Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 4: Mathematics For Elementary School, One-Year Instructional Plan
Uploaded by
Shawanda ClarkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 4: Mathematics For Elementary School, One-Year Instructional Plan
Uploaded by
Shawanda ClarkCopyright:
Available Formats
Copyright !
2006 by Global Education Resources
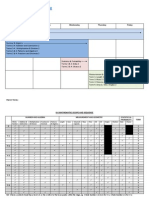
Mathematics for Elementary School Grade 4, One-Year Instructional Plan
1st Trimester
Month
April (15)
Unit
[Volume 1] 1. Large Numbers p. 4-14
# of periods
9
Instructional contents Units and size of numbers up to oku (hundred millions) and cho
(trillions), and their numeration and decimal system [oku, cho]
Decimal notation system and meaning of decimal notation Multiplication calculations involving 3-digit numbers as their
Review 1 p. 15 2. Angles p. 16-24 May (15) 7 (1)
multipliers [product] Multiplication calculations involving a vacant place value in the multiplier, including the case involving 0s at the end of numbers Reviewing previously learned content
Size of angles formed by rotation Unit of angle degree, Unit relationship of one right angle = 90 How to measure and draw angles by using a protractor
[degree ()]
3. Division p. 25-39
15
Mental calculation of division by 10s numbers A method for checking answers in division calculations How to estimate or adjust the quotient Division calculation of 3 to 4-digit numbers divided by 2 digit numbers Division calculation involving 0s at the end of numbers Problem solving that requires thinking about the difference of two quantities How to a create two-dimensional table omissions and duplications of data Meaning of approximate numbers
Division calculation of 2 to 3 digit numbers divided by 2 digit
June (20) Sports Festival p. 40-41 4. How to Organize Data p. 42-47 5. Approximate Numbers p. 48-56 (2) 4
Organizing and summarizing data by using a table, without
7 [approximate number]
Meaning and method of rounding
July (10) Review 2 p. 57 6. Line Graphs p. 58-67 Review 3 (2) p. 68-69 st 7 (1) Different ways to express approximate numbers numbers
[rounding]
Addition and subtraction calculations involving approximate
[sum, difference] Reviewing previously learned content
How to read and draw line graphs
How to read line graphs, particularly those that focus on the relationship between two quantities Retaining and reinforcing the content students learned in the first trimester
Standard # of periods in 1 trimester: 60 periods
49 periods
(Adjustable periods ( ): 6 periods) (Optional periods: 5 periods) Total of 11 periods (6 + 5)
Grade 4 page 1
Copyright ! 2006 by Global Education Resources
2nd Trimester
Month
Sept. (20)
Unit
7. Math Sentences and Calculation p. 70-79
# of periods
8 sentence
Instructional contents Order of operations where parentheses are used in a math Order of operations when the four fundamental rules of arithmetic
(addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) are mixed together in a math sentence
Distributive law and its application Relationships between multiplication and division, relationships
between addition and subtraction them 8. Quadrilaterals p. 80-99 14
Concepts of perpendicular and parallel lines and how to draw
[perpendicular, parallel] Examination of the size of angles formed when a line intersects parallel lines rhombi
Oct. (20)
Concepts and characteristics of trapezoids, parallelograms, and
[trapezoid, parallelogram, rhombus] How to draw a trapezoid, a parallelogram, and a rhombus Characteristics of diagonals of various quadrilaterals [diagonals] Relationships of various quadrilaterals Understanding orientations of plane figures and the essence of their structures through a hands on activity Reviewing previously learned content
Tangrams p. 100-101 Review 4 p. 102 [Volume 2] 9. Decimal Numbers p. 4-18
(2)
(1) 12
Principles of place value of decimal numbers
[ 1 ' s place, 1 place, second decimal place, 's 100 1000 third decimal place] How to read and express decimal numbers on a number line
Structure and relative size of decimal numbers Addition and subtraction calculations involving decimal numbers
Nov. (20) The Botanical Garden p. 19 Using Four 4s p. 20-21 10. Area p. 22-36 11 (1) Corresponding and eliminating the common parts of two quantities and grasping the relationship of the quantities in a simpler way Using four 4s and calculation operation symbols to construct math sentences that have answers from 0 to 9
(2)
Concepts of area
