Professional Documents
Culture Documents
34 Stages of Adolescence1
Uploaded by
Lisa AndriyaniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
34 Stages of Adolescence1
Uploaded by
Lisa AndriyaniCopyright:
Available Formats
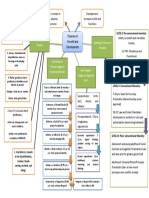
Stages of Adolescent Development
Stages of Adolescence Physical Development Cognitive Development Social-Emotional Development
Early Adolescence Approximately 11 13 years of age
Puberty: grow body hair, increase perspiration and oil production in hair and skin, Girls breast and hip development, onset of menstruation Boys growth in testicles and penis, wet dreams, deepening of voice Tremendous physical growth: gain height and weight Greater sexual interest Puberty is completed Physical growth slows for girls, continues for boys
Growing capacity for abstract thought Mostly interested in present with limited thought to the future Intellectual interests expand and become more important Deeper moral thinking
Struggle with sense of identity Feel awkward about ones self and ones body; worry about being normal Realize that parents are not perfect; increased conflict with parents Increased influence of peer group Desire for independence Tendency to return to childish behavior, particularly when stressed Moodiness Rule- and limit-testing Greater interest in privacy Intense self-involvement, changing between high expectations and poor self-concept Continued adjustment to changing body, worries about being normal Tendency to distance selves from parents, continued drive for independence Driven to make friends and greater reliance on them, popularity can be an important issue Feelings of love and passion Firmer sense of identity Increased emotional stability Increased concern for others Increased independence and self-reliance Peer relationships remain important Development of more serious relationships Social and cultural traditions regain some of their importance
Middle Adolescence Approximately 14 18 years of age
Continued growth of capacity for abstract thought Greater capacity for setting goals Interest in moral reasoning Thinking about the meaning of life
Late Adolescence Approximately 19 21 years of age
Young women, typically, are fully developed Young men continue to gain height, weight, muscle mass, and body hair
Ability to think ideas through Ability to delay gratification Examination of inner experiences Increased concern for future Continued interest in moral reasoning
Adapted from the American Academy of Child and Adolescents Facts for Families. All rights reserved. 2008
You might also like
- PERDEV Week3Document44 pagesPERDEV Week3Jessa Amarillo VillarealNo ratings yet
- LP16 SHS Personal DevelopmentDocument6 pagesLP16 SHS Personal Developmentann delacruzNo ratings yet
- S6.M22.PPT (Parenting Style)Document12 pagesS6.M22.PPT (Parenting Style)Texa Fredyan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Workplace Emotions and AttitudesDocument27 pagesWorkplace Emotions and AttitudesDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- Individual Values Assessment - An UpdateDocument3 pagesIndividual Values Assessment - An Updatedarff45No ratings yet
- Personality AssignmentDocument4 pagesPersonality Assignmentapi-461452779No ratings yet
- Lesson 04 PsychologyDocument43 pagesLesson 04 PsychologyKimper poNo ratings yet
- 8 Philosophers in Understanding The Self PDFDocument4 pages8 Philosophers in Understanding The Self PDFDorothy Dame LandinginNo ratings yet
- Guia - AdolescentesDocument6 pagesGuia - AdolescentesCentro De Psicoterapia Condesa100% (1)
- Perceived Parenting Styles in Pakistani Adolescents: A Validation StudyDocument23 pagesPerceived Parenting Styles in Pakistani Adolescents: A Validation StudyTOOBA KANWAL100% (1)
