Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VI Baltic Chemistry Olympiad
Uploaded by
Yarga PuritzaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VI Baltic Chemistry Olympiad
Uploaded by
Yarga PuritzaCopyright:
Available Formats
VI Baltic Chemistry Olympiad
May 12-14, 1998, Tartu Theoretical problems
PROBLEM 1 The analysis laboratory received a white crystalline material for analysis. The analyst weighed out two samples of the material. Sample 1. with a mass of 1.084 g was dissolved in water. As the material dissolved 26.17 ml of gas, having a mass of 37.39 mg, was released. The resulting solution was found to be very acidic. Addition hydrochloric acid caused a precipitate to form. After addition of 47.5 ml 0.0983 molar HCl no more precipitate was formed. The precipitate was recovered, dried and weighed. The mass of precipitate obtained was 0.6693 g. Sample 2 with a mass of 1.120 g was heated to above 300o C. During heating 324.6 ml of a gas, with a mass of 599.0 mg, was collected. After heating a light colored metal with a mass of 0.521 g remained. The gas was dissolved in 100 ml of water. Not all the gas dissolved, 54.10 ml, with a mass of 77.2 mg, remained. The pH of the solution was found to be 1.015. a) What was the initial substance? b) What reactions took place during the analysis? PROBLEM 2 A sample of a compound was heated at 600oC. A solid with a mass of 4.51 g remained after heating and 21.48 l of gas were liberated at 600o. The solid contains 21.25% oxygen. After cooling to room temperature the gas occupies 2.69 l and has a density of 1.61 g/l. After passing the gas through alkaline solution, there remained 1.34 l. of a combustible gas having a density of 1.25 g/l. Find the original compound and write all appropriate equations. PROBLEM 3 R(+)-glycerol aldehyde can be transformed to (-)-malic acid (2-hydroxybutanedioic acid) according to the following scheme. R(+)-glycerol aldehyde was treated with hydrogen cyanide and two isomeric compounds were formed, namely A and B. Those compounds were separated by fractional crystallisation. Only isomer B was used for further transformations. This compound was converted to C (C4H8O5) upon hydrolysis then oxidised by conc. nitric acid to produce compound D (C4H6O6). Further compound D was treated with phosphorus tribromide thus compound E (C4H5BrO5) was formed. Finally, compound E was converted to (-)-malic acid after reaction of zinc with an acid. a) Write equations of all reactions using stereochemical (Fisher projections) formulae. b) Explain why only one isomer E was formed from D (hint: consider mechanism of the reaction)? How many isomers of E can be formed if the starting compound for synthesis would be an isomer A? PROBLEM 4 Mustard gas (2,2'-dichlorodiethylsulfyde) is a chemical weapon. In contact with humidity it produces gaseous hydrogen chloride. In comparison 1,5-dichloropenthane is hydrolysed much
more slowly. a) Write mechanism of the above described reaction for both compounds. Explain the difference in reactivity. b) Which well-known compound might be used to destroy this gas? Write equation of the reaction. c) Write synthetic pathway to produce the mustard gas. PROBLEM 5 The thermal decomposition of azomethane (compound A) follows the equation: H3CN = NCH3(g) C2H6(g) + N2(g) The total pressure of the mixture of gases at the temperature of 298.0 C was measured at different time periods: t (min) p (Torr) 10.0 491.9 21.0 548.0 35.0 609.7 861.6
a) Prove that the process is a first order reaction. b) Calculate the average value of the rate constant at 298.0 C. c) The half life of compound A at 320.6 C is 9.5 min. Determine the activation energy of the reaction. PROBLEM 6 Eriochrome Black T (H3Ind) is a typical metal ion indicator that is used in complex-formation titrations with EDTA (Na2H2Y). This compound contains a sulfonic acid group, which is completely dissociated in water, and two phenolic groups, which dissociate only partially (Ka1=5.010-7 and Ka2=2.810-12). H2O + H2Ind- = HInd2- + H3O+ red blue H2O + HInd2- = Ind3- + H3O+ blue orange a) The metal complexes of Eriochrome Black T are generally red. Calculate the minimum pH at which Eriochrome Black T can be used as a indicator in complex-formation titrations (assume, that the detectable color change requires tenfold excess of one or other colored specie). b) Determine the transition range for Eriochrome Black T in titrations of Mg2+ and Ca2+ at pH 10.0, given that the (thermodynamic) formation constant for MgInd- is 1.0 107 and for CaInd- is 2.58 105. c) 50.00 ml of 0.00500 M Mg2+ and Ca2+ solutions were both titrated with 0.0100 M EDTA solution at pH 10. Conditional formation constants (Instead of the equilibrium concentration of Y 4the total concentratioini of all forms of EDTA is used) at that pH are 1.72 108 for MgY2- and 1.75 1010 for CaY2-. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of the metal cations at the equivalence point. Determine the sign of the relative error, connected with assuming that stoichometry point is judged to be approached at the first change of color of solution.
