Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Servicing Guide To British Motor V Ehicles
Uploaded by
Stephen CarterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Servicing Guide To British Motor V Ehicles
Uploaded by
Stephen CarterCopyright:
Available Formats
Servicing Guide to British Motor V ehicles
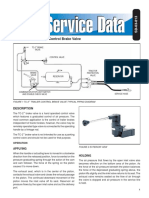
Construction slightly depressed. The fluid can pass between the return spring. When this happens the piston
the end of the piston rod and its seating on the rod end is clear of its seat in the plunger and so
The main component of the servo is the plunger, through the centre of the plunger, and fluid can pass through the seal and plunder,
body and cylinder, treated as one unit as they through the small hole in the seal. From the allowing normal recuperation of the system.
are jig-assembled for concentricity. There are hydraulic cylinder the pressure is applied to In the event of the vacuum servo failing, the
three union mountings on the servo unit, the the wheel cylinders via the outlet union. At the return spring ensures that the piston rod end is
uppermost in the drawing being the vacuum same time the small plunger is subject to clear of the cone seating, thus fluid can pass
pipe, the one at the side being the supply from pressure. If the pedal pressure is slightly through the servo so that the brakes operate as a
the master cylinder, and the one on the increased the force applied by the plunger, normal non-assisted system.
projecting cylinder being the outlet to the multiplied by the effect of the lever, is
normal circuit. The cylinder, closed by an end sufficient to overcome the loading of the Lubrication
diaphragm spring. Initial movement of the Follow vehicle manufacturer’s specification.
plate with a breather, contains the piston
diaphragm causes the cage to be withdrawn Notice that on no account should any type of
assembly, consisting of a leather cup with
until the disc valve under the influence of the mineral oil be used. General recommendation is
expander ring supported by steel plates and
clamped between a flange on the piston rod and internal spring seats on the lip of the cage. Molytone C Grease available from Rocol Ltd,
a lock nut. A return spring is fitted between the This seals off the air vent to atmosphere of the Rocol House, Swillington, nr. Leeds.
closed end of the cylinder and the piston. piston. Further pressure causes further
movement of the cage, so that the lip of the Cleaning and Examination
The other end of the piston rod is conical
Cage withdraws the disc valve from the To clean, remove unit complete, after
and passes through a seal into the hydraulic
vacuum port. When this happens the chamber brushing away all dirt near pipe connections.
chamber. This conical end can seat inside a
behind the diaphragm, and thus the cylinder, Unscrew union nuts, disconnect all hydraulic
plunger, which, with a seal with a small central
are subject to vacuum. The piston now has and vacuum connections (and breather, if
hole, seal abutment collar and compression
atmospheric pressure on one side and a applicable) and plug open end of pipes.
spring, are fitted inside a hydraulic cylinder
vacuum on the other. This pressure difference Supporting servo from below, remove three set-
screwed into the body and sealed by a copper
causes the piston to move inwards, overcoming screws securing unit to chassis, lower and
washer. Note that when the servo is not
the return spring. As it moves, the tapered-end remove from vehicle.
operating, the piston rod end is clear of the cone
piston rod seats in the plunger, sealing off the Plug open connections to prevent entry of
seating, the plunger being returned by the
fluid passage, and forces the plunger and seal foreign matter and clean exterior with a rag
copper washer.
into the hydraulic cylinder, causing a high dipped in carbon tetrachloride, petrol or
Near the vacuum inlet is the reaction valve.
pressure in the wheel cylinder circuit. This is paraffin. Do not immerse in or add excess of
This consists of an annular diaphragm clamped
the start of the boost, and it occurs at a low liquid, otherwise seals will deteriorate.
at its outer periphery between the body and a
pedal pressure so that there is no noticeable Cleanliness is essential. Handle unit with care to
domed metal cover, and at its inner periphery by
"step”. Notice that in addition to the servo avoid damaging seals.
the two halves of the valve cage. The cage
piston effort, the plunger is also subject to Between major overhauls dismantling the
contains a spring-loaded rubber-faced disc valve
pedal-pressure on the annular area around the servo is not necessary, but routine service
which seats on the vacuum inlet port or on the
rod, and the brake supplying force and procedure is as follows: —
lip of the cage. At the opposite end of the cage
reaction force are “locked” inside the cylinder Stand unit with hydraulic cylinder upright and
are a series of holes for air venting, and through
and servo body. allow fluid to drain from vacuum cylinder
the centre passes the valve operating spindle.