- Life Pro Cess From Bir TH To Old AgeDocument145 pagesLife Pro Cess From Bir TH To Old AgeDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- Stress Management: Employees at WorkplaceDocument21 pagesStress Management: Employees at WorkplaceDanielNo ratings yet
- Adulthood Development: Physical, Cognitive and Social Changes Throughout the LifespanDocument42 pagesAdulthood Development: Physical, Cognitive and Social Changes Throughout the LifespanRUBION AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Eriksons Psychosocial TheoryDocument16 pagesEriksons Psychosocial Theoryapi-448144386No ratings yet
- CDDQDocument7 pagesCDDQapi-311436009No ratings yet
- Pastoral Counselling Reading ReportDocument6 pagesPastoral Counselling Reading ReportClinton GriffienNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence - Session 1 PDFDocument4 pagesEmotional Intelligence - Session 1 PDFAnderson CastroNo ratings yet
- Sson 4 Coping With Stress in Middle and Late Adolescence 1Document42 pagesSson 4 Coping With Stress in Middle and Late Adolescence 1rinajoylavariaz4No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation Lesson1bDocument12 pagesPowerpoint Presentation Lesson1bSheryn Mae Mantaring Sadicon100% (1)
- Intrapersonal Skills Questionaire ResultDocument3 pagesIntrapersonal Skills Questionaire Resultapi-534625560No ratings yet
- Allport's Theory of Personality Traits and MotivationDocument13 pagesAllport's Theory of Personality Traits and MotivationNiharika SpencerNo ratings yet
- Pilgrim Christian College: School of Arts and Sciences First Semester S.Y. 2021-2022 GE1-Understanding The SelfDocument28 pagesPilgrim Christian College: School of Arts and Sciences First Semester S.Y. 2021-2022 GE1-Understanding The SelfNorhaima MatanogNo ratings yet
- Personal Growth Guide to Self-ImprovementDocument5 pagesPersonal Growth Guide to Self-ImprovementJoannix V VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Managing Stress and Coping With Covid 19Document26 pagesManaging Stress and Coping With Covid 19Czarinah PachecoNo ratings yet
- Developmental Tasks and ChallengesDocument16 pagesDevelopmental Tasks and Challengespaklah_comeyNo ratings yet
- The Challenges of The Adolescence Period: Nistor Daniela Gabriela Hancu Sarah AndreeaDocument10 pagesThe Challenges of The Adolescence Period: Nistor Daniela Gabriela Hancu Sarah AndreeaMaria100% (1)
- Here are the group labels for the core values:1. Community2. Growth3. Creativity4. Happiness5. KnowledgeDocument4 pagesHere are the group labels for the core values:1. Community2. Growth3. Creativity4. Happiness5. Knowledgeedmar bobadillaNo ratings yet
- Growth Mindset Week 1: Grade/Subject: Health Unit: Growth Mindset Lesson Duration: 45 MinDocument8 pagesGrowth Mindset Week 1: Grade/Subject: Health Unit: Growth Mindset Lesson Duration: 45 Minapi-485518104100% (1)
- Values, Interests and Norms As The Spiritual Basis of PersonalityDocument15 pagesValues, Interests and Norms As The Spiritual Basis of PersonalityLa MayeNo ratings yet
- Small Group Results ReportDocument1 pageSmall Group Results Reportrichie foremanNo ratings yet
- The persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of informationDocument39 pagesThe persistence of learning over time through the storage and retrieval of informationNix Dotarot100% (1)
- Theories of Guidance and Counselling, Cont : Person-Centred TheoryDocument61 pagesTheories of Guidance and Counselling, Cont : Person-Centred TheoryEMMANUEL RINGONo ratings yet
- Foundations of Guidance: Philosphy Psychology Biology Anthropolog y SociologyDocument1 pageFoundations of Guidance: Philosphy Psychology Biology Anthropolog y SociologyCleaford Tabaco JenisanNo ratings yet
- Building ResilienceDocument24 pagesBuilding ResilienceDR-MöŞəb ThənınNo ratings yet
- BB-6-Detective Work and Disputation PDFDocument7 pagesBB-6-Detective Work and Disputation PDFNitaNo ratings yet