You might also like
- Austrian 25Document13 pagesAustrian 25Vo Tung LamNo ratings yet
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 55 Estonian National Chemistry Olympiad 2008 PDFDocument27 pages55 Estonian National Chemistry Olympiad 2008 PDFVincent Badescu100% (1)
- The Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsDocument29 pagesThe Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsMinh TieuNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2014Document152 pagesGerman Problems 2014Yosi W KusumaNo ratings yet
- 36th Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National CompetitionDocument13 pages36th Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National CompetitionGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2012Document107 pagesGerman Problems 2012Stephen PramatyaNo ratings yet
- Австри 2009 ХариултDocument13 pagesАвстри 2009 ХариултGerel BayrmagnaiNo ratings yet
- 49 IMO - 2nd Tour - ProblemsDocument3 pages49 IMO - 2nd Tour - ProblemsPhan Nhật Duật100% (1)
- Prep Problems Icho40 0521Document104 pagesPrep Problems Icho40 0521Simona TudorNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2010Document143 pagesGerman Problems 2010Stephen PramatyaNo ratings yet
- Task 1 53 BP 19 RP F 0.35849 From Physical ChemistryDocument12 pagesTask 1 53 BP 19 RP F 0.35849 From Physical ChemistrysyavinaNo ratings yet
- UK Chemistry Olympiad Round 1 Mark Scheme 2016Document11 pagesUK Chemistry Olympiad Round 1 Mark Scheme 2016Rhan AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument84 pagesSolutionsKasi RuddrarajuNo ratings yet
- TH TH TH TH: 8 Theoretical Problems 2 Practical ProblemsDocument17 pagesTH TH TH TH: 8 Theoretical Problems 2 Practical Problemslos sabiosNo ratings yet
- 70 Practice Problems For CH 7Document10 pages70 Practice Problems For CH 7ULFA TUFFAHATINo ratings yet
- Preparatory Problems: 46 International Chemistry Olympiad (Icho - 2014)Document92 pagesPreparatory Problems: 46 International Chemistry Olympiad (Icho - 2014)Lê Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- 2016 Chimie Internationala Proba Teoretica SubiectebaremeDocument51 pages2016 Chimie Internationala Proba Teoretica SubiectebaremeCristinaNo ratings yet
- 2004 Nasional BelarusDocument14 pages2004 Nasional BelarusFeni Utari BasyarNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2003 PDFDocument99 pagesGerman Problems 2003 PDFJeykco Wilfredo Villavicencio HuanilaNo ratings yet
- Hop Chat HC Don Chuc Tap 1 PGS TS Truong The KiDocument322 pagesHop Chat HC Don Chuc Tap 1 PGS TS Truong The KiKen PhanNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2013Document152 pagesGerman Problems 2013Stephen PramatyaNo ratings yet
- Problem Ver 2Document133 pagesProblem Ver 2NuteLLa Gaming (EFL)No ratings yet
- Alkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFDocument45 pagesAlkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFPrasad Yarra100% (1)
- Ejnd OJpe 5 RQDocument2,350 pagesEjnd OJpe 5 RQLê LâmNo ratings yet
- Fukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 2001/08/22: N N N HDocument2,429 pagesFukuyama Group - Group Meeting Problems 2001/08/22: N N N HGia PhướcNo ratings yet
- 37 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad: Name:.......................................Document22 pages37 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad: Name:.......................................syavinaNo ratings yet
- 175th Anniversary of Dmitriy MendeleevDocument29 pages175th Anniversary of Dmitriy MendeleevAryanNo ratings yet
- 56 Estonian National Chemistry Olympiad: University of Tartu The Gifted and Talented Development CentreDocument12 pages56 Estonian National Chemistry Olympiad: University of Tartu The Gifted and Talented Development CentremikkasNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2007Document156 pagesGerman Problems 2007Paul AdrianNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Worksheet SolutionsDocument11 pagesElectrochemistry Worksheet SolutionsAnivia12100% (1)
- Austrian National Chemistry Olympiad 1998Document21 pagesAustrian National Chemistry Olympiad 1998Muhammad GhifariNo ratings yet
- Solved Multiple Choice Questions Chemical EquilibriumDocument16 pagesSolved Multiple Choice Questions Chemical EquilibriumAliLakhoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesUnit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsSAMBASIVA RAO YEMINENINo ratings yet