[area, formula] Units for area square centimeter, square meter, are, hectare, and square kilometer and the relationships between those units 2 2 2 [cm , m , a, ha, km ] How to find the area of a composite figure Reviewing previously learned content
Formulae for the area of rectangles and squares
Review 5 p. 37 (1)
Grade 4 page 2
Copyright ! 2006 by Global Education Resources
11. Fractions p. 38-51
11
Concepts and structures of proper fractions, mixed numbers, and
Dec. (10)
improper fractions [proper fraction, mixed number, improper fraction] How to show fractions on a number line, comparison of the size of fractions Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions and vice-versa
Relationship of equivalent fractions Addition and subtraction calculation of proper fractions with like
Review 6 p. 52-53 (2)
denominators Addition and subtraction calculation of mixed numbers with like denominators Retaining and reinforcing the content the students learned in the second trimester
Standard # of periods in 2nd trimester: 70 periods
56 periods
(Adjustable periods ( ): 9 periods) (Optional periods: 5 periods) Total of 14 periods (9 + 5)
Grade 4 page 3
Copyright ! 2006 by Global Education Resources
3rd Trimester
Month
Jan. (15)
Unit
12. Investigating Changes in Quantities p. 54-59 13. Multiplication and Division of Decimal Numbers p. 60-75
# of periods
5 15
Instructional contents
Using ! and ! to express a relationship between two quantities with a math sentence Finding all the combinations of corresponding numbers without omissions and examining changes in the quantities numbers numbers
Multiplication calculation of decimal numbers multiplied by whole Division calculation of decimal numbers divided by whole Division calculation of decimal numbers or whole numbers
divided by whole numbers when you continue to divide (quotients become decimal numbers) Expanding the meaning of decimal numbers (decimal numbers can be used to show how many times as much) Decision making involving multiplication or division calculations with decimal numbers Reviewing previously learned content
Feb. (20)
What Kind of Calculation Do We Need to Use? p. 76 Review 7 p. 77 14. Rectangular Prisms and Cubes p. 78-89
(1)
(1) 9
Concepts and characteristics of rectangular prisms and cubes Examining the components needed to determine the size of a
[face, rectangular prism, cube]
March (10)
Abacus p. 90-91 Town Environment p. 92-93 4 Grade Review p. 94-98
th
2 (2)
rectangular prism or cube Meaning of sketch [sketch] Meaning of net and how to draw it [net] Location relationship of edges and faces of a rectangular prism and a cube (perpendicular, parallel) How to represent points (or locations) on a plane or a space Place value of decimal numbers on the abacus Addition and subtraction calculations using the abacus Application of previously learned content across different domains Mathematical examination of everyday life phenomena (water resources) th Review of all the content learned in the 4 grade
(5)
Standard # of periods in 3rd trimester: 45 periods
31 periods
(Adjustable periods ( ): 9 periods) (Optional period: 5 periods) Total of 14 periods (9 + 5)
Standard # of periods in a year: 175 periods
Note:
136 periods*
(Adjustable periods ( ): 24 periods) (Optional periods: 15 periods) Total of 39 periods (24 + 15)
One period is 45 minutes. The numbers indicated in the ( ) in the month column show the number of available periods in the month. The symbol in the unit column indicates the periods teachers can adjust by considering students state of learning. The symbol in the instructional contents column indicates important content. The [ students learn in the unit. ] contains terms and symbols
Grade 4 page 4
You might also like
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Mathematics Syllabus - Year 6: Properties of Numbers and Number SequencesDocument9 pagesMathematics Syllabus - Year 6: Properties of Numbers and Number SequencesAhn DanielNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 8 Long Range Plans 2016 2017Document4 pagesMath Grade 8 Long Range Plans 2016 2017api-266320227100% (1)
- Teaching Program Year 7Document41 pagesTeaching Program Year 7Evan TranNo ratings yet
- Area, Data & Trig Test PrepDocument3 pagesArea, Data & Trig Test PrepNick DilesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022Document9 pagesMathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022iqra darNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Math Grade 6 Teacher Branka CurcicDocument6 pagesCambridge Primary Math Grade 6 Teacher Branka CurcicBranchi LitesNo ratings yet