- Leading and Leadership Development LectureDocument0 pagesLeading and Leadership Development LectureSyed Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Foster Care Youth Best PracticesDocument4 pagesFoster Care Youth Best Practicesapi-311896275No ratings yet
- Career GuidanceDocument31 pagesCareer GuidanceFelicitas MagleoNo ratings yet
- AngerDocument58 pagesAngerasdfNo ratings yet
- NCE Study GuideDocument62 pagesNCE Study GuideSusana MunozNo ratings yet
- Development in Middle ChildhoodDocument42 pagesDevelopment in Middle ChildhoodArielle Kate Estabillo100% (1)
- The Power of Positive Parenting: Conducted by (Practitioner Name)Document42 pagesThe Power of Positive Parenting: Conducted by (Practitioner Name)Rocky PandianNo ratings yet
- Personal ValuesDocument2 pagesPersonal Valuesapi-372302973No ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument18 pagesMental HealthBibith BibuNo ratings yet
- Faml 160 - Top Ten ListDocument2 pagesFaml 160 - Top Ten Listapi-544252233No ratings yet
- Values Formation (Most Recent)Document4 pagesValues Formation (Most Recent)Lady Lyanna of House Mormont100% (1)
- ch2.6 Basic Motivation ConceptsDocument25 pagesch2.6 Basic Motivation ConceptsdevaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual and Moral DevelopmentDocument14 pagesSpiritual and Moral DevelopmentPatrick Tew75% (4)
- Theories of growth and developmentDocument1 pageTheories of growth and developmentMary SutingcoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Notes - Bascos - BSN 1GDocument25 pagesUnderstanding The Self Notes - Bascos - BSN 1Gmaria jones100% (1)
- Self-Awareness: Done By: Aleena Vinoji Valliyam ThadathilDocument20 pagesSelf-Awareness: Done By: Aleena Vinoji Valliyam ThadathilViNo ratings yet
- Student How To Manage AnxietyDocument4 pagesStudent How To Manage Anxietyadargoblockchain100% (1)
- Topic No. 21 Child-Friendly EnvironmentDocument3 pagesTopic No. 21 Child-Friendly Environmentjezza linglingNo ratings yet
- International College Offers General Psychology CourseDocument4 pagesInternational College Offers General Psychology Courseaize20No ratings yet
- BS Notes MODULE 5Document3 pagesBS Notes MODULE 5pvr2k1No ratings yet
- Executive Skills Questionnaire Results and StrategiesDocument5 pagesExecutive Skills Questionnaire Results and StrategiesAlguémNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Presentation PDFDocument31 pagesMental Health Presentation PDFjhurNo ratings yet
- School Counseling Curriculum Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSchool Counseling Curriculum Lesson PlanJaraed ThomasNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Aug ReportDocument44 pagesPersonal Development Aug ReportK-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Adolescent Development ExplainedDocument1 pageStages of Adolescent Development ExplainedhelenNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Knowledge, Making InferenceDocument3 pagesVocabulary Knowledge, Making InferenceLisa Andriyani100% (1)
- 32 Bfe 50 F 962 BD 4 B 4 AcDocument8 pages32 Bfe 50 F 962 BD 4 B 4 AcLisa AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- 34 Stages of Adolescence1Document1 page34 Stages of Adolescence1Lisa AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- BalanceDocument8 pagesBalanceLoganathan ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Tabel Angka Kecukupan Gizi 2004Document1 pageTabel Angka Kecukupan Gizi 2004I Komang Candra WigunaNo ratings yet
- Shumwaycook M.dgi 2013 AppendixDocument7 pagesShumwaycook M.dgi 2013 AppendixLisa AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Tabel Angka Kecukupan Gizi 2004Document1 pageTabel Angka Kecukupan Gizi 2004I Komang Candra WigunaNo ratings yet
- Tabel Angka Kecukupan Gizi 2004Document1 pageTabel Angka Kecukupan Gizi 2004I Komang Candra WigunaNo ratings yet
- Deep Ecology Debate on Humans' Environmental RoleDocument8 pagesDeep Ecology Debate on Humans' Environmental RoleVidushi ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- Emma Castelnuovo's use of concrete materials in mathematics teachingDocument6 pagesEmma Castelnuovo's use of concrete materials in mathematics teachingNenden Mutiara SariNo ratings yet
- Shinde R.Document8 pagesShinde R.rutuja shindeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument10 pagesCorporate Governance and Corporate Social ResponsibilityrichaNo ratings yet
- 2012 PhenomenaDocument17 pages2012 PhenomenaInderdip ShereNo ratings yet
- BJ HabibieDocument4 pagesBJ HabibieDea Salsabila siregarNo ratings yet
- Assmann, The Ancient Egyptian Myth of The Journey of The SunDocument14 pagesAssmann, The Ancient Egyptian Myth of The Journey of The Sunousermontou-1No ratings yet
- 5th Sem Strategic Management Notes by Yatharth ChauhanDocument63 pages5th Sem Strategic Management Notes by Yatharth ChauhanVikas Prajapati100% (5)
- The Key To Extra Terrestrial Disclosure May Be The Lake Erie UFO's!Document34 pagesThe Key To Extra Terrestrial Disclosure May Be The Lake Erie UFO's!Michael Lee Hill100% (1)
- The Program For Better VisionDocument223 pagesThe Program For Better VisionBlasa100% (6)
- What Is SociolinguisticsDocument3 pagesWhat Is SociolinguisticsRahma BouaitaNo ratings yet
- Song of Songs of SolomonDocument103 pagesSong of Songs of SolomonAndré Rademacher100% (3)
- Errant RPG Character SheetDocument2 pagesErrant RPG Character SheetMathCleLenNo ratings yet
- Benmergui Housing Policy, Slums and Sqatter Settlements in Rio de Janeiro Brazil and Buenos Aires 1948-1973 PDFDocument423 pagesBenmergui Housing Policy, Slums and Sqatter Settlements in Rio de Janeiro Brazil and Buenos Aires 1948-1973 PDFDiego RoldánNo ratings yet
- Ken Done Lesson 2Document4 pagesKen Done Lesson 2api-364966158No ratings yet
- The Thorny Way of Truth Part6 MarinovDocument332 pagesThe Thorny Way of Truth Part6 MarinovEvaldas StankeviciusNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language EssayDocument14 pagesFigurative Language EssayRosalía ImlNo ratings yet
- Crash Film AnalysisDocument4 pagesCrash Film AnalysisstNo ratings yet
- CWR Resources 2011Document56 pagesCWR Resources 2011Adam Dickens0% (1)
- Laila Majnoon and IndiaDocument29 pagesLaila Majnoon and IndiaPunnakayamNo ratings yet
- Conversion Between Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration - CBMAppsDocument3 pagesConversion Between Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration - CBMAppsniraj_hwbNo ratings yet
- Kohlberg Moral Stages and MoralizationDocument12 pagesKohlberg Moral Stages and MoralizationJoy Sib-aten100% (1)
- EVE Online Chronicles PDFDocument1,644 pagesEVE Online Chronicles PDFRazvan Emanuel GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem Math PDFDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem Math PDFapi-201420601No ratings yet
- Macabenta Vs Davao Stevendor Terminal Company, GR No. L-27489Document4 pagesMacabenta Vs Davao Stevendor Terminal Company, GR No. L-27489AddAllNo ratings yet
- Brock, Roger-Greek Political Imagery From Homer To Aristotle-Bloomsbury Academic (2013)Document273 pagesBrock, Roger-Greek Political Imagery From Homer To Aristotle-Bloomsbury Academic (2013)juanemmma100% (1)
- Value of Life Sample Student EssaysDocument10 pagesValue of Life Sample Student EssayshannamunirahNo ratings yet
- Self Knowledge Self DisciplineDocument320 pagesSelf Knowledge Self DisciplineJose Kouassi88% (8)
- Telephone Etiquette: Identify YourselfDocument3 pagesTelephone Etiquette: Identify YourselfGisela AlvesNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V7I6P7) :shatha AlsaediDocument6 pages(IJCST-V7I6P7) :shatha AlsaediEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet