Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical Viva Physics
Uploaded by
Pulkit JainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Viva Physics
Uploaded by
Pulkit JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics VIVA Class XII
Q1. Give the principal behind moving coil galvanometer. A1.When a current carrying coil is placed in ext magnetic field it experiences torque = m x B where
m is magnetic moment = NiA B is magnetic field
=m B sin
The torque tends to align m B Q2. Why is the field radial?
A2.(i) For radial field m is always to B hence sin =1 so torque is maximum
(ii)To make the scale linear. ie A3. No.
Q3. Can a galvanometer measure alternating current? Q4.What is meant by current sensitivity of galvanometer? A4. is = / i Q5. A voltmeter,ammeter is nothing but a modified galvanometer.Explain A5. A high resistance is connected in series Inside a galvanometer voltmeter. A low resistance is connected in parallel Inside a galvanometer ---ammeter
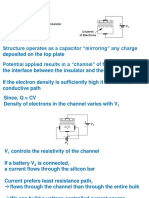
Q6. What is the principle behind Potentiometer? VL V/L = for constant current in the wire. potential gradient is constant
Q7. What is the nature of wire stretched on potentiometer? A7. It is constanan. It has high resistivity. It is an alloy. It has low tempr co efficient( ). of resistivity Resistance and Resistivity
The resistivity of a material is found to be dependent on the temperature. Different materials do not exhibit the same dependence on tempr. Over a limited range of temperatures, that is not too large, the resistivity of a metallic conductor is approximately given by, T = 0 [1 + (TT0)]
Some materials like Nichrome (which is an alloy of nickel, iron and chromium) exhibit a very weak dependence of resistivity with temperature (Fig. 3.10). Manganin and constantan have similar properties. These materials are thus widely used in wire bound standard resistors sincetheir resistance values would change very little with temperatures. Unlike metals, the resistivities of semiconductors decrease with increasing temperatures. A typical dependence is shown in Fig. 3.11.
thus depends inversely both on the number n of free electrons per
unit volume and on the average time between collisions. (As we increase temperature, average speed of the electrons, which act as the carriers of crrent, increases resulting in more frequent collisions. The average time f collisions, thus decreases with temperature.) In a metal, n is not dependent on temperature to any appreciable xtent and thus the decrease in the value of with rise in temperature caues to increase as we have observed.
For insulators and semiconductors, however, n increases with temp. This increase more than compensates any decrease in in Eq.(3.23) so that for such materials, decreases with temperature.
emf is the potential difference between the positive and negative electrodes in
an open circuit, i.e., when no current is flowing through the cell.
If however R is finite, I is not zero.
V=
I r r
The maxi current that can be drawn from a cell is for R = 0 and it is Imax = /
The Wheatstone bridge and its balance condition provide a practical
method for determination of an unknown resistance. Keeping known resistances R1 and R2 in the first and second arm of the bridge, we go on varying R3 till the galvanometer shows a null deflection. The bridge then is balanced, and from the balance condition the value of the unknown resistance R4 is given by,
The potentiometer is a device to compare potential differences. Since the method involves a condition of no current flow, the device can be used to measure potential difference; internal resistance of a cell and compare emfs of two sources.
You might also like
- Physics Investigatory Project On - ChargDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project On - ChargSatyam KurumNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument11 pagesContentjashwanth kumar58No ratings yet
- KVS Physics Study Material for Class XIIDocument172 pagesKVS Physics Study Material for Class XIIamtripathiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectKunal PalweNo ratings yet
- List of Officers of DGHSDocument5 pagesList of Officers of DGHSPraveen PrasadNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board 2020 - Physics PDFDocument9 pagesPre-Board 2020 - Physics PDFYASH PRANESHNo ratings yet
- Viva Class XII Physics PracticalDocument1 pageViva Class XII Physics PracticalAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Guwahati Region 2 Pre Board Exam 2018-19 Class: Xii Time: 3 Hrs Subject: Mathematics MM: 100Document3 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Guwahati Region 2 Pre Board Exam 2018-19 Class: Xii Time: 3 Hrs Subject: Mathematics MM: 100Anji KaringuNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS LAB VIVA Important Questions by ATSDocument2 pagesPHYSICS LAB VIVA Important Questions by ATSNikkilesh Vivekanandan50% (4)