- National German Competition: 47. International Chemistry Olympiad Azerbaijan 2015Document132 pagesNational German Competition: 47. International Chemistry Olympiad Azerbaijan 2015ahmad ahdalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I Extra Synthesis Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Extra Synthesis Practice ProblemsVinh HoangNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Document10 pagesPractice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Arianne Foster100% (1)
- 43 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National Competition Theoretical Tasks 2017-05-25Document35 pages43 Austrian Chemistry Olympiad National Competition Theoretical Tasks 2017-05-25Quốc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl Compounds Tutorial 6 Key ConceptsDocument21 pagesHydroxyl Compounds Tutorial 6 Key ConceptsJohnNo ratings yet
- 1-50 QuestionsDocument48 pages1-50 Questionsbolla reddyNo ratings yet
- German Problems 2014 Thu Nghiem 1Document447 pagesGerman Problems 2014 Thu Nghiem 1Hảo ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Zhihan Nan - Theory and Problems For Chemistry Olympiad - Challenging Concepts in Chemistry-WS Education (2019)Document557 pagesZhihan Nan - Theory and Problems For Chemistry Olympiad - Challenging Concepts in Chemistry-WS Education (2019)Nguyễn Việt Hải0% (1)
- Ionic Equillibrium PDFDocument26 pagesIonic Equillibrium PDFHaltz t00nNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- Common Foundation Organic Q in A LevelDocument21 pagesCommon Foundation Organic Q in A Level黄维燕No ratings yet
- Section I. Analytical Chemistry: Problem 1Document21 pagesSection I. Analytical Chemistry: Problem 1hakuna mata taNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Olympiad 2011 Problems and SolutionsDocument127 pagesChemistry Olympiad 2011 Problems and SolutionsSyauqie AlifianNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry PDFDocument253 pagesAnalytical Chemistry PDFJerome MamauagNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I Practice: Sn1 and Sn2 Reaction MechanismsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Practice: Sn1 and Sn2 Reaction MechanismsRam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Organic Reagent BookDocument77 pagesThe Organic Reagent Bookshubu2006.ssNo ratings yet
- 2006 R enDocument23 pages2006 R enMəmməd MəmmədliNo ratings yet
- Xenon 21-22 Sheet Without Answer (EUDIOMETRY)Document3 pagesXenon 21-22 Sheet Without Answer (EUDIOMETRY)Krishna GoyalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 2Elsw FewNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL CHAPTER 1 by DR - KavirajaaDocument4 pagesTUTORIAL CHAPTER 1 by DR - Kavirajaaathirah ashikinNo ratings yet
- Soal Reaksi EksotermDocument8 pagesSoal Reaksi EksotermJack ReacherNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 3rd Long Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesChem 16 3rd Long Exam Reviewerggwp21No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-27-08 - 11th (J-Batch) WADocument15 pagesCHEMISTRY-27-08 - 11th (J-Batch) WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Uther Mokin WsDocument11 pages4 Uther Mokin WsCarlos ChNo ratings yet
- A12Document1 pageA12Yarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- 06 Diffraction IIDocument12 pages06 Diffraction IIehagar60No ratings yet
- A11Document2 pagesA11Yarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- A 9Document2 pagesA 9Yarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- MsdsDocument1 pageMsdsYarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Ijmee 20160501 03Document6 pages10 5923 J Ijmee 20160501 03Yarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- Manual - Solutions-Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems 6th Ed. by WildiDocument109 pagesManual - Solutions-Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems 6th Ed. by WildiLeonardo Lira100% (3)
- Soal2 BiologiDocument2 pagesSoal2 BiologiYarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- Expansion: Science: PhysicsDocument12 pagesExpansion: Science: PhysicsYarga PuritzaNo ratings yet
- Amount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Document4 pagesAmount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- LNG NGL IntegrationDocument16 pagesLNG NGL IntegrationSubhransu BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Leica TCS SP8 HyD-Flyer - ENDocument2 pagesLeica TCS SP8 HyD-Flyer - ENhisto.haritNo ratings yet
