationship between the force produced in a collision and the
time of impact.
Nyatakan hubungan antara daya yang dihasilkan dalam suatu
perlanggaran dengan masa hentaman.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) Mark (\ ) for the correct statement about the change of momentum of the
watermelons in both situations above.
Tandakan (\ ) pada pernyataan yang betul mengenai perubahan momentum
pada tembikai dalam dua situasi di atas.
The change of momentum of the watermelon in Diagram 5.1 is greater
than that of the watermelon in Diagram 5.2.
Perubahan momentum pada tembikai dalam Rajah 5.1 adalah lebih
besar daripada tembikai dalam Rajah 5.2.
The change of momentum of the watermelon in Diagram 5.2 is greater
than that of the watermelon in Diagram 5.1.
Perubahan momentum pada tembikai dalam Rajah 5.2 adalah lebih
besar daripada tembikai dalam Rajah 5.1.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 27
The change of momentum of the watermelon in Diagram 5.1 is equal
to that of the watermelon in Diagram 5.2.
Perubahan momentum pada tembikai dalam Rajah 5.1 adalah sama
dengan tembikai dalam Rajah 5.2.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(d) Suggest a suitable material for surface B.
Cadangkan satu bahan yang sesuai bagi permukaan B.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(e)
Diagram 5.3
Rajah 5.3
By referring to the Diagram 5.3, explain how the driver is able to avoid serious
injuries when the car stopped suddenly.
Merujuk pada Rajah 5.3, terangkan bagaimana pemandu itu dapat
mengelakkan kecederaan yang parah ketika kereta berhenti dengan tiba-tiba.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 28
3. Diagram 7 shows a spring.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan satu spring.
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
(a) When a load is attached to the spring ;
Apabila satu beban dilekatkan pada spring ;
(i) What happen to the length of the spring?
Apakah yang berlaku pada panjang spring?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) What is the energy stored in the spring?
Apakah tenaga yang tersimpan dalam spring?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) If the number of load is increased, what will happen to the energy in
7a(ii)?
Jika bilangan beban ditambah, apakah yang akan berlaku kepada
tenaga di 7 a(ii)?
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 29
(b) The initial length of a spring is 15 cm. When a load with mass 300g is
attached to the spring, the length of the spring is 21 cm.
Panjang asal spring adalah 15 cm. Apabila beban berjisim 300g dilekatkan
pada spring. panjang spring adalah 21 cm.
What is the length of the spring if a load with mass 500g is attached to the
spring?
Berapakah panjang spring jika beban berjisim 500g dilekatkan pada spring?
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(c) The spring in Diagram 7 is not suitable to be used as a spring cradle.
Suggest modifications to be done based on the characteristics given below.
Spring dalam Rajah 7 tidak sesuai digunakan untuk buaian spring.
Cadangkan pengubahsuaian-pengubahsuaian yang perlu dilakukan
berdasarkan ciri-ciri yang diberi di bawah.
(i) Arrangement of the springs
Susunan spring
..
Reason
Sebab
...
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(ii) Stiffness of the spring
Kekerasan spring
...
Reason
Sebab
..
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 30
CHAPTER 2 : FORCE AND MOTION
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 B 7 B 13 A 19 C
2 C 8 B 14 C 20 B
3 C 9 D 15 D 21 A
4 B 10 B 16 C 22 D
5 A 11 C 17 A 23 A
6 A 12 A 18 A
PAPER 2
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1 (a) P = Lifting Force
Q = Weight / Gravitational Force Attraction
1
1
2
(b) P = Q 1 1
(c) Lifting Force / P 1 1
TOTAL 4
2(a)
Change of momentum 1
1
(b)(i) Force on the watermelon in Diagram 5.1 is larger
than the force on the watermelon in Diagram 5.2
1
3
(b)(ii) Time of impact on surface A is shorter than time of
impact on surface B
1
(b)(iii) A shorter time of impact will produce a larger force 1
(c) The change of momentum of the watermelon in
Diagram 5.1 is equal to that of the watermelon in
Diagram
1 1
(d) Sponge/carpet/towel/cloth/grass & other suitable
materials
1 1
M1 Body will be hold back by the seat belt when
car stopped suddenly
M2 The seat belt will lengthen slightly, the
impulsive force inflicted on the body will be
less
1
1
2
TOTAL 8
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 31
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
3 (a)(i) Length increases/ longer 1
3
(a)(ii) Elastic potential energy 1
(a)(iii) Increase 1
(b)
M1 =
=
M2 x = 10 cm
M3 l = 10 + 15 // 25 cm
3 3
(c)(i) Parallel 1
2
Load is shared equally among the spring / can support
bigr load
1
(c)(ii) Big 1
2 Spring constant is high/ great/big /. Not easily broken /
able to support large weight
1
TOTAL 10
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 32
CHAPTER 3: FORCE AND PRESSURE
PAPER 1
1 Which of the following wooden rod exert the highest pressure on the floor?
Each rod has the same mass.
Manakah antara rod kayu berikut mengenakan tekanan yang paling besar terhadap
lantai. Setiap rod mempunyai jisim yang sama.
2. Diagram 1 shows two identical bricks X and Y placed in two different ways on a
sandy ground were pressed by an identical force, F.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan dua bongkah bata X dan Y yang serupa diletakkan dalam dua
keadaan berbeza di atas tanah berpasir sedang ditekan dengan daya yang serupa, F.
What is the factor that causes brick Y to sink more into the sand?
Apakah faktor yang menyebabkan bata Y lebih tenggelam ke dalam pasir?
A Force, F B Weight of the block
Daya, F Berat blok
A
B C D
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 33
C Pressure, P D Density of the block
Tekanan,P Ketumpatan blok
3. Diagram 2 shows the arrangement of an apparatus for an experiment.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan susunan radas bagi satu eksperimen.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
Which of the following conclusions is correct ?
Yang manakah antara kesimpulan-kesimpulan berikut adalah betul ?
A Liquid pressure acts perpendicularly to its surface.
Tekanan cecair bertindak tegak pada permukaannya.
B Liquid pressure increases with depth.
Tekanan cecair bertambah dengan kedalaman.
C Liquid pressure does not depend on the shape of the container.
Tekanan cecair tidak bergantung pada bentuk bekas isiannya.
D Liquid pressure is caused by its weight acting on a surface.
Tekanan cecair disebabkan oleh beratnya yang bertindak ke atas permukaan.
4. Diagram 3 shows a block of wood is being pushed into water.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan satu bongkah kayu ditolak masuk ke dalam air.
Diagram 3
liquid
cecair
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 34
Rajah 3
Which graph shows the correct relationship between the pressure, P exerted on the
block and depth, X?
Manakah graf yang menunjukkan hubungan yang betul di antara tekanan, P yang
dikenakan ke atas bongkah dan kedalaman, X ?
A B
C D
5. Diagram 4 shows a cylinder containing cooking oil.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan sebuah silinder yang mengandungi minyak masak.
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
The density of cooking oil is 800 kg m
-3.
The pressure exerted by the cooking oil at
the base is 2.4 x 10
3
Pa. What is the height of oil in the container?
Ketumpatan minyak masak ialah 800 kg m
-3
.
Tekanan yang dikenakan oleh minyak
masak pada dasar bekas 2.4 x 10
3
Pa. Berapakah ketinggian minyak di dalam bekas?
A 24 cm B 30 cm
C 80 cm D 2400 cm
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 35
6 The density of substance X is 200 kgm
-3
.
In which liquid will substance X floats?
Ketumpatan bagi bahan X ialah 200 kgm
-3
.
Didalam cecair yang manakah bahan X akan terapung?
Liquid Density (kgm
-3
)
Cecair Ketumpatan (kgm
-3
)
A P 150
B Q 170
C R 190
D S 220
7. Diagram 5 shows four identical container are filled with same amount of different
liquid.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan empat bekas yang sama diisi dengan jumlah cecair yang sama
tetapi berbeza ketumpatannya.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Which container exerts the highest pressure at the bottom?
Bekas manakah yang menghasilkan tekanan pada bahagian dasar yang paling tinggi?
A Liquid P B Liquid Q
Cecair P Cecair Q
C Liquid R D Liquid S
Cecair R Cecair S
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 36
8. Which of the following pressure,P in liquid against depth,h, graphs is correct?
Manakah antara graf tekanan di dalam cecai,r P melawan kedalaman, h, berikut
adalah betul?
A B
C D
9. Which of the following can be done to increase the kinetic energy of gas molecules in
an air-tight container?
Manakah yang berikut dapat dilakukan untuk menambah tenaga kinetik molekul-
molekul gas dalam satu bekas yang kedap udara?
A Increase the volume of the container.
Menambah isipadu bekas.
B Decrease the volume of the container.
Mengurang isipadu bekas.
C Increase the temperature of the container.
Menambah suhu bekas.
D Decrease the temperature of the container.
Mengurang suhu bekas.
10 Why the atmospheric pressure at higher altitude is lower?
Mengapa tekanan atmosfera semakin berkurang pada tempat yang semakin tinggi
altitudnya ?
A Temperature is decreasing B The layer of air is thinner
Suhu semakin berkurang Lapisan udara semakin nipis
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 37
C Density of air increasing D The volume of air does not
Ketumpatan udara meningkat. change
Isipadu udara tidak berubah
11. Diagram 6 shows a manometer is connected to a gas supply.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan satu manometer yang disambung ke satu bekalan gas.
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
The difference in height, h will increase if
Beza pada ketinggian, h akan bertambah jika
A the pressure of the gas supply is decreased.
Tekanan bekalan gas dikurangkan.
B the water is replaced with a liquid of greater density
air diganti dengan cecair yang lebih tumpat
C the water is replaced with a liquid of smaller density
air diganti dengan cecair yang kurang tumpat
D the manometer is placed at a region of higher atmospheric pressure.
Manometer itu diletak pada kawasan yang tekanan atmosfera
lebih tinggi.
12. Diagram 7 shows a suction pump is pressed on a smooth surface. P and Q are the
pressure acted towards the outer surface and the inner surface of the suction pump
respectively.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan satu pam penyedup yang sedang ditekan pada satu
permukaan yang licin. P dan Q adalah tekanan yang bertindak di permukaan luar
dan di permukaan dalam pam penyedup masing-masing.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 38
The pump is stuck to the smooth surface due to
Pam itu melekat ke permukaan licin disebabkan oleh
A P < Q B P > Q
C P = Q D Q = 0
13. Diagram 8 shows a simple mercury barometer.
How does the length, y and the pressure in space X change as the barometer is
taken from the base to the top of the mountain?
Rajah 8 menunjukkan satu barometer merkuri ringkas.
Bagaimanakah panjang y dan tekanan dalam ruang X berubah jika barometer itu
dibawa dari kaki bukit ke puncak bukit itu?
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
LENGTH, y PRESSURE
PANJANG, Y TEKANAN
A Decreases Decreases
smooth surface
permukaan licin
suction pump
pam penyedup
Q
P
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 39
Berkurang Berkurang
B Decreases No change
Berkurang Tidak berubah
C Increases Decreases
Bertambah Berkurang
D Increases No change
Bertambah Tidak berubah
14. Diagram 9 shows a simple mercury barometer. Which of the height A, B, C or D
shows the measurement of the atmospheric pressure?
Rajah 9 menunjukkan satu barometer merkuri ringkas. Yang manakah antara
ketinggian A, B, C atau D yang menunjukkan ukuran bagi tekanan atmosfera?
Diagram 9
Rajah 9
15. Diagram 10 shows a hydraulic pump is used to raise a car of mass 1600 kg.
Rajah 10 menunjukkan satu pam hidraulik digunakan untuk mengangkat sebuah
kereta berjisim 1600 kg.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 40
Diagram 10
Rajah 10
The ratio of the diameter of the larger piston to the diameter of the smaller piston is 4.
What is the force required to raise the car?
Nisbah diameter omboh besar kepada diameter omboh kecil ialah 4. Berapakah daya
untuk menaikkan kereta tersebut?
A 100 N B 400 N
C 1000 N D 4000 N
16. Diagram 11 shows a hydraulic pump.
Rajah 11 menunjukkan sebuah pam hidraulik.
Diagram 11
Rajah 11
Which of the following is true about hydraulic pump?
Antara berikut, yang manakah benar tentang pam hidraulik?
A The most suitable type of liquid used is water.
Jenis cecair yang paling sesuai digunakan ialah air.
B Weight of load,W equivalent to force applied,F.
Berat beban, W sama dengan daya yang digunakan, F.
C Pressure on Piston A is bigger than pressure on Piston B.
Tekanan pada omboh A lebih besar daripada tekanan pada omboh B.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 41
D The bigger the surface area of piston A, the bigger the weight of load,W can
be put on.
Semakin bertambah luas permukaan omboh A, semakin bertambah berat
beban, W dapat diletakkan.
17. Diagram 12 shows a hydraulic system which is in equilibrium. When the piston A is
pushed in, the piston B will be lifted up
Rajah 12 menunjukkan satu sistem hidraulik dalam keseimbangan. Apabila omboh
kecil ditekan ke dalam, omboh besar akan terangkat ke atas
Which of the following statements is true?
Yang manakah antara kenyataan-kenyataan berikut adalah benar?
A The pressure on the piston A is smaller than the pressure on the piston B.
Tekanan pada omboh A lebih kecil daripada tekanan pada omboh B.
B The pressure on the piston A is bigger than the pressure on the piston B.
Tekanan pada omboh A lebih besar daripada tekanan pada omboh B.
C The pressure on the piston A is equal to the pressure on the piston B.
Tekanan pada omboh A sama dengan tekanan pada omboh B.
18. Diagram 13 shows an apple is floating in a beaker of water.
Rajah 13 menunjukkan sebiji epal sedang terapung dalam sebuah bikar berisi air.
hydraulic fluid
cecair hidraulik
Piston B
Omboh B
Piston A
Omboh A
pushed in
ditekan ke dalam
lifted up
terangkat ke atas
Diagram 12
Rajah 12
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 42
Diagram 13
Rajah 13
Which of the following statements describes the buoyant force correctly?
Manakah pernyataan berikut menerangkan daya keapungan dengan betul?
A The buoyant force equals to the mass of the apple.
Daya keapungan sama dengan jisim epal.
B The buoyant force equals to the weight of the apple.
Daya keapungan sama dengan berat epal.
C The buoyant force equals to the mass of the water displaced.
Daya keapungan sama dengan jisim air yang disesarkan.
D The buoyant force equals to the volume of the water displaced.
Daya keapungan sama dengan isipadu air yang disesarkan.
19. Diagram 14 shows a ship full with load floating on the surface of sea water.
Rajah 14 menunjukkan sebuah kapal yang penuh dengan beban terapung di atas
permukaan air laut.
Diagram 14
Rajah 14
If the water displaced by the ship is 350 m
3
, what is the buoyant force acted on the
ship?
[Density of sea water = 1030 kgm
-3
]
Apple
epal
Air
water
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 43
Jika air yang tersesar oleh kapal ialah 350 m
3
, berapakah daya tujah yang bertindak
ke atas kapal?
[Ketumpatan air laut = 1030 kgm
-3
]
A 3.6 x 10
5
N B 3.6 x 10
6
N
C 3.6 x 10
7
N D 3.6 x 10
8
N
20. Diagram 15 shows a spring balance supporting a metal block is immersed slowly into
a beaker, A which filled with water. The compression balance shows the reading of
the weight, W of a beaker, B filled with water.
Rajah 15 menunjukkan sebuah neraca spring menyokong satu blok logam yang
direndamkan secara beransur-ansur ke dalam satu bikar, A yang berisi air. Neraca
mampatan menunjukkan bacaan berat, W bagi sebuah bikar, B yang berisi air.
Which of the following W against x graphs is correct?
Yang manakah antara graf-graf W melawan x adalah betul?
A B
Diagram 15
Rajah 15
W
x
0
W
x
0
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 44
C D
21. Diagram 16 shows a Bernoullis tube. Air is blown from left to right.
Rajah 16 menunjukkan sebuah tiub Bernoulli. Udara ditiup dari arah kiri ke kanan.
Diagram 16
Rajah 16
Which of the following diagram shows the correct level of water in tube T, U, V
and W?
Antara rajah- rajah berikut, yang manakah menunjukkan aras air yang betul pada
tiub T, U, V dan W?
A.
B.
W
x
0
W
x
0
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 45
C.
D.
22 Diagram 17 shows a baseball which is thrown forward with a spinning, is moving in
a curve.
Rajah 17 menunjukkan satu bola lisut yang dilontar ke hadapan dengan suatu
putaran, sedang bergerak dalam satu lengkungan.
This situation can be explained by using
Keadaan ini boleh diterangkan dengan menggunakan
Diagram 17
Rajah 17
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 46
A Archimedes principle
Prinsip Archimedes
B Bernoullis principle
Prinsip Bernoulli
C Pascals principle
Prinsip Pascal
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 2.1 shows two different containers filled with water. The water pressure at
point P and point Q are the same.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan dua bekas berlainan diisi dengan air. Tekanan air pada titik
P dan titik Q adalah sama.
Diagram 2.1
Rajah 2.1
(a) What is the meaning of pressure?
Apakah maksud tekanan?
......
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) State one factor that affect the water pressure at point P and Q.
Nyatakan satu faktor yang mempengaruhi tekanan air di titik P dan titik Q.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 47
.....
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) Calculate the water pressure at point P.
[Density of water = 1000 kgm
-3
]
Hitungkan tekanan air pada titik P.
[Ketumpatan air = 1000 kgm
-3
]
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) Diagram 2.2 shows the water spurt when a hole is made near the base of
container B.
Rajah 2.2 menunjukkan pancutan air apabila satu lubang dibuat berdekatan
dengan dasar bekas B.
Diagram 2.2
Rajah 2.2
Diagram 2.3 shows the water in container B is replaced by liquid X which has
higher density than water.
Rajah 2.3 menunjukkan air dalam bekas B digantikan dengan cecair X yang
mempunyai ketumpatan yang lebih tinggi daripada air.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 48
Diagram 2.3
Rajah 2.3
Sketch the spurt of liquid X on Diagram 2.3.
Lakarkan pancutan cecair X pada Rajah 2.3. 1 mark]
[1 markah]
2. Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2 show two balloons A and B exerted with the same
force .
Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2 menunjukkan dua belon A dan B dikenakan daya yang
sama.
Diagram 5.1 Diagram 5.2
Rajah 5.1 Rajah 5.2
(a) What is meant by pressure ?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan tekanan ?
..
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 49
(b) Based on Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2,
Berdasarkan Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2
(i) Which balloon will burst easily?
Belon manakah yang akan mudah pecah ?
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Compare the pressure exerted to the balloon
Bandingkan tekanan yang dikenakan ke atas belon.
.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Compare the surface area of finger and needle which in contact with
the balloon.
Bandingkan luas permukaan jari dan jarum yang bersentuh pada
belon
.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iv) Relate the pressure exerted on the balloon with the surface area
Hubungkaitkan antara tekanan yang dikenakan pada belon dengan
luas permukaan
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(v) What happens to the pressure on the balloon if force exerted is
increased?
Apakah yang akan berlaku kepada tekanan yang dikenakan ke atas
belon, jika daya yang dikenakan bertambah ?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 50
(c) State the physics concept involved
Nyatakan konsep fizik yang terlibat dalam Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(d) State one application of physics concept in 5 (c) in our daily life
Nyatakan satu aplikasi konsep fizik dalam 5 (c) dalam kehidupan seharian
kita
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
PAPER 2 SECTION C
3. Diagram 11.1 shows two boats of the same weight floating on the surface of water in
the sea and in the river.
Rajah 11.1 menunjukkan dua buah kapal berjisim sama , terapung di permukaan air
di sungai dan di laut.
Diagram 11.1
Rajah 11.1
(a) (i) What is meant by weight?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan berat?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Explain why the boat is able to float?
Terangkan kenapa kapal itu boleh terapung? [1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 51
(iii) Explain why the sinking levels of the boats are different in the
river and in the sea.
Terangkan kenapa paras kapal yang tenggelam berbeza di dalam
sungaii dan di dalam laut? [3 marks]
[3 markah]
(b) If the volume of the boat that sinks in sea water is 250 m
3
and the density of
sea water is 1080kgm
-3
, calculate
Jika isipadu kapal yang tenggelam dalam air laut ialah 250 m
3
dan
ketumpatan air laut a dalah 1080 kgm
-3
, kirakan
(i) upthrust which acts on the boat.
tujahan yang bertindak ke atas kapal. 3 marks]
[3 markah]
(ii) the volume of water displaced when the boat is in the river.
[Density of river water = 1000 kgm
-3
]
isipadu air yang disesarkan apabila kapal itu berada dalam sungai.
[Ketumpatan air sungai = 1000 kgm
-3
]
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c) Diagram 11.2 shows the specifications of four hydrometers P, Q, R and S.
Rajah 11.2 menunjukkan keterangan-keterangan bagi empat hydrometer P, Q,
R dan S.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 52
Diagram 11.2
Rajah 11.2
You are asked to measure the density of an acid solution.
Anda ditugaskan untuk mengukur ketumpatan suatu larutan asid.
(i) Study hydrometers P,Q,R and S in diagram 11.2 and explain the
suitability of each features to determine the density of acid solution.
Kaji semua hidrometer P,Q,R dan S dalam rajah 11.2 dan terangkan
kesesuaian setiap binaan untuk mengukur ketumpatan suatu larutan
asid.
(ii) Determine the most suitable hydrometer to be used to measure the
density of an acid solution.
Give reasons for your choice.
Tentukan hidrometer yang paling sesuai untuk digunakan bagi
mengukur ketumpatan suatu larutan asid.
Beri sebab untuk pilihan anda.
[10 marks]
[10 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 53
PAPER 3 SECTION A
1 A student carried out an experiment to investigate the relationship between the depth,
h, of a test tube which floats vertically in water and the number of steel ball
bearings, N, in the test tube.
The results of this experiment are shown in the graph of h against N in Diagram 2.1
Seorang murid telah menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat hubungan antara
kedalaman, h satu tabung uji yang terapung tegak dalam air dan bilangan bebola
logam, N dalam tabung uji itu.
Keputusan eksperimen ini ditunjukkan oleh graf h melawan N pada Rajah 2.1
(a) Based on graph in Diagram 2.1 :
Berdasarkan graf pada Rajah 2.1 :
(i) State the relationship between h and N.
Nyatakan hubungan antara h dan N.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Determine the value of h when N = 0.
Show on the graph, how you determine the value of h.
Tentukan nilai h apabila N = 0.
Tunjukkan pada graf itu bagaimanaanda menentukan nilai h.
h = .. cm
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(iii) Determine the value of N when h = 12.6 cm
Show on the graph how you determine the value of N.
Tentukan nilai N apabila h = 12.6 cm.
Tunjukkan pada graf itu bagaimana anda menentukan nilai N.
N = ..
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 54
h /cm
12
13
14
11
10
0 2 8 4 10 6
N
Diagram 2.1
Rajah 2.1
12 14
Graph of h against N
Graf h lawan N
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 55
(b) Calculate the gradient, k, of the graph.
Show on the graph how you calculate k.
Hitung kecerunan, k, bagi graf itu.
Tunjukkan pada graf itu bagaimana anda menghitung k.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(c) The mass, m, of a steel ball bearing is given by the formula m = 5.455 d
2
k,
where k is the gradient of the graph and d is the diameter of a steel ball
bearing. In this experiment, d = 2.50 cm.
Calculate the value of m.
Jisim, m, bagi bebola logam itu diberi oleh formula m = 5.455 d
2
k,
dengan keadaan k ialah kecerunan graf dan d ialah diameter bebola logam.
Dalam eksperimen ini, d = 2.50 cm.
Hitung nilai m.
m = .
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) State one precaution that should be taken to improve the accuracy of the result
of this experiment.
Nyatakan satu langkah berjaga-jaga yang perlu diambil untuk memperbaiki
ketepatan bacaan dalam eksperimen ini.
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 56
PAPER 3 SECTION B
2 Diagram 3.1 shows an inverted beaker contains an air trapped is converted and
immersed in the water.
Diagram 3.2 shows the volume of air trapped in the beaker decreased when the beaker
is pushed down in the water.
Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan satu bikar yang ditelangkupkan mengandungi udara yang
terperangkap ditenggelamkan ke dalam air.
Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan isipadu udara terperangkap di dalam bikar berkurang
apabila bikar ditolak ke dalam air.
Diagram 3.1 Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.1 Rajah 3.2
Based on your observation on the volume of air trapped in the beaker;
Berdasarkan pemerhatian ke atas isipadu udara terperangkap di dalam bikar;
(a) State one suitable inference,
Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) State one appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated,
Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang boleh disiasat [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c ) With use of apparatus such as a syringe , thick rubber tube and other
apparatus, escribe an experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in 2(b)
Dengan menggunakan radas yang seperti sebuah picagari, tiub getah tebal
dan lain-lain radas yang sesuai, terangkan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat
hipotesis yang dinyatakan di 2(b).
In your description, state clearly the following :
Dalam penerangan anda, jelaskan perkara berikut;
(i) The aim of an experiment
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 57
Tujuan eksperimen
(ii) The variable in experiment
Pembolehubah eksperimen
(iii) The list of apparatus and materials
Senarai alat radas dan bahan
(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus
Susunan alat radas
(v) The procedure of the experiment.
Describes how to control and measure the manipulated variables and
how to measure the responding variables.
Prosedur eksperimen.
Jelaskan bagaimana mengawal dan mengukur pembolehubah
manipulasi dan
Bagaimana mengukur pembolehubah bergerakbalas.
(vi) The way to tabulate tabulate the data
Kaedah menjadual data
(vii) The way to analyze the data
Kaedah menganalisa data
[10 marks]
[10 markah}
3 Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 show a worker using a piece of straight long and
uniform wood to determine the depth of a hole filled with water.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 58
Rajah 3 menunjukkan seorang pekerja menggunakan sebatang kayu panjang yang
seragam untuk menentukan kedalaman sebuah lubang yang dipenuhi air.
Diagram 3.1 Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.1 Rajah 3.2
When the worker pushed the wood into the water as shown in Diagram 3.1 , he has
to apply only a small force .
When the worker pushed the wood deeper as shown in Diagram 3.2, he has to apply
a larger force.
Apabila pekerja itu menolak kayu itu ke dalam air seperti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah
3.1, dia perlu mengenakan daya yang kecil.
Apabila pekerja itu menolak kayu lebih ke dalam seoerti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah
3.2, dia perlu mengenakan daya yang lebih besar.
Based on the observation and the information;
Berdasarkan pemerhatian dan maklumat;
(a) State one suitable inference,
Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) State one appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated,
Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang boleh disiasat [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c ) With use of apparatus such as a metal block , spring balance, beaker and other
apparatus, describe an experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in 3(b).
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 59
Dengan menggunakan radas seperti bonkah logami,neraca spring, bikar
dan Lain-lain radas yang sesuai, terangkan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat
hipotesis yang dinyatakan di 3(b).
In your description, state clearly the following :
Dalam penerangan anda, jelaskan perkara berikut;
(i) The aim of an experiment
Tujuan eksperimen
(ii) The variable in experiment
Pembolehubah eksperimen
(iii) The list of apparatus and materials
Senarai alat radas dan bahan
(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus
Susunan alat radas
(v) The procedure of the experiment.
Describes how to control and measure the manipulated variables and
how to measure the responding variables.
Prosedur eksperimen.
Jelaskan bagaimana mengawal dan mengukur pembolehubah
manipulasi dan bagaimana mengukur pembolehubah bergerakbalas.
(vi) The way to tabulate tabulate the data
Kaedah menjadual data
(vii) The way to analyze the data
Kaedah menganalisa data
[10 marks]
[10 markah]
CHAPTER 3 : FORCE AND PRESSURE
S
C
H
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 60
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 D 7 D 13 D 19 B
2 C 8 C 14 C 20 A
3 C 9 C 15 D 21 A
4 C 10 B 16 D 22 B
5 B 11 B 17 C
6 D 12 B 18 B
PAPER 2
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1 (a)
Pressure =
1 1
(b) Depth / Density / gravity
1
1
(c) P = hg
= 0.12 x 1000 x 10
= 1200 Pa.
1
1
2
(d)
1 1
TOTAL 5
1 (a)
Pressure = 1 1
(b) (i) Balloon B /diagram 5.2 is bigger 1
(ii) Pressure of needle is higher/greater than finger/vice versa 1
NO SCHEME SUB MARK TOTAL
MARK
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 61
(iii) The surface area of needle is smaller than finger/ vice
versa
1
5 (iv) As the pressure increases, the surface area decreases/
pressure is inversely proportional to surface area.
1
(v) Pressure increase
1
(c) Pressure depends on force and surface Area // pressure
1 1
(d) The handle of the bag has large area to reduce the
pressure on the hand/the edge of knifes blade is small/the
studs of football is small/ skis have large area/ suitable
item
1 1
TOTAL 8
3(a)(i) Weight is the gravitational force acts an object. 1
5
(ii) Upthrust = weight of the boat 1
(iii) Sea water is denser
Boat displaced less sea water and gain the same upthrust .
Therefore boat sinks less in sea water
1
1
1
(b)(i) Upthrust = mass of sea water displaced
= mg
= Vg
= 250 X 1080 X 10 = 2.7 X 10
6
N
1
1
1
5
(b)(ii) 2. 7 X 10
6
= V X 1000 X 10
V = 270 m
3
1
1
(c)(i)
Specifications Reasons
Small stem
and long.
Increase the sensitivity where the
scale
divisions are far apart so that small
changes in density can be detected.
2
Glass wall Do not erode and small adhesive
force.
2
Large
diameter of
bulb.
High upthrust /displaces more
liquid/to
be able to float easily.
2
Lead shots Hydrometer can stay upright. 2
8
10
(c)(ii) P is chosen
Small and long stem, glass wall, large diameter of bulb and
lead shots used.
1
1
TOTAL 20
NO SCHEME SUB MARK TOTAL
MARK
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 62
1(a)(i) h increased linearly with N.
1
6
(ii) - Extrapolate line intercept h axis.
- show on graph the value of h (with unit)
- state the value of h = 12.6 cm
1
1
1
- show horizontal line from 13.4 cm touches the
graph then vertical line until it touches the n axis.
- N = 9 (from the graph = 9.2)
1
1
(b) show A with an acceptable size. ( > 8 cm x 8 cm)
- substitute correctly
y
2
y
1
13.2 -11.0
-------- = -----------
x
2
x
1
12.0 2.0
- state the value of gradient and its value k = 0.22 cm
1
1
1
3
(c) m = 5.455 d
2
k
= 5.455 (2.5)
2
(0.22) .. gantian betul
= 7.5 (tanpa unit)
1
1
2
(d) The position of eye should be in line with the scale of
reading as measurement to be taken, as to avoid parallax
error // Do repeated readings for h three times for aech
value of N and find the average value of h as to increase
the accuracy of readings
1 1
TOTAL 12M
2(a) Pressure depends on volume// Volume influences pressure
1 1
(b) When the volume decrease , the pressure increase ,
1 1
(c) M1 Menyatakan tujuan dengan betul
To investigate the relationship between
volume and pressure
M2 Menyatakan pembolehubah manipulasi dan
bergerakbalas dengan betul
Manipulated : volume
Responding : pressure
M3 Menyatakan pembolehubah yang dimalarkan dengan
betul
Fixed : mass of gas // temperature
M4 Menyatakan alat radas dan bahan
Syringe, clip , thick rubber tube, bourdon gauge
NO SCHEME SUB MARK TOTAL
MARK
M5 Melukis/Menyatakan Set-Up radas yang betul
10
12
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 63
M6 Menyatakan kaedah mengawal pembolehubah
manipulasi
The piston of the 100 cm
-3
syringe is adjusted until
the volume of air in the syringe at atmospheric
pressure.The other end of the rubber tube is connected
to bourdon gauge and the pressure of the air in the
syringe is read on the gauge.
The piston of the syringe is pushed in until the
enclosed volume is 98 cm
3
/ V
1
.
M7 Menyatakan kaedah mengawal pembolehubah
bergerakbalas.
The pressure on the Bourdon gauge is recorded.
M8 Menyatakan ulangan eksperimen
The steps is repeated for an enclosed volume of
96 cm
3
/V
2
, 94 cm
3
/V
3
, 92cm
3
/V
4
, 90 cm
3
/V
5
M9 Menyatakan kaedah menjadual data dengan betul
tajuk//symbol dengan unit yang betul
Volume, V (cm
3
) Pressure, P (Nm
-2
)
98
96
94
92
90
M10 Menyatakan kaedah menganalisa data dengan betul
3 (a) Inference: The buoyant force depends on volume of water displaced 1
(b) Hypothesis: As the volume of water displaced increases, the buoyant force
will also increase
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 64
(c) (i) Aim: To investigate the relationship between the volume of water
displaced and the buoyant force acting on an object.
1
(ii) Variables: Manipulated: Volume Of Water displaced
Responding: Buoyant Force
Constant: Density of liquid
1
1
(iii) Apparatus And Material:
Spring balance, metal rod, measuring cylinder
1
(iv) Arrangement of apparatus:
1
(v) Procedure
- Weight of cylinder in air is measured.using spring balance, W
- Rod is lowered into the water until the volume immersed , V is 50 cm
3
- The reading of spring balances is then recorded, W
o
.
- Buoyant force, F
b,
is calculated by F
b
= W W
o
- The experiment is then repeated for volume of the rod V = 100 cm
3
, 150
cm
3
, 200 cm
3
, and 250 cm
3
.
1
1
1
(vi) Way you tabulate data
V / cm
3
W / N W
o
/ N Buoyant
Force, F
b
50
100
150
200
250
1
(vii) Analyse data
1
TOTAL 12
CHAPTER 4: HEAT
PAPER 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 65
1. Diagram 1 shows block L and block M of different material are in thermal
equilibrium .
Rajah 1 menunjukkan bongkah L dan bongkah M daripada bahan yang berlainan
berada dalam keseimbangan termal.
o o
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Which of following statements is true?
Yang manakah antara pernyataan berikut adalah benar?
A specific heat capacity of L = specfic heat capacity of M
muatan haba tentu L = muatan haba tentu M.
B The net rate of heat transferred is equal
Kadar pemindahan haba bersih adalah sama
C The net rate of heat transferred is zero
Kadar pemindahan haba bersih adalah sifar
D Temperature of L is higher than temperature of M.
Suhu L lebih tinggi daripada suhu M.
2. Water takes a shorter time to boil when heated at high lands than at low lands,
although the same amount of energy is used.
Air lebih cepat mendidih apabila dipanaskan di kawasan tanah tinggi berbanding
kawasan rendah walaupun jumlah tenaga yang sama digunakan
This observation is due to
Pemerhatian ini disebabkan oleh
A the temperature is lower at high lands
suhu lebih rendah di kawasan tanah tinggi
B the atmospheric pressure is lower at high lands
tekanan atmosfera lebih rendah di kawasan tanah tinggi
Thermometer
termometer
Thermometer
termometer
L M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 66
C the air is less damp at high lands
kelembapan udara lebih rendah di kawasan tanah tinggi
D the rate of heat lost is faster at high lands
kadar pembebasan haba lebih cepat di kawasan tinggi
3. Diagram 2 shows a thermometer.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan sebuah termometer.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
Which modification will increase the sensitivity of the thermometer?
Pengubahsuaian yang manakah akan menambah kepekaan termometer?
A Using a longer capillary tube
Menggunakan tiub rerambut yang lebih panjang
B Using a glass stem with a thicker wall
Menggunakan dinding batang kaca yang lebih tebal
C Using a bulb with thicker wall
Menggunakan dinding bebuli yang lebih tebal
D Using a narrower bore of capillary tube
Menggunakan liang tiub rerambut yang lebih halus
4 Diagram 3 shows a mercury thermometer which has not been calibrated. The length
of mercury column in the thermometer is 5 cm at 0
0
C and 50 cm at 100
0
C.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan sebuah termometer merkuri yang belum ditentukur. Panjang
Bulb
bebuli
Mercury
merkuri
Capillary tube
Tiub rerambut
Glass stem
Batang kaca
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 67
turus merkuri pada thermometer ialah 5 cm pada 0
0
C dan 50 cm pada 100
0
C.
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
When the thermometer is placed in hot water, the length of the mercury column is
35 cm. What is the temperature of hot water?
Apabila termometer itu dimasukkan ke dalam air panas, panjang turus merkuri
menjadi 35 cm. Berapakah suhu air panas?
A 35.0
0
C B 40.0
0
C
C 66.7
0
C D 70.0
0
C
5. The temperature of 5 kg of water rises by 50
0
C when heated. What is the
temperature rise when 8 kg of water is heated by the same amount of heat energy?
Suhu bagi 5 kg air meningkat sebanyak 50
0
C apabila dipanaskan. Berapakah
peningkatan suhu apabila 8 kg air dipanaskan dengan jumlah tenaga haba yang
sama?
A 20.75
0
C B 31.25
0
C
C 40.00
0
C D 80.00
0
C
6 Diagram 4 shows the cooling curve of a substance.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan lengkung penyejukan suatu bahan.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 68
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
At which phase, A, B, C or D is the substance is in solid and liquid at the same time?
Pada fasa manakah, A, B, C atau D bahan itu dalam keadaan pepejal dan cecair
pada masa yang sama?
7. Diagram 5 shows the heating curve of water.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan lengkung pemanasan bagi air.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 69
Which of the following statements is correct to explain the effect of the heat absorbed
by the water between point R and S?
Yang manakah antara penyataan-pernyataan berikut adalah betul untuk
menerangkan kesan haba yang diserap oleh air antara titik R dan S?
A Weakens the forces between the water molecules
Melemahkan daya-daya antara molekul-molekul air
B Breaks the bonds between the water molecules
Memutuskan ikatan-ikatan antara molekul-molekul air
C Increases the kinetic energy of the water molecules
Menambah tenaga kinetik molekul-molekul air
D Strengthens the bonds between the water molecules
Menguatkan ikatan-ikatan antara molekul-molekul air
8. Diagram 6 shows two blocks M and N of equal masses and initial temperature are
being heated with the same amount of heat energy.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 70
Rajah 6 menunjukkan dua blok M dan N yang sama jisim dan suhu awal sedang
dipanaskan dengan jumlah tenaga haba yang sama.
.
It is observed that M is hot faster than N. This observation is due to
Diperhatikan bahawa M lebih cepat panas berbanding dengan N. Pemerhatian ini
adalah disebabkan oleh
A density M < density N
ketumpatan M < ketumpatan N
B density M > density N
ketumpatan M > ketumpatan N
C specific heat capacity M < specific heat capacity N
muatan haba tentu M < muatan haba tentu N
D specific heat capacity M > specific heat capacity N
muatan haba tentu M > muatan haba tentu N
9. Table 1 shows the specific heat capacity for materials R, S and T.
Jadual 1 menunjukkan muatan haba tentu bagi bahan-bahan R, S dan T.
.
Which of the following pairs is most suitable for making the base and the handle of
the frying pan?
Material Specific heat capacity/Jkg
-1
C
-1
R 428
S 850
T 3500
Heat shield
Perisai haba
stove
dapur
Block M
Blok M
Block N
Blok N
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
Table 1
Jadual 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 71
Yang manakah antara pasangan-pasangan berikut adalah paling sesuai untuk
dijadikan dasar dan pemegang bagi kuali memanas?
Base of the frying pan Handle of the frying pan
Dasar kuali memanas Pemegang kuali memanas
A R T
B T R
C S T
D T S
10 Diagram 7 shows a balloon filled with cool air is placed in a hot room.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan sebiji belon berisi dengan udara sejuk diletakkan dalam
sebuah bilik yang panas.
After a while, what happens to the balloon?
Selepas seketika, apakah yang berlaku kepada belon itu ?
A. It rises to the ceiling B. It falls to the floor
Ia naik ke siling Ia jatuh ke lantai
C. It expands D. It contracts
Ia mengembang Ia mengecut
11. Diagram 8 shows a metal cylinder of mass 5.0 kg and specific heat capacity
400 J kg
1 o
C
1
is heated with a heater of power 1 KW.
balloon
belon
cool air
udara sejuk
hot room
bilik panas
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 72
Rajah 8 menunjukkan satu silinder logam yang berjisim 5.0 kg dan muatan haba
tentu 400 Jkg
1 o
C
1
dipanaskan dengan pemanas yang berkuasa 1 KW.
What is the rise in temperature of the cylinder if the heater is switched on for 10
seconds?
Berapakah kenaikan suhu silinder itu jika pemanas dihidupkan selama 10 saat ?
A 0.20
o
C B 0.80
o
C
C 1.25
o
C D 5.00
o
C
PAPER 2 SECTION A
thermometer
termometer
heater
pemanas
metal cylinder
silinder logam
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 73
1. Diagram 1 shows a metal sphere with initial temperature of 30
o
C is immersed in
boiling water.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan sebiji sfera logam yang mempunyai suhu awal 30
o
C direndam
dalam air mendidih.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
(a) (i) What happen to the temperature of the metal sphere?
Apakah yang berlaku kepada suhu sfera logam ?
....
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Give a reason for the answer in 1(a)(i).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan dalam 1(a)(i).
....
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) After sometime, the metal sphere and the boiling water have the same
temperature.
Selepas beberapa ketika, sfera logam dan air mendidih itu mempunyai suhu
yang sama.
(i) Tick ( ) in the box below for the correct statement about heat flows
between the metal sphere and the boiling water.
Tandakan ( ) dalam kotak di bawah bagi pernyataan yang betul
tentang pengaliran haba di antara sfera logam dan air mendidih.
The rate of heat flows from boiling water < the rate of heat
flows from metal sphere.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 74
Kadar pengaliran haba dari air mendidih < kadar pengaliran
haba dari sfera logam.
The rate of heat flows from boiling water = the rate of heat
flows from metal sphere.
Kadar pengaliran haba dari air mendidih = kadar pengaliran
haba dari sfera logam.
The rate of heat flows from boiling water > the rate of heat
flows from metal sphere.
Kadar pengaliran haba dari air mendidih > kadar pengaliran
haba dari sfera logam.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) State the physics concept involve in 1(b) (i).
Nyatakan konsep fizik yang terlibat dalam 1(b) (i).
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
2. A substance X with mass 0.5 kg is heated by using a heater 100 W.
Diagram 2 shows graph temperature against mass for the substance.
Suatu bahan X berjisim 0.5 kg dipanaskan dengan menggunakan pemanas 100 W.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan graf suhu melawan masa bagi bahan tersebut.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
(a). What is the time taken by substance X to achieve melting point ?
Berapakah masa yang diambil oleh bahan X untuk mencapai takat lebur?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 75
[1 mark]
[ 1markah]
(b). Based on information on graph, find specific latent heat for the substance X.
Berdasarkan maklumat yang diberi pada graf, hitungkan haba pendam tentu
bagi bahan X
[2 marks]
[ 2 markah]
(c). By using kinetic theory, explain why there is no increase in temperature at
QR.
Dengan menggunakan teori kinetik, terangkan mengapa tiada kenaikan suhu
pada QR.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
[ 2 markah]
3. Diagram 3 shows a wet towel is placed on the forehead of a boy who has high fever.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan tuala yang basah diletakkan di atas dahi seorang budak lelaki
yang mengalami demam panas.
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
(a) What is the meaning of thermal equilibrium?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan keseimbangan terma?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 76
..
[1 mark]
(b) Explain how a thermal equilibrium is achieved in Diagram 3.
Terangkan bagaimana keseimbangan terma tercapai dalam Rajah 3.
........
[2 marks]
(c) The mass of water used to wet the towel is 0.3 kg and the specific heat
capacity for water is 4 200 J kg
-1 o
C
-1
. The initial temperature of the towel is
30
o
C and the final temperature is 38
o
C. Find the amount of heat energy from
the boy is removed by the wet towel.
Jisim air yang digunakan untuk membasahkan tuala adalah 0.3 kg dan
muatan haba tentu air adalah 4 200 J kg
-1 o
C
-1
. Suhu awal tuala adalah 30
o
C
dan suhu akhir adalah 38
o
C. Hitung jumlah tenaga haba yang telah
dibebaskan daripada budak itu oleh tuala basah.
[2 marks]
(d) What happens to the final temperature if the water used to wet the towel is
mixed with ice cubes?
Apakah yang berlaku kepada suhu akhir jika air yang digunakan untuk
membasahkan tuala dicampurkan dengan ketulan ais?
....
[1 mark]
PAPER 2 SECTION B
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 77
1. Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2 show the heating curves obtained when 50 g and 80 g
of the solid substance are heated respectively. The melting point of the substance is
78
o
C.
Rajah 9.1 dan Rajah 9.2 menunjukkan graf pemanasan yang diperolehi apabila 50 g
dan 80 g bahan itu dipanaskan masing-masing. Takat lebur bahan itu adalah 78
o
C.
Diagram 9.1
Rajah 9.1
Diagram 9.2
Rajah 9.2
(a) (i) What is the meaning of melting point?
Apakah maksud takat lebur?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Based on the information and the observation on Diagram 9.1 and
Diagram 9.2, compare the mass, the time taken to reach the melting
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 78
point and the time taken by the substance to change into liquid
completely.
Berdasarkan maklumat dan pemerhatian pada Rajah 9.1 dan Rajah
9.2, bandingkan jisim,masa yang diambil untuk mencapai takat lebur
dan masa yang diambil untuk bahan itu berubah kepada cecair
sepenuhnya.
Relate the mass and the time taken by the substance to change into
liquid completely to make a deduction on the relationship between the
mass and the latent heat of fusion absorbed by the substance.
Hubungkaitkan antara jisim dengan masa yang diambil untuk bahan
berubah kepada cecair sepenuhnya untuk membuat kesimpulan
tentang hubungan antara jisim dengan haba pendam peleburan yang
diserap oleh bahan itu.
[5 marks]
[5 markah]
(b) Diagram 9.3 shows the phenomenon of sea breeze.
Rajah 9.3 menunjukkan fenomena bayu laut.
Diagram 9.3
Rajah 9.3
Using the concept of specific heat capacity, explain how the phenomenon of
sea breeze occurs.
Menggunakan konsep muatan haba tentu, terangkan bagaimana fenomena
bayu laut berlaku.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(c) Diagram 9.4 shows a design of central heating system used in cold country to
heat and keep houses warm.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 79
Rajah 9.4 menunjukkan suatu rekabentuk sistem pemanasan berpusat yang
digunakan di negara yang berhawa sejuk untuk memanas dan mengekalkan
haba di dalam rumah.
Diagram 9.4
Rajah 9.4
Suggest and explain how to build a house central heating system which can
function effectively based on the following aspects:
Cadang dan terangkan bagaimana untuk membina suatu sistem pemanasan
berpusat sebuah rumah yang boleh berfungsi dengan cekap berdasarkan
aspek-aspek berikut:
(i) The specific heat capacity of the liquid
Muatan haba tentu cecair
(ii) The boiling point of the liquid
Takat didih cecair
(iii) The properties of material used for transmission pipe
Sifat-sifat bahan yang digunakan untuk paip penghantaran cecair
(iv) The size of the fan used to blow the heat from radiator
Saiz kipas yang digunakan untuk meniup haba daripada radiator
[10 marks]
[10 markah]
PAPER 2 SECTION C
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 80
5. (a) What is the meant by specific heat capacity?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan muatan haba tentu?
[1 mark]
Diagram 11.1
Rajah 11.1
(b) Diagram 11.1 shows phenomenon which occur in our daily life. Using a
physics concept,
Rajah 11.1menunjukkan fenomena yang berlaku dalam kehidupan seharian
kita. Menggunakan konsep fizik,
(i) explain how the phenomenon occurs
terangkan bagaimana fenomena berlaku
[3 marks]
(ii) Name the phenomenon that occurs
Namakan fenomena yang berlaku
[1 mark]
(c) Diagram 11.2 shows a graph of temperature against time taken for heating
500 g of a liquid using an immersion heater of 48 W.
Rajah 11.2 menunjukkan graf suhu melawan masa yang diambil untuk
memanaskan 500 g cecair dengan menggunakan pemanas rendam 48 W.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 81
Diagram11.2
Rajah 11.2
Calculate
Hitung
(i) the specific heat capacity of the liquid
muatan haba tentu cecair itu [3 marks]
(ii) the final temperature of the mixture, if after 5 minutes of heating, the
liquid is poured into a beaker that contains 1 kg of water at temperature
of 25
o
C.
Suhu akhir campuran, jika selepas pemanasan selama 5 minit, cecair
itu dituang ke dalam sebuah bikar yang mengandungi 1 kg air pada
suhu 25
o
C.
[2 marks]
(d) Diagram 11.3 shows the arrangement of the apparatus to determine the
specific heat capacity of Aluminium block.
Rajah 11.3 menunjukkan susunan radas untuk menentukan muatan haba tentu
bagi bongkah Aluminium.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 82
Diagram 11.3
Rajah 11.3
Table 11.1 shows the materials that are able to be use in the arrangement of
the apparatus. You are assigned to investigate the materials shown in Table
11.1.
Jadual 11.1 menunjukkan bahan-bahan yang boleh digunakan dalam susunan
radas itu. Anda ditugaskan untuk menyiasat bahan-bahan yang ditunjukkan
dalam Jadual 11.1
Set of
apparatus
Set radas
Material
Bahan
Plate X
Kepingan X
Liquid Y
Cecair Y
Material Z
Bahan Z
Power of
immersion heater
Kuasa pemanas
rendam
P
Wood
Kayu
Water
Air
Tissue
Kertas tisu
12 W
Q
Asbestos
Asbestos
Alcohol
Alkohol
Plain Paper
Kertas biasa
48 W
R
Wood
Kayu
Oil
Minyak
Plain Paper
Kertas biasa
24 W
S
Asbestos
Asbestos
Oil
Minyak
Tissue
Kertas tisu
48 W
T
Copper
Kuprum
Water
Air
Tissue
Kertas tisu
24 W
Table 11.1
Jadual 11.1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 83
Explain the suitability of each material in Table 11.1, then determine the most
suitable set of apparatus to be used to determine the specific heat capacity of
Aluminium.
State the reason for your answer.
