Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 - Mains Water Pipe Sizing
Uploaded by
starykltOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
0 - Mains Water Pipe Sizing
Uploaded by
starykltCopyright:
Available Formats
Mains Water Pipe Sizing
Pipe Sizing Procedure
1. Reference the pipe section. 2. Calculate flow rates from Table below. 3. Estimate flow rates in each section. Keep velocity below 2 m/s. See also CIBSE Guide G (2003) part 2, Table 2.19. 4. Estimate pipe diameter from pipe sizing tables in CIBSE Guide C. 5. Measure the pipe run from drawings. 6. Calculate length of pipe equal to resistance of fittings. The Total equivalent length of a fitting = Equivalent Length x Pressure Loss factor z (Zeta). 7. Calculate effective pipe length. 8. Determine pressure loss due to friction from CIBSE Tables. 9. Calculate pressure consumed due to friction (Pa) = effective pipe length (m) x pressure loss due to friction (Pa/m) 10. Calculate total pressure consumed = Friction loss + Static pressure loss 11. Determine pressure at start of section. 12. Calculate pressure available at end of section = Pressure at start of section - Total pressure consumed If pressure available at end of section is less than the maximum allowable pressure drop then we can accept this pipe size. 13. Determine pressure required at end of section, this can be the minimum pressure that is required for terminal equipment. 14. If the pressure available at the end of the section is more than or equal to the pressure required at the end of the section then the pipe size is correct.
Water Flow Rates Cold water flow rates for sanitary appliances for small installations may be found from the table below. Approximate hot or cold water demand Basin (spray tap) Basin (tap) Bath (private) Bath (public) Flushing cistern Shower (nozzle) Shower (100mm rose) Sink (15mm tap) Sink (20mm tap) Wash fountain
Flow rate (l/s) 0.05 0.15 0.30 0.60 0.10 0.15 0.40 0.20 0.30 0.40
In larger more complex buildings where many sanitary appliances are installed simultaneous demand should be considered from tables CIBSE Guide B (1986) B4.20 and B4.21. Notes:An alternative method of pipe sizing is to use a nomogram. This can be found in CIBSE Guide G (2004) Public Health Engineering Figure 2.21. Pipe Sizing table
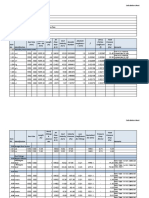
Pressurised Cold Water Pipe Sizing Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Ref
Demand Units if required
Flow Rate (l/s)
Estimated Pipe Dia. (mm)
Measured Pipe Run (m)
Length of Effective Pipe Equal to Pipe Length Fittings Col . 5 + 6 Resistances (m) (m)
From CIBSE Tables
Pipe Pressure Loss (Pa/m)
Pressure Friction loss + Consumed due Static to Friction pressure loss Col. 7 x 8 = Total (Pa) Pressure Consumed (Pa)
Pressure at Start of Section (Pa)
Pressure Pressure Available at Required End of at End of Section Section (Pa) (Pa)
Final Pipe Size (mm)
Example 1
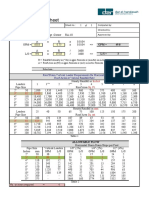
Calculate an appropriate pipe size for the system shown above. Use Copper Table X pipework for water at 10oC.. Answer The maximum allowable pressure drop along the length of pipe = 300,000 Pa 250,000 Pa = 50,000 Pa Pressurised Cold Water Pipe Sizing Table
1
Ref
2
Demand Units if required
3
Flow Rate (l/s)
4
Estimated Pipe Dia. (mm)
5
Measured Pipe Run (m)
8
Pipe Pressure Loss (Pa/m)
10
11
Pressure at Start of Section (Pa)
12
Pressure Available at End of Section (Pa)
13
Pressure Required at End of Section (Pa)
14
Final Pipe Size (mm)
Length of Effective Pipe Equal to Pipe Length Fittings Col . 5 + 6 Resistances (m) (m)
A A
none none
0.8 0.8
22 28
50 50
none none
50 50
Pressure Friction loss + Consumed due Static to Friction pressure loss Col. 7 x 8 = Total From CIBSE (Pa) Pressure Tables Consumed (Pa)
3500 1000
175,000 50,000
175,000 50,000
300,000 300,000
125,000 250,000
250,000 250,000
Too small 28
Pipe Sizing Procedure 1. Reference the pipe section - section A.
2. 3.
Calculate demand units or loading units from Tables in CIBSE guide (attached). not required, see No.3 below. Estimate flow rates in each section. Keep velocity below 2 m/s. - given
4. Estimate pipe diameter from pipe sizing tables in CIBSE Guide C. 22mm (velocity too high at approx 2.4 m/s) or 28mm (velocity is 1.5 m/s). 5. 6. 7. 8. Measure the pipe run from drawings. 50m Calculate length of pipe equal to resistance of fittings. no fittings Calculate effective pipe length. - 50m Determine pressure loss due to friction from CIBSE Tables. See Table 4.18 in Guide C (CD version).
9. Calculate pressure consumed due to friction (Pa) = effective pipe length (m) x pressure loss due to friction (Pa/m). Column 7 x 8 in Pipe Sizing Table. 10. Calculate total pressure consumed = Friction loss + Static pressure loss. There are no vertical pipe sections and therefore no static pressure loss. 11. 12. Determine pressure at start of section. Given in drawing as 300,000 Pa. Calculate pressure available at end of section = Pressure at start of section - Total pressure consumed. 300,000 175,000 = 125,000 Pa. (22mm) ..300,000 50,000 = 250,000 Pa (22mm). If pressure available at end of section is less than the maximum allowable pressure drop then we can accept this pipe size.
13. Determine pressure required at end of section, this can be the minimum pressure that is required for terminal equipment. Given in drawing as 250,000 Pa. 14. If the pressure available at the end of the section is more than or equal to the pressure required at the end of the section then the pipe size is correct. 28mm pipe is correct, 22mm is too small since there is not enough pressure available at the end of the section and the water velocity is also too high.
Example 2
Calculate an appropriate pipe size for the system shown above. Use Copper Table X pipework for water at 10oC.. Answer The maximum allowable pressure drop along the length of pipe = 120,000 Pa 90,000 Pa = 30,000 Pa
Pressurised Cold Water Pipe Sizing Table
1
Ref
2
Demand Units if required
3
Flow Rate (l/