- Grade 8: The Learning Equation Math: TimelineDocument5 pagesGrade 8: The Learning Equation Math: TimelineAnusha PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus – Yr 6 SummaryDocument9 pagesMathematics Syllabus – Yr 6 SummaryAnonymous X5rzmINo ratings yet
- Academic Standards in Maths PDFDocument47 pagesAcademic Standards in Maths PDFora1userNo ratings yet
- Maths Scheme of Work Class 2Document12 pagesMaths Scheme of Work Class 2Anonymous yEPScmhs2qNo ratings yet
- YEAR 3 CHECKLIST MathsDocument6 pagesYEAR 3 CHECKLIST MathsChong Chin WeiNo ratings yet
- S.Y 2022-2023 Mathematics 5 Course Outline: I. DescriptionDocument11 pagesS.Y 2022-2023 Mathematics 5 Course Outline: I. DescriptionPrincess Mae LumawagNo ratings yet
- 1 Standards HorizontalDocument2 pages1 Standards Horizontalapi-105565933No ratings yet
- CCSSI Math Standards 1Document4 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 1establoid1169No ratings yet
- G4 Math Course of Study 2018-2019Document10 pagesG4 Math Course of Study 2018-2019Kenneth OdgienNo ratings yet
- Number Maths Edexel GcseDocument1 pageNumber Maths Edexel GcseAnishka JainNo ratings yet
- K-10 Mathematics continuum for curriculum developmentDocument1 pageK-10 Mathematics continuum for curriculum developmentJedda Decker100% (1)
- Mathematics Curriculum - Year 2: Number - Number and Place ValueDocument3 pagesMathematics Curriculum - Year 2: Number - Number and Place ValueMiguel Angel Nadal TurNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Lesson Plan Template For Creating Lesson Plans During On-Campus Lectures Edtp 121 2023Document9 pagesAssignment - Lesson Plan Template For Creating Lesson Plans During On-Campus Lectures Edtp 121 2023Malibongwe MweliNo ratings yet
- Teaching of SpaceDocument5 pagesTeaching of SpaceHaniza HossenNo ratings yet
- First Math StandardsDocument2 pagesFirst Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- Mathematics Stage 6 - tcm142-354162Document4 pagesMathematics Stage 6 - tcm142-354162hildebrandokNo ratings yet
- Math Unit CoverDocument17 pagesMath Unit Coverroza.ardalanNo ratings yet
- Pupil Level DescriptorsDocument7 pagesPupil Level DescriptorsPritpal SinghNo ratings yet
- E Math Syllabus 4048Document16 pagesE Math Syllabus 4048hu1qunNo ratings yet
- SpecsDocument16 pagesSpecskjwenfeNo ratings yet
- Math - KS1&2 - UK - National Curriculum-39-45Document7 pagesMath - KS1&2 - UK - National Curriculum-39-45Peerawat JantanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1Document2 pagesGrade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1manilaNo ratings yet
- Final Study Material Maths Class X 2012 2013Document105 pagesFinal Study Material Maths Class X 2012 2013gomathi_nellaiNo ratings yet
- Class X Math Study MaterialDocument105 pagesClass X Math Study MaterialmicrodotcdmNo ratings yet
- Act Math FormulasDocument9 pagesAct Math FormulasMiles100% (1)
- Statutory Requirements - YEAR 5 (Number and Place Value) : Mathematics National Curriculum For Year 5Document4 pagesStatutory Requirements - YEAR 5 (Number and Place Value) : Mathematics National Curriculum For Year 5ShaminaNo ratings yet
- D - Mathematics - Notes - Booklet - Pdffilename - UTF-8D Mathematics Notes Booklet PDFDocument76 pagesD - Mathematics - Notes - Booklet - Pdffilename - UTF-8D Mathematics Notes Booklet PDFMuhammad Abdullah0% (1)
- Summer Enhancement Program On Mathematics 2018 - Elementary LevelDocument23 pagesSummer Enhancement Program On Mathematics 2018 - Elementary LevelAnthony Feraer Balatar Jr.No ratings yet
- Gce o Level Sec 4 MathDocument17 pagesGce o Level Sec 4 Mathaiwen_wong2428No ratings yet
- Stage 9 Maths Curriculum Framework 2018 (Checkpoint)Document4 pagesStage 9 Maths Curriculum Framework 2018 (Checkpoint)Mahmoud SalaheldinNo ratings yet
- CCSSI Math Standards 5Document6 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 5establoid1169No ratings yet
- KS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapDocument20 pagesKS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapGrace TabfNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Curriculum and Educational System in North AmericaDocument44 pagesMathematical Curriculum and Educational System in North AmericaMieca FloresNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Glossary For Teachers in Key Stages 1 To 4: January 2001Document40 pagesMathematics Glossary For Teachers in Key Stages 1 To 4: January 2001zeohuntNo ratings yet