- Kantha Ocean Mixed LayerDocument8 pagesKantha Ocean Mixed LayerAdrianio LozhadaNo ratings yet
- 1.0-Introduction: Technical Proposal R.O. SystemDocument13 pages1.0-Introduction: Technical Proposal R.O. SystemZarkKhanNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ConversionDocument24 pagesAmmonia ConversionKashan AslamNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Sci5Document1 pageBudget of Work Sci5Jhoy Angeles PinlacNo ratings yet
- Castrol Deformation RangtrainingDocument32 pagesCastrol Deformation RangtrainingcotteNo ratings yet
- Heat ConductionDocument8 pagesHeat ConductionJameel MalikNo ratings yet
- Landfill Environmental Impact 2Document60 pagesLandfill Environmental Impact 2Demamu TageleNo ratings yet
- Mycotoxin Detection: For CannabisDocument20 pagesMycotoxin Detection: For CannabisЛабораторија За КонтаминентиNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MCQ QuestionsDocument24 pagesUnit 1 MCQ Questionsanand anithaNo ratings yet
- Conducting Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements To Determine The Corrosion Susceptibility of Small Implant DevicesDocument9 pagesConducting Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements To Determine The Corrosion Susceptibility of Small Implant DevicesHenry Esteban Orozco PerezNo ratings yet
- Tehnički Opis R32 Monobloc S THERMA VDocument16 pagesTehnički Opis R32 Monobloc S THERMA VMladen DusmanovicNo ratings yet
- CLASS 12 PHYSICAL Diwali Assignment ChemistryDocument8 pagesCLASS 12 PHYSICAL Diwali Assignment ChemistryPrashantNo ratings yet
- 2.1.7. Balances For Analytical PurposesDocument3 pages2.1.7. Balances For Analytical PurposesTrung Dương Đức100% (1)
- Paper 1. Theory of pH-Stat TitrationDocument10 pagesPaper 1. Theory of pH-Stat TitrationLisett Del Pilar Rodriguez OyarceNo ratings yet
- Inter 2 Physics Success SeriesDocument12 pagesInter 2 Physics Success SeriesZain AliNo ratings yet
- Implant MaterialsDocument100 pagesImplant Materialsmegha bhola75% (4)
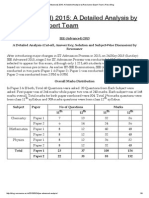
- JEE (Advanced) 2015 - A Detailed Analysis by Resonance Expert Team - Reso BlogDocument9 pagesJEE (Advanced) 2015 - A Detailed Analysis by Resonance Expert Team - Reso BlogGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Energy Measurement PDFDocument354 pagesNatural Gas Energy Measurement PDFHenry Maeda100% (3)
- PROTECT WORKER HEALTH WITH INDUSTRIAL HYGIENEDocument31 pagesPROTECT WORKER HEALTH WITH INDUSTRIAL HYGIENEDANICA JORIELLE PALOGANNo ratings yet
- Outlines of Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesOutlines of Organic Chemistrycoolnsmarttt100% (3)
- Geochemistry of Coal Mine DrainageDocument22 pagesGeochemistry of Coal Mine DrainageFirmanullahyusufNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Properties of AC HVAF Sprayed Ni60WC Composite Coating 2009 Journal of Alloys and CompoundsDocument5 pagesMicrostructure and Properties of AC HVAF Sprayed Ni60WC Composite Coating 2009 Journal of Alloys and CompoundsastronotusNo ratings yet
- Smart materials enable responsive constructionDocument10 pagesSmart materials enable responsive constructionNiveditha jNo ratings yet
- Anton FilikovDocument7 pagesAnton FilikovKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Microalloying With Boron On Properties of Austenite Stainless Steel X8crnis18-9Document6 pagesThe Influence of Microalloying With Boron On Properties of Austenite Stainless Steel X8crnis18-9IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Oregon Geology Map and Report DetailsDocument24 pagesOregon Geology Map and Report DetailskctreeNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon Surface Modifications by Nitric Acid, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Ammonium Peroxydisulfate TreatmentsDocument7 pagesActivated Carbon Surface Modifications by Nitric Acid, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Ammonium Peroxydisulfate TreatmentsxavikxavikNo ratings yet
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresFrom EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNo ratings yet
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualFrom EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryFrom EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)