Terangkan kesesuaian setiap bahan dalam Jadual 11.1 dan seterusnya
tentukan set radas yang paling sesuai digunakan untuk menentukan muatan
haba tentu pepejal Aluminium itu.
Beri sebab untuk jawapan anda.
[10 marks]
PAPER 3 SECTION A
1. A student carries out an experiment to investigate the relationship between the
temperature, u, of a fixed mass of liquid and the time, t, it has been heated. This
experiment is carried out using the same immersion heater to heat up 400 g of the
liquid. The results of this experiment are shown in the graph of u against t in
Diagram 2.1.
Seorang murid menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk mengkaji hubungan antara suhu,
u, bagi suatu cecair yang berjisim tetap dengan masa, t, ia dipanaskan. Eksperimen
ini dijalankan menggunakan pemanas rendam yang sama untuk memanas 400 g
cecair tersebut. Keputusan eksperimen ini ditunjukkan oleh graf u melawan t pada
Rajah 2.1.
(a) Based on the graph in Diagram 2.1:
Berdasarkan graf pada Rajah 2.1:
(i) What happens to u as t increases?
Apakah yang berlaku pada u apabila t bertambah?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Determine the value of u when t = 0 s.
Show on the graph, how you determine the value of u.
Tentukan nilai u apabila t = 0 s.
Tunjukkan pada graf itu bagaimana anda menentukan nilai u.
u = .
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 84
u/
0
C
t /s
Graph of u against t
Graf u melawan t
1 2 3 4 5 6
Diagram 2.1
Rajah 2.1
0
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 85
(iii) Calculate the gradient, k, of the graph.
Show on the graph how you determine k.
Hitung kecerunan, k, bagi graf itu.
Tunjukkan pada graf itu bagaimana anda menentukan k.
k =
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(b) (i) Specific heat capacity, c, of the liquid is given by the equation:
Muatan haba tentu, c, bagi cecair diberi oleh persamaan,
Where m = mass of the liquid used in this experiment.
k = gradient of the graph.
Dimana m = jisim cecairyang diguna dalam eksperimen ini.
k = kecerunan graf.
Calculate the value of the specific heat capacity, c, of the liquid.
Hitungkan nilai muatan haba tentu, c, cecair tersebut.
c = ..
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 86
(ii) What is the value of c if 800 g of the liquid is used in the experiment?
Berapakah nilai c jika 800 g cecair tersebut digunakan dalam
eksperimen ini?
c = [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) State two precautions that should be taken to improve the results of this
experiment.
Nyatakan dua langkah berjaga-jaga yang perlu diambil untuk memperbaiki
keputusan eksperimen ini.
2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 87
CHAPTER 4 : HEAT
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 C 4 C 7 C 10 C
2 B 5 B 8 C 11 D
3 D 6 C 9 A
PAPER 2-SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a)(i) Increases 1
2
(ii) Metal sphere absorbs heat from boiling water. 1
(b) (i)
The rate of heat flows from boiling water = the rate of
heat flows from metal sphere.
1
2
(ii) Thermal equilibrium 1
TOTAL MARK 4M
2(a) 300 s 1
1
(b) Pt = ml
M1 100 x ( 1050 300) = 0.5 l
M2 l = 150 000 J kg
-1
(with unit)
1
1
2
(c) M1 Heat supplied is used to break up bonds between
molecules
M2 Heat is not used to increase kinetic energy
1
1
2
TOTAL MARK 5M
3(a) Net heat flow is zero / temperature is equal 1
1
(b) M1 The initial temperature of cloth is lower than the body
temperature
M2 Heat energy is transferred until temperature is equal / no
heat loss
1
1
2
(c) M1 0.3 (4200) ( 38 30 )
M2 10080 J (with unit)
1
1
2
(d) Decrease 1
1
TOTAL MARK 6M
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 88
PAPER 2-SECTION B
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
4(a)(i) The temperature in which a solid substance change to liquid at
atmospheric pressure
1
6
(ii) 1. The mass of substance in Diagram 9.1 < in Diagram 9.2
2. Time taken to reach the melting point in Diagram 9.1 < in
Diagram 9.2
3. Time taken by the substance to change into liquid
completely in Diagram 9.1 < in Diagram 9.2
4. The greater the mass the longer the time taken by the
substance to change into liquid completely.
5. The greater the mass the greater the latent heat of fusion
absorbed
1
1
1
1
1
(b) 1. In daytime the sun warms the land to higher temperature
than the sea.
2. The land has a lower specific heat capacity than sea-
water.
3. The air above the land is heated and rises
4. The cooler air above the sea moving to land.
1
1
1
1
4
(c)
Aspect Explanation
High specific heat capacity
of liquid
Becomes hot faster
High boiling point of liquid Not easily change into vapour
Low rate of rusting material Long lasting // not easily rust
Strong material Not easily breaks
The size of the fan is big To blow large amount of heat
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
PAPER 2-SECTION C
5(a) The amount of heat energy required to increase the
temperature of 1 kg mass by 1
o
C
1 1
(b)(i) M1 Land has a smaller specific heat capacity than sea //
Land faster increase in temperature // Land is warmer
than the sea
M2 Air above the land is heated up and rises
M3 Cooler air from the sea moves towards the land
1
1
1
3
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 89
NO SCHEME SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
OR DIAGRAM
M1 Label Sea(cold), Land (Hot)
M2 Show Hot air on land rises up
M3 Show Cold air moves towards the sea
3 3
(ii) Sea Breeze 1 1
(c)(i)
M1 Q = Pt // 48 x 5 x 60 // 14 400 J
M2 14 400 = 500 x 10
-3
( c ) ( 80 40 )
M3 720 Jkg
-1o
C
-1
(with unit )
1
1
1
5
(ii) M1 Heat supplied by liquid = Heat received by water
( 500 x 10
-3
)(4200)(80 - u) = (1) ( 4200)( u - 25 )
M2 29.34
o
C (with unit)
1
1
(d)
Characteristics Explanation
Plate X - asbestos a good heat insulator
Liquid Y oil
good heat contact between thermometer
and the Aluminium block // to ensure
thermal equilibrium between
thermometer and aluminium block
Material Z tissue reduce / prevent heat lost to the
surrounding
Immersion heater has high
power
can increase the temperature faster //
fast to heat // supply more heat energy
S Because ...... ( M1,M3,M5 & M7)
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 90
PAPER 3 - SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1 (a)(i) increasing linearly with t 1
6
(ii) M1 Show on graph - Extend the line to intercept at y axis
M2 = 27.3 C
1
1
(iii) M1 Big Triangle is drawn on the graph (at least 8 cm x 8 cm )
M2 36 -29
5- 1
M3 1.75 C / min // 0.0292 C / s
1
1
1
(b)(i)
M1 c = 50
mk
M2 50
0.4 x 0.0292
M3 4.28 x 10
3
J kg
-1
C
-1
1
1
1
4
(ii) Same / 4.28 x 10
3
J kg
-1
C
-1
1
(c) The liquid must be stirred throughout the experiment //
Do repeated readings for temperature for each tme for three
times and get the average reading as to increase the accuracy
// Avoid from wind // Eyes is perpendicular to the scale of
thermometer and stop watch when mesurement is taken as to
avoid parallax error
Any 2 2
TOTAL MARK 12M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 91
CHAPTER 5: LIGHT
PAPER 1
1 Which of the following are the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror?
Yang manakah antara berikut adalah ciri-ciri imej yang dihasilkan oleh cermin
satah?
A. Inverted, same size and real
Songsang, sama saiz dan nyata
B Upright, same size and real
Tegak, sama saiz dan nyata
C Upright, magnified and laterally inverted
Tegak, dibesarkan dan songsang sisi
D Laterally inverted, same size and virtual
Songsang sisi, sama saiz dan maya
2 Which diagram shows the correct reflection of light by a concave mirror?
Rajah manakah yang menunjukkan pantulan cahaya yang betul oleh sebuah cermin
cekung?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 92
3. Which of the following ray diagrams shows the correct reflection of light from a
curved mirror?
Antara rajah-rajah sinar berikut, yang manakah yang menunjukkan pantulan cahaya
yang betul daripada sebuah cermin melengkung?
A
B
C
D
4. Table 1 shows the refractive indices of water and perspex.
Jadual 1 menunjukkan indeks biasan bagi air dan perspek.
Medium
Medium
Refractive index, n
Indeks biasan,n
Water
Air
1.33
Perspex
Perspek
1.49
Table 1
Jadual 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 93
Based on the information in Table 1, which light ray, A, B, C or D is correct?
Berdasarkan maklumat dalam Jadual 1, sinar cahaya A, B, C atau D adalah betul?
5. Diagram 1 shows the path of light travelling from a glass block to air
Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu lintasan cahaya yang merambat melalui satu blok kaca ke
udara .
g
The refractive index of the glass block is
Indeks biasan bagi blok kaca ialah
A B
C D
6. Diagram 2 shows an object placed at a distance, x from a convex lens with a focal
length, f.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu objek diletakkan pada jarak x dari kanta cembung dengan
panjang fokus,f.
42
o
Glass block
Blok kaca
air
udara
normal
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 94
The image formed is virtual and magnified. The object is at
Imej yang terbentuk adalah maya dan diperbesarkan. Objek itu berada di
A x > 2f B x = 2f
C x < f D f < x < 2f
7. If u is object distance, v is image distance and f is focal length of a lens, which of the
following equations is true?
Jika u ialah jarak objek, v ialah jarak imej dan f ialah panjang focus bagi suatu
kanta, manakah antara persamaan berikut adalah benar?
A f =
v u
uv
+
B f =
v u +
1
C
f
1
=
v u
uv
+
D
f
1
=
v u +
1
8. Diagram 3 shows a converging lens producing an upright and virtual image.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan kanta penumpu yang menghasilkan imej tegak dan maya.
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
Which optical instrument uses this arrangement?
x
Convex lens
Kanta cembung
Object
objek
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 95
Manakah alat optik yang menggunakan susunan rajah ini?
A Camera B Slide Projector
Kamera Projektor Slaid
C Telescope D Magnifying Glass
Teleskop Kanta pembesar
9. An object of 3 cm height is placed 15 cm from a convex lens. The image is formed at
30 cm from the lens. What is the height of the image?
Sebuah objek yang berketinggian 3 cm diletakkan 15cm dari kanta cembung. Imejnya
terbentuk pada 30 cm dari kanta. Berapakah ketinggian imej itu?
A. 1.5 cm B 3.0 cm
C 4.5 cm D 6.0 cm
10. Diagram 4 shows an arrangement of a simple astronomical telescope at normal
adjustment.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan binaan sebuah teleskop astronomi ringkas pada pelarasan
normal.
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
The focal length of objective lens, Q and the eyepiece, P are f
Q
and f
P
respectively.
Which of the following is correct?
Panjang fokus kanta mata, Q dan kanta objektif, P masing-masing ialah f
Q
dan f
P
.
Yang manakah berikut adalah betul?
A L = f
Q
+ f
P
B L > f
Q
+ f
P
C L > f
Q
f
P
11. Diagram 5 shows a ray diagram of a convex lens with focal length, f.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 96
Rajah 5menunjukkan rajah sinar sebuah kanta cembung yang mempunyai panjang
fokus,f.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Which statement is correct to explain the diagram?
Pernyataan yang manakah betul untuk menerangkan rajah di atas?
A The object distance is equal to f.
Jarak objek adalah kurang dari f
B The object distance is equal to 2f.
Jarak objek adalah sama dengan 2f.
C The convex lens acts as a magnifying glass.
Kanta cembung bertidak sebagai kanta pembesar.
D The characteristics of image are real, magnified and upright.
Ciri-ciri imej yang terbentuk adalah sahih, lebih besar dan tegak.
12. The focal length of the objective lens of an astronomical telescope is 100 cm. The
magnification of the telescope is 20 times.
What is the focal length of the eyepiece?
Panjang fokus bagi kanta objektif bagi satu teleskop astronomi ialah 100 cm.
Pembesaran teleskop astronomi ialah 20 kali.
Berapakah panjang fokus bagi kanta mata?
A 5 cm B 20 cm
C 80 cm D 120 cm
13. Diagram 6 shows a ray , X, is directed into a glass block. The critical angle of the
glass is 42
o
.
Which direction does the light travels from point Y?
Rajah 6, menunjukkan suatu sinar, X ditujukan ke dalam blok kaca. Sudut genting
kaca ialah 42
0
.
Dalam arah manakah sinar merambat dari titik Y?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 97
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
14. Diagram 7 shows light ray travels through an optical fibre.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan sinar cahaya bergerak melalui sebuah gentian optik.
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Which statement is correct?
Pernyataan yang manakah betul?
A Angle of is smaller than critical angle of inner core.
Sudut lebih kecil dari sudut genting teras dalam.
B Angle of is smaller than critical angle of outer cladding.
Sudut lebih kecil dari sudut genting pembalut luar.
C The inner core is denser than the outer cladding.
Teras dalam lebih tumpat dari pembalut luar.
D The outer cladding is denser than the inner core.
Pembalut luar lebih tumpat dari teras dalam.
PAPER 2 SECTION A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 98
1. Diagram 1 shows an object, O with height 2 cm placed on the left side of a convex
lens, X. The focal length of the convex lens is 10 cm.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu objek,O dengan ketinggian 2 cm diletakkan di sebelah kiri
kanta cembung,X. Panjang fokus kanta cembung ini ialah 10 cm.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
(a) On Diagram 1 draw the ray path from the object to form an image.
Pada Rajah 1 lukiskan lintasan sinar dari objek untuk membentuk imej.
[2 mark]
[2 markah]
(b) State the characteristics of the image formed.
Nyatakan ciri-ciri imej yang terbentuk.
.................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) If the object is placed at a distance 30 cm from the lens, calculate:
Jika objek diletakkan pada jarak 30 cm dari kanta, hitung:
(i) the image distance.
jarak imej
[2 mark]
[2 markah]
(ii) linear magnification.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 99
pembesaran linear.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(d) You are given another convex lens, Y with power 2 Diopter. You are required
to create a simple astronomical telescope using convex lenses X and Y.
Anda diberi satu kanta cembung yang lain, Y dengan kuasa 2 Diopter. Anda
dikehendaki mereka satu teleskop astronomi ringkas menggunakan kedua-dua
kanta cembung X dan Y.
(i) Which lens is suitable to be objective lens and eyepiece?
Kanta manakah yang sesuai dijadikan kanta objek dan kanta mata?
Objective lens:
Kanta objek
Eyepiece :
Kanta mata
[2 mark]
[2 markah]
(ii) Give one reason to your answer in (d) (i).
Berikan alasan bagi jawapan di ( d) (i).
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(e) Draw the arrangement of the lenses and sketch the ray path from distance
object using convex lenses X and Y to form a simple astronomical telescope.
Lukiskan susunan kanta dan lakarkan lintasan sinar dari satu objekyang
jauh dengan menggunakan kanta cembung X dan Y untuk membentuk satu
teleskop astronomi ringkas.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
PAPER 2 - SECTION B
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 100
2. (a) Diagram 2.1 shows a ray of light directed perpendicularly at a side of the semi
circular glass block. The ray passes through the glass block to a point O before
leaving the glass block.
The angle of incidence in the glass block is 30.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan satu bongkah kaca semi bulatan. Satu sinar cahaya
ditujukan secara tegak ke suatu sisi blok kaca itu. Sinar itu kemudiannya
memasuki bongkah kaca itu dan menuju ke titik O sebelum keluar semula.
Sudut tuju sinar itu di dalam kaca adalah 30.
Diagram 2.1
Rajah 2.1
(i) What is meant by angle of incidence? [1mark]
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan sudut tuju? [1markah]
(ii) Explain how total internal reflection is able to occur in Diagram 2.1.
[4 marks]
Terangkan bagaimana pantulan dalam penuh boleh berlaku dalam
Rajah 2.1? [4 markah]
(b) Diagram 2.2 and Diagram 2.3 show two rectangular glass blocks with
different optical density and refractive index. Ray of light is directed toward
the glass blocks with the same angle of incidence 30.
Rajah 2.2 dan Rajah 2.3 menunjukkan dua buah bongkah kaca yang berlainan
ketumpatan dan indeks biasannya. Sinar cahaya ditujukan kepada kedua-dua
bongkah kaca itu dengan sudut tuju 30.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 101
Density = 2600 kgm
-3
Density = 2670 kgm
-3
Ketumpatan = 2600 kgm
-3
ketumpatan = 2670 kgm
-3
Diagram 2.2 Diagram 2.3
Rajah 2.2 Rajah 2.3
Based on Diagram 2.2 and Diagram 2.3,
Berdasarkan Rajah 2.2 dan Rajah 2.3,
(i) compare the densities of the glass blocks ? [1mark]
bandingkan ketumpatan bongkah kaca itu. [1markah]
(ii) compare the refractive index of the glass blocks? [1mark]
bandingkan indeks biasan bongkah kaca itu. [1markah]
(iii) compare the angle of refraction of the glass blocks? [1mark]
bandingkan sudut tuju pembiasan bongkah kaca itu. [1markah]
(iv) relate the angle of refraction, r and the density of the glass block?
[1mark]
hubungkaitkan sudut pembiasan,r dengan ketumpatan blok kaca.
[1markah]
(v) relate the angle of refraction, r and the refractive index of the glass
blocks? [1mark]
hubungkaitkan sudut pembiasan,r dengan indeks biasan kaca.
[1markah]
(c) Diagram 2. 4 shows a fibre optic.
Rajah 2 .4 menunjukkan gentian optik.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 102
Diagram 2.4
Rajah 2.4
You are required to give suggestions to design a fibre optics which can works
efficiently. Using your knowledge on light, and the properties of material,
explain the suggestion based on the following aspects;
Anda diminta untuk memberikan cadangan untuk mereka bentuk satu gentian
optik yang dapat berfungsi dengan cekap. Menggunakan pengetahuan anda
tentang cahaya dan sifat bahan, terangkan cadangan anda berdasarkan aspek
berikut;
(i) the refractive index of outer and inner layer [2marks]
indeks biasan lapisan luar dan dalam [2markah]
(ii) flexibility [2marks]
kelenturan [2 markah]
(iii) strength [2marks]
kekuatan [2 markah]
(iv) thickness [2marks]
ketebalan [2 markah]
(v) density of the glass [2marks]
ketumpatan kaca [2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 103
3 Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 show parallel rays are directed towards the lenses P
and Q with focal point F.
Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan sinar selari menuju permukaan kanta P dan Q
dengan titik fokus F.
Diagram 3.1 Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.1 Rajah 3.2
(a) What is meant by focal point? [1 mark]
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan titik fokus? [1 markah]
(b) Using Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 , compare the thickness, the focal length
and power of the lens. Relate the thickness of the lens with the focal length to
make a deduction regarding the relationship between thickness of the lens and
the power of lens. [5 marks]
Menggunakan Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2, bandingkan ketebalan, panjang focus
dan kuasa kanta tersebut. Hubungkaitkan ketebalan kanta dengan panjang
fokus untuk membuat satu deduksi tentang hubungan antara ketebalan dengan
kuasa kanta. [5 markah]
(c) Diagram 3.3 shows lens P is used as a magnifying glass.
Rajah 3.3 menunjukkan kanta P digunakan sebagai kanta pembesar.
Diagram 3.3
Rajah 3.3
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 104
(i) At which position the object should be placed so that lens P will acts as
a magnifying glass?
Pada kedudukan manakah objek patut diletakkan supaya kanta P
bertindak sebagai kanta pembesar?
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image formed by lens P
in Diagram 3.3.
Lukiskan rajah sinar untuk menunjukkan pembentukan imej yang
terbentuk oleh kanta P dalam Rajah 3.3.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(d) Diagram 3.4 shows a compound microscope.
Rajah 3.4 menunjukkan sebuah mikroskop majmuk.
Diagram 3.4
Rajah 3.4
Using an appropriate physics concept, suggest and explain suitable
modifications or ways to enable the microscope to increase its efficiency and
to form a brighter and clear image.
Your modifications can be emphasized on the following aspects;
Menggunakan konsep fizik yang sesuai, cadang dan terangkan pengubah
suaian atau cara yang boleh dilakukan untuk meningkatkan kecekapan dan
menghasilkan imej yang terang dan jelas.
Pengubahsuaian anda boleh berdasarkan kepada aspek-aspek berikut:
(i) The selection of lens as objective lens and as an eyepiece [2 marks]
Pemilihan kanta sebagai kanta objek dan kanta mata [2 markah]
(ii) The position of the object [2 marks]
kedudukan objek [2 markah]
(iii) The position of the eye piece [2 marks]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 105
Kedudukan kanta mata [2 markah]
(iv) The distance between the objective lens and eyepiece [2 marks]
Jarak antara kanta objek dan kanta mata [2 markah]
(v) Condition of the place to store the microscope [2 marks]
Keadaan tempat penyimpaann mikroskop [2 markah]
PAPER 2 SECTION C
4 Diagram 4.1 shows two convex lenses, P and Q, used in an astronomical telescope.
The focal length of P is 40 cm and for Q is 10 cm
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan dua kanta penumpu , P dan Q, yang digunakan dalam sebuah
teleskop astronomi. Panjang fokus bagi kanta penumpu P adalah 40 cm dan panjang
fokus bagi kanta Q adalah 10 cm.
Diagram 4.1
Rajah 4.1
(a) What is the meaning of focal length of lens? [ 1mark ]
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan panjang fokus kanta? [1 markah]
(b) By using suitable apparatus, explain how the focal length of both lenses can be
estimated. [ 4 marks ]
Dengan menggunakan peralatan yang sesuai terangkan bagaimana panjang
fokus kedua-dua kanta dapat di anggarkan. [4 markah]
(c) Diagram 4.2 shows an arrangement of lenses to construct a simple
astronomical telescope using lens P and lens Q.
Rajah 4.2 menunjukkan satu susunan kanta untuk membina sebuah teleskop
astronomi ringkas menggunakan kanta P dan kanta Q.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 106
Diagram 4.2
Rajah 4.2
You are asked to investigate the arrangement and characteristics of the lenses
used to construct the simple astronomical telescope as shown in Table 1
Anda ditugaskan untuk menyiasat susunan kanta dan sifat-sifat kanta yang
akan digunakan untuk membina sebuah teleskop astronomi ringkas seperti
dalam Jadual 1
Table 1
Jadual 1
Arrangement
of lenses
Susunan
kanta
Focal length of
objective lens,
f
o
/cm
Panjang fokus
kanta objek,
f
0
/cm
Magnification
of image
Pembesaran
imej
Distance
between
objective lens
and eyepiece,D /
cm
Jarak antara
kanta objek
dengan kanta
mata, D / cm
Diameter of
objective lens,
d /cm
Diameter kanta
objek , d / cm
J 40.0 4.00 50.0
Large
Besar
K 40.0 0.25 60.0
Small
Kecil
L 10.0 4.00 50.0
Large
Besar
M 10.0 0.25 60.0
Small
Kecil
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 107
Explain the suitability of the arrangement and each characteristic of the lenses
and determine the arrangement which can produce the brightest and the
sharpest image at normal adjustment.
Terangkan kesesuaian susunan dan sifat-sifat kanta dan tentukan susunan
yang dapat menghasilkan imej yang paling terang dan paling tajam pada
pelarasan normal.
[10 marks]
[10 markah]
(d) A camera has a convex lens of focal length 5 cm is used to capture an object
of 1 m in height and 4 m from the camera.
Sebuah kamera yang mempunyai kanta cembung berjarak fokus 5 cm,
digunakan untuk menangkap gambar suatu objek dengan ketinggian 1 m dan
pada jarak 4 m kamera tersebut.
(i) Determine the image distance from the camera [2marks]
Tentukan jarak imej yang terbentuk dari kamera [2 markah]
(ii) Calculate the height of image produced in the camera [2 marks]
Hitung tinggi imej yang terhasil dalam dalam kamera [2 markah]
(iii) State the characteristics of image formed in the camera [1 marks]
Nyatakan ciri-ciri imej yang terbentuk dalam kamera [1 markah]
PAPER 3 SECTION A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 108
1. A student carries out an experiment to investigate the relationship between the angle
of incidence, i and angle of refraction, r of a glass block. The arrangement of the
apparatus is shown in Diagram 1.1. A normal line is traced and the ray box is placed
at the angle of incidence, i.
Seorang pelajar menjalankan satu eksperimen mengkaji hubungan antara sudut tuju ,
i dengan sudut biasan, r bagi suatu blok kaca. Susunan radas ditunjukkan pada Rajah
1.1. Satu garis normal disurih dan kotak sinar diletakkan pada sudut tuju, i.
Diagram 1.1
Rajah 1.1
A fine beam of light from ray box is directed to the glass block at P with angle of incidence, i
20
o
from the normal line. Traces of light which leaving the glass block at Q is marked with
X. A line from P to Q is drawn. A protractor is used to measure the angle of refraction, r as
shown in Diagram 1.2 .
Satu sinar cahaya halus ditujukan ke permukaan blok kaca di P pada sudut 20
o
daripada
garis normal. Cahaya yang keluar pada Q ditanda dengan X. Satu garis dari P ke Q dilukis.
Protraktor digunakan untuk mengukur sudut biasan, r seperti yang ditunjukkan pada
Rajah 1.2.