- O Level - Amath SyllabusDocument12 pagesO Level - Amath SyllabusRaja PandianNo ratings yet
- Gcse Math Revised Support 6523Document32 pagesGcse Math Revised Support 6523Brian StevensonNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesPrecalculus Daily Lesson Logjun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- GCE N (T) Level Mathematics (4043 - 2012)Document17 pagesGCE N (T) Level Mathematics (4043 - 2012)Winson ChuaNo ratings yet
- Y1-6 Maths Statements - FractionsDocument2 pagesY1-6 Maths Statements - FractionsAndy BrookeNo ratings yet
- Maths Program s3 Yr 6 t1Document37 pagesMaths Program s3 Yr 6 t1S TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Open Term 4Document54 pagesOpen Term 4ernsteinsNo ratings yet
- K To 5 - Go Math Scope and SequenceDocument18 pagesK To 5 - Go Math Scope and SequenceMaram HabibNo ratings yet
- Teaching Program Year 8Document29 pagesTeaching Program Year 8Evan Tran100% (1)
- 1003000608Document186 pages1003000608Jayant Kirpekar0% (1)
- GR 11-IG Maths Syllabus Overview 2020-21Document5 pagesGR 11-IG Maths Syllabus Overview 2020-21AnikaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Qualification: BETC National Diploma in Mechanical Engineering/Year (2), Class (A) Unit No: Unit TitleDocument8 pagesScheme of Work Qualification: BETC National Diploma in Mechanical Engineering/Year (2), Class (A) Unit No: Unit TitleOsama HassanNo ratings yet
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9From EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9No ratings yet
- Master Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1From EverandMaster Fundamental Concepts of Math Olympiad: Maths, #1No ratings yet
- The Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroFrom EverandThe Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroNo ratings yet
- Photograph by Sándor Csizmadia. This Photo Is A Present of "Experience Workshops". Learn More Under WWW - Experienceworkshop.huDocument13 pagesPhotograph by Sándor Csizmadia. This Photo Is A Present of "Experience Workshops". Learn More Under WWW - Experienceworkshop.huShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- 100 Practice Arithmetic TestsDocument151 pages100 Practice Arithmetic TestsShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Use DragonBox+ to Teach Solving Equations Step-by-StepDocument1 pageUse DragonBox+ to Teach Solving Equations Step-by-StepShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Subtraction and Addition 2Document65 pagesSubtraction and Addition 2Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Family Ps 20Document2 pagesFamily Ps 20Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Decimal Word Problems 1Document2 pagesDecimal Word Problems 1Jonathan Jontarciego SantosNo ratings yet
- Use DragonBox+ to Teach Solving Equations Step-by-StepDocument1 pageUse DragonBox+ to Teach Solving Equations Step-by-StepShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Decimal Word Problems 1Document2 pagesDecimal Word Problems 1Jonathan Jontarciego SantosNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Properties in DragonBox Algebra 12Document5 pagesAlgebraic Properties in DragonBox Algebra 12Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- FR Act Word Problems #3Document2 pagesFR Act Word Problems #3Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- 978 0 7660 3371 9Document65 pages978 0 7660 3371 9Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- 1$20 CountingDocument42 pages1$20 CountingShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- PratomDocument16 pagesPratomShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- 50 Fabulous Discussion-Prompt Cards For Reading GroupsDocument19 pages50 Fabulous Discussion-Prompt Cards For Reading GroupsShawanda Clark100% (5)
- Fun Math FlapsDocument32 pagesFun Math FlapsShawanda Clark50% (2)
- 15 Minutes A Day To Colossal VocabularyDocument72 pages15 Minutes A Day To Colossal VocabularyShawanda Clark100% (1)
- Understanding Ratios and ProportionsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Ratios and ProportionsShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- 2$20 ReasoningDocument28 pages2$20 ReasoningShawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 6 v4Document5 pagesMath Grade 6 v4Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 1 v4Document3 pagesMath Grade 1 v4Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 5 v4Document4 pagesMath Grade 5 v4Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Writing PromptsDocument56 pagesWriting PromptsShawanda Clark100% (12)
