Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Titration Is The Test Method Used in The Acid-Base Neutralization. Acid-Base Neutralization
Uploaded by
tosalleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Titration Is The Test Method Used in The Acid-Base Neutralization. Acid-Base Neutralization
Uploaded by
tosalleCopyright:
Available Formats
ACID-BASE NEUTRALIZATION A.
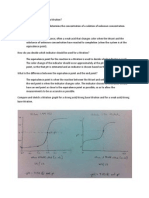
Discussion Generally, an acid is a substance that releases H + ions in water, while base is a substance that releases OH-ions in water. Titration is the test method used in the acid-base neutralization. Acid-base neutralization reaction is a reaction by the acid-base neutralized and produces water. The indicators which are used are the universal indicator and the indicator phenolphthalein. Universal indicator is used to determine the pH o the solution, whereas phenolphthalein indicator used in the titration process be ore titrant is done. This indicator will chan!e color when the e"uivalent point occurs rom colorless to pin#. To obtain the accuracy o the titration endpoint chosen as close as possible to the e"uivalent point, this can be done by selectin! the appropriate indicators and conducted in accordance with the titration. $ircumstances in which the titration is stopped by means o the color chan!e indicator re erred to as the end point titration. This e%periment was conducted three times. The purpose is per ormed in order to obtain accurate results. And pH measurements per ormed be ore the addition o &aOH, a ter the addition o ' ml o &aOH, while achievin! e"uivalent point and a ter passin! the e"uivalent point. The solution used in this e%periment is a solution o &aOH and H$l solution. The reaction can be written( At pH measurements were carried out irst be ore the addition o &aOH H$l pH obtained is e"ual to '. pH shows that the solution is stron!ly acid. A ter that, the addition o ' ml o &aOH and then measure the pH a!ain and !ained H$l pH is ). *t is not much di erent rom the theoretical results is '.'+ pH because the pH obtained is stron!ly acid. And still below pH ,. This means the addition o &aOH not only chan!ed H$l pH -.' . sli!htly.
Then, a!ain addin! some ml &aOH to reach the e"uivalent point the pH value e"ual to ,. *t shows the solution pH is neutral. A!ain addin! ' ml o &aOH a ter reachin! the e"uivalent point, where pH is obtained a ter the addition o successive '', ') and ') pH. This shows that the pH o the solution already is al#aline, not acidic anymore, in terms o total base more than the amount o acid, with an avera!e volume o ,.-+ ml. The errors occur caused by observer lac# o ri!or in addin! a ew ml &aOH to reach the e"uivalent point compared to the pH theory o the irst e%periment. /"uivalent point is the point where the concentration o the acid or base is e"ual to each other, or the point where the amount o base added e"uals to the number o the acid neutralized. pH obtained rom this e%periments are pH 0, '- and '' with an avera!e volume o ,.-+ ml. 1hile the theory is based on the addition o a ew ml o &aOH solution till the pH reached a point e"uivalent to a volume e"ual to , with 2 ml o &aOH. 3o the data obtained are less accurate. 4ased on theory and the charts, the results o these observations, not in accordance with the theory, which a ter the addition o ' ml o &aOH with a pH e"ual to ) and when they reach the e"uivalent point is al#aline, because pH is obtained rom trial account a ter reachin! a point that is e"uivalent to 0, '- and '' are supposed to pH , 5neutral pH6. .oment conditions e"uivalent '
point is called the end point titration or the circumstances in which the titration is stopped by means o the color chan!e in the solution.
B.
Conclusion 4ased on the purpose o the e%periment, it can be concluded that the acid-base titration use universal indicator and the indicator phenolphthalein. *n e"uivalent point, the amount o acid titrated e"uivalent to the amount o base used. And to determine the e"uivalent point is to use an indicator that chan!es color phenolphthalein as it reaches a point e"uivalent.