- Assignment PotentialDocument4 pagesAssignment Potentialshruti baruaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Notes and QuestionsDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Notes and Questionsnamas62No ratings yet
- Physics XII Assignment 1 M.M 30 Part A (1 Marks Question)Document9 pagesPhysics XII Assignment 1 M.M 30 Part A (1 Marks Question)Nisha RajnwalNo ratings yet
- Iodine Clock ReactionDocument6 pagesIodine Clock Reactionilias19730% (1)
- Bangalore Sahodaya Math Class 12Document2 pagesBangalore Sahodaya Math Class 12Gayatri KamathNo ratings yet
- Cbse Model QP Class Xii (KMS)Document269 pagesCbse Model QP Class Xii (KMS)aleenaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFDocument22 pagesCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFHrithik RajNo ratings yet
- Charging & Discharging Capacitor CircuitDocument4 pagesCharging & Discharging Capacitor CircuitHemanth GedelaNo ratings yet
- Notes On 2nd Physics by Asif RasheedDocument31 pagesNotes On 2nd Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed Rajput100% (1)
- Electro Statics Worksheet CbseDocument19 pagesElectro Statics Worksheet CbseAmanNo ratings yet
- Key titration questionsDocument2 pagesKey titration questionsUmang Soni100% (1)
- Talentsprint We Selection Assessment Pattern: Mode of Assessment: Online - Proctored Exam Assessment PatternDocument4 pagesTalentsprint We Selection Assessment Pattern: Mode of Assessment: Online - Proctored Exam Assessment PatternIt's VSPNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: InvestigatoryDocument10 pagesChemistry: InvestigatorynitsNo ratings yet
- 50 QuestionDocument5 pages50 QuestionAftabNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 12: Solution of Book Questions 2 Year PhysicsDocument17 pagesChapter # 12: Solution of Book Questions 2 Year PhysicsAsif Rasheed Rajput0% (1)
- CBSE Physics electricity question bankDocument5 pagesCBSE Physics electricity question bankAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- E.over.m RatioDocument8 pagesE.over.m Ratiobrain221304No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual 2016 17 PDFDocument49 pagesPhysics Lab Manual 2016 17 PDFAYUSH ANANDNo ratings yet
- Impt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and Ans (II PU) - 2Document23 pagesImpt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and Ans (II PU) - 2Vishwaradhya KarastalmathNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS FORMULAE AND CONCEPTSDocument24 pagesELECTROSTATICS FORMULAE AND CONCEPTSSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- J3 Uo WHC Awbsrywm 6 XN 7 RDocument48 pagesJ3 Uo WHC Awbsrywm 6 XN 7 RShivam NishadNo ratings yet
- Lab#7 I&M 078Document9 pagesLab#7 I&M 078Asad saeedNo ratings yet
- AIM/OBJECTIVE-Determination of Steady State Response of R - L, R-C and R-L-C Circuit and Calculation of Impedance and Power FactorDocument9 pagesAIM/OBJECTIVE-Determination of Steady State Response of R - L, R-C and R-L-C Circuit and Calculation of Impedance and Power FactorSoumyarup Basu100% (1)
- Chapter # 21 Nuclear PhysicsDocument7 pagesChapter # 21 Nuclear PhysicsAsif Rasheed RajputNo ratings yet
- Thevenin Equivalent CircuitsDocument5 pagesThevenin Equivalent CircuitsAhmed HamoudaNo ratings yet
- 10 Physics Worksheet 2 PDFDocument1 page10 Physics Worksheet 2 PDFTajiriMollelNo ratings yet
- Order of Experiments: Color Solubility Experiment Result SaltDocument4 pagesOrder of Experiments: Color Solubility Experiment Result SaltEshwar Parthiban100% (1)
- Impedance Spectroscopy Material Science ApplicationsDocument18 pagesImpedance Spectroscopy Material Science ApplicationsMatch BoxNo ratings yet
- MOSFETSDocument102 pagesMOSFETSVedant WaliaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Test Paper CH 9 1Document6 pages12 Physics Test Paper CH 9 1ChinmayiNo ratings yet
- 13.kinetic Theory PDFDocument30 pages13.kinetic Theory PDFNaliniNo ratings yet
- Resistor circuit questionsDocument1 pageResistor circuit questionsJeferson MendozaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT LABDocument23 pagesELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT LABDhinakarrajNo ratings yet
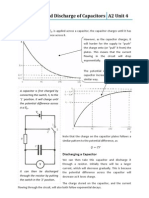
- Charge and Discharge of CapacitorsDocument2 pagesCharge and Discharge of Capacitorsphydotsi100% (3)
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticDocument15 pagesElectrostaticRanjan LohmorhNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Physics - ElectricityDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics - Electricitybadnight4u100% (1)
- Electrostatics and Current ElectricityDocument10 pagesElectrostatics and Current ElectricityUdaibir PradhanNo ratings yet
- Band Gap Determination Lab ManualDocument32 pagesBand Gap Determination Lab ManualRaj Shekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Viva 1 PDFDocument11 pagesPhysics Practical Viva 1 PDFJamuna BeheraNo ratings yet
- Theory of Ballastic GalvanometerDocument4 pagesTheory of Ballastic GalvanometerAniket Patel (Annu)No ratings yet
- BCS Theory of SuperconductivityDocument21 pagesBCS Theory of SuperconductivityMuhammad_abdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 - ElectrostaticsDocument29 pagesChapter - 14 - ElectrostaticsMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- 5.fermi Level in Itrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorDocument10 pages5.fermi Level in Itrinsic and Extrinsic SemiconductorAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Charging & Discharging of A Capacitor by MR - CharisDocument5 pagesCharging & Discharging of A Capacitor by MR - CharisCharis Israel Ancha67% (3)
- Electrical Energy and Capacitance ReviewDocument9 pagesElectrical Energy and Capacitance ReviewReymond CañoneroNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-DFrom EverandNuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-DJoseph CernyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-AFrom EverandNuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-AJoseph CernyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Unit-I - Partial DifferentiationDocument4 pagesTutorial - Unit-I - Partial DifferentiationArya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Hgpe Formulas 2022Document21 pagesHgpe Formulas 2022Malikah AliNo ratings yet
- DLL WITH TMDI Metric SystemDocument14 pagesDLL WITH TMDI Metric SystemMaila AsimNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.ABISHEK AJAYNo ratings yet
- ENG MECH DYNAMICSDocument4 pagesENG MECH DYNAMICSSuhaib AshrafNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics FundamentalsDocument13 pagesElectrostatics FundamentalsPriyanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Measurement System BehaviorDocument22 pagesChapter - 3 Measurement System BehaviorNhân Phạm ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- TESTING Armature WindingsDocument2 pagesTESTING Armature Windingsronald allan liviocoNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE All India Test Series Test - 1Document13 pagesIIT-JEE All India Test Series Test - 1Er. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)No ratings yet
- 16 PDFDocument129 pages16 PDFgNo ratings yet
- SAQs ACCELERATED MOTIONDocument4 pagesSAQs ACCELERATED MOTIONGiorgioNo ratings yet
- FP 29Document0 pagesFP 29yu3zaNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial 3 Forces and AccelerationDocument4 pagesPhysics Tutorial 3 Forces and AccelerationTAN XIN YINo ratings yet
- 14AP Physics C - Work and EnergyDocument19 pages14AP Physics C - Work and Energyshahrukh995No ratings yet
- 9702 s14 Ms 22 PDFDocument4 pages9702 s14 Ms 22 PDFMCHNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 11 of Applied Physics TanzeelDocument10 pagesAssignment No 11 of Applied Physics TanzeelAmeer JaanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 110 Kirchhoff's Laws: Group Leader: Group Number: Group MembersDocument6 pagesExperiment 110 Kirchhoff's Laws: Group Leader: Group Number: Group MembersJuan Emmanuel EspinoNo ratings yet
- Complex PermittivityDocument59 pagesComplex PermittivitymanusmrityNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Solutions-1Document28 pagesFinal Exam Solutions-1Yuzhang LiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits LABDocument42 pagesElectrical Circuits LABMustafa MhmoodNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument27 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Second Law of ThermodynamicsAriane Valdez100% (1)
- Fluid Properties Lab ReportDocument15 pagesFluid Properties Lab ReportMauricio ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PSA Lecture 7 Unsymmetrical FaultsDocument27 pagesPSA Lecture 7 Unsymmetrical FaultsTamanna RushaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow TheoryDocument27 pagesFluid Flow TheoryG RianNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 3 Group 6Document5 pagesLaboratory Report 3 Group 6Lyka Jane BucoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Notes EditedDocument7 pagesPressure Notes EditedSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- MEASURING CAPACITANCE USING DE SAULTY'S MODIFIED BRIDGEDocument4 pagesMEASURING CAPACITANCE USING DE SAULTY'S MODIFIED BRIDGEManish Kumar BisoiNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry:: Psychrometric Chart: A Psychrometric Chart Is A Graphical Representation ofDocument1 pagePsychrometry:: Psychrometric Chart: A Psychrometric Chart Is A Graphical Representation ofvikasbnsl1No ratings yet
- XI PHYSICS CLASS ASSIGNMENT ON WORK, ENERGY AND POWERDocument3 pagesXI PHYSICS CLASS ASSIGNMENT ON WORK, ENERGY AND POWERAyush GogiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For First Year Class by Dr. Ram ChandDocument141 pagesPhysics Notes For First Year Class by Dr. Ram ChandRam C100% (5)