- Math Grade 3 v4Document3 pagesMath Grade 3 v4Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Helping Kids With Math: What's Important?Document4 pagesHelping Kids With Math: What's Important?Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Science Fair SuccessDocument64 pagesScience Fair SuccessShawanda Clark100% (1)
- Math Grade 2 v4Document3 pagesMath Grade 2 v4Shawanda ClarkNo ratings yet
- Terrific TransitionsDocument65 pagesTerrific Transitionswa7di100% (2)
- Sandwich Bag ScienceDocument64 pagesSandwich Bag ScienceShawanda Clark100% (1)
- Vectors QuestionsDocument17 pagesVectors QuestionsKesithan AnandarashNo ratings yet
- PT - MATHEMATICS 4 - Q4 V1 (AutoRecovered)Document5 pagesPT - MATHEMATICS 4 - Q4 V1 (AutoRecovered)marivic dyNo ratings yet
- DLL_MATHEMATICS 4_Q4_W2Document5 pagesDLL_MATHEMATICS 4_Q4_W2alyn.cantanoNo ratings yet
- 1920 Unit 17 Area, Perimeter and Volume (Worksheet)Document14 pages1920 Unit 17 Area, Perimeter and Volume (Worksheet)Kogilan Bama DavenNo ratings yet
- 2013 WMI Competition Grade 8 Part 1 Logical Reasoning Test: Problems 1-30: 5 Points Each For A Total of 150 PointsDocument5 pages2013 WMI Competition Grade 8 Part 1 Logical Reasoning Test: Problems 1-30: 5 Points Each For A Total of 150 PointsBadtzNo ratings yet
- Making lanterns and pickled fruits in Jakarta grade 3Document4 pagesMaking lanterns and pickled fruits in Jakarta grade 3uusNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesNorolyn SantosNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimeterDocument25 pagesArea and PerimeterSundari MuruganNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Cbse Math 2nd Term Sample Paper 1Document2 pagesGrade 8 Cbse Math 2nd Term Sample Paper 1Dhana AryalNo ratings yet
- TrapeziumDocument4 pagesTrapeziumPAWAN NAGALNo ratings yet
- Art Talk Textbook - CH 5Document38 pagesArt Talk Textbook - CH 5ﹺ ﹺ ﹺ ﹺNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter Division I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter Division I. ObjectivesRonald Matias CristobalNo ratings yet
- Q3 Math, Week 4 Online ClassDocument13 pagesQ3 Math, Week 4 Online ClassJUNE KATHLEEN BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE International Mathematics Paper 41 Summer 2013Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE International Mathematics Paper 41 Summer 2013mpoer72850% (1)
- Fundamental Geometry ConceptsDocument0 pagesFundamental Geometry ConceptsRohit Sharma70% (10)
- 1859 Wilcox - An Elementary Treatise Upon The Theory of Rifle FiringDocument308 pages1859 Wilcox - An Elementary Treatise Upon The Theory of Rifle FiringHugh KnightNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test Math 9Document3 pagesThird Periodical Test Math 9Ma Elena ClaroNo ratings yet
- Geometry Glossary of TermsDocument8 pagesGeometry Glossary of Termsapi-66400853No ratings yet
- Grade 4 Students Learn Formulas for Area of Triangles, ParallelogramsDocument45 pagesGrade 4 Students Learn Formulas for Area of Triangles, ParallelogramsCherylyn DevanaderaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Heron's FormulaDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 9 Heron's Formulavinod1577100% (1)
- What is Symmetry? Explained in 40 CharactersDocument13 pagesWhat is Symmetry? Explained in 40 CharactersMainul AbedinNo ratings yet
- CentroidsDocument6 pagesCentroidsLaquando YoungNo ratings yet
- Children's Misconceptions in GeometryDocument19 pagesChildren's Misconceptions in GeometryMichael de Villiers100% (1)
- MATHEMATICS GRADE 8 TERM 2 Lesson PlansDocument41 pagesMATHEMATICS GRADE 8 TERM 2 Lesson PlansAishvarya RashmiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 4: Identifying and Describing QuadrilateralsDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 4: Identifying and Describing QuadrilateralsMary Joyce Camille Paras100% (1)
- Heron's Formula ExplainedDocument14 pagesHeron's Formula ExplainedyugiNo ratings yet
- 2012 NzmocDocument4 pages2012 NzmocJoaquim MarquesNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Assignment 11 PDFDocument9 pagesMensuration Assignment 11 PDFRitesh SethiaNo ratings yet
- 1603938800SAT Math Level 1 Set 2Document11 pages1603938800SAT Math Level 1 Set 2Manish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 3 Module 2 Properties of Trapezoids and KitesDocument22 pagesMath 9 Quarter 3 Module 2 Properties of Trapezoids and Kitesilovebarney0% (1)