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- WINSEM2022-23 BBIT206P LO VL2022230503900 Reference Material I 23-12-2022 Experiment 2 Acid-Base Titration PH Meter FADocument4 pagesWINSEM2022-23 BBIT206P LO VL2022230503900 Reference Material I 23-12-2022 Experiment 2 Acid-Base Titration PH Meter FAGravity JaiNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument16 pagesAcid Base TitrationsyazaismailNo ratings yet
- HCL + Naoh Nacl + H O: (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) 2 (L)Document3 pagesHCL + Naoh Nacl + H O: (Aq) (Aq) (Aq) 2 (L)Ilmiati ZakinahNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Salt & PH of Buffer Solution (Sample)Document8 pagesHydrolysis of Salt & PH of Buffer Solution (Sample)Iskandar RambliNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Acid Base TitrationDocument48 pagesUNIT II Acid Base TitrationDr Priti JainNo ratings yet
- PH Is A Measure of The Acidity or Basicity of A Solution.: Glass ElectrodeDocument9 pagesPH Is A Measure of The Acidity or Basicity of A Solution.: Glass Electrodehelion45No ratings yet
- Instrumental Analytical Methods Experiment 9 - Ph-Metric Titration of Acetic AcidDocument3 pagesInstrumental Analytical Methods Experiment 9 - Ph-Metric Titration of Acetic Acidapi-235187189No ratings yet
- Laporan Kimdal Percobaan Unit 1Document7 pagesLaporan Kimdal Percobaan Unit 1rulmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Titration of HCL With NaOH - C12!5!10Document5 pagesTitration of HCL With NaOH - C12!5!10irishlass94No ratings yet
- 1.ACIDS AND BASES Lecture 1Document6 pages1.ACIDS AND BASES Lecture 1Protusha RakshitNo ratings yet
- TITRATIONDocument14 pagesTITRATIONGezem GigantoNo ratings yet
- Name: Yambesa Surname: Mphathiswa STUDENT NUMBER: 202250111 Group D1 Experiment 3Document10 pagesName: Yambesa Surname: Mphathiswa STUDENT NUMBER: 202250111 Group D1 Experiment 3YAMBESA MphathiswaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document4 pagesExperiment 7Vinitra PillaiNo ratings yet
- Titration Curves ExplainedDocument10 pagesTitration Curves Explainedryan1230987No ratings yet
- Titration LABDocument20 pagesTitration LABapi-359167484No ratings yet
- Presentation 54 - PH and pOH ScaleDocument30 pagesPresentation 54 - PH and pOH ScaleRyan RegoNo ratings yet
- pH Titration Lab Experiment Ka DeterminationDocument4 pagespH Titration Lab Experiment Ka DeterminationxmusiqaNo ratings yet
- TITRATIONDocument6 pagesTITRATIONnawalfathima732No ratings yet
- 19 Reactions of Acids and BasesDocument19 pages19 Reactions of Acids and BasesrachelelizabethNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsapi-203606735No ratings yet
- Exp 2Document24 pagesExp 2Dhiyyah MardhiyyahNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10Document1 pageExperiment 10SELEUCIDNo ratings yet
- Vinegar Is A Dilute Solution Containing Acetic AcidDocument1 pageVinegar Is A Dilute Solution Containing Acetic AcidMuhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Titration - Chemistry For Non-Majors - Course HeroDocument8 pagesTitration - Chemistry For Non-Majors - Course HeroZada FinnikinNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument16 pagesAcid-Base TitrationChloe KittyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Titration II - Acid Dissociation ConstantDocument8 pagesExperiment 6 Titration II - Acid Dissociation ConstantPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Titration Curve Determines Unknown Acid pKaDocument3 pagesPotentiometric Titration Curve Determines Unknown Acid pKaDaniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Potentiometric TitrationDocument11 pagesExperiment 4 - Potentiometric TitrationJoemer Absalon Adorna100% (2)
- Chem Lab ReportDocument18 pagesChem Lab Reportapi-514523338No ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationsDocument34 pagesAcid-Base TitrationsAisha IltafNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titration: Experiment 10Document3 pagesAcid-Base Titration: Experiment 10dudewheresmycar3628No ratings yet
- Publication 2 8978 1091Document13 pagesPublication 2 8978 1091زياد المرسوميNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric TitrationDocument12 pagesPotentiometric TitrationTien Haminh100% (1)
- AP Chemistry Investigation 4 - Judy, Paul, AnthonyDocument13 pagesAP Chemistry Investigation 4 - Judy, Paul, AnthonyAnthony HowerNo ratings yet
- Bronsted ConsepDocument17 pagesBronsted ConsepMANASI VASUDEONo ratings yet
- PH y CurvasDocument7 pagesPH y CurvasSANTIAGO SANCHEZ ALZATENo ratings yet
- Name-Siddhant Kumar REG. NO - 2018UGCE002 Subject - Environmental Engineering LabDocument28 pagesName-Siddhant Kumar REG. NO - 2018UGCE002 Subject - Environmental Engineering LabGolu kumarNo ratings yet
- Detection of Ions in Solutions Using Acid/Base Chemistry: A Quality Control TestDocument4 pagesDetection of Ions in Solutions Using Acid/Base Chemistry: A Quality Control TestRuchika Sood100% (1)
- Reading Material For Experiment 3Document4 pagesReading Material For Experiment 3Abdallah AlhasanNo ratings yet
- YesDocument4 pagesYesaccel.cyclone.099No ratings yet
- Titration: Lab ReportDocument18 pagesTitration: Lab Reportapi-327697210No ratings yet