P
Q
white paper
kertas putih
ray box
kotak sinar
light ray
sinar cahaya
glass block
bongkah kaca
normal line
garis normal
i
Normal line
Garis normal
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 109
Diagram1.2
Rajah 1.2
The reading of the protractor, r, is shown in Diagram 1.3
Bacaan protraktor, r ditunjukkan pada Rajah 1.3
Angle of incidence, i = 20
o
r =
Diagram 1.3
Rajah 1.3
The procedure is repeated with angle of incidence ,i = 30
o
, 40
o
, 50
o
and 60
o
. The
corresponding readings of protractor, r, are shown in Diagram 1.4, 1.5, 1.6 and 1.7 .
P
Q
Normal line
Garis normal
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 110
Prosedur diulangi dengan sudut tuju , i= 30
o
, 40
o
, 50
o
and 60
o
. Bacaan protraktor ,
r yang sepadan adalah ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1.4,1.5, 1.6 and 1.7.
Normal line
Garis normal
Angle of incidence, i = 30
o
Angle of incidence, i = 40
o
Sudut tuju, i = 30
o
Sudut tuju, i = 40
o
r = . r =
Diagram 1.4 Diagram 1.5
Rajah 1.4 Rajah 1.5
Normal line
Garis normal
Normal line
Garis normal
Normal line
Garis normal
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 111
Angle of incidence, i = 50
o
Angle of incidence, i = 60
o
Sudut tuju,i = 50
o
Sudut tuju, i = 60
o
r = .. r = .
Diagram 1.6 Diagram 1.7
Rajah 1.6 Rajah 1.7
a) For the experiment described , identify ;
Bagi eksperimen yang diterangkan di halaman 2 dan 3 kenal pasti ;
(i) The manipulated variable
Pemboleh ubah manipulasi
.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) The responding variable
Pemboleh ubah bergerak balas
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) The constant variable
Pmbolehubah dimalarkan
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 112
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Based on diagram 1.2, 1.3,1.4,1.5 and 1.6 ,
Berdasarkan rajah 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 dan 1.6 ,
(i) Record the angle of refraction, r , in the space provided
Catat bacaan sudut biasan , r , dalam ruangan yang disediakan
[ 2 marks ]
[ 2 markah ]
(ii) Tabulate your result for all values of r , sin i and sin r for all values of
i , in the space below.
Jadualkan keputusan anda bagi r, sin i , sin r untuk semua nilai i
dalam ruangan di bawah.
[5 marks]
[5 markah]
(c) On the graph paper , plot a graph of sin r against sin i.
Pada kertas graf, plot graf sin r melawan sin i.
5 marks ]
[5 markah]
d) Based on your graph in 1 (c) , state the relationship between i and r .
Berdasarkan graf anda di 1 (c), nyatakan hubungan antara i dengan r.
.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
PAPER 3 SECTION B
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 113
2. Diagram 2.1 shows a line under a glass block. Diagram 2.2 shows an identical line
under a Perspex block of the same size. An observer noticed that the image of the line
formed in the glass block is nearer to the surface of the block.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan satu garisan di bawah satu blok kaca. Rajah 2.2
menunjukkan garisan yang serupa di bawah blok perspek yang bersaiz sama.
Seorang pemerhati mendapati imej garisan yang terbentuk dalam blok kaca adalah
lebih dekat dengan permukaan blok itu.
Diagram 2.1 Diagram 2.2
Rajah 2.1 Rajah 2.2
Based on the information and observation:
Berdasarkan maklumat dan pemerhatian tersebut :
(a) State one suitable inference [1 mark]
Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai. [1 markah]
(b) State one hypothesis that could be investigated. [1 mark]
Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang boleh disiasat. [1 markah]
(c ) With the use of apparatus such as a tall beaker, water and other apparatus and
material, describe one experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in
2(b).
Glass block
Blok kaca
Line
Garisan
Paper
Kertas
Line
Garisan
Image of the line
Imej garisan
Perspex block
Blok perspek
Observer
Pemerhati
Observer
Pemerhati
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 114
Dengan menggunakan radas seperti sebuah bikar yang tinggi, air dan lain-
lain radas, terangkan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat hipotesis yang
dinyatakan di 2(b).
.
In your description, state clearly the following:
Dalam penerangan anda nyatakan dengan jelas perkara berikut
(i) The aim of an experiment.
Tujuan eksperimen
.
(ii) The variables in the experiment
Pemboleh ubah dalam eksperimen
(iii) The list of apparatus and materials.
Senarai radas dan bahan
(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus
Susunan radas
(v) The procedure of the experiment.
Describe how to control the manipulated variable and how to measure
the responding variable.
Prosedur yang digunakan dalam eksperimen.
Terangkan bagaimana mengawal pembolehubah dimanipuasikan dan
bagaimana mengukur pembolehubah bergerak balas.
(vi) The way to tabulate the data
Cara anda menjadualkan data
(vii) The way to analyse the data
Cara untuk menganalisis data.
[10 marks]
[10 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 115
CHAPTER 5 : LIGHT
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 D 7 D 13 C
2 B 8 C 14 A
3 A 9 A
4 D 10 C
5 D 11 A
6 C 12 A
PAPER 2 SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a)
M1 Light from object parallel to the principal axis and
converged to focal point
M2 Light from object pass through the center of lens and
intercept with the first line
AND the image is shown on the diagram
1
1
2
(b) Real, diminished, inverted (all correct) 1 1
(c)(i)
M1 = +
M2 15 cm
1
1
3
(c)(ii)
// 0.5
1
(d)(i) Objective lens = convex lens Y
Eyepiece = convex lens X
2
3
(d)(ii) Power of convex lens X > power of convex lens Y // Focal
length of X < focal length of Y
1
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 116
NO SCHEME SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(e)
M1 Y is objective lens and X is eye piece
M2 The distance in between X and Y is f
o
+ f
e
/50 cm
M3 Show the correct ray path
1
1
1
3
TOTAL 12
PAPER 2 SECTION B
2(a)(i) Angle between incident ray and normal line 1
5
(a)(ii) - Increase the angle of incidence, i, then angle of
refraction, r will also increase.
- Keep on increasing the angle of incidence until angle
of refraction is 90
- The angle of incidence is called critical angle
- Increase the angle of of incidence more than the
critical angle, the ray will be reflected into the glass
block
4
(b) (i) Density in Diagram 2.2 is less than / smaller than / < Density
in Diagram 2.3
1
5
(ii) Refractive index in Diagram 2.2 is less than / smaller than / <
Refractive index in Diagram 2.3
1
(iii) Angle of refraction in Diagram 2.2 is more than / bigger than
/ > angle of refraction in Diagram 2.3
1
(iv) When the density decreases, the angle of refraction increases 1
(v) When the angle of refraction increases, the refractive index
decreases
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 117
NO SCHEME SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(c)
Suggestion Explanation
Use refractive index of outer
layer is less than the
refractive index of outer
layer
So that total internal
reflection can happen in the
fiber optic.
Use high flexibility material so that it can be bend
Use strong material do not break easily
Use thin material Lighter // can be use in
small area
Low density material Lighter
2
2
2
2
2
10
TOTAL 20
3(a) Distance between optical centre and focal point
1 1
(b) M1 The thickness of lens in Diagram 3.1 is smaller
M2 Focal length in Diagram 3.1 is bigger
M3 Power of lens in Diagram 3.1 is smaller
M4 When the thickness of lens decreases, the focal length
increases
M5 When the thickness of lens decreases, the power of lens
decreases
1
1
1
1
1
5
(c)(i) At u < f 1
4
(c)(ii)
3
(d) M1 P as eye piece and Q as objective lens
M2 Focal length of eyepiece > focal length of objective
lens
M3 fo < u < 2fo / Object is placed inbetween f
o
and 2f
o
M4 to produce real, inverted and magnified image
M5 Adjusted so that u < fe
M6 to produce virtual, inverted and bigger image // to acts
magnifying glass
M7 Distance between lenses > fo + fe
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 118
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
M8 To produce bigger image from the eyepiece // to
increase the magnification
M9 Store in a cool and dry place
M10 To avoid formation fungus at the lenses
1
1
1
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
PAPER 2 SECTION C
4(a) Distance between focal point and the optical centre of a lens 1
1
(b) M1 The convex lens is aimed/focused to a distant object
(infinity)
M2 The screen is adjusted until a sharp image is formed on
the screen
M3 The distance between the screen and the lens is
measured
M4 Focal length = distance between the screen and the lens
1
1
1
1
4
(c)
Aspect Explanation
Longer focal length To produce real, inverted and smaller
image
High magnification Produce bigger image
Distance = fo + fe Produce image at normal adjustment //
image at infinity
Bigger diameter More light can enter objective lens //
image brighter
J is chosen Longer focal length, higher
magnification, Distance between two
lenses = fo + fe and bigger diameter
1,1
1,1
1,1
1,1
1,1
10
(d)(i)
= +
M2 v = 5.063 cm
1
1
5
(ii)
M1 =
M2 1.27 cm
1
1
(iii) Real , inverted and diminished
1
TOTAL MARKS 20
PAPER 3 SECTION A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 119
NO SCHEME SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a)(i) Angle of incidence//i 1
3
(ii) Angle of refraction/r
1
(iii) Refractive index of the glass block/density of the glass block 1
(b) (i) i/
0
r/
0
20 13
30 19
40 25
50 30
60 36
All values of r correct - 2 marks
1 2 values of r incorrect 1 mark
3 or more values of r incorrect 0 mark
2
7
(ii)
Incidence
angle, i /
0
Refractive
angle,r /
0
sin i sin r
20 13 0.34 0.22
30 19 0.50 0.33
40 25 0.64 0.42
50 30 0.77 0.50
60 36 0.87 0.59
1) All quantities i, r, sin i and sin r correct --
2) Units for all quantities correct ----
3) * All values of sin i correct -----
* 1 value of sin i incorrect ------
* > 1 value of sin i incorrect ------ 0
4) * All values of sin r correct -----
* 1 value of sin r incorrect ------
* > 1 value of sin r incorrect ------ 0
5) Consistency of decimal point for sin i ---
6) Consistency of decimal point for sin r ---
Score Mark
7 8 5
5 6 4
3 4 3
2 2
1 1
0 0
5
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 120
NO SCHEME SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(c) On the graph paper.
1) Correct title at axis-----
2) Correct Units -------
3) Even scale -------
4) * All points correctly plotted --------
- 1 point incorrectly plotted -------
- > 1 point incorrectly plotted ------ 0
5) Best fit straight line --------
6) > 50% graph paper --------
Score Mark
6 7 5
5 4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
5
5
(d) sin r is directly proportional to sin i 1 1
TOTAL MARK 16M
PAPER 3 SECTION B
2(a) Inference :
Apparent depth depends on the density/type of
block/material
1 1
(b) Hypothesis :
When the density (of material) increase , the apparent depth
decrease/depth of image
1 1
(c) M1 Aim : To investigate the relationship between density
and apparent depth/depth of the image
M2 Variables :
manipulated V : density// mass of salt
responding V : apparent depth/depth of image
M3 fixed V : real depth , volume of water
M4 Apparatus and materials :
Tall Beaker/cylinder, pin, retort stand , water , salt ,
meter rule, triple beam balance
1
1
1
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 121
SCHEME SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(c) M5 Set up apparatus
M6 State way to fix FV
The beaker is filled with volume of water, V = 1000
cm
3
State way to measure MV
Mass of salt, m = 20.0 g is measured and put into the
beaker. Density of liquid, =
M7 State way to measure RV
A pin O is placed into the liquid. The position of the
pin I (at the retort stand) is adjusted by observing
above the beaker until it appears in line with the i
image of pin O
The apparent depth of the straight line,d is measured
M8 The experiment is repeated with mass of salt , m =
30.0 g , 40.0 g, 50.0 g, and 60.0 g .
M9 Tabulating data
Mass of salt,m/g Apparent depth,d /cm
30.0
40.0
50.0
60.0
70.0
M10 Graph Plotting
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
TOTAL MARK 12 M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 122
CHAPTER 6: WAVES
PAPER 1
1. Diagram 1 shows an oscillating pendulum experiences a damping effect.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan sebuah bandul berayun mengalami kesan pelembapan.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Which of the following amplitude against time is correct?
Yang manakah antara graf amplitud melawan masa berikut adalah betul?
A
B
C
time
masa
A
O
B
Amplitude
amplitud
time
masa
A
O
B
Amplitude
amplitud
time
masa
A
O
B
Amplitude
amplitud
B A
O
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 123
2. Diagram 2 shows waves in a slinky spring when the spring is vibrated at 5 Hz.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan gelombang spring slinki apabila ia digetarkan pada frekuensi
5 Hz.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
What is the speed of the wave ?
Apakah halaju gelombang itu ?
A 30 cms
-1
B 40 cms
-1
C 60 cms
-1
D 120 cms
-1
3. Diagram 3 shows a boy producing a transverse wave along a long string by
vibrating one end of the string.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan seorang budak sedang menghasilkan satu gelombang
melintang di sepanjang satu tali dengan ayunan pada hujung tali itu.
time
masa
A
O
B
Amplitud
Amplitude
D
24 cm
String
Tali
Direction of vibration
Arah ayunan
1.5 m
Wall
Dinding
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 124
If the boys hand moves up-and-down four complete cycles per second, what is the
speed of the transverse wave along the string?
Jika tangan budak itu bergerak naik-turun pada empat ayunan lengkap per saat,
apakah laju gelombang melintang sepanjang tali itu?
A 3 ms
-1
B 6 ms
-1
C 12 ms
-1
D 14 ms
-1
4. Diagram 4 shows a slinky spring being moved left and right continuously.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan sebuah spring slinki digerakkan secara berterusan ke kiri dan
ke kanan.
Wavelength is the distance between the points
Panjang gelombang ialah jarak antara titik-titik
A JM B KM
C KN D JK
5. What happens to the frequency and loudness of sound waves when it is reflected?
Apakah yang berlaku kepada frekuensi dan kekuatan bagi suatu gelombang bunyi
apabila dipantulkan?
Frequency
Frekuensi
Loudness
Kekuatan
A Unchanged
Tidak berubah
Decreases
Berkurang
B Increases
Bertambah
Decreases
Berkurang
C Unchanged
Tidak berubah
Increases
Bertambah
slinky spring
spring slinki
Direction of hand movement
Arah gerakan tangan
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
hand
tangan
Direction of wave propagation
Arah perambatan gelombang
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 125
D Increases
Bertambah
Unchanged
Tidak berubah
6. Diagram 5 shows a fisherman boat used sonar to determine a shoal of fish under sea
Rajah 5 menunjukkan bot nelayan menggunakan sonar untuk mengesan kumpulan
ikan di dalam laut.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
The wave phenomena relates to the situation of
Fenomena gelombang yang berkaitan ialah
A interference B reflection
interferens pantulan
C diffraction D refraction
pembelauan pembiasan
7. Diagram 6 shows water waves propagate in an area of different depths.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan gelombang air merambat dalam kawasan yang berbeza
kedalaman.
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 126
Which of the following diagrams show the propagation of the waves correctly?
Antara berikut manakah menunjukkan perambatan gelombang yang betul?
A B
C D
8. Which of the following methods is to reduce the echo inside a closed hall?
Antara kaedah-kaedah berikut , yang manakah adalah untuk mengurangkan gema di
dalam sebuah dewan yang tertutup?
A Wall is designed using a hard and smooth material
Dinding direkabentuk menggunakan bahan yang keras dan licin
B The inner wall is covered with sponge
Dinding di bahagian dalam dilitupi dengan span
C. The floor is designed using a smooth material
Lantai direkabentuk menggunakan bahan yang licin
D All curtains at the doors and windows are removed
Kesemua langsir-langsir di pintu-pintu dan di tingkap-tingkap ditanggalkan
9. Which of the following statements is best explaining why sound is easily diffracted
compared to light?
Manakah kenyataan berikut adalah paling baik menerangkan mengapa bunyi lebih
mudah di belau berbanding cahaya?
A Sound needs medium for its propagation.
Bunyi memerlukan medium untuk perambatannya.
B Sound is a longitudinal wave.
Bunyi ialah gelombang membujur.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 127
C The speed of sound is slower than light.
Laju bunyi lebih lambat berbanding cahaya.
D The wavelength of sound is longer than light.
Panjang gelombang bunyi lebih panjang berbanding cahaya.
10. Diagram 7 shows water waves moving towards a harbour.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan gelombang air sedang menuju ke sebuah pelabuhan.
Which of the following statements is correct about the waves at Q?
Antara pernyataan-pernyataan berikut, yang manakah betul mengenai ombak di Q?
A The frequency decrease
Frekuensi berkurang
B The velocity increase
Halaju bertambah
C The wave length increase
Panjang gelombang bertambah
D The energy decrease
Tenaga berkurang
Entrance
laluan masuk
Harbour
pelabuhan
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Q
Water waves
Gelombang air
Retaining wall
tembok penahan
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 128
11. Diagram 8 shows the bright and dark bands of the waves pattern formed on the
screen in two different experiments to study the waves phenomenon .
Rajah 8 menunjukkan jalur cerah dan gelap bagi corak gelombang yang terbentuk
pada tabir dalam dua eksperimen yang berlainan untuk mengkaji fenomena
gelombang.
The waves phenomenon P and Q are
Fenomena gelombang P dan Q adalah
P Q
A Interference Refraction
Interferens Pembiasan
B Diffraction Interference
Pembelauan Interferens
C Diffraction Reflection
pembelauan Pantulan
D Refraction Interference
Pembiasan Interferens
bright band
jalur cerah
bright band
jalur cerah
dark band
jalur gelap
dark band
jalur gelap
phenomenon P
fenomena P
phenomenon Q
fenomena Q
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 129
12. In a Youngs double slit experiment using red light, the interference pattern
produced on a screen is as shown in Diagram 9
Dalam satu eksperimen dwicelah Young menggunakan cahaya merah, corak
interferens yang terhasil di atas skrin adalah seperti dalam Rajah 9
Diagram 9
Rajah 9
When red light is replaced by blue light, which of the fringes pattern is formed on the
screen?
Apabila cahaya merah digantikan dengan cahaya biru, corak pinggir yang manakah
akan terbentuk di atas skrin?
A
B
C
D
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 130
13. Diagram 10 shows a fringe pattern formed on a screen in theYoungs double-slit
experiment
Rajah 10 menunjukkan corak pinggir yang dihasilkan di atas skrin dalam eksperimen
dwicelah Young.
Diagram 10
Rajah 10
The distance between double slit and screen is 1 m and the wavelength of light is
5 x 10
-7
m. What is the distance between two slits?
Jarak diantara dwicelah dan skrin ialah 1 m dan panjang gelombang cahaya yang
digunakan ialah 5 x 10
-7
m. Apakah jarak di antara dua celah?
A 5.0 x 10
-3
m B 1.0 x 10
-4
m
C 1.3 x 10
-3
m D 1.0 x 10
-3
m
14. Diagram 11 shows an interference of sounds wave emitted from two loud speakers
which are coherence.
Rajah 11 menunjukkan satu interferens gelombang bunyi yang dihasilkan oleh dua
pembesar suara yang koheren.
Diagram 11
Rajah 11
0.05 cm
dark
bright
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 131
Destructive inteference occurs at
Interferens memusnah berlaku di,
A P B Q
C R D S
15. Diagram 12 shows the traces of sound waves X and Y being displayed using same
cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) settings.
Rajah 12 menunjukkan surihan gelombang bunyi X dan Y yang dipaparkan pada
skrin osiloskop sinar katod dalam pelarasan yang sama.
Which of the following statement is true?
Antara pernyataan berikut, yang manakah adalah benar?
A Sound Y is louder than sound X.
Bunyi Y lebih nyaring daripada bunyi X.
B Sound Y has a higher pitch than sound X.
Bunyi Y lebih lansing daripada bunyi X.
C Sound Y has a lower pitch than sound X.
Bunyi Y kurang lansing daripada bunyi X.
Sound X
Bunyi X
Sound Y
Bunyi Y
Diagram 12
Rajah 12
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 132
16. Which of the following statements is correct about the loudness and the pitch of the
sound when the amplitude and frequency of the sound waves are increased?
Yang manakah antara pernyataan-pernyataan berikut adalah betul mengenai
kenyaringan dan kelansingan bunyi apabila amplitud dan frekuensi gelombang bunyi
ditambah ?
LOUDNESS PITCH
KENYARINGAN KELANSINGAN
A decrease increase
berkurang bertambah
B increase decrease
bertambah berkurang
C increase increase
bertambah bertambah
D no change decrease
tidak berubah berkurang
17. Diagram 13 shows incomplete electromagnetic waves spectrum.
Rajah 13 menunjukkan spektrum gelombang electromagnet yang tidak lengkap.
Diagram 13
Rajah 13
Which of the following is true?
Antara berikut yang manakah betul?
S T U
A Visible light X-ray Radiowave
Cahaya nampak Sinar-X Gelombang radio
B Visible light Radiowave X-ray
Cahaya nampak Gelombang radio Sinar-X
C X-ray Visible light Radiowave
Sinar-X Cahaya nampak Gelombang radio
S
T
Infra-
red
Gama -ray
Ultra-
violet
Micro
wave
U
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 133
D Radiowave X-ray Visible light
Gelombang radio Sinar-X Cahaya nampak
18. What type of electromagnetic waves is used on a remote control?
Apakah jenis gelombang elektromagnet yang digunakan dalam kawalan remote?
A Gamma ray B Ultraviolet rays
Sinar gamma Sinar ultra ungu
C Microwaves D Infrared rays
Gelombang mikro Sinar infra merah
19. Diagram 14 shows the spectrum of the electromagnetic waves.
Rajah 14 menunjukkan spektrum gelombang elektromagnet
The parts labeled R, S and T are
Bahagian berlabel R, S dan T adalah
A X-ray, Infra red, Radio wave
X-ray, Infra merah, Gelombang radio
B Infra red, X-ray. Radio wave
Infra merah, Sinar-X, Gelombang radio
C Radio wave, Infra red, X-ray
Gelombang radio, Infra merah, Sinar-X
D X-ray , Radio wave, Infra red
Sinar-X, Gelombang radio, Infra merah
Gamma
ray
Sinar
gama
R
Ultra violet
Lampau
ungu
Visible light
Cahaya
nampak
S
Micro wave
Gelombang
mikro
T
Diagram 14
Rajah 14
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 134
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 6.1 and 6.2 shows an experiment to determine the wavelength of
monochromatic light waves.
Diagram 6.1 used a blue light source and Diagram 6.2 used a red light source.
Rajah 6.1 dan 6.2 menunjukkan satu eksperimen dwicelah Young untuk menentukan
panjang gelombang cahaya monokromatik.
Rajah 6.1 menggunakan sumber cahaya berwarna biru manakala Rajah 6.2
menggunakan sumber cahaya berwarna merah.
Blue fringe
Pinggir biru
Red fringe
Pinggir merah
screen
skrin
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 135
The separation between two slits, a, and the distance between the double slits and the
screen, D, in both diagrams are constant.
Dark and bright fringes are produced after the light passes through the slit.
Pemisahan dua celah, a, dan jarak antara dwicelah dengan skrin dalam kedua-dua
rajah, D, dalam kedua-dua rajah adalah malar.
Pinggir-pinggir gelap dan cerah dihasilkan setelah cahaya merambat melalui
celahan.
(a). What is the meaning of monochromatic light?
Apakah maksud cahaya monokromatik?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Compare the wavelength of red light and blue light.
Tick (\ ) the correct answer in the box provided.
Bandingkan jarak gelombang cahaya merah dan cahaya biru.
Tanda (\ ) jawapan yang betul dalam petak yang disediakan.
Wavelength of red light > wavelength of blue light
Jarak gelombang cahaya merah > Jarak gelombang cahaya biru
Wavelength of red light < wavelength of blue light
Jarak gelombang cahaya merah > Jarak gelombang cahaya biru
Wavelength of red light = wavelength of blue light
Jarak gelombang cahaya merah > Jarak gelombang cahaya biru
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 136
(c) Based on the pattern of fringes formed on the screen in Diagram 6.1 and
Diagram 6.2, state two observations about the distance between consecutive
fringes for red and blue light.
Berdasarkan corak pinggir-pinggir yang terbentuk pada skrin dalam Rajah
6.1 dan Rajah 6.2, nyatakan dua pemerhatian tentang jarak antara pinggir-
pinggir berturutan bagi cahaya merah dan cahaya biru.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) State the relationship between the wavelength and the distance between
consecutive bright fringes in this experiment.
Nyatakan hubungan antara jarak gelombang dengan jarak di antara pinggir-
pinggir terang dalam eksperimen ini.
.........................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(e) (i) What happens to the distance between two consecutive bright fringes if
the separation between two slits is increased? .
Apakah yang akan berlaku kepada jarak antara pinggir-pinggir terang
jika pemisahan antara dua celah ditambah?
............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (e) (i).
Berikan sebab bagi jawapan anda di (e) (i).
............................................................................................................
............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 137
(f) State a wave phenomenon which occurs in this experiment.
Nyatakan satu fenomena gelombang yang berlaku dalam eksperimen ini.
........
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
2. Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 show the bright and dark fringes of the waves formed
on the screen when a light rays pass through a double slit plate.
Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan pinggir cerah dan gelap bagi gelombang yang
terbentuk pada tabir apabila satu sinar cahaya melalui plat dwicelah.
Diagram 6.1
Rajah 6.1
Diagram 6.2
Rajah 6.2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 138
(a) What is the meaning of coherent source?
Apakah maksud sumber koheren?
.[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Observe Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2,
Perhatikan Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2,
(i) Compare the distance between two slits
Bandingkan jarak antara dua celah
...
.[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Compare the distance between consecutive bright fringes
Bandingkan jarak antara pinggi-pinggir cerah berturutan
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Compare the distance between the double slit plate and the screen.
Bandingkan jarak antara plat dwicelah dengan tabir
.[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) (i) Relate the distance between the two slits with the distance between
consecutive bright fringes
Hubungkaitkan jarak antara dua celah dengan jarak antara pinggir-
pinggir cerah berturutan
.[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 139
(ii) Name the wave phenomenon which forms the pattern of the fringes in
Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2
Namakan fenomena gelombang yang menghasilkan corak pinggir
dalam Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2
.[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(d) Explain how the formation of bright fringes and dark fringes occur.
Terangkan bagaimana pembentukan pinggir-pinggir cerah dan gelap terhasil.
................
.................
.[2 marks]
[2 markah]
3. Diagram 8 shows an electric bell produces sound waves.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan satu loceng elektrik menghasilkan gelombang bunyi.
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 140
(a) (i ) Name the type of wave produced by the electric bell.
Namakan jenis gelombang yang dihasilkan oleh loceng elektrik.
...........................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) When the air in the electric bell is sucked out by using vacuum pump,
what happen to the sound produced?
Apabila udara dalam loceng elektrik disedut keluar dengan
menggunakan pam vakum, apakah yang berlaku kepada bunyi yang
dihasilkan?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Give one reason for the answer in 3 (a) (ii).
Berikan satu sebab bagi jawapan di 3(a) (ii).
.............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Diagram 8.2 shows a sound wave form produced by a tuning fork displayed on
the screen of cathode ray oscilloscope.
Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan suatu bentuk gelombang bunyi yang dihasilkan oleh
suatu tala bunyi ditunjukkan pada skrin tiub sinar katod.
Diagram 8.2
Rajah 8.2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 141
On Diagram 8.3, draw the sound wave form produced when the loudness is
increased.
Pada Rajah 8.3, lukiskan bentuk gelombang bunyi yang dihasilkan bila
kekuatan bunyi ditambah.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Diagram 8.3
Rajah 8.3
(c) Diagram 8.4 shows an electromagnetic wave spectrum.
Rajah 8.4 menunjukkan satu spektrum gelombang elektromagnet.
Radio
wave
Gelombang
Radio
Microwave
Gelombang
mikro
P
Visible
light
ahaya
nampak
Q
X-ray
Sinar-x
Gamma
ray
Sinar
Gama
Diagram 8.4
Rajah 8.4
( i) Name the wave for;
Namakan gelombang bagi;
P :
Q :
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 142
( ii) Choose one wave that harmful to human body.
Pilih satu gelombang yang merbahaya kepada badan manusia.
. ............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Give one reason for the answer in 3 (c) (ii).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan di 3 (c )(ii).
...............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iv) Choose one wave that used in telecommunications.
Pilih satu gelombang yang sesuai digunakan dalam telekomunikasi.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(v) Give one reason for the answer in 3 (c) (iv).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan di 3 (c) (iv).
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
( vi) Choose the suitable wave that can be used in cancer treatment.
Pilih gelombang yang sesuai digunakan untuk rawatan penyakit
kanser.
...............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(vii) Give one reason for the answer in 3 (c) (vi).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan di 3 (c) (vi).
...
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 143
CHAPTER 6 : WAVES
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 B 7 A 13 A 19 A
2 B 8 B 14 C
3 C 9 D 15 B
4 B 10 D 16 C
5 A 11 B 17 C
6 B 12 C 18 D
PAPER 2 SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a) The light which has one wavelength / one colour
Cahaya yang mempunyai satu panjang gelombang / satu
warna
1 1
(b) Wavelength of red light > Wavelength of blue light
Panjang gelombang cahaya merah > cahaya biru
1 1
(c) The distance between consecutive bright fringes for red light is
more than that of blue light./
The distance between consecutive bright fringes for the same
light are constant.
Jarak diantara pinggir cerah berturutan bagi cahaya merah
lebih besar daripada cahaya biru /
Jarak diantara pinggir cerah berturutan bagi cahaya yang
sama adalah malar
1
1
2
(d) The longer the wavelength, the longer the distance between
consecutive bright fringes
Semakin bertambah panjang gelombang, semakin bertambah
jarak diantara pinggir cerah berturutan
1 1
(e)(i) The distance between two consecutive bright fringes will
decrease
Jarak diantara dua pinggir cerah berturutan akan berkurang
1 1
(ii) a is inversely proportional to x
a berkadar secara songsang x
1 1
(f) Diffraction // Interference
Pembelauan // Interferens
1 1
TOTAL MARK 8M
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 144
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
2(a) Coherence sources have same frequency, same amplitude and
in same phase. /same phase different
Sumber koheren mempunyai frekuensi yang sama, amplitud
yang sama dan sama fasa / beza fasa yang sama
1 1
(b)(i) a in Diagram 6.2 > a in Diagram 6.1
a dalam Rajah 6.2 > a dalam Rajah 6.1
1 1
(ii) x in Diagram 6.2 < x in Diagram 6.1
x dalam Rajah 6.2 < x dalam Rajah 6.1
1 1
(iii) Same
sama
1 1
(c) (i) Inversely proportional
Berkadar secara songsang
1 1
(ii) Diffraction / interference
Pembelauan / Interferens
1 1
(d) (i) M1 When crest meets crest/ trough meets trough constructive
interference occur, so bright fringes is produce
Apabila pucak bertemu puncak / lembangan bertemu
lembangan, interferens membina terhasil, jadi pinggir
cerah dihasilkan
M2 When crest meets trough destructive interference occur,
so dark fringes is produce
Apabila pucak bertemu lembangan, interferens
memusnah terhasil, jadi pinggir gelap dihasilkan
1
1
2
TOTAL MARK 8M
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
3(a)(i) Longitudinal wave / mechanical wave
Gelombang membujur / gelombang mekanikal
1 1
(ii) No sound / sound cannot be heard
Tiada bunyi / bunyi tiada boleh didengari
1 1
(iii) Sound wave cannot propagate // sound energy cannot be
transferred
Gelombang bunyi tidak boleh dirambat // tenaga bunyai tidak
boleh di pindahkan
1 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 145
(b)
1. Amplitude of the wave drawn is bigger
1. Amplitud gelombang dilukis dengan lebih besar
Note: accept as long as the amplitude drawn is slightly
bigger.
1
1
(c) (i) P Infrared
P Inframerah
Q Ultraviolet
Q - Utraungu
1
1
2
(ii) Gamma ray / ultraviolet / x-Ray
Sinaran gama /Utraungu / Sinar - x
1 1
(iii) Can kills the life cell / skin burn or skin cancer /
Boleh membunuh sel hidup / kulit terbakar / kanser kulit
Note: the reason given must be related to the answer in
(c) (ii)
1 1
(iv) Radio wave / microwave
Gelombang radio / gelombang mikro
1 1
(v) High frequency / high energy / high penetrating power
Frekuensi ynag tinggi / tenaga yang tinggi / Kuasa
penembusan yang tinggi
1 1
(vi) Gamma Ray
Sinaran gama
1 1
(vii)
high energy / high penetrating power
Tenaga yang tinggi / Kuasa penembusan yang tinggi
1 1
TOTAL 12M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 146
CHAPTER 7: ELECTRIC
PAPER 1
1. Diagram 1 shows the electric field pattern formed by two charged spheres P and Q.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan corak medan elektrik dibentuk oleh dua sfera bercas P dan Q.
Which of the following explain the charge of P and Q?
Manakah yang berikut menerangkan cas pada P dan Q?
P Q
A Negative
Negatif
Negative
Negatif
B Negative
Negatif
Positive
Positif
C Positive
Positif
Negative
Negatif
D Positive
Positif
Positive
Positif
P
Q
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 147
2. Diagram 2 shows the electric field lines of a pair of charged particles, Q
1
and Q
2
.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan garis-garis medan elektrik bagi sepasang zarah bercas, Q
1
dan Q
2
.
What are the type of charges of Q
1
and Q
2
?
Apakah jenis cas bagi Q
1
dan Q
2
?
Q
1
Q
2
A Positive Negative
Positif Negatif
B Positive Positive
Positif Positif
C Negative Positive
Negatif Positif
D Negative Negative
Negatif Negatif
Q
1
Q
2
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 148
3. Diagram 3 shows a charged conducting sphere is oscillates between two plates which
are connected to an Extra High Tension (EHT) power supply.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan satu sfera konduktor bercas berayun di antara dua plat yang
telah disambung ke satu bekalan voltan lampau tinggi (VLT).
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
The frequency of the oscillation of the sphere will increase if
Frekuensi ayunan bebola akan bertambah jika
A the distance between the plates is increased.
jarak antara dua plat ditambah.
B the size of the sphere is increased.
saiz sfera ditambah.
C the length of the thread is increased.
panjang benang ditambah.
D the voltage of the EHT is increased.
voltan VLT ditambah.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 149
4. Diagram 4 shows a Voltage-Current graph.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan graf Voltan- Arus.
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
Which of the following circuit diagrams will give the result as the graph above?
Manakah litar elektrik berikut akan memberi keputusan seperti pada graf di atas?
A B
C D
V
I
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 150
5. Which circuit can be used to determine the relationship between voltage and electric
current of a constantan wire?
Litar manakah boleh digunakan untuk menentukan hubungan antara voltan dengan
arus elektrik bagi satu dawai konstantan?
6. Which of the following factors influences resistance of a wire?
Antara faktor berikut yang manakah mempengaruhi rintangan bagi suatu dawai?
A. Hardness of the wire
Kekerasan dawai
B. Density of the wire
Ketumpatan dawai
C. Length of the wire
Panjang dawai
D. Mass of the wire
Jisim dawai
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 151
7. Diagram 5 shows a potential difference against current graph for four different
conductors J, K, L and M.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan graf beza keupayaan melawan arus untuk empat konduktor
yang berlainan.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Which conductor has the least resistance?
Konduktor yang manakah mempunyai rintangan yang paling rendah?
A J B K
C L D M
8.. Diagram 6 shows four bulbs in a circuit.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan empat mentol di dalam satu litar.
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
6V
Q
S
P
R
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 152
Which of the following is observed when the switch is on?
Manakah yang berikut dapat diperhatikan apabila suis dihidupkan?
A Both bulbs P and S show the same brightness.
Kedua-dua mentol P dan mentol S sama cerah.
B Both bulbs Q and R show the same brightness.
Kedua-dua mentol Q dan mentol R sama cerah.
C Bulb Q is brighter than bulb R.
Mentol Q lebih cerah daripada mentol R.
D Bulb R is brighter than bulb P.
Mentol R lebih cerah daripada mentol P.
9. Which of the following arrangements of three identical resistors will has the least
effective resistance between point X and point Y?
Yang manakah antara susunan-susunan bagi tiga perintang yang serupa berikut,
mempunyai rintangan berkesan antara titik X dan titik Y yang paling kecil?
A
B
C
D
X Y
X Y
Y X
Y X
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 153
10. Diagram 7 shows a circuit with three identical resistors , R and two measuring
instruments X and Y.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan satu litar elektrik yang mengandungi tiga perintang yang
serupa, R dan dua alat pengukur X dan Y.
Which of the following is correct?
Antara berikut yang manakah adalah betul?
11 Diagram 8 shows identical resistors are connected in 3 different circuit, P,Q and R
respectively.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan perintang yang serupa disambungkan dalam 3 litar yang
berbeza, P,Q dan R masing-masing.
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
X Y
A Ammeter Ammeter
B Voltmeter Voltmeter
C Ammeter Voltmeter
D Voltmeter Ammeter
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 154
Which of the following is correct for I
p
, I
q
and I
r
?
Antara berikut, yang manakah betul untuk I
p
, I
q
dan I
r
?
A I
p
< I
q
< I
r
B I
p
< I
r
< I
q
C I
q
< I
p
< I
r
D I
q
< I
r
< I
p
12. Diagram 9 shows an electric circuit.
Rajah 9 menunjukkan satu litar elektrik.
Diagram 9
Rajah 9
Calculate the total current flowing in the circuit.
Hitungkan jumlah arus yang mengalir dalam litar itu.
A 0.3 A B 1.5 A
C 3.0 A D 6.0 A
13. Which of the following circuit arrangement is correct to determine the electromotive
force of a battery?
Antara susunan litar berikut yang manakah betul bagi menentukan daya gerak
elektrik sebuah bateri?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 155
14. Diagram 10 shows a potential difference, V against current, I graph.
Rajah 10 menunjukkan graf beza keupayaan,V, melawan arus, I,.
What is the internal resistance of the cell?
Berapakah rintangan dalam bagi sel itu?
A 2.40 B 1.50
C 1.25 D 0.40
15. An electric bulb is labeled 240V, 60W. How much energy is used by the bulb in
one minute if the bulb is connected to a 240V power supply?
Satu mentol berlabel 240V, 60W. Berapakah tenaga yang digunakan oleh mentol
tersebut dalam satu minit jika ia disambung kepada bekalan kuasa 240V?
A 60 J B 360 J
C 600 J D 3600 J
Diagram 10
Rajah 10
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 156
16 Diagram 11 shows an electric circuit consisting of three resistors and power supply
12 V.
Rajah 11 menunjukkan satu litar elektrik yang mengandungi tiga perintang dan
bekalan kuasa 12V.
Diagram 11
Rajah 11
What is the power loss due to the resistors in the circuit?
Berapakah kuasa yang hilang disebabkan oleh perintang-perintang di dalam litar
di atas?
A. 1.5 W B. 3.0 W
C. 10.3 W D 12.0 W
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 3.1 shows photograph of an electric circuit. The circuit contains four
identical bulbs connected to four identical new dry cells
Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan forograf bagi satu litar elektrik. Litar itu mengandungi empat
mentol serupa disambung kepada empat sel kering baru yang serupa.
Diagram 3.1
Rajah 3.1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 157
(a) What is the type of the circuit ?
Apakah jenis litar elektrik tersebut?
.........................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
(b) Draw an electric circuit diagram for the above arrangement of apparatus using
appropriate symbols.
Lukiskan satu rajah litar elektrik bagi susunan radas diatas dengan
menggunakan simbol-simbol yang sesuai.
[2 marks]
[ 2 markah]
(c) Compare the brightness of the lamps J , K ,L and M.
Tick () one box below.
Bandingkan kecerahan mentol J , K , L dan M.
Tandakan satu () pada kotak yang berkenaan.
The brightness of lamp J >lamp K > lamp L > lamp M
Kecerahan mentol J>mentol K > mentol L > mentol M
The brightness of lamp L >lamp K > lamp J > lamp M
Kecerahan mentol L >mentol K > mentol J > mentol M
The brightness of lamp J = lamp K = lamp L = lamp M
Kecerahan mentol J =mentol K = mentol L = lamp M
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
(d) Give one reason for your answer in (c).
Beri satu sebab bagi jawapan anda dalam (c).
........................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
(e) Explain why the circuit above is used in the house lighting circuit.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 158
Terangkan mengapa litar di atas digunakan dalam system pendawaian di
rumah.
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
2. Diagram 4.1 shows a polystyrene ball that coated with metallic paint is hung in an
electric field between two metal plates.
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan sebiji bola polisterin yang disalut dengan cat logam
digantung dalam suatu medan elektrik di antara dua plat logam.
Diagram 4.1
Rajah 4.1
(a) (i) What is the meaning of electric field?
Apakah maksud medan elektrik?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) State the change on the strength of the magnetic field when the
potential difference of the high voltage supply increases.
Nyatakan perubahan ke atas kekuatan medan magnet bila beza
keupayaan bekalan voltan lampau tinggi bertambah.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) The polystyrene ball then is touched to the negative plate.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 159
Bola polisterin itu kemudian dibawa menyentuh plat negatif.
(i) State the type of charge received by the polystyrene ball.
Nyatakan jenis cas yang diterima oleh bola polisterin itu.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) What happen to the polystyrene ball when it is released from negative
plate?
Apakah berlaku kepada bola polisterin itu bila ia lepaskan dari plat
negatif?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) (i) The polystyrene ball in Diagram 4.1 is replaced by a burning candle.
On Diagram 4.2, draw the shape of the candle flame observed in the
electric field.
Bola ping-pong dalam Rajah 4.1 itu digantikan dengan sebatang lilin
yang menyala.
Pada Rajah 4.2, lukiskan bentuk nyalaan lilin yang diperhatikan
dalam medan elektrik itu.
Diagram 4.2
Rajah 4.2
[1 mark]
[1 markah ]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 160
(ii) Explain why the shape of the candle flame observed as drawn in
answer 2(c)(i).
Terangkan mengapa bentuk nyalaan lilin yang diperhatikan adalah
seperti yang dilukis dalam jawapan 2(c)(i).
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
3. Diagram 3.1 shows a circuit used to investigate the relationship between current and
potential difference across a constantan wire s.w.g. 24 with length of 10 cm.
Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan sebuah litar yang digunakan untuk menyiasat hubungan
antara arus dan beza keupayaan yang merentasi dawai konstantan s.w.g. 24 dengan
panjang 10 cm.
Diagram 3.1
Rajah 3.1
(a) Name the measuring instruments labeled X and Y in Diagram 3.1.
Namakan alat pengukur yang berlabel X dan Y dalam Rajah 3.1.
X :
Y :
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 161
(b) (i) What is the relationship between the reading of the measuring
instruments X and Y?
Apakah hubungan antara bacaan pada alat pengukur X dan Y ?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) State the physics law involved in 3b(i).
Nyatakan hukum fizik yang terlibat dalam 3b(i).
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) The experiment is repeated by using a constantan wire s.w.g 36 with the same
length. Diagram 3.2 shows the graph V against I for the experiments.
Eksperimen itu diulangi dengan menggunakan dawai konstantan s.w.g 36
dengan panjang yang sama. Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan graf V melawan I untuk
eksperimen tersebut.
Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.2
Based on graph in Diagram 3.2 ;
Berdasarkan graf pada Rajah 3.2 ;
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 162
(i) What is the physical quantity represented by the gradient of the graph?
Apakah kuantiti fizik yang diwakili oleh kecerunan graf ?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Which of the constantan wire has the higher resistance ?
Dawai konstantan yang manakah mempunyai rintangan yang lebih
tinggi ?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Explain your answer in 3c(ii)
Jelaskan jawapan anda di 4c(ii)
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
PAPER 2 SECTION B
4. Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2 show two circuits. Each circuit contains an ammeter,
4 cells and a filament lamp labeled 6V, 24 W.
Diagram 10.3 and Diagram 10.4 show the thickness of coiled wire of the filament
lamp M and N, respectively.
Rajah 10.1 dan Rajah 10.2 menunjukkan dua litar. Setiap litar itu mengandungi satu
ammeter, empat sel dan satu lampu filamen berlabel 6V, 24 W.
Rajah 10..3 dan Rajah 10..4 menunjukkan ketebalan gegelung dawai bagi lampu
filamen M dan N, masing-masing
Diagram 10.1
Rajah 10.1
Diagram 10.2
Rajah 10.2
6V
Filament lamp M
Lampu filamen M
6V
Filament lamp N
Lampu filamen N
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 163
(a) What is the meaning of the labeled 6V, 12 W on the filament lamp?
[1 mark]
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan label 6V, 12 W pada lampu filamen?
1 markah]
(b) (i) Observe Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2.
Compare the reading of the ammeter and the brightness of the
filament lamp M and N. [2 marks]
Perhatikan Rajah 10.1 dan Rajah 10.2.
Bandingkan bacaan pada ammeter dan kecerahan lampu filamen M
dan N. [2 markah]
(ii) Observe Diagram 10.3 and 10.4.
Compare the thickness of coiled wire of the filament lamps. 1 mark]
Perhatikan Rajah 10.3 dan 10.4.
Bandingkan ketebalan gegelung dawai bagi lampu-lampu filamen itu.
[1 markah]
(iii) Relate the brightness of the filament lamp with the thickness of coiled
wire to make a deduction on the relationship between resistance and
the current. [2 marks]
Hubungkaitkan kecerahan lampu filamen dengan ketebalan gegelung
dawai untuk membuat kesimpulan tentang hubungan antara rintangan
dengan arus. [2 markah]
Diagram 10.3
Rajah 10.3
Filament lamp M
Lampu filamen M
Filament lamp N
Lampu filamen N
Diagram 10.4
Rajah 10.4
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 164
(c) Diagram 10.5 show two types of plug for the electric kettle that can be
connected to the electric supply.
Diagram 10.5(a) uses two pin plug, while Diagram 10.5(b) uses a three pin
plug with an earth wire.
Rajah 10.5 menunjukkan dua jenis plug untuk cerek elektrik yang boleh
disambungkan pada bekalan kuasa.
Rajah 10.5(a) menggunakan palam dua pin, manakala Rajah 10.5(b)
menggunakan palam tiga pin dengan dawai bumi.
(i) Explain why a three pin plug is more suitable compared with a two pin
plug. [2 marks]
Terangkan mengapa palam tiga pin adalah lebih sesuai berbanding
dengan palam dua pin. [2 markah]
(d) Diagram 10.6 shows a water heater used to boil water.
Rajah 10.6 menunjukkan satu pemanas rendam digunakan untuk mendidihkan
air.
Diagram 10.6
Rajah 10.6
Water
air
Electric kettle
Cerek elektrik
Diagram 10.5(a)
Rajah 10.5(a)
Electric kettle
Cerek elektrik
Diagram 10.5(b)
Rajah 10.5(b)
2 pin plug
Palam 2 pin
3 pin plug
Palam 3 pin
Diagram 10.5
Rajah 10.5
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 165
Using appropriate physics concepts, suggest and explain how to build a water
heater which can boils a larger quantity of water faster , more efficient, and
more safety based on the following aspects;
Dengan menggunakan konsep-konsep Fizik yang sesuai, cadang dan
terangkan bagaimana untuk membina satu pemanas rendam yang boleh
mendidihkan kuantiti air yang lebih besar dengan lebih cepat, lebih cekap dan
lebih selamat , berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut ;
(i) material used for the heating element of the water heater
bahan yang digunakan untuk elemen pemanas bagi pemanas renam
(ii) shape of the heating element of the water heater
bentuk elemen pemanas bagi pemanas rendam
(iii) melting point of the heating element of the water heater
takat lebur elemen pemanas bagi pemanas rendam
(iv) rate of rusting of the heating element of the water heater
kadar pengaratan elemen pemanas bagi pemanas rendam
[10 marks]
10 markah]
PAPER 2 SECTION C
5 Diagram 12.1 shows an electrical circuit.
Rajah 12.1 menunjukkan satu litar elektrik .
Diagram 12.1
Rajah 12.1
Q
Slider
Gelongsor
Q
Switch
Suis
Bulb
Mentol
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 166
(a) (i) What is the function of rheostat in the circuit ? [1 mark]
Apakah fungsi rheostat dalam litar itu? [1 markah]
(ii) State the energy transformation occurs at the bulb in the circuit .
[1 mark]
Nyatakan perubahan tenaga yang berlaku pada mentol dalam litar itu.
[1 markah]
(iii) Draw the diagram of circuit in Diagram 12.1 using symbols.
[1 mark]
Lukiskan litar dalam Rajah 12.1 menggunakan simbol [1 markah]
(b). Explain why the brightness of the bulb increases when the slider is adjusted
close to Q.
Terangkan mengapa kecerahan mentol bertambah apabila gelongsor
dilaraskan mendekati Q.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c) Diagram 12.2 shows an electric circuit consist of two bulbs R and S labeled
6V 3W and 6V 12W respectively connected to a 6V battery.
Rajah 12.2 menunjukkan satu litar elektrik terdiri dari dua mentol, R dan S
yang masing-masing berlabel 6V 3W dan 6V 12W disambungkan pada sebuah
bateri 6V.
Diagram 12.2
Rajah 12.2
When the switch is turned on, calculate:
Apabila suis dihidupkan , hitungkan:
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 167
(i) the total current in the circuit .
Jumlah arus yang m,engalir didalam litar.
[ 3 marks]
[ 3 markah]
(ii) the energy used by a bulb , R in one minute.
tenaga yang digunakan oleh mentol R dalam satu minit.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) National Grid Network is a system of electric transmission from power station
to the consumer in our country. Diagram 12.3 shows a block diagram of the
system.
Rangkaian Grid Nasional ialah satu system penghantaran tenaga elektrik
daripada stesen janakuasa ke kawasan pengguna di negara kita. Rajah 12.3
menunjukkan gambarajah blok sistem tersebut.
Diagram 12.3
Rajah 12.3
Using your knowledge about electrical and Diagram 4.3 , you are asked to
determine the most suitable item used in the system J, K, L, M and N for a
National Grid Network system in Diagram 12.4.