If the pedal is further depressed the disc through breather. Check valve lever for freedom
The entire valve unit is free to move with the
valve will be drawn farther from the vacuum of movement and lubricate pivot pins. If lever
diaphragm, which is itself spring-loaded by a
port, giving an increased vacuum and greater and pins are removed, pins must be replaced
compression spring returned by the domed
braking effort until the limit of the servo effect with heads towards servo fixing bosses. Wide
cover. A passage connects the closed end of the
is reached. Beyond this point, where the clearances on valve lever assembly are
vacuum cylinder with the chamber enclosed by
vacuum valve is fully open, increased pedal intentional, not to be confused with excessive
the diaphragm.
pressure will increase the total braking effort wear. Check fitting of split pins.
From the hydraulic inlet union a passage
by the direct action of this on the annular Remove end cover, withdraw piston assembly
connects with a space between the piston rod
plunge area. If the brake is applied, and then and return spring. Wipe cylinder walls and piston
seal and the plunger, and from here a cross-
“held”, the vacuum behind the diaphragm will assembly with clean cotton cloth and re-lubricate,
drilling connects with a small cylinder into
build up until the pressure on the diaphragm, clean piston return spring, replace in cylinder, and
which fits a spherical-ended plunger, with a
plus the load of the diaphragm spring, balances carefully insert piston rod in seal. Push piston
pressure seal. The valve lever is pivoted on a
that of the smaller plunger acting through its assembly into cylinder and replace end cover.
forked lug on the body (note that there are
alternative positions for the pivot pin). Near the leverage. When this balance occurs the cage is
in such a position that the vacuum port is
Bleeding
pivot the lever is in contact with the outer end of
the small plunger, and at the opposite end it is closed by the disc valve, the pressure difference After fitting servo to chassis and re-
linked to the valve-operating spindle. in the cylinder being sustained. Since the connecting pipes, hydraulics systems should be
pressure on the small plunger is that provided bled in normal manner. As hydraulic unit of
by the master cylinder, and the vacuum is servo will be refilled during the operation,
Operation. common to the diaphragm and the cylinder, it volume of air expelled at wheel cylinders will
To consider the operation, it is first necessary is apparent that at this point of balance the be more than usual. It is essential that fluid
to visualize the state of the various components braking effect is directly proportional to the level in reservoir is maintained during this
before the brake is operated. All the hydraulic applied pedal effort, in a fixed ratio. operation. After bleeding, start engine and
passages are filled with fluid under the slight When the effort of the brake pedal is apply footbrakes several times, after which
pressure provided by the master cylinder to released, the pressure on the smaller plunger is system should be re-bled to clear any air
keep the seals in their correct conformation. The reduced, and the diaphragm return spring pockets from internal passages of servo.
piston is kept at the outer end of its travel by the overcomes this force, moving the cage farther
return spring, and the plunger is held against inwards. This causes the interior spring load to Dismantling and Assembling
the copper washer by the compression spring. be overcome, unseating the disc valve from the Complete dismantling and assembling should
Spring pressure also presses the reaction valve lip of the cage, and thus permitting air to pass not be necessary, as recommended procedure is to
fully home. In this position the disc valve seals through the cage into the diaphragm chamber return unit to manufacturer for attention or to
the vacuum port, but is pushed clear of the lip of and the vacuum cylinder, reducing the pressure follow procedure given in fault-finding chart.
the cage, so that the vacuum cylinder is vented difference to which the piston is subject, Note, however, that cleanliness is essential, that
to atmosphere by the passage, diaphragm thereby reducing the braking effort. If the extreme are must be used to prevent damage to
chamber, the interior of the valve cage, and the pedal is completely released, the atmospheric seals, that vacuum cylinder should not be removed
drillings in its end. valve is fully opened so that the vacuum is from body, and that seals must not come in contact
Now assume that the brake pedal is destroyed, and the piston is fully withdrawn by with degreasing fluids or mineral lubricants.