- PDF PH TITRATIONDocument16 pagesPDF PH TITRATIONعبدالله هنيةNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.2. PH and Buffer SystemsDocument13 pagesLesson 3.2. PH and Buffer SystemsGemma CabañasNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titration LabDocument8 pagesAcid-Base Titration LabErica Jenson100% (4)
- Lab Report Acid BaseDocument4 pagesLab Report Acid Basexuni34No ratings yet
- PH Scale: Introduction and DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPH Scale: Introduction and DefinitionsUpen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Titration Lab ReportDocument13 pagesTitration Lab Reportapi-341133750No ratings yet
- IndicatorsDocument26 pagesIndicatorsDeepa DevanathanNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and PHDocument4 pagesAcids Bases and PHsatheeshNo ratings yet
- Titration Curves: Strong Acid-Strong Base TitrationsDocument15 pagesTitration Curves: Strong Acid-Strong Base TitrationssandalailaNo ratings yet
- PH Measurement BasicsDocument8 pagesPH Measurement Basicsviralshukla85No ratings yet
- Identifying An Unknown Weak Acids ExperimentDocument18 pagesIdentifying An Unknown Weak Acids ExperimentZati TarhiziNo ratings yet
- Weak Acid Strong Base Titration LabDocument8 pagesWeak Acid Strong Base Titration Labapi-265089380100% (1)
- Acid Base TitrationDocument12 pagesAcid Base TitrationMsfaeza HanafiNo ratings yet
- Lec Week 11 Neutralization Titrations - Sample Calculations - For ClassDocument50 pagesLec Week 11 Neutralization Titrations - Sample Calculations - For ClassTrisha PurcaNo ratings yet
- Enviromental Engineering Lab CE463: Name:omar Hayel Darabseh ID:103118 SEC#: 6Document8 pagesEnviromental Engineering Lab CE463: Name:omar Hayel Darabseh ID:103118 SEC#: 6Omar H DarabsehNo ratings yet
- pH Electrode Titration Curve AnalysisDocument14 pagespH Electrode Titration Curve AnalysisMina VoNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument14 pagesBasic ChemistryPitherNo ratings yet
- Physics SL Paper 3 TZ2Document20 pagesPhysics SL Paper 3 TZ2Dongjean SeoNo ratings yet
- 2oo3plus - A New Design of Electro-Hydraulic Safety Controls For Critical ApplicationsDocument6 pages2oo3plus - A New Design of Electro-Hydraulic Safety Controls For Critical Applicationsultrasonic81No ratings yet
- Complex Numbers: BY Shreya Kuchhal Darshika Kothari Riya Gupta Simran SardaDocument18 pagesComplex Numbers: BY Shreya Kuchhal Darshika Kothari Riya Gupta Simran Sardasimran sardaNo ratings yet
- ME 555 Stress Analysis Unit 4Document57 pagesME 555 Stress Analysis Unit 4TheoNo ratings yet
- SMS LteaDocument11 pagesSMS LteaArdi CikaNo ratings yet
- Wiring DiagramDocument24 pagesWiring DiagramReji Raju0% (1)
- Fundamentals of the Pickett Plot: Recognizing Reservoir PatternsDocument9 pagesFundamentals of the Pickett Plot: Recognizing Reservoir PatternsAngelMeso100% (1)
- Activity MergedDocument9 pagesActivity MergedSoham MondalNo ratings yet
- Rebound Hammer Test Procedure For Concrete HardnessDocument4 pagesRebound Hammer Test Procedure For Concrete HardnessSite Engineer.2p2No ratings yet
- Mathematics and RealityDocument13 pagesMathematics and RealityIan Thorpe100% (1)
- Francis Bacon, Logic of SensationDocument2 pagesFrancis Bacon, Logic of SensationShrankhla NaryaNo ratings yet
- EE221 Solution Problem Set2Document10 pagesEE221 Solution Problem Set2srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter 18 Carboxylic AcidsDocument0 pagesPractice Chapter 18 Carboxylic AcidsRochelle BartiletNo ratings yet
- Hawkins, Jaq - Elemental ChaosDocument3 pagesHawkins, Jaq - Elemental Chaoscaligari2000No ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Forces on SurfacesDocument12 pagesHydrostatic Forces on SurfacesPajhmanAwghanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3DaxNo ratings yet
- Steam Engineering Principles and Heat TransferDocument99 pagesSteam Engineering Principles and Heat Transferalex mobileNo ratings yet
- April 2015-Vacuum Drying Chem Eng PDFDocument9 pagesApril 2015-Vacuum Drying Chem Eng PDFAlvaro BarbozaNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Lorentz Transformation (A Simple Derivation of Lorentz Transformation)Document5 pagesThe Physics of Lorentz Transformation (A Simple Derivation of Lorentz Transformation)Glen PeachNo ratings yet
- Methods of Re-Apportioning Service Cost Centre CostsDocument7 pagesMethods of Re-Apportioning Service Cost Centre CostsUserNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design Report - Docx 150Document17 pagesBridge Design Report - Docx 150nephembaniNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential EquationDocument20 pagesOrdinary Differential EquationRadeanindaNo ratings yet
- Hvs-313. Maximum Demand ControllerDocument3 pagesHvs-313. Maximum Demand ControllerHari BabuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument74 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumGuiller Lanuza100% (1)
- Motion 1Document3 pagesMotion 1Fenil ShahNo ratings yet
- Light Class 7 Science Chapter 15Document11 pagesLight Class 7 Science Chapter 15Gaurav Sethi100% (1)
- Mock Exam P2Document13 pagesMock Exam P2Abin LalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2ue06037No ratings yet
- Pivot Interactives Motion Graphing A Dry Ice Puck On A RampDocument2 pagesPivot Interactives Motion Graphing A Dry Ice Puck On A RampSophia0% (1)