Menggunakan pengetahuan anda mengenai elektrik dan Rajah 4.3 , anda
dikehendaki mengenalpasti ciri-ciri yang digunakan dalam system J, K, L, M
dan N untuk Rangkaian Grid Nasional dalam Rajah 12.4.
Power Stesen
Stesen Janakuasa
Transformer P
Transformer P
ppp
Transformer Q
Transformer Q
Consumer
Pengguna
Electric Cable
Kabel elektrik
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 168
Diagram 12.4
Rajah 12..4
Study the specification of the five system and explain the suitability of each
based on following aspects;
Kaji spesifikasi kelima-lima sistem itu dan terangkan kesesuaiain setiap
satunya berdasarkan aspek berikut:
(i) type of transformer P and Q
jenis transformer P dan Q
(ii) characteristic of cable used
ciri-ciri kabel yang digunakan
System
Sistem
Type of
Transformer
Jenis transformer
Diameter of
conductor cable
Diameter
konduktor kabel
Transmission
voltage
Voltan
Penghantaran
Cable
Position
Kedudukan
kabel
J
P is step up
Q is step down
P injak naik
Q injak turun
Big diameter
conductor
Diameter
konduktor besar
Curent with
Low voltage
Arus dengan
voltan rendah
On the
Pylon
Di atas
pilon
K
Q is step up
P is step down
Q injak naik
P injak turun
Small diameter
Conductor
Diameter
konduktor kecil
Current with
higher voltage
Arus dengan
voltan tinggi
On
concrete
piller
Di atas
tiang
konkrit
L
P is step up
Q is step down
P injak naik
Q injak turun
Big diameter
conductor
Diameter
konduktor besar
Current with
higher voltage
Arus dengan
voltan tinggi
On the
Pylon
Di atas
pilon
M
Q is step up
P is step down
Q injak naik
P injak turun
Small diameter
Conductor
Diameter
konduktor kecil
Curent with
Low voltage
Arus dengan
voltan rendah
On
concrete
pylon
Di atas
tiang
konkrit
N
P is step up
Q is step up
P injak naik
Q injak naik
Small diameter
Conductor
Diameter
konduktor kecil
Current with
higher vltage
Arus dengan
voltan tinggi
On
concrete
piller
Di atas
tiang
konkrit On
piller
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 169
(iii) potential difference transmission of electric
beza keupayaan elektrik yang dihantar
(iv) the position of cable
kedudukan kabel
Explain the suitability of each aspects and determine the most suitable system.
Give reasons for your choice.
Terangkan kesesuaian setiap aspek dan tentukan siatem yang paling sesuai.
Beri sebab bagi jawapan anda.
[ 10 marks]
[10 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 170
CHAPTER 7 : ELECTRIC
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 D 5 A 9 A 13 A
2 A 6 C 10 C 14
C
3 D 7 D 11 B 15
D
4 B 8 B 12 C 16
C
PAPER 2 SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a) parallel circuit 1 1
(b)
M1 All symbols correct
M2 Circuit correct
1
1
2
(c) The brightness of lamp J = lamp K = lamp L = lamp M 1 1
(d) The voltage is the same 1 1
(e) One bulb blow , other bulbs can still lights up 1 1
TOTAL MARK 6M
2(a) (i) A region in which there is an electric force // a region around a
charged object which gives electric force on another charged
object.
1
2
(ii) Increases 1
(b)(i) Negative charged 1
2
(ii) Attracted to positive plate // Repelled away from negative
plate
1
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 171
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(c) (i) Note : The flame flatten and spread out more toward negative
plate
1
3
(ii) 1. The heat of burning candle produces positive and negative
ions.
2. The positive ions which are heavier is pulled towards
negative plate with a large proportion flame
1
1
TOTAL MARK 7M
3 (a) X : Ammeter
Y: Voltmeter
1
1
2
(b)(i) Directly proportional 1
2
(ii) Ohms Law 1
(c) (i) Resistance 1
3
(ii) Constantan s.w.g 36 1
(iii) Higher gradient 1
TOTAL MARK 7M
PAPER 2 SECTION B
4(a) 24 J of energy is consumed in 1 s if connected to a 6V power
supply // if the voltage is 6 V the power produced is 24 W
1
1
(b)(i) M1 Reading of ammeter is the same
M2 The brightness of filament lamp in Diagram 10.1 is
brighter than Diagram 10.2 // vice versa // Filament M
is brighter
1
1
5 (ii) The thickness of wire in Diagram 10.4 is bigger than in
Diagram 10.3 // vice versa // Filament M is thinner
1
(iii) M1 The thinner the wire the brighter the lamp // vice versa
M2 The thinner the wire the more the heat produced by the
lamp.
1
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 172
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(c) 1 Two pin plug has no earth wire // three pin plug has earth
wire
2 using 2 pin plug, if there is leakege of current it will also
flow through the metal body // using 3 pin plug if there is
leakege of current it will flow to the ground
3 The person who touches the metal body will experiences
electric shock // using 3 pin plug, the current will be
earthed
4 using 2 pin is not safe to the consumer // Using 3 pin plug
is more safer to the consumer
1
1
1
1
4
(d)
Aspect Explanation
Use tungsten High melting point
Coiled longer wire, increase the resistance
high melting point not easy to melt under high temperature
Low rate of rusting Does not get rust easily
use termostat When temperature reach 100
o
C, the water
heater will automatically turned off
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
PAPER 2 SECTION C
5(a)(i) to control the current flow in circuit 1
3
(ii) electric energy light energy + heat energy 1
(iii)
1
(b) M1 When the slider near to Q the resistance of rheostat is
smaller.
M2 The current in circuit increase and bulb brighter
1
1
2
(c)(i) M1 I
R
= 3/6 = 0.5 A
M2 I
S
= 12/6 = 2A
M3 I = 0.5 + 2 = 2.5 A
1
1
1 5
(ii) M1 E = Pt = 3 (60)
M2 180 J
1
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 173
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(d) M1 P is step up transformer and Q is step down
transformer
M2 because the current transmits in high voltage in a long
distance and reduced by step down transformer for
consumer
M3 Use a large diameter of cable
M4 because low resistance.
M5 Electric is transmitting with high voltage
M6 to reduce the power lost as heat due to high resistance
of cable.
M7 Cable is support by the pylon
M8 cable is situated at high position for safety
M9 L
M10 Because ..... M1, M3, M5, M7
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 174
CHAPTER 8: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
1. Diagram 1 shows a current flowing in a conductor which is placed in a magnetic field.
In which direction, A, B, C or D does a force act on the conductor?
Rajah 1 menunjukkan konduktor berarus yang diletakkan dalam satu medan magnet.
Dalam arah manakah, A, B, C atau D daya yang terhasil beryindak pada konduktor
itu?
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
2. Diagram 2 shows the structure of an ideal transformer.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu struktur transformer yang unggul.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
What is the potential difference across the bulb?
Berapakah beza keupayaan yang merentasi mentol itu?
A 6 V B 60 V
C 96 V D 200 V
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 175
3. A student is trying to determine the direction of the magnetic field produced by a
current in a straight wire.
Which of the following method is correct?
Seorang pelajar sedang mencuba untuk mencari medan megnet yang terhasil
oleh arus dalam satu dawai lurus.
Antara kaedah berikut, yang manakah benar?
A B
C D
4. Diagram 3 shows an electromagnet made of a soft iron cylinder which can
attract a maximum of 8 metal paper clips.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan sebuah elektromagnet dibuat daripada selinder besi lembut
yang boleh menarik 8 klip kertas logam
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
Metal paper clips
Klip kertas logam
Dry cells
Sel kering
Soft iron cylinder
Selinder besi lembut
Copper coil
Gegelung kuprum
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 176
The maximum number of metal paper clips attracted to the electromagnet can be
increased by
Bilangan maksimum klip kertas logam yang boleh ditarik oleh elektromagnet dapat
ditingkatkan dengan
A using a steel cylinder as the core
menggunakan selinder keluli sebagai teras
B increasing the number of turns of the coil
menambahkan bilangan lilitan gegelung
C using a copper wire of smaller diameter
menggunakan wayar kuprum yang berdiameter lebih kecil
D Increasing the resistance of wire
meningkatkan rintangan wayar
5. Diagram 4 shows a coil which carries a current. Iron filings are sprinkled onto the
cardboard to trace the pattern of the magnetic field.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan sebuah gegelung yang membawa arus. Serbuk besi ditaburkan
keatas kadbod untuk memetakan corak medan magnet.
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
Which of the following is the correct pattern of the magnetic field?
Antara yang berikut yang manakah merupakan corak medan magnet yang
betul?
Current
Arus
Coil carries a current
Gegelung berarus
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 177
A.
B.
C.
D.
6. Diagram 5 shows the galvanometer pointer deflects when a magnet is pushed into a
coil of wire.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan jarum penunjuk sebuah galvanometer terpesong apabila
sebatang magnet ditolak memasuki satu gelung dawai.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 178
Which actions will cause the deflection of galvanometer increases?
Langkah yang manakah akan menyebabkan pesongan galvanometer bertambah?
A increase the number of coils
menambah bilangan lilitan
B push the magnet slower towards the coil
menolak magnet perlahan kearah gegelung.
C use coil that is made from insulated wire
menggunakan gegelung yang dibuat daripada wayar bertebat.
D reverse the magnetic pole of the magnet
menyongsangkan kekutuban magnet.
7. Diagram 6 shows a uninsulated copper rod is placed in a magnetic field.
In which direction the copper rod will deflect when the current is switched on?
Rajah 6 menunjukkan rod kuprum tidak bertebat di letakkan di dalam medan magnet.
Pada arah manakah rod kuprum itu akan terpesong apabila arus dihidupkan?
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 179
8. Diagram 7 shows an electric circuit consisting of a solenoid, an iron core and a
switch.
Rajah 7 menunjukkan satu litar elektrik yang terdiri daripada satu solenoid, satu
teras besi lembut dan satu suis.
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
What happens to the bar magnet when the switch is switched on?
Apa berlaku kepada magnet batang bila suis dihidupkan?
A Does not move
Tidak bergerak
B Move away from the solenoid
Tertolak menjauhi solenoid
C Attract towards the solenoid
Tertarik mendekati solenoid.
D Oscillate to the right and to the left
Berayun ke kanan dan ke kiri.
9. Which of the following option is correct about the electricity transmission from the
power station to consumers?
Antara pilihan berikut yang manakah betul tentang sistem penghantaran tenaga
elektrik dari stesen kuasa kepada pengguna?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 180
Type of current
Jenis arus
Magnitude of voltage supply
Magnitud voltan yang dihantar
A Direct current
Arus terus
High voltage
Voltan tinggi
B Alternating current
Arus ulangalik
High voltage
Voltan tinggi
C Direct current
Arus terus
Low voltage
Voltan rendah
D Alternating current
Arus ulangalik
Low voltage
Voltan rendah
10. Diagram 8 shows a transformer that is used to light up a bulb.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan sebuah transformer yang digunakan untuk menghidupkan sebiji
mentol.
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
Which of the following statements is true about the transformer?
Antara pernyataan-pernyataan yang berikut, yang manakah benar tentang
transformer itu?
Type of transformer
Jenis transformer
Voltage across the bulb
Voltan merentasi mentol
A Step-up
Injak naik
480 V
B Step-up
Injak naik
960 V
C Step-down
Injak turun
50 V
D Step-down
Injak turun
60 V
11. Diagram 9 shows a straight wire passes through a horizontal cardboard.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 181
Rajah 9 menunjukkan satu wayar lurus melalui suatu kadbod yang mengufuk.
When the switch is closed, which of the following patterns of the magnetic field is
correct?
Bila suis ditutup, yang manakah antara corak-corak medan magnet berikut adalah
betul?
A B
C D
12. Diagram 10 shows the arrangement of the apparatus of an experiment to study the
effect of an electromagnet.
Rajah 10 mennjukkan susunan radas yang digunakan bagi satu eksperimen untuk
mengkaji kesan keelektromagnetan.
Cardboard
Kadbod
Straight wire
Wayar lurus
Switch
Suis
Diagram 9
Rajah 9
Iron rod
Rod besi
Wire coil
Gegelung
dawai
Paper clips
Klip kertas
Diagram 10
Rajah 10
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 182
Which of the following methods will increase the number of paper clips attached to
the iron rod?
Yang manakah antara kaedah-kaedah berikut akan menambahkan bilangan klip
kertas yang melekat pada rod besi itu?
A Reduce the number of coils
Kurangkan bilangan lilitan gegelung
B Use a thinner wire to form the coil
Gunakan dawai yang lebih halus untuk membentuk gegelung
C Increase the magnitude of current flow through the coils
Tambahkan magnitud arus yang mengalir melalui gegelung
D Replace the iron rod with aluminum rod
Gantikan rod besi dengan rod aluminium
13. Which of the following instruments uses the concept of electromagnet?
Antara alat-alat berikut , yang manakah menggunakan konsep keelektromagnetan?
A Dynamo B Circuit breaker
Dinamo Pemutus litar
C Electric Motor D Transformer
Motor elektrik Transformer
14. Diagram 11 shows a current carrying conductor is placed in between two permanent
magnets. In which direction, A, B, C or D will the conductor move when the current
flows out of the paper?
Rajah 11 menunjukkan suatu konduktor yang mengalirkan arus elektrik diletakkan
diantara dua magnet kekal . Dalam arah manakah A, B, C, atau D konduktor itu akan
bergerak apabila arus mengalir keluar daripada kertas?
Permanent magnet
Magnet kekal
Permanent magnet
Magnet kekal
Diagram 11
Rajah 11
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 183
15. The purpose of using soft iron core in a transformer is to
Tujuan menggunakan teras besi lembut dalam transformer adalah untuk
A reduce the eddy current
mengurangkan arus pusar
B easily magnetised and demagnetised the iron core
mudah memagnetkan dan menyahmagnetkan teras besi
C prevent flux leakage
mengelakkan kebocoran fluks
D reduce the resistance
mengurangkan rintangan
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 4 shows a bar magnet is hung on a spring that attached to a retort stand. The
bar magnet is displaced downwards and released so it can oscillate through a solenoid
which is connected to a centre-zero galvanometer.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan satu magnet bar digantung pada satu spring yang dilekatkan
pada kaki retot. Bar magnet itu disesarkan ke bawah dan dilepaskan supaya ia boleh
berayun melalui satu solenoid yang disambungkan kepada sebuah galvanometer
pusat-sifar.
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
Centre-zero galvanometer
Galvanometer pusat-sifar
Solenoid
Bar magnet
Magnet bar
Spring
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 184
(a) What is meant by electromagnetic induction?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan aruhan elektromagnet?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) When the bar magnet move towards the solenoid, the galvanometer pointer
deflect for a while.
Bila magnet bar bergerak mendekati solenoid, jarum galvanometer terpesong
seketika.
(i). Explain why the galvanometer pointer deflects?
Terangkan mengapa jarum galvanometer terpesong?
................
........
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(ii). State the polarity of end A and end B of the solenoid.
Nyatakan kutub pada hujung A dan hujung B pada solenoid itu.
A : ......................... ..
B : ........................................................
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c). If the spring is replaced by a stiffer spring,
Jika spring itu diganti dengan spring yang lebih keras,
(i). state the change to the angle of deflection of the galvanometer pointer?
nyatakan perubahan pada sudut pesongan jarum galvanometer itu?
........
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 185
(ii). Give reason for your answer.
Berikan sebab bagi jawapan anda.
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
2. Diagram 2 shows a simple electromagnet.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu elektromagnet ringkas.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
(a) What is the meaning of electromagnet?
Apakah maksud elektromagnet?
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) When the switch is turned on ;
Bila suis dihidupkan ;
( i) draw the pattern of magnetic field on Diagram2.
lukis corak medan magnet pada Rajah 2.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 186
(ii) state the magnetic pole at P
nyatakan kutub magnet pada P.
......................
. [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) state what happens to the pin.
nyatakan apa yang berlaku kepada pin itu.
......................
. [1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) State one application of electromagnet.
Nyatakan satu kegunaan elektromagnet.
.......................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
3. Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 show the pattern of iron filing formed when the
solenoids are connected to the battery.
Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan corak susunan serbuk besi yang terbentuk
apabila solenoid disambungkan kepada bateri.
Diagram 6.1 Diagram 6.2
Rajah 6.1 Rajah 6.2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 187
(a) What is the meaning of electromagnet?
Apakah maksud elektromagnet?
...
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) A compass is located at P in Diagram 6.1.
By using an arrow, mark the direction of the pointer of the compass.
Sebuah kompas diletakkan pada titik P dalam Rajah 6.1.
Dengan menggunakan anak panah, tandakan arah penunjuk kompas.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) Based on Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2, compare;
Berdasarkan Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2, bandingkan;
(i) the number of turns of the coil.
bilangan lilitan solenoid.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) the number of magnetic field line of force.
bilangan garis daya medan magnet.
......................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) the current passing through the solenoid.
magnitud arus yang mengalir melalui soleniod.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(d) State the relationship between the number of turns of the coil and the strength
of the magnetic field.
Nyatakan hubungan antara bilangan lilitan gegelung dengan kekuatan medan
magnet.
........................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 188
(e) (i) What happen to the strength of the electromagnet if a soft iron core is
inserted into the solenoid?
Apakah yang terjadi kepada kekuatan elektromagnet jika satu teras
besi lembut dimasukkan ke dalam solenoid?
.........
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Explain your answer in 3(e)(i).
Terangkan jawapan anda dalam 6 (e) (i).
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
PAPER 2 SECTION B
4. Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2 show a copper wire carrying current is placed in a
permanent magnetic field. The magnetic field produced is called catapult field.
Rajah 10.1 dan Rajah 10.2 menunjukkan satu dawai kuprum yang membawa arus
diletakkan dalam medan magnet kekal. Medan magnet yang terhasil dipanggil medan
lastik.
Diagram 10.1 Diagram 10.2
Rajah 10.1 Rajah 10.2
(a) What is meant by catapult field ?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 189
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan medan lastik ?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Using Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2, compare the number of magnet used,
the angle of deflection of the cooper wire and the angle of deflection of
ammeter indicator.
Menggunakan Rajah 10.1 dan Rajah 10.2, bandingkan bilangan magnet yang
digunakan, sudut pesongan dawai kuprum dan sudut pesongan penunjuk
ammeter.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(c) State the relationship between the strength of the catapult field produced and
Nyatakan hubungan antara kekuatan medan magnet lastik yang terhasil
dengan
(i) number of magnet used
bilangan magnet yang digunakan
(ii) angle of deflection of copper wire
sudut pesongan dawai kuprum [2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) Diagram 10.3 shows a set up used to study the effects of magnetic field of a
current-carrying copper rod
Rajah 10.3 menunjukkan susunan radas yang digunakan untuk mengkaji kesan
medan magnet terhadap rod kuprum yang membawa arus elektrik.
Diagram 10.3
Rajah 10.3
(i) Explain what happens to the copper rod when the switch is turned on.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 190
Terangkan apa yang berlaku kepada rod kuprum apabila suis
dihidupkan.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(ii) The dry cells are replaced with 12 V a.c. Explain what happens to
copper rod when the switch is turned on.
Sel bateri ditukarkan dengan 12 V a.u .Terangkan apa yang berlaku
kepada rod kuprum apabila suis dihidupkan.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(e) Diagram 10.4 shows a d.c. electric motor .
Rajah 10.4 menunjukkan sebuah motor elektrik a.t.
Diagram 10.4
Rajah 10.4
(i) Explain how the motor is able to rotate.
Terangkan bagaimana motor tersebut boleh berputar.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(ii) Suggest three modifications that need to be done on the d.c electric
motor to increase the efficiency of the motor. Give an expalanation for
each suggestion given.
Cadangkan tiga pengubahsuaian yang perlu dilakukan terhadap
motor elektrik a.t itu untuk menambah kecekapan motor tersebut.
Berikan penjelasan untuk setiap cadangan yang diberikan.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 191
[6 marks]
[6 markah]
5. Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2 show the deflection of the galvanometer when a bar
magnets are pushed into two identical solenoids.
Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2 menunjukkan pesongan galvanometer apabila magnet bar
ditolak ke dalam dua solenoid yang serupa.
(a) What is meant by electromagnetic induction?
Apakah maksud aruhan electromagnet? [1 mark]
(b) Using Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2,
Menggunakan Rajah 10.1 dan Rajah 10.2,
Bar magnets
Magnet bar
P
P
Diagram 10.2
Rajah 10.2
Galvanometer
P
Bar magnet
Magnet bar
Diagram 10.1
Rajah 10.1
Galvanometer
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 192
(i) state the magnetic pole at the end P when the bar magnets are pushed
into the solenoids.
nyatakan kutub magnet pada hujung P apabila magnet bar ditolak
ke dalam solenoid.
[1 mark]
(ii) compare the number of bar the magnets and the deflection of the
galvanometer.
bandingkan bilangan magnet bar dengan pesongan galvanometer.
[2 marks]
(c) State the relationship between
Nyatakan hubungan antara
(i) the number of bar magnets and the strength of the magnetic field,
bilangan magnet bar dengan kekuatan medan magnet,
[1 mark]
(ii) the strength of the magnetic field and the deflection of the
galvanometer.
kekuatan medan magnet dengan pesongan galvanometer.
[1 mark]
(d) Diagram 10.3 shows an ideal transformer.
Rajah 10.3 menunjukkan satu transformer unggul.
(i) Name the type of transformer.
Namakan jenis transformer ini. [1 mark]
240 V
ac
12 V
ac
Primary coil
Gegelung primer
Secondary coil
Gegelung sekunder
Diagram 10.3
Rajah 10.3
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 193
(ii) Explain how current is induced in the secondary coil?
Terangkan bagaimana arus diaruh di dalam gegelung sekunder?
[3 marks]
(e) Diagram 10.4 shows an ac generator.
Rajah 10.4 menunjukkan sebuah penjana a.u.
Diagram 10.4
Rajah 10.4
Suggest modifications that can be made to increase the output current to the
generator in Diagram 10.4. State and explain the modifications based on the
following aspects:
Cadangkan pengubahsuaian yang boleh dilakukan pada penjana dalam
Rajah 10.4. Nyatakan dan beri penerangan tentang pengubahsuaian itu
berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut:
(i) Strength of the magnet
Kekuatan magnet
(ii) Shape of the magnet
Bentuk magnet
(iii) Number of turns of the coil
Bilangan lilitan gegelung
(iv) Diameter of the wire of the coil
Diameter dawai pada gelung
(v) The speed of rotation
Laju putaran gelung
[10 marks]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 194
PAPER 2 SECTION C
6. Diagram 12.1 shows a simple transformer.
Rajah 12.1 menunjukkan satu transformer mudah.
Diagram 12.1
Rajah 12.1
(a) State the transformations of energy involved in Diagram 12.1.
Nyatakan pemindahan bentuk tenaga yang terlibat dalam Rajah 12.1
[ 1mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Explain how the transformer works
Terangkan bagaimana transformer berfungsi.
[ 4 marks]
[4 markah]
(c) You are asked to investigate the design and the characteristic of four
transformers shown in Diagram 12.2.
Explain the suitability of each characteristics of the transformer and determine
the transformer which can be use as an ideal transformer.
Give reasons for your choice.
Anda ditugaskan untuk mengkaji rekabentuk dan ciri-ciri bagi empat
transformer seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 12.2.
Terangkan kesesuaian setiap ciri transformer itu dan tentukan transformer
yang boleh digunakan sebagai transformer unggul.
Beri sebab untuk pilihan anda.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 195
P
Q
R
S
Diagram 12.2
Rajah 12.2
[10 marks]
[ 10 markah]
(d) Diagram 12.3 shows a 12V, 48W bulb lights up with normal brightness when
it is connected to a 240V main supply through a transformer.
Rajah 12.3 menunjukkan sebuah mentol 12V, 48W menyala dengan
kecerahan ormal bila ia disambungkan pada 240V bekalan utama melalui
satu transformer.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 196
Diagram 12.3
Rajah 12.3
Calculate:
Hitung:
(i) the output voltage of the transformer
voltan output bagi transformer
(ii) the number of turns of the primary coil
bilangan lilitan pada gelung utama
(iii) the efficiency of the transformer .
kecekapan transformer itu .
[ 5 marks]
[5 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 197
PAPER 3 SECTION A
1. A student carries out an experiment to find out the relationship between number of
turns, N and the current induce, I. A coil is wound with an insulated cooper wire with
40 turns. The coil is connected to a microammeter. The arrangement of the apparatus
for the experiment is shown in Diagram 1.1.
Seorang pelajar menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk mencari hubungan antara bilangan
lilitan,N, dan arus teraruh, I . Satu gegelung dililitkan dengan dawai kuprum bertebat
dengan 40 lilitan. Gegelung itu disambungkan kepada sebuah mikroammeter. Susunan radas
bagi eksperimen itu ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1.1.
Diagram 1.1
Rajah 1.1
A bar magnet from a height, h of 50.0 cm is released so that it passes through the coil.
The induce current, I is measured from the maximum reading of the microammeter .
The actual maximum reading of the microammeter is shown in Diagram 1.2.
The experiment is repeated by using coils with number of turns 60, 80, 100 and 120.
The maximum readings of the microammeter are shown in Diagram 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 and
1.6.
Satu magnet bar daripada ketinggian,h 50.0 cm dilepaskan supaya ia melalui gegelung.
