Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agglutination
Uploaded by
kiedd_04100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views2 pagesClumping of antigen-coated cells or beads by specific antibody (normally use IgM)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentClumping of antigen-coated cells or beads by specific antibody (normally use IgM)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views2 pagesAgglutination
Uploaded by
kiedd_04Clumping of antigen-coated cells or beads by specific antibody (normally use IgM)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
AGGLUTINATION
Clumping of antigen-coated cells or beads by specific antibody (normally use
IgM)
Methods enhancing agglutination to detect incomplete Ab (like IgG)
o Adding a second antibody in the indirect Coomb’s test
o Adding of colloid to the suspension
o Incubation in LISS (lower ionic strength solution)
o Treat RBC with proteolytic enzymes (zeta potential)
o Use substance (dextrin, BSA) to increase the viscosity of reaction medium
Classification of agglutination reactions:
1. Direct agglutination reactions: RBC (Ag) + specific Ab isohemagglutinins (anti A
or anti B) = IgM (agglutination)
Common agglutination based assays:
ABO blood group typing
Rheumatoid factor assay
Rh (D) Ag
Qualitative pregnancy test
Mono spot test
2. Passive (indirect) agglutination
Patient serum, Ab (IgM) + soluble Ag adsorbed particle = agglutination
Methods to increase efficiency of Ag adsorption to cells:
Mild treatment of RBC with tannic acid or other oxidizing agents
Using covalent cross-linking agents (glutaraldehyde)
3. Direct Coomb’s or direct anti globulin test (DAT)
Detection of incomplete Ab (anti Rh IgG)
Incomplete Ab (anti Rh IgG Ab) + RBC (Rh IgG Ag) = bind (no
agglutination)
Incomplete Ab (specific anti Rh IgG Ab) (first Ab) + RBC (Rh IgG Ag) +
rabbit anti human IgG (second Ab against first Ab) = agglutination
Clinical agglutination assay:
Rose Wanler test:
o Rheumatoid arthritis patient serum (IgM / Ab) + sheep RBC coated with
rabbit IgG (Ag) = agglutination.
o Rheumatoid factor (RF) (IgM-anti IgG) agglutinate latex beads coat with
IgG
Pregnancy test: assay to measure hCG
o Agglutination assays
o RIA (very quantitative and sensitive)
o Direct latex particle agglutination (pregnancy) tests:
Anti hCG (Ab) coated latex (known) + sample with hCG (Ag) =
agglutination
o Hemagglutination inhibition latex agglutinate – inhibition
o Particles coated with hCG (Ag) + anti hCG (Ab) + patient sample with β-
hCG (Ag) = no agglutination (added free hCG blocks agglutination)
o Particles coated with hCG (Ag) + anti hCG (Ab) + patient sample with no
β-hCG (Ag) = agglutination
Mono spot test.
o Rapid, specific, and sensitive test for heterophil Ab or IM.
o Patient serum (IM) Ab + sheep RBC (Ag) = agglutination
o Infectious mononucleosis (IM):
Heterophile Ab: Ab reacting with Ag or cells from various
mammals
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- "Traditional" Exegeses of Q 4:34Document15 pages"Traditional" Exegeses of Q 4:34kiedd_04No ratings yet
- From The Bodies of Bees Classical and Christian Echoes in Surah Al-NahlDocument25 pagesFrom The Bodies of Bees Classical and Christian Echoes in Surah Al-Nahlkiedd_04No ratings yet
- Iklan Jabatan Pengajian Tinggi (Permohonan Kemasukan Tevt & Ilka) Sesi 2011/2012Document2 pagesIklan Jabatan Pengajian Tinggi (Permohonan Kemasukan Tevt & Ilka) Sesi 2011/2012kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument61 pagesCell Physiologykiedd_04100% (4)
- The Place For Others in IslamDocument27 pagesThe Place For Others in Islamkiedd_04No ratings yet
- Fadhilat Surah at TakwirDocument1 pageFadhilat Surah at Takwirkiedd_04No ratings yet
- SYNAPSEDocument35 pagesSYNAPSEkiedd_04100% (3)
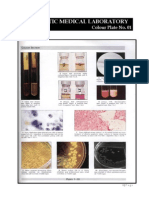
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.8Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.8kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.9Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.9kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Odors of Santity Distinctions of The Holy in Early Christianity and IslamDocument13 pagesOdors of Santity Distinctions of The Holy in Early Christianity and Islamkiedd_04100% (1)
- Refleks ArcsDocument34 pagesRefleks Arcskiedd_04100% (1)
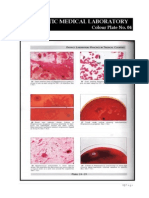
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.6Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.6kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Mitigation of Climate ChangeDocument25 pagesMitigation of Climate Changekiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.1Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.1kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.5Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.5kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.7Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.7kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.4Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.4kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.2Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.2kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.3Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.3kiedd_04No ratings yet