Note 1: ROCOL, ROCOL House, Swillington, Leeds LS26 8BS
TEL: +44 (0) 113 232 2600
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version www.software-partners.co.uk
You might also like
- Popular Mechanics: How to Fix Anything: Essential Home Repairs Anyone Can DoFrom EverandPopular Mechanics: How to Fix Anything: Essential Home Repairs Anyone Can DoRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Hydraulic Rod Jar: Instruction Manual 4010Document8 pagesHydraulic Rod Jar: Instruction Manual 4010Foros IscNo ratings yet
- M. Saleem Raza Ali, SEDocument33 pagesM. Saleem Raza Ali, SEgoda gi420No ratings yet
- Exhaust ValvesDocument3 pagesExhaust ValvesJitendra Kumar100% (1)
- Bendix TC-2 Trailer Control Brake Valve: DescriptionDocument4 pagesBendix TC-2 Trailer Control Brake Valve: Descriptionjorge chavarriaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Servomotor For Main Description and Reheat Stop ValvesDocument1 pageSteam Turbine Servomotor For Main Description and Reheat Stop Valvesparthibanemails5779No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Servomotor For Main Description and Reheat Stop ValvesDocument1 pageSteam Turbine Servomotor For Main Description and Reheat Stop Valvesparthibanemails5779No ratings yet
- Section 908: Exhaust ValveDocument14 pagesSection 908: Exhaust ValveMade AgusNo ratings yet
- Dixon Hose Valve Installation InstructionDocument2 pagesDixon Hose Valve Installation InstructionJMNo ratings yet
- W.RT. Reciprocating Air Compressor Explain The Cause of The Following FaultsDocument51 pagesW.RT. Reciprocating Air Compressor Explain The Cause of The Following FaultsSri VasanNo ratings yet
- 08 Co 178 Realiance Saf Val 2 LRDocument2 pages08 Co 178 Realiance Saf Val 2 LRAli AliNo ratings yet
- General Valve Four-Way Diverter BrochureDocument16 pagesGeneral Valve Four-Way Diverter BrochureOndRechTacLetMovNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Valves: Rocker Operation of Valves Presents Certain ProblemsDocument4 pagesExhaust Valves: Rocker Operation of Valves Presents Certain ProblemscamalielNo ratings yet
- Cat PSGV Dewdr 0002 enDocument22 pagesCat PSGV Dewdr 0002 enGaiu George LucianNo ratings yet
- Valves NotesDocument15 pagesValves NotessudheeshNo ratings yet
- Crispin Valve Maintenance ManualDocument17 pagesCrispin Valve Maintenance ManualJohnny VargasNo ratings yet
- Report On ValvesDocument15 pagesReport On ValvesAnonymous b9J5NMNo ratings yet
- S02-Equip OperationDocument6 pagesS02-Equip OperationRishiNo ratings yet
- Valvula DireccionDocument8 pagesValvula DireccionVictor Manuel Lozada ObessoNo ratings yet
- GENERAL VALVE Four Way Diverter ValveDocument16 pagesGENERAL VALVE Four Way Diverter ValveLuis Miguel EstradaNo ratings yet
- Válvula Solenoide S7ADocument4 pagesVálvula Solenoide S7Aroque100% (1)
- PumpDocument25 pagesPumpIbrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Check Valves: Sub-ObjectiveDocument7 pagesLesson Check Valves: Sub-Objectivemister pogiNo ratings yet
- Summary Compressor TrainingDocument44 pagesSummary Compressor Traininggi_mampuzNo ratings yet
- 26850A005Document12 pages26850A005Luciano AlencastroNo ratings yet
- Bucyrus: Technical ManualDocument7 pagesBucyrus: Technical ManualJohn GrayNo ratings yet
- 2) Air Start VV & Indicator VVDocument13 pages2) Air Start VV & Indicator VVHrishikesh MoreNo ratings yet
- WWW Spiraxsarco Com Check ValveDocument8 pagesWWW Spiraxsarco Com Check ValveMashudi FikriNo ratings yet
- Check ValvesDocument12 pagesCheck ValvesddphilosophyNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technical Vocational Teacher Education: Sorsogon State University Education & Accountancy DepartmentDocument2 pagesBachelor of Technical Vocational Teacher Education: Sorsogon State University Education & Accountancy DepartmentAriel PortugalNo ratings yet
- Control Valve - Theory & SizingDocument29 pagesControl Valve - Theory & SizingSandeep KulathapallilNo ratings yet
- Check Valves: Block 12 Pipeline AncillariesDocument14 pagesCheck Valves: Block 12 Pipeline AncillariesMarcelo RiveroNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Valves: Safetygram 23Document12 pagesCylinder Valves: Safetygram 23Gore JiangNo ratings yet
- Equipment Descriptions, Operating Characteristics, and RequirementsDocument50 pagesEquipment Descriptions, Operating Characteristics, and RequirementslcremaschiNo ratings yet
- Ttymuy, MuiDocument41 pagesTtymuy, MuiAjayNo ratings yet
- Valves General For DummiesDocument42 pagesValves General For Dummiesdito100% (7)
- Types of PumpsDocument8 pagesTypes of Pumpskarthick_sailor100% (2)
- Why Piston Valves Are Better Isolation Shut Off ValveDocument2 pagesWhy Piston Valves Are Better Isolation Shut Off ValveShantanu KulkarniNo ratings yet
- WSA Engineering Branch Training 3Document30 pagesWSA Engineering Branch Training 3rene almonacidNo ratings yet
- Types of ValvesDocument5 pagesTypes of Valvesjeamnard balitaanNo ratings yet
- A1 Side Suction NRVDocument4 pagesA1 Side Suction NRVMugeshNo ratings yet
- Basics of ValvesDocument8 pagesBasics of ValvesIsmael KhalilNo ratings yet
- Valves Election SizingDocument24 pagesValves Election SizingzoltanNo ratings yet
- Safety Valves For Power PlantDocument56 pagesSafety Valves For Power Planttek_surinder100% (1)
- Reciprocating PumpDocument8 pagesReciprocating Pump123rahul456No ratings yet
- Safety ValvesDocument8 pagesSafety ValvesvenkeekuNo ratings yet
- Valve StudentDocument68 pagesValve StudentToniNo ratings yet
- Sliding Sleeve - WikipediaDocument7 pagesSliding Sleeve - Wikipediawilliam MadingNo ratings yet
- AccessoriesDocument31 pagesAccessoriesLuke ArandidNo ratings yet
- NRV Philosophy and ApplicationDocument13 pagesNRV Philosophy and ApplicationnasirmuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Valva MechanismDocument38 pagesValva MechanismAnkitSingh100% (1)
- I & M Mark 57: Ideal InstallationDocument4 pagesI & M Mark 57: Ideal Installationbenzerga karimNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Dewar Maintenance: Bell Jar GasketDocument4 pagesCryogenic Dewar Maintenance: Bell Jar GasketPaslab UjfiNo ratings yet
- Check ValvesDocument14 pagesCheck ValvesEryl YeongNo ratings yet
- Control Valves BasicsDocument203 pagesControl Valves Basicszeeshansuboor100% (1)
- O M ManualDocument8 pagesO M ManualAmjed HNo ratings yet
- MB-1 Component No 1 (Code Book) PDFDocument329 pagesMB-1 Component No 1 (Code Book) PDFBorysNo ratings yet
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementFrom EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNo ratings yet
- So How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkDocument12 pagesSo How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkAyesha MAhmoodNo ratings yet
- Catalogo EnerpacDocument258 pagesCatalogo EnerpacAlejandro Zambrano Morales100% (1)
- Bow Visor DesignDocument23 pagesBow Visor DesignSahil JawaNo ratings yet
- Reparacion de CilindrosDocument20 pagesReparacion de CilindrosMonserrat Hernández SánchezNo ratings yet
- LIEBHERR Pumps and MotorsDocument80 pagesLIEBHERR Pumps and Motorsxxsh100% (6)
- VTU EDUSAT Hydraulic CircuitsDocument38 pagesVTU EDUSAT Hydraulic CircuitshamidouNo ratings yet
- Bectochem: Consultants & Engineers Pvt. LTDDocument15 pagesBectochem: Consultants & Engineers Pvt. LTDanita shindeNo ratings yet
- Clutch System: Clutch Unit (Air Servo Type)Document13 pagesClutch System: Clutch Unit (Air Servo Type)irwan yuniardiNo ratings yet
- GR 600EX SpecsheetDocument16 pagesGR 600EX SpecsheetTeguh Nugraha NatawijayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document39 pagesChapter 5Pink FloydaNo ratings yet
- Mining Excavator: Operating Weight With Backhoe Attachment: Shovel Attachment: Engine: Loading CapacityDocument22 pagesMining Excavator: Operating Weight With Backhoe Attachment: Shovel Attachment: Engine: Loading CapacityAvir YadavNo ratings yet
- Back Hoe Loader SOPDocument2 pagesBack Hoe Loader SOPHasnul Wafa100% (1)
- Magnum Tanker Parts PDFDocument207 pagesMagnum Tanker Parts PDFMónica Rada Urbina100% (1)
- Is 11146 (1999) - Iso 7181 (1991)Document6 pagesIs 11146 (1999) - Iso 7181 (1991)sandeepNo ratings yet
- Abre BridasDocument26 pagesAbre BridasYeyePulidoNo ratings yet
- Design of Mini Hydraulic Press Machine (2) HyDocument48 pagesDesign of Mini Hydraulic Press Machine (2) Hyyifruseyife60No ratings yet
- Manual - InterSystems HD-PRT-HYD SamplerDocument40 pagesManual - InterSystems HD-PRT-HYD Sampler张群利No ratings yet
- Catalogo Actuadores HidraulicosDocument68 pagesCatalogo Actuadores HidraulicosErnesto Sánchez GómezNo ratings yet
- Construction Working and Maintenance of Stackers and Reclaimers For Bulk MaterialsDocument46 pagesConstruction Working and Maintenance of Stackers and Reclaimers For Bulk MaterialsLargyla Torres MendesNo ratings yet
- Brace 2020 Tool Catalog PDFDocument238 pagesBrace 2020 Tool Catalog PDFDanilNo ratings yet
- HydraulicCylinderTubeST52 ST52 3Document1 pageHydraulicCylinderTubeST52 ST52 3rjramanathanNo ratings yet
- Auto Mat Is MeDocument58 pagesAuto Mat Is MeBouallegue Mounir100% (1)
- Installation and User Guide: Pellicon 3 CassettesDocument16 pagesInstallation and User Guide: Pellicon 3 CassettesCHIRANJEEVINo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Unit Supplemental Instruction Manual: Trio Engineered Products 12823 Schabarum Ave. Irwindale, CA 91706Document21 pagesHydraulic Power Unit Supplemental Instruction Manual: Trio Engineered Products 12823 Schabarum Ave. Irwindale, CA 91706Chancadores ChileNo ratings yet
- Overview Bearing ElementsDocument1 pageOverview Bearing ElementsPatrick BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- S600P Slag Hauler PDFDocument133 pagesS600P Slag Hauler PDFAdi PutraNo ratings yet
- Lokotrack LT1213S S N 73253Document634 pagesLokotrack LT1213S S N 73253Fabian Cortes Serrano100% (13)
- D31EX-21 D31PX-21: 56 KW 75 HP at 2000 RPMDocument12 pagesD31EX-21 D31PX-21: 56 KW 75 HP at 2000 RPMfery setyawanNo ratings yet
- Part ListDocument8 pagesPart ListPhilNo ratings yet
- 22 Control MechanismDocument14 pages22 Control MechanismAntonio FugaciuNo ratings yet