Arusteraruh, I diukur daripada bacaan maksimum mikroammeter. Bacaan maksimum
sebenar mikroammeter adalah ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1.2.
Eksperimen diulangi dengan menggunakan gegelung-gegelung dengan bilangan lilitan 60,
80, 100 dan 120. Bacaan-bacaan maksimum mikroammeter ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1.3,
1.4, 1.5 dan 1.6.
h
Bar magnet
Magnet bar
Cardboard cylinder
Silinder kadbod
Coil
Gegelung
microammeter
mikrometer
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 198
Number of turns = 40 turns
Bilangan lilitan = 40 lilitan
Diagram 1.2
Rajah 1.2
Number of turns = 60 turns
Bilangan lilitan = 60 lilitan
Diagram 1.3
Rajah 1.3
A
A
I = A
I = A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 199
Number of turns = 80 turns
Bilangan lilitan = 80 lilitan
Diagram 1.4
Rajah 1.4
Number of turns = 100 turns
Bilangan lilitan = 100 lilitan
Diagram 1.5
Rajah 1.5
A
I = A
I = A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 200
Number of turns = 120 turns
Bilangan lilitan = 120 lilitan
Diagram 1.6
Rajah 1.6
(a) For the experiment described, identify :
Bagi eksperimen yang diterangkan, kenal pasti:
(i) The manipulated variable.
Pemboleh ubah di manipulasikan.
..
[ 1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) The responding variable.
Pemboleh ubah bergerakbalas
..
[ 1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) The constant variable.
Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan
..
[ 1 mark]
[1 markah]
I = A
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 201
(b) For this part of the question, write your answers in the spaces provided in the
corresponding diagrams.
Untuk bahagian soalan ini, tulis jawapan anda dalam ruang yang disediakan
dalam rajah-rajah yang sepadan.
(i) Based on Diagram 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6, record the reading of I.
Berdasarkan Rajah 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 dan 1.6 , catat bacaan I.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(ii) Tabulate your results for all the values of N and I in the space below.
Jadualkan keputusan anda bagi semua nilai N dan I dalam ruang di bawah.
[ 4 marks]
[4 markah]
(c) On the graph paper on, draw a graph of I against N.
Pada kertas graf di halaman 8, lukis graf I melawan N.
[ 5 marks]
[5 markah]
(d) Based on your graph in 1(c), state the relationship between N and I.
Berdasarkan graf anda di 1(c), nyatakan hubungan antara I dan N.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 202
Graph of I against N
Graf I melawan N
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 203
PAPER 3 SECTION B
2. Diagram 4.1 and 4.2 show the electric bell which are connected to the similar
batteries.
Rajah 4.1 dan 4.2 menunjukkan dua loceng elektrik yang disambungkan kepada
bateri yang mempunyai voltan yang sama.
Diagram 4.1 Diagram 4.2
Rajah 4.1 Rajah 4.2
When the switch is on, the bell in Diagram 4.2 ring loudly than the bell in Diagram
4.1 .
Apabila suis dihidupkan , loceng dalam Rajah 4.2 berbunyi lebih kuat daripada
loceng dalam Rajah 4.1.
Based on your observation
Berdasarkan pemerhatian anda;
(a) State one suitable inference, [1 mark]
Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai
(b) State one appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated [1 mark]
Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang boleh disiasat
(c ) With use of apparatus such as a insulated copper wire , small iron pins and
other apparatus, describe an experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in
2(b)
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 204
Dengan menggunakan radas seperti , dawai kuprum bersalut, pin besi kecil
dan lain-lain radas yang sesuai, terangkan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat
hipotesis yang dinyatakan di 4(b).
In your description, state clearly the following :
Dalam penerangan anda , jelaskan perkara berikut;
(i) The aim of an experiment
Tujuan eksperimen
(ii) The variable in experiment
Pembolehubah eksperimen
(iii) The list of apparatus and materials
Senarai alat radas dan bahan
(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus
Susunan alat radas
(v) The procedure of the experiment.
Describe how to control and measure the manipulated variables and
how to measure the responding variables.
Prosedur eksperimen.
Jelaskan bagaimana mengawal dan mengukur pembolehubah
manipulasi dan bagaimana mengukur pembolehubah bergerakbalas.
(vi) The way to tabulate tabulate the data
Kaedah menjadual data
(vii) The way to analyze the data
Kaedah menganalisa data
[10 marks]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 205
CHAPTER 8 : ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 A 5 A 9 B 13 B
2 A 6 A 10 D 14
D
3 A 7 A 11 D 15
B
4 B 8 B 12 C
PAPER 2 SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a) The process where induced current / e.m.f in a conductor when
the conductor experiences a change in magnetic flux.
1 1
(b)(i) Solenoid experiences a change in magnetic field.
An induced current / e.m.f induced in the solenoid
1
1
4
(b)(ii) A : North pole - 1m
B : South pole - 1m
1
1
(c)(i) Increases 1
2
(ii) The magnitude of induced current increases // the rate of
change of the magnetic flux increases
1
TOTAL MARK 7M
2 (a) A temporary magnet when there is a flow of electric current 1
1
(b)(i)
1
3
(ii) South / S 1
(iii) Attracted to iron nail (electromagnet) 1
(c) Magnetic lifting machine / circuit breaker / electric bell /
electric relay / ticker timer / magnetic levitated train /
electronic card /parking machine /tape recorder.
1
1
TOTAL MARK 5M
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 206
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
3 (a)
An electromagnet is a solenoid which can produce magnetic
field when current passes through it. When the current is
switch off, the solenoid loses its magnetism.
1 1
(b) Due to left 1
1
(c)(i)
In diagram 6.2 the number of turns of the coils more than 6.1 1
3
(ii)
In diagram 6.2 the number of magnetic field line is more than
that in Diagram 6.1
1
(iii)
The current flow in Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 are the same 1
(d)
As the number of turns of solenoid increase the strength of an
electromagnet increase
1 1
(e)(i) The strength of electromagnet increase 1
2
(ii) The magnetic field line are closer // magnetic field line will be
concentrate
1
TOTAL MARK 8M
PAPER 2 SECTION B
4 (a) A resultant field due to the combination of the magnetic field
due to the current in the conductor and external magnetic field
// Diagram
1
1
(b) M1 Number of turns in D10.2 is bigger
M2 angle of deflection of the ammeter indicator in D10.2 is
bigger
M3 the reading of spring balance in D10.2 is smaller
M4 as current flows is bigger, force acting upwards is
bigger
M5 the reading of spring balance is smaller as ,the force
upwards that act on the coils is bigger
1
1
1
1
1
5
(c)(i) M1 Force acting on the cooper rod
M2 moved the cooper rod towards the magnet
1
1
4
(ii) M1 the cooper rod vibrates
M2 as current change direction
1
1
(d)(i) M1 When the current flow into the coil, magnetic field
is produced. And forces are produced
M2 Catapult field is produced
M3 The forces are in the opposite direction
M4 These pair of forces produce the turning effect on
the coil.
1
1
1
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 207
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(ii) M1 Increase the strength of magnet / add more magnet
M2 increase the strength of magnetic field
M3 Increase the number of turns in the coils
M4 to increase the magnitude of force
M5 Increase the magnitude of current
M6 to increase the magnitude of force / increase the
strength of magnetic field
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
5 (a) The effect of producing emf /current, when there is a relative
motion/cutting between conductor and magnetic field
1
1
(b)(i) North pole 1
3
(ii) The bar magnets in Diagram 10.2 is more than in Diagram 10.1
The deflection of the galvanometer in Diagram 10.2 is more
than in Diagram 10.1
1
1
(c)(i) The more the bar magnets, the stronger the magnetic field
strength. -
1
2
(ii) The stronger the magnetic field strength, the greater/larger the
deflection of the galvanometer
1
(d) (i) Step down transformer 1
4
(ii) 1. When an alternating current flows through the primary
coil,
2. a changing magnetic field will be produced.
3. The changing magnetic field will cut through the
secondary coil, an alternating emf /current of the same
frequency to be induced in the coil.
1
1
1
(e)
Modifications Explanations
Use strong magnet.
Strong magnet produced strong magnetic field,
when a conductor cutting through a strong magnetic
field, high emf/current will be induced.
Concave poles of
magnet.
Concave poles provide a radial field which ensures
the cutting of the magnetic field is always
maximum.
Coil with more turns. More turns mean more conductor cutting through
magnetic field, therefore more emf/current is
induced.
Larger area of coils.
The larger the area of the coil, the more the
magnetic field will be cut through, therefore more
emf/current is induced.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 208
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
Wires are wound on a
soft iron core which
is called armature.
The armature becomes magnetized and increases
the strength of the magnetic field
10
TOTAL MARK 20M
PAPER 2 SECTION C
6(a) Electrical energy light energy 1
1
(b) 1. When an a.c. voltage is supplied to the primary coil, the
soft - iron core is magnetized
2. The magnet produced varies in magnitude and direction
3. This causes a changing magnetic flux to pass through the
secondary coil
4. Induced e.m.f across the secondary coil is produced.
1
1
1
1
4
(c)
Aspect Explanation
Soft iron core Easy to magnetized and demagnetised
Laminated Less eddy current/ reduce energy lost
Thick wire Reduce the resistance/more current
Copper wire Low resistance/ reduce the lost of heat
Q
Soft iron core, Laminated , thick wire,
Copper wire
10
(d)(i) 12 V 1
1
(ii) Np = Vp
Ns Vs
Np = 240 x 200
12
= 4000
1
1
2
(iii) Efficiency = Po x 100
Pi
= 240 x 0.2 x 100
48
= 100 %
1
1
2
TOTAL MARK 20M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 209
CHAPTER 9: ELECTRONIC
PAPER 1
1. Which of the following about the electrons emitted in a cathode-ray tube
is not true?
Yang manakah antara berikut adalah tidak benar mengenai elektron-elektron yang
keluar dari tiub sinar katod?
A Move in straight lines.
Bergerak dalam satu garis lurus
B Move with speed of light.
Bergerak dengan halaju yang sama dengan halaju cahaya
C Can be deflected by electric and magnetic fields
Dipesongkan oleh medan elektrik dan medan magnet
D The speed of electrons is affected by the potential difference
between the cathode and the anode.
Kelajuan elektron dipengaruhi oleh beza keupayaan antara katod dan anod
2. Diagram 1 shows the symbol of a transistor. What are the names of the teminal P, Q
and R?
Rajah 1 menunjukkan symbol bagi satu transistor. Apakah nama bagi terminal P, Q
dan R?
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 210
P Q R
A
Collector
Pengumpul
Base
Papak
Emitter
Pengeluar
B
Collector
Pengumpul
Emitter
Pengeluar
Base
Tapak
C
Base
Tapak
Collector
Pengumpul
Emitter
Pengeluar
D
Emitter
Tengeluar
Base
Tapak
Collector
Pengumpul
3. Diagram 2 shows a logic gate circuit which has two inputs, X and Y.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu litar get logik yang mempunyai dua input, X dan Y.
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
If the logic state of X is 0 and the logic state of Y is 1, what are the logic states at P, Q
and R?
Jika keadaan logik X ialah 0 dan keadaan logik Y ialah 1, apakah keadaan logic bagi
P, Q dan R?
P Q R
A 0 0 1
B 0 1 1
C 1 1 0
D 1 0 1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 211
4. Diagram 4 shows a trace on the CRO screen when an alternating current power supply
is connected to the Y-input of the CRO.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan surihan pada skrin OSK apabila bekalan kuasa arus ulang alik
disambungkan pada input-Y OSK.
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
Which of the following traces form on the screen when the alternating current power
supply is replaced by a dry cell?
Yang mana satu antara surihan-surihan berikut akan terbentuk di atas skrin
apabila bekalan kuasa arus ulang alik digantikan dengan sel kering ?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 212
5. Which of the following circuits will light up the bulb?
Antara sambungan litar-litar berikut, yang manakah akan menyalakan mentol?
A
B
C
D
bulb
mentol
bulb
mentol
bulb
mentol
bulb
mentol
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 213
6. Diagram 5 shows a circuit consists of a transistor used to light up LED during dark.
Unfortunately, the circuit does not work.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan satu litar yang mempunyai transistor digunakan untuk
menyalakan LED ketika gelap. Malangnya, litar itu tidak berfungsi,
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Which of the following would most likely correct the fault in the circuit?
Yang manakah diantara berikut, yang besar kemungkinan boleh membetulkan
kesilapan dalam litar tersebut?
A Reconnect the dry cells with its terminals reversed
Sambung semula sel kering dengan terminalnya disongsangkan
B Reconnect the LED with its terminals reversed
Sambung semula LED dengan terminalnya disongsangkan
C Interchange the positions of the LDR and the resistor R
2
Saling tukar kedudukan LDR dan perintang R
2
D Replaced the LDR with a thermistor
Ganti PPC dengan termistor
LED
LDR
PPC
R
2
R
1
Dry cells
Sel kering
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 214
7. Diagram 6 shows a combination of three logic gates.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan kombinasi tiga get logik.
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
Which truth table is correct for the combination of the three logic gates ?
Jadual kebenaran yang manakah betul bagi kombinasi tiga get logik itu?
A B
C D
A B X
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
A B X
0 0 1
0 1 0
1 0 1
1 1 1
A B X
0 0 1
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
A B X
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 1
1 1 1
A
B
X
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 215
8. Diagram 7 shows the traces of a C.R.O. (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) for an
alternating current (a.c).
Rajah 7 menunjukkan surihan O.S.K (Osiloskop Sinar Katod) bagi suatu arus
ulang alik.(a.u).
What is the peak voltage if the Y-gain is set at 5 V cm
-1
?
Berapakah voltan puncak jika pelarasY dilaraskan pada 5 V cm
-1
?
A 5 V B 10 V
C 15 V D 30 V
9. Which of the following circuits does not light up the bulb?
Antara litar-litar berikut, yang manakah tidak menyalakan mentol?
A
Voltage (V)
Voltan (V)
Time (s)
Masa (s)
Diagram 7
Rajah 7
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 216
B
C
D
10. Diagram 8 shows a logic gate circuit which has two inputs, X and Y.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan satu litar get logik yang mempunyai dua input, X dan Y.
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 217
If the logic state of X is 0 and the logic state of Y is 1, what are the logic states at P, Q
and R?
Jika keadaan logik X ialah 0 dan keadaan logik Y ialah 1, apakah keadaan logik bagi P, Q
dan R?
P Q R
A 0 0 1
B 0 1 1
C 1 1 0
D 1 0 1
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1. Diagram 3.1 shows a cross section of a Maltese cross tube used to study the
characteristics of cathode ray.
Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan keratan rentas sebuah tiub palang Maltese yang digunakan
untuk mengkaji sifat-sifat sinar katod.
Diagram 3.1
Rajah 3.1
(a) What is the meaning of cathode ray?
Apakah yang di maksudkan dengan sinar katod?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 218
(b) When switch S
1
and switch S
2
are turned on, two overlapping shadows are
formed on the screen. Explain why the shadows are formed on the screen.
Apabila suis S
1
dan suis S
2
dihidupkan, dua bayang-bayang yang bertindih
terbentuk diatas skrin. Terangkan kenapa bayang-bayang ini terbentuk di atas
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) Calculate the velocity of cathode ray in the Maltese cross tube .
Hitungkan halaju sinar katod di dalam tiub palang maltese .
[ Charge of electron, e = 1.6 x 10
-19
C ; Mass of one electron, m
e
= 9 x 10
-31
kg ]
[ Cas bagi elektron, e = 1.6 x 10
-19
C ;Jisim bagi elektron, m
e
= 9 x 10
-31
kg ]
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) Diagram 3.2 shows a pair of magnet with opposite poles are placed at the sides
of the tube. One of the shadow deflects.
Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan sepasang magnet dengan kutub berbeza diletakkan
pada sisi tiub tersebut. Satu daripada bayang-bayang tersebut terpesong.
Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.2
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 219
(i) By using an arrow, show the direction of the shadow which deflects in
Diagram 3.2.
Dengan menggunakan anak panah, tunjukkan arah pesongan bayang
pada skrin di Rajah 3.2.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) State the physics rule used to determine the direction of the shadow.
Nyatakan peraturan fizik yang digunakan untuk menentukan arah
bayang tersebut.
..................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 220
2. (a) Diagram 7.1 shows a resistance against temperature graph for a thermistor.
Rajah 7.1 menunjukkan graf rintangan melawan suhu untuk satu termistor.
Diagram 7.1
Rajah 7.1
(i) State how the resistance of the thermistor varies with temperature ?
Nyatakan bagaimana rintangan termistor berubah dengan suhu?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
0 10
20
30
80 70 60 50
40
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
Temperature /
o
C
Suhu /
o
C
Resistance / O
Rintangan / O
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 221
(ii) What is the resistance of the thermistor at 30
o
C . Show on the graph
how you determine the value of resistance.
Apakah rintangan termistor pada suhu 30
o
C. Tunjukkan di atas graf
bagaimana rintangan ditentukan.
....
[2 mark]
[2 markah]
(b) A thermistor and a light dependence resistance (LDR) are used to make a
simple switch which control an air conditioner in a room as shown in
Diagram 7.2.
Termistor dan perintang peka cahaya (PPC) digunakan untuk membina satu
suis ringkas yang m engawal penyaman udara di dalam sebuah bilik seperti
ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 7.2.
Diagram 7.2
Rajah 7.2
The air-conditioner is only activated either on a sunny day or at a hot night
Penyaman udara akan dihidupkan pada waktu siang dan pada malam yang
panas.
Keys : Input P : during the day logic 1
Kunci : Input P : waktu siang logik 1
Input P: at night - logic 0
Input P : waktu malam- logik 0
Input Q : when hot - logic 1
Input Q : apabila panas logik 1
LDR
Thermistor
P
R
Q
Air-conditioner
Penyaman
udara
0 V
12V
AC ,240
V
Relay
Geganti
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 222
Input Q : when cold - logic 0
Input Q : apabila sejuk - logik 0
Relay switch : switch on when output logic is 1
Suis geganti : dihidupkan apabila logik output 1
Relay switch : switch off when output logic 0
Relay switch : dimatikan apabila logik0
Table 7 shows a truth table operation indicates the logic gates which control
the air-conditioner system.
Jadual 7 menunjukkan jadual kebenaran operasi get logic bagi mengawal
system penyaman udara.
Input
Input
Output
Output
P Q R
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
Table 7
Table 7
(i) Using the keys given, complete the table 7
Menggunakan kunci yang diberi, lengkapkan jadual 7.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Name the logic gate in the circuit in Diagram 7.
Namakan get logik dalam litar pada Rajah 7.
........
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) In the space below , draw a symbol of the logic gate in 2b(ii).
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 223
Dalam ruangan di bawah lukiskan simbol bagi get logic di 2b(ii).
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) Diagram 7.3 shows a light dependent resistance, LDR , used in transistor
circuit to control a road lamp labeled 240 V. 100 W.
Rajah 7.3 menunjukkan perintang peka cahaya digunakan dalam litar
transistor untuk mengawal lampu jalan yang berlabel 240 V, 100 W
Diagram 7.3
Rajah 7.3
At night the road lamp is switched on automatically.
Pada waktu malam lampu jalan dihidupkan secara automatik
(i) What is the function of resistor R
1
?
Apakah fungsi perintang R
1
?
........
[1mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Explain how the circuit function at night.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 224
Jelaskan bagaimana litar itu berfungsi pada waktu malam.
[2 mark]
[2 markah]
(iii) Why the lamp is not connected directly to the transistor circuit?
Mengapa lampu jalan itu tidak disambungkan terus pada litar
transistor ?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
3. (a) Diagram 8.1 shows a relay used in an electrical circuit.
Rajah 8.1 menunjukkan satu geganti yang digunakan dalam satu litar elektrik.
Diagram 8.1
Rajah 8.1
(i) What is the function of a relay?
Apakah fungsi geganti?
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 225
(ii) Explain what will happen when an electric current flow in the main
circuit?
Terangkan apakah yang akan berlaku apabila arus elektrik mengalir
dalam litar utama?
....
..
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(b) Diagram 8.2 shows a circuit consists of an automatic switch using a relay to
switch on a street light at night.
Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan satu litar yang terdiri daripada sau suis automatik
menggunakan geganti untuk menghidupkan satu lampu jalan pada waktu
malam.
Diagram 8.2
Rajah 8.2
(i) Name the component labeled Q.
Namakan komponen berlabel Q.
...
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) State the main characteristic for component Q.
Nyatakan ciri utama bagi komponen Q.
...
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 226
(iii) Explain how the component Q light up the street light.
Terangkan bagaimana komponen Q menghidupkan lampu jalan.
..
..
..
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
(c) Diagram 8.3 shows a simple tsunami control system used to detect an
earthquake and eruption volcano at the sea bed which will produced tsunami.
Rajah 8.3 menunjukkan satu sistem kawalan tsunami ringkas yang digunakan
untuk mengesan gempa bumi dan letupan gunung berapi di dasar laut yang
akan menghasilkan tsunami.
Diagram 8.3
Rajah 8.3
The circuit consists of vibration sensor, V, and water temperature sensor,T, at
the sea bed.
The vibration and increase in temperature detected will produced signals
which will be sent to a logic gate and then to the tsunami operation detector
room through the transmitter.
Litar adalah terdiri daripada pengesan gegaran, V, dan pengesan suhu air, T
di dasar laut.
Gegaran dan kenaikan suhu air yang dikesan akan menghasilkan isyarat yang
akan dihantar kepada get logik dan seterusnya dihantar ke bilik operasi
pengesan tsunami melalui pemancar.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 227
Keys ;
Kekunci;
Vibration sensor, V : With vibration Logic 1
Pengesan gegaran, V : Dengan gegaran Logik 1
Vibration sensor, V : Without vibration Logic 0
Pengesan gegaran, V : Tiada gegaran Logik 0
Water temperature sensor, T : High temperature Logik 1
Pengesan suhu air, T : Suhu tinggi Logik 1
Water temperature sensor, T : Low temperature Logik 0
Pengesan suhu air, T : Suhu rendah Logik 0
Output S : Radar is activated Logic 1
Output S : Radar diaktifkan Logic 1
Output S : Radar is deactivated Logic 0
Output S : Radar is tidak diaktifkan Logic 0
Tsunami will occur when there is a vibration or change of high temperature at
the sea bed.
Tsunami akan berlaku apabila terdapat gegaran atau perubahan suhu tinggi
di dasar laut.
Table 8 is a truth table which shows the operation of the logic gate in the
tsunami control system.
Jadual 8 adalah jadual kebenaran yang menunjukkan oparasi get logik dalam
sistem kawalan tsunami.
V T S
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
Table 8
Jadual 8
(i) Using the keys given, complete Table 8.
Menggunakan kekunci yang diberikan, lengkapkan jadual 8.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 228
(ii) Name the logic gate in the circuit in Diagram 8.3.
Namakan get logik dalam litar pada Rajah 8.3.
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) In the space below, draw the logic gate symbol in 3 c(ii).
Pada ruangan di bawah, lukis symbol get logik dalam 3 c(ii).
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 229
CHAPTER 9 : ELECTRONIC
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 B 5 B 9 C
2 A 6 C 10 D
3 C 7 A
4 B 8 C
PAPER 2 SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a) Beam of electron moving at high speed
Alur elektron berhalaju tinggi
1 1
(b) 1. Light from the filament is blocked by the cross
Cahaya dari filament dihalang oleh palang
// Cathode ray is blocked by the cross
Sinar katod dihalang oleh palang
1
1
(c) 1. Correct substitution
2 (1.6 x 10
-19
) ( 3000)
9 x 10
-31
2. Correct answer with unit
3.27 x 10
7
ms
-1
1
1
2
(d) (i)
1
1
(ii) Flemings left- hand rule // Peraturan tangan kiri Fleming 1 1
TOTAL MARK 6M
S
C
H
E
M
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 230
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
2 a)(ii) Temperature high, resistance low
Suhu tinggi, Rintangan rendah
1
3
(ii) - Lines drawn on the graph.
-1.35
- garis dilukiskan pada graf
-1.35
1
1
(b) (i) Output,R
0
1
1
1
1
3
(ii) OR
ATAU
1
(iii)
1
(c) (i)
To limit the current flows into the base terminal.
Menghad arus yang mengalir ke dalam terminal tapak
1
5
(ii) At night, no light fall on the LDP, resistance, R of LDP high.
As R high, the voltage, V across the LDP also high.
V across the base circuit > V
min
, this will switch on the
transistor and the collector circuit works.
Pada waktu malam, tiada cahaya dalam LDP, rintangan, R
bagi LDP tinggi,
Apabila R tinggi, voltan, V mengalirdalam LDP juga tinggi.
V melalui litar tapak > V
min,
suis transistor akan dihidupkan
dan litar pengumpul akan berkerja
1
1
1
(iii) The voltage 6 V in the collector circuit will not light up the
bulb.
Voltan 6V dalam litar pengumpul tidak akan menyalakan
mentol
1
TOTAL MARK 10M
3(a)(i) As an automatic switch to switch on the second circuit
Sebagai suis automatik dihidupkan pada litar kedua
1
3
(ii) - Relay coil will be an electromagnet
- attracts soft iron armature
- second circuit will be operated (Max 2M)
- gegelung geganti akan di electromagnet
- angker besi lembut ditarik
- litar kedua akan beroperasi (Maks 2M)
1
1
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 231
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
(b)(i) LDR 1 1
(ii) The resistance of LDR is low when there is light // vice versa
Rintangan bagi LDR adalah rendah apabila ada cahaya //
sebaliknya
1 1
(iii) At night, resistance Q is higher
V
Q
higher > V
be
of battery
I
b
increase, I
c
increase ; (Relay is switch on
Pada waktu malam, rintangan Q adalah tinggi
V
Q
tinggi > V
be
bagi bateri
I
b
bertambah, I
c
bertambah ;Geganti akan dihidupkan
1
1
1
3
(c) (i)
V T S
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
2
4
(ii) OR Gate
Get ATAU
1
(iii)
1
TOTAL MARK 12M
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 232
CHAPTER 10: RADIOACTIVITY
PAPER 1
1 Diagram 1 shows the decay sequence from nucleus uranium-234 to radon-222.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan siri pereputan nukleas uranium-234 kepada radon-222.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
What are the numbers of alpha particles and beta particles that are emitted in this
process ?
Berapakah bilangan zarah alfa dan zarah beta yang dibebaskan dalam proses ini ?
Number of alpha
particles
Bilangan zarah alfa
Number of beta
particles
Bilangan zarah beta
A 1 2
B 2 1
C 3 0
D 0 3
2 Diagram 2 shows the radioactivity decay graph for a radioactive material.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan graf pereputan radioaktif bagi satu bahan radioaktif.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 233
Diagram 2
Rajah 2
What is the half-life of the radioactive material?
Berapakah separuh hayat bahan radioaktif itu?
A 1.0 s B 2.0 s
C 3.0 s D 5.0 s
3 Diagram 3 shows the path of particle P when it moves close to a nucleus.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan lintasan bagi zarah P apabila ia bergerak berhampiran dengan
satu nukleus.
Identify the particle P.
Kenal pasti zarah P.
A -particle B -particle
zarah- zarah-
Particle P
Zarah P
nucleus
nukleus
Diagram 3
Rajah 3
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 234
C -ray D neutron
sinar- neutron
4 Diagram 4 shows an equation of a nuclear reaction.
Rajah 4 menunjukkan persamaan suatu tindakbalas nukleus.
/tenaga
What are the values of P and Q?
Berapakah nilai P dan Q?
P Q
A 3 1
B 2 1
C 4 2
D 3 2
5 Diagram 5 shows the decay curve of a radioactive sample.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan lengkung reputan bagi satu sampel radioaktif.
Diagram 5
Rajah 5
Diagram 4
Rajah 4
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 235
What is the half life of the radioactive sample?
Berapakah separuh hayat bagi sampel radioaktif tersebut?
A 0.2 years B 0.4 years
0.2 tahun 0.4 tahun
C 1.0 years D 1.2 years
1.0 tahun 1.2 tahun
6 In a nuclear fission reaction, 0.005 u mass of a radioactive element is changed to
nuclear energy.
Calculate the energy released.
Dalam proses penyusutan nuklear, 0.005 u.j.a. jisim telah ditukarkan kepada tenaga
nuklear.
Hitung tenaga yang dibebaskan.
[1u = 1.7 x 10
-27
kg , speed of light = 3.0 x 10
8
ms
-1
]
[1 u.j.a. = 1.7 x 10
-27
kg , halaju cahaya = 3.0 x 10
8
ms
-1
]
A 2.55 x 10
-21
J B 5.10 x 10
-19
J
C 3.83 x 10
-13
J D 7.65 x 10
-13
J
7. Which of the following is correct about the penetrating power of o ,| and ?
Antara berikut yang manakah adalah benar mengenai kuasa penembusan o ,| dan
?
A
B
paper
kertas
aluminum
aluminium
3 cm
o
|
o
|
lead
plumbum
10 cm
3 cm
o
|
10 cm
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 236
C
D
8 Diagram 6 shows the arrangement of a radioactive source and a detector to monitor
the thickness of aluminum sheets in a factory.
Rajah 6 menunjukkan susunan satu sumber radioaktif dan satu alat pengesan untuk
memantau ketebalan kepingan aluminium di dalam sebuah kilang.
Which of the following would be most suitable to be used as the radioactive source?
Antara berikut, yang manakah adalah paling sesuai digunakan sebagai sumber
radioaktif itu?
Radiation emitted Half life
aluminum
aluminium
lead
plumbum
aluminum
aluminium
3 cm
o
|
lead
plumbum
10 cm
Roller
Penggelek
Radioactive source
Sumber radioaktif
Aluminum sheet
Kepingan aluminium
Radiation detector
Pengesan sinaran
Counter
Pembilang
Diagram 6
Rajah 6
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 237
Sinaran yang dipancar Setengah hayat
A alpha 5 days
alfa 5 hari
B gamma 5 years
gama 5 tahun
C beta 5 days
beta 5 hari
D alpha 5 years
alfa 5 tahun
PAPER 2 SECTION A
1 Diagram 1 shows the deflection of three types of radioactive emission in an electric
field.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan pesongan tiga jenis pancaran radioaktif di dalam suatu medan
elektrik.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
(a) What is the meaning of radioactivity?
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 238
Apakah maksud keradioaktifan?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) (i) Name the type of radioactive emission.
Namakan jenis pancaran radioaktif.
X :
Z:
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(ii) Give one reason why the deflection of Z more than the deflection of X.
Berikan satu sebab kenapa pesongan Z lebih daripada pesongan X.
................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(c) In a reactor nuclear, Uranium 235 is bombarded by a neutron produces Barium
141 and Kripton 92 by releasing three neutrons. This reaction experiences a
mass defect.
Dalam suatu tindak balas nuklear, Uranium 235 ditembak dengan satu
neutron menghasilkan Barium 141 dan Kripton 92 dengan membebaskan tiga
neutron. Tindakbalas ini mengalami kecacatan jisim.
(i) Name the type of nuclear reaction.
Namakan jenis tindak balas nuklear ini.
...
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Complete the equation of the reaction by writing the appropriate
number in the boxes provided.
Lengkapkan persamaan tindak balas dengan menulis nombor yang
sesuai dalam kotak yang disediakan.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 239
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iiii) The nuclear reaction of one nucleus of uranium - 235 experiences a
mass defect of 2.988 x 10
-28
kg.
Calculate the energy released in the nuclear reaction. The velocity of
light is 3 x 10
8
ms
-1
.
Tindak balas nuklear bagi satu nucleus uranium - 235 mengalami
kecacatan jisim sebanyak 2.988 x 10
-28
kg.
Hitungkan tenaga yang dibebaskan dalam tindak balas itu. Halaju
cahaya adalah 3 x 10
8
ms
-1
.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) Radioactive substances give out radiations which are harmful to our body.
Bahan-bahan radioaktif mengeluarkan sinaran yang berbahaya kepada badan
kita.
(i) Suggest one precaution that need to be taken when handling a
radioactive source.
Cadangkan satu langkah berjaga-jaga yang perlu diambil semasa
mengendalikan sumber radioaktif.
...............................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Give one reason for the answer in 1 (d) (i).
Berikan satu sebab bagi jawapan di 1 (d) (i).
............
[1 mark]
PAPER 2 SECTION C
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 240
2. As a researcher, you are assigned to investigate the characteristics of a certain
radioactive isotope that could be used to detect the thickness of paper in paper
factory.
Sebagai seorang penyelidik, anda ditugaskan untuk mengkaji ciri-ciri bagi beberapa
isotop radioaktif untuk digunakan sebagai bahan pengesan ketebalan kertas di
sebuah kilang kertas.
(a) What is meant by radioisotope mean?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan isotop?
[1 mark]
(b) Table 12 below shows the characteristics of five radioisotopes.
Jadual 12 di bawah menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi lima jenis radi isotop.
Radioisotope
Radioisotop
Characteristics Of Isotope
Ciri-ciri Radioisotop
State of matter
Keadaan jirim
Emitted radiation
Radiasi Pancaran
Half-life
Separuh hayat
Penetrating
power
Kuasa
penembusan
Strontium-90
Solid
Pepejal
Beta
Beta
28 years
28 tahun
Medium
Sederhana
Cobalt-60
Solid
Pepejal
Gamma
Gama
5 years
5 tahun
High
Tinggi
Xenon-133
Gas
Gas
Beta
Beta
5 days
5 hari
High
Tinggi
Water
containing H-3
Liquid
cecair
Beta
Beta
12 years
12 tahun
Medium
Sederhana
Polonium-210
Solid
Pepejal
Alpha
Alfa
140 days
140 hari
Low
Rendah
Table 1
Jadual 1
Based on the table above;
Berdasarkan jadual di atas;
(i) Explain the suitable characteristics of the radioisotopes so that it can be
used to detect the thickness of paper in a paper factory.
Terangkan kesesuaian ciri-ciri radio isotop boleh digunakan untuk
mengesan ketebalan kertas di sebuah kilang kertas.
(ii) Determine the most suitable radioisotope to be used and give your
reason for your choice.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 241
Tentukan radioisotop yang paling sesuai digunakan dan berikan sebab
bagi pilihan anda.
[10 marks]
(c) Explain the arrangement of the paper thickness detector apparatus and state
how radioactivity is used to detect the thickness of the paper.
Terangkan satu susunan alat radas pengesan ketebalan kertas dan nyatakan
bagaiman radioaktif digunakan untuk mengesan ketebalan kertas.
[4 marks]
(d) Sketch a graph of activity against time to illustrate how radioactive materials
decay. Use your graph to explain how the half-life is determined.
Lakarkan satu graf aktiviti melawan masa bagi menunjukkan pereputan suatu
bahan radioaktif. Gunakan graf anda untuk menerangkan bagaimana separuh
hayat bahan itu dapat ditentukan.
[3 marks]
(e) The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5 years.
Calculate the time taken for the activity of this isotope to decay to 12.5% of its
initial activity.
Separuh hayat bagi kobalt-60 ialah 5 tahun.
Hitungkan masa yang diambil oleh isotop ini untuk menjadi 12.5% daripada
nilai aktiviti asalnya
[2 marks]
3 Radioactive material has some important uses in the field of agriculture such as to
study the effectiveness of fertilizers and control the population of pests.
Bahan radioaktif mempunyai beberapa kegunaan penting dalam bidang pertanian
seperti mengkaji keberkesanan baja dan pengawalan populasi serangga.
(a) A researcher conducted an investigation using posphorus-32 to study the
absorption and movement of fertilizers in the plant.
Diagram 3 shows how radioisotope posphorus-32 is injected to the stem of the
plant. The half-life of posphorus-32 is 14 days and emits |-particles.
Seorang penyelidik telah menjalankan satu penyiasatan menggunakan
fosforus-32 untuk mengkaji penyerapan dan pergerakan baja dalam satu
tumbuhan .
Rajah 3 menunjukkan bagaimana fosforus-32 disuntik kedalam batang
tumbuhan itu. Separuh hayatbagi fosforus-32 ialah 14 hari dan memancarkan
zarah-|
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 242
.
Diagram 12
Rajah 12
Based on the information on radioactivity and Diagram 12 :
Berdasarkan maklumat dalam keradioakifan dan Rajah 12:
(i) What is meant by half life?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan separuh hayat?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) What is |-particles.?
Apakah zarah-| ? 1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Name the most suitable detector could be used to detect |-
particles.
Namakan satu alat pengesan yang paling sesuai digunakan untuk
mengesan zarah-|.
[1 marks]
[1 markah]
(b) The initial posphorus-32 activity is 800 counts per second.
Calculate the time taken for the phosphorus-32 activity to decrease to 50
counts per second.
Keaktifan awal fosforus-32 ialah 800 bilangan per saat.
Hitung masa yang diambil untuk keaktifan fosforus-32 berkurang
menjadi 50 bilangan per saat.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c) The population of pests can be controlled using radiation from radioactive
source.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 243
You are assigned to study the characteristics of some radioisotopes that are
suitable for use in controlling the population of pests.
Table 2 shows the characteristics of four radioisotopes.
Populasi serangga dapat dikawal dengan menggunakan sinaran radioaktif
dari satu sumber radioaktif.
Anda ditugaskan untuk mengkaji ciri-ciri bagi beberapa radioisotope yang
sesuai untuk digunakan dalam mengawal populasi serangga.
Jadual 2 menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi empat radioisotop.
Radioisotope
Radioisotope
Characteristics of radioisotope
Ciri-ciri radioisotop
State of matter
Keadaan jirim
Types of ray
Jenis sinar
Half-life
Separuh hayat
Iodine-131
Iodin-131
Liquid
Cecair
Gamma
Gama
8 days
8 hari
Xenon-133
Xenon-133
Solid
pepejal
Beta
Beta
days
5 hari
Cobalt-60
Kobalt-60
Solid
Pepejal
Gamma
Gama
5 years
5 tahun
Strontium-90
Strontium-90
liquid
cecair
Beta
Beta
8 years
8 tahun
Table 2
Jadual 2
Explain the suitability of the characteristics of the radioisotope to be used in
the controlling the population of pests based on the following aspects:
Terangkan kesesuian ciri-ciri radioisotope untuk digunakan dalam mengawal
populasi serangga berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut:
- State of matter
Keadaan jirim
- Types of ray
Jenis sinar
- Half-life
Separuh hayat
Determine the most suitable radioisotope to be used and give the reason for
your choice.
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 244
Tentukan radioisotope yang paling sesuai digunakan dan beri sebab bagi
pilihan anda.
[8 marks]
[8 markah]
(c) The following equation shows a fission reaction of Uranium-235.
Persamaan berikut menunjukkan satu persamaan tindakbalas pembelahan
nukleus Uranium-235.
(i) What is meant by a nuclear fission?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan pembelahan nucleus?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Nuclear fission produces a chain reaction.
Describe how the chain reaction occurs in a nuclear fission of an
atom of Uranium- 235.
Pembelahan nukleus menghasilkan tindakbalas berantai.
Huraikan bagaimana tindakbalas berantai berlaku dalam pembelahan
satu atom uranium-235.
[4 marks]
[4 markah
(iii) The nuclear energy produced in the fission reaction of uranium-
235 is 2.9 x 10
-11
J.
Calculate the total lost of mass in the reaction.
[ c = 3.0 x 10
8
ms
-1
]
Tenaga nuklear yang dihasilkan dalam tindakbalas pembelahan itu
ialah 2.9 x 10
-11
J.
Hitungkan jumlah kehilangan jisim dalam tindakbalas itu
[ c = 3.0 x 10
8
ms
-1
]
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
CHAPTER 10 : RADIOACTIVITY
S
C
H
E
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 245
PAPER 1
NO ANSWER NO ANSWER NO ANSWER
1 C 5 C 9 C
2 C 6 D
3 A 7 B
4 A 8 B
PAPER 2 SECTION A
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
1(a) Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of unstable
nucleus with the emission of energetic particles or photons
1 1
(b)(i) X - alpha particle
Z beta particle
1
1
3
(ii) Z is lighter than X 1
(c) (i) Nuclear Fission 1
4
(ii)
1
(iii) E = mc
2
= (2.988 x 10
-11
)(3 x 10
8
)
2
= 2.67 x 10
-11
J
1
1
(d) (i) -strong radioactive substances are handled using remote
controlled mechanical arms from a safe distance //
-weak radioactive substance can be handled by forceps
-workers should wear a special badge //
-wearing protective suits and gears such as gloves, eye
glasses//
1
2
(ii) -to avoid direct contact
- detect the amount of radiation they are exposed to//
* the reason should be related to the answer given in (d)(i)
1
TOTAL MARK 10M
PAPER 2 SECTION C
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 246
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
2(a) The atoms of an element that contain the same number of
protons but differing number of neutrons are called isotopes. //
The atom number is the same but the nucleon number is
different.
1 1
(b) (i)
& (ii)
- Isotope in the solid form
- it is easily handled and does not make a mess.
- Beta principles
- medium penetration power
- medium penetration power
- able to penetrate paper and less dangerous compared
to gamma rays.
- The half-life of the isotope must be long
- to ensure that the isotope can be used for a longer
period of time.
- Strontium-90
- it is a solid, it emits beta principles, has a half life of
28 years and has medium penetration power.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
(c) Radioactive materials and the radioactive ray detector are
arranged as shown in the diagram. High readings from the
diagrams indicate a thin paper where a low reading indicates a
thick paper.
3
3
(d)
3 3
(e) 100% 50% 25% 12.5%
5 years 5 years 5 years
Time = 3(5 years)
= 15 years
1
1
1
3
TOTAL MARK 20M
NO SCHEME
SUB
MARK
TOTAL
MARK
Modul Pecutan Akademik 2012
Modul Pecutan Akademik_FIZIK/2012 Page 247
3(a)(i) The time taken for half of nucleus radioactive material to
decay.
1
3
(ii) Fast moving electron / electron 1
(iii) Geiger-Muller tube 1
(b)
800 400 - 200 - 100 - 50 // No. of T
1/2
= 4
4 x 14 days / 64 days
1
1
2
(c) - The state of matter of radioisotope is solid.
- Easier to handled.
- Emits gamma-ray.
- Penetrating power is high.
- Long half-life.
- Last longer.
The most suitable radioisotope is Cobalt-60.
- Because the state of matter is solid, emits gamma-ray and
long half-life
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
(d)(i) The process of breaking up of on heavy nucleus into lighter
nucleus.
1
7
(ii) - Neutron bombarded a uranium nucleus //
Diagram
- Three neutrons produced // Diagram
- The new neutron bombarded a new uranium
nucleus // Diagram
- For every reaction, the neutrons produced will
generate a chain reaction // Diagram - 1m
1
1
1
1
(iii) E = mc
2
2.9 x 10
-11
= m x (3.0 x 10
8
)
2
m = 3.22 x 10
-28
kg
1
1
TOTAL MARK 20M
You might also like
- Asas Nombor Latihan Format SPMDocument4 pagesAsas Nombor Latihan Format SPMJiajia LauNo ratings yet
- BAB 4 - Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument64 pagesBAB 4 - Jadual Berkala UnsurNini Asnini Ismail0% (1)
- Modul Fizik SPM Kertas 2 & 3Document291 pagesModul Fizik SPM Kertas 2 & 3Farihah Ha50% (4)
- Fizik Tingkatan 5Document199 pagesFizik Tingkatan 5thrrishaNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tingkatan 4 Ujian 1Document7 pagesMatematik Tingkatan 4 Ujian 1Snow WeissNo ratings yet
- Kedah Trial Fizik Kertas 2 SPMDocument22 pagesKedah Trial Fizik Kertas 2 SPMfarahibbNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2014 - Modul Pecutan - Modul X A PlusDocument219 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Chemistry SPM 2014 - Modul Pecutan - Modul X A PlusCikgu Faizal100% (3)
- 03 - Modul Kuantum Fizik Kertas 3 Tingkatan 4 Dan 5Document54 pages03 - Modul Kuantum Fizik Kertas 3 Tingkatan 4 Dan 5Helmi Tarmizi100% (2)
- Modul 12 JanjangDocument19 pagesModul 12 JanjangSujairi AmhariNo ratings yet
- FIZIK1SET3Document27 pagesFIZIK1SET3Mister HafizalNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 FizikDocument24 pagesPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 FizikHilmi Din0% (1)
- p2 FizikDocument24 pagesp2 Fizikdiana100% (1)
- Pat Fiz 2018 K2Document32 pagesPat Fiz 2018 K2Syikin ZainalNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Gelombang fIZIK F5Document36 pagesBab 1 Gelombang fIZIK F5Rafizam Mohd100% (1)
- Modul FizikDocument11 pagesModul FizikAin FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Fizik Ting 4Document26 pagesFizik Ting 4zaliniabdullahNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Memahami KantaDocument27 pages5.4 Memahami KantaAnonymous UypCttWNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Rumus Algebra Latihan TambahanDocument3 pagesModul 3 Rumus Algebra Latihan TambahanEmilyNo ratings yet
- Modul Skor A+ Fizik - RadioaktifDocument18 pagesModul Skor A+ Fizik - RadioaktifCikita IsmailNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial Physics SBP 2012Document89 pagesSPM Trial Physics SBP 2012Ruquan PhuahNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik SPM 2015 Kedah 3.0Document71 pagesModul Fizik SPM 2015 Kedah 3.0Mohd Tarmizi Mohd Nor83% (6)
- 1 2 Unit PengukuranDocument5 pages1 2 Unit Pengukuranslokkro100% (2)
- 9 1 Struktur AtomDocument7 pages9 1 Struktur Atomslokkro100% (12)
- Bab 2 Hukum Linear Shortened Past YearsDocument4 pagesBab 2 Hukum Linear Shortened Past YearsSharifah NafisahNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Memahami GelombangDocument24 pages1.1 Memahami Gelombanghidayahnurul100% (1)
- Taran Dan GelombangDocument63 pagesTaran Dan Gelombangsnazneen2No ratings yet
- BAB 4 Fizik Tingkatan 5: ElektronikDocument34 pagesBAB 4 Fizik Tingkatan 5: ElektronikSyazwan Aizad Abdul Mutalib0% (1)
- PAT Kimia T4 P2 2016Document21 pagesPAT Kimia T4 P2 2016ejalzz100% (1)
- Soalan Fizik Kertas 3Document12 pagesSoalan Fizik Kertas 3jacylin_a_663291230No ratings yet
- Bab 6 Gelombang (Fizik Tingkatan 5)Document15 pagesBab 6 Gelombang (Fizik Tingkatan 5)Zune LeeNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 GelombangDocument91 pagesBab 1 GelombangHafiz Ibrahim100% (1)
- Ujian Matematik Tingkatan 4Document8 pagesUjian Matematik Tingkatan 4Waheeda Wahee33% (3)
- Penjelmaan t5 (SPM Sebenar)Document18 pagesPenjelmaan t5 (SPM Sebenar)Mary Yan AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 2018 SMK SG Pasir Kechil k2 Matematik TambahanDocument15 pages2018 SMK SG Pasir Kechil k2 Matematik TambahanhafabaNo ratings yet
- T5B5 (Latihan 5.4)Document2 pagesT5B5 (Latihan 5.4)ChewLee TanNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Pahang 2017Document30 pagesKertas 2 Pahang 2017Bryan Wong0% (1)
- Modul Cemerlang Sejarah Tingkatan 4Document9 pagesModul Cemerlang Sejarah Tingkatan 4Faridah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Fizik 5.2 PembiasanDocument9 pagesFizik 5.2 PembiasanAnas AjmalNo ratings yet
- Modul Bab 1 Gelombang t5Document41 pagesModul Bab 1 Gelombang t5DequeNo Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Menganalisis Pantulan GelombangDocument7 pages1.2 Menganalisis Pantulan GelombanghidayahnurulNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kepada FizikDocument41 pagesPengenalan Kepada FizikSakawi LenNo ratings yet
- Fizik T4 P2&P3Document16 pagesFizik T4 P2&P3mohd fauzi100% (1)
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 1Document2 pagesLatihan Sains Tingkatan 1Nurul NahariahNo ratings yet
- Modul Kem Gilap Mutiara Fiz Dhs 2016Document14 pagesModul Kem Gilap Mutiara Fiz Dhs 2016nickphysics4927No ratings yet
- Matematik Tingkatan 1Document32 pagesMatematik Tingkatan 1widad.osman50% (2)
- LPKPM SPM 2011 Sejarah Kertas 1, 2Document24 pagesLPKPM SPM 2011 Sejarah Kertas 1, 2Ashwin Josiah SamuelNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Tajuk GelombangDocument15 pagesBab 6 Tajuk Gelombangsyahrilizaham78100% (1)
- Keupayaan Elektrod PiawaiDocument10 pagesKeupayaan Elektrod Piawaisarahothman9No ratings yet
- Kertas 2Document17 pagesKertas 2NOR JAMALIAH BINTI MOHAMAD TARMIZI MoeNo ratings yet
- Ujian MacDocument7 pagesUjian MacMUHAMMAD FIRDAUS BIN MOHD FAUZAI MoeNo ratings yet
- Modul PDPR Ppdkinta Utara 2 2020 - CompressedDocument262 pagesModul PDPR Ppdkinta Utara 2 2020 - CompressedMHD AMIN OMARNo ratings yet
- k2 FizikDocument16 pagesk2 FizikHatena ContennaNo ratings yet
- Modul Pelajar Potensi PDFDocument104 pagesModul Pelajar Potensi PDFSaidah Bt MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Revision p1 Fiz c1f4Document8 pagesRevision p1 Fiz c1f4cikgu_inaNo ratings yet
- FIZIK Set 2 KERTAS 2Document26 pagesFIZIK Set 2 KERTAS 2Jim Juan OsmanNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bulanan Ting 4 Bab 1Document16 pagesUjian Bulanan Ting 4 Bab 1Sakawi LenNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Document25 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2NALLATHAMBYNo ratings yet
- Kertas PenilaianDocument9 pagesKertas PenilaianKero Malek50% (2)
- Kertas 1 Mid Year 2014 LatestDocument24 pagesKertas 1 Mid Year 2014 LatestmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Pat T4 K2 2017Document22 pagesPat T4 K2 2017siti haizaNo ratings yet