- API® CoryneDocument4 pagesAPI® Corynekiedd_04No ratings yet
- Philosophical Consolation in Christianity and Islam Boethious and Al-KindiDocument10 pagesPhilosophical Consolation in Christianity and Islam Boethious and Al-Kindikiedd_04No ratings yet
- Mitigation of Climate ChangeDocument41 pagesMitigation of Climate Changekiedd_04No ratings yet
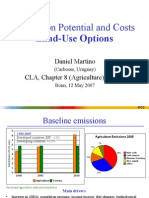
- Mitigation Potential and Costs Land-Use OptionsDocument9 pagesMitigation Potential and Costs Land-Use Optionskiedd_04No ratings yet
- Oxidase TestDocument1 pageOxidase Testkiedd_04100% (1)
- Carnitine DeficiencyDocument21 pagesCarnitine Deficiencykiedd_04100% (1)
- Advance Diagnostic Medical Laboratory: The AP 20E® For Identification of BacteriaDocument1 pageAdvance Diagnostic Medical Laboratory: The AP 20E® For Identification of Bacteriakiedd_04100% (1)
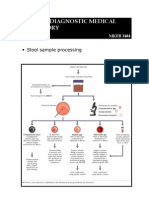
- Stool Sample ProcessingDocument1 pageStool Sample Processingkiedd_04No ratings yet
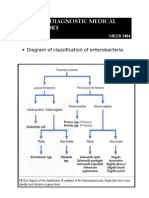
- Diagram of Classification of EnterobacteriaDocument1 pageDiagram of Classification of Enterobacteriakiedd_04100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Beta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsDocument43 pagesBeta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsAriel OlshevskyNo ratings yet
- Aetna Insurance DecisionDocument13 pagesAetna Insurance DecisionJeffStelling1No ratings yet
- Biology SPMDocument17 pagesBiology SPMbloptra18No ratings yet
- Orthodontics!!Document9 pagesOrthodontics!!Ayesha AwanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Properties of Allicin From GarlicDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial Properties of Allicin From GarlicEdward Kenneth DragasNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Revision Test - Basics 1Document16 pagesComprehensive Revision Test - Basics 1drpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- PolygraDocument15 pagesPolygraAbdul Aziz Akil RiasNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For PicuDocument32 pagesDrug Therapy For PicuNeethu Mariya MathewNo ratings yet
- Final Compre Exam Key AnswersDocument14 pagesFinal Compre Exam Key Answersmj CanilangNo ratings yet
- Disease Impact 2Document31 pagesDisease Impact 2Seed Rock ZooNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic CholecystitisDocument10 pagesAcute and Chronic Cholecystitisissam_1994No ratings yet
- Case Study For Beta Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-All)Document15 pagesCase Study For Beta Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-All)Shakira HashimNo ratings yet
- Ummer Roject Resentation ON Herbal Healthcare Industry in IndiaDocument14 pagesUmmer Roject Resentation ON Herbal Healthcare Industry in IndiaSaurabh RustagiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Skin Bleach in SocietyDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Skin Bleach in SocietySalma BahNo ratings yet
- Mri Report - Left Knee Joint: Name Patient ID Accession No Age/Gender Referred by DateDocument2 pagesMri Report - Left Knee Joint: Name Patient ID Accession No Age/Gender Referred by Datefaiyaz432No ratings yet
- 12.4 Female Reproductive DiseasesDocument20 pages12.4 Female Reproductive Diseasessanat kr pratiharNo ratings yet
- Wmh-Cidi Papi Interview: Screening Section (SC)Document9 pagesWmh-Cidi Papi Interview: Screening Section (SC)Monia AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument3 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionmcvirgo014100% (1)
- Chapter 1-3Document55 pagesChapter 1-3Mark Ryan Nagales0% (1)
- Nabh Entry LevelDocument64 pagesNabh Entry LevelRenuka MuruganNo ratings yet
- User Manual For Applications Xformer Exe EnglishLightDocument51 pagesUser Manual For Applications Xformer Exe EnglishLightNunoClaudinoNo ratings yet
- Initial Nurse Patient InteractionDocument1 pageInitial Nurse Patient InteractionBryan Jay Carlo PañaNo ratings yet
- How To Achieve Good Health & Longevity?Document57 pagesHow To Achieve Good Health & Longevity?lauchen32100% (1)
- Pharmacology Fundamental ConceptsDocument84 pagesPharmacology Fundamental Conceptsteaforschool filesNo ratings yet
- Documentary Requirements and Format of Simplified CSHPDocument1 pageDocumentary Requirements and Format of Simplified CSHPRhalf AbneNo ratings yet
- Pre-Diabetes:: Don't Let It Lead To Type-2Document1 pagePre-Diabetes:: Don't Let It Lead To Type-2ARIA MINDNo ratings yet
- Clinical Abstract FormDocument1 pageClinical Abstract FormHihiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Midterm Study GuideDocument17 pagesPharmacology Midterm Study GuidebkearnestNo ratings yet
- Case Study AnalysisDocument13 pagesCase Study Analysisapi-317809407No ratings yet
- Primitive Man and His Food - Arnold DeVriesDocument97 pagesPrimitive Man and His Food - Arnold DeVriessamui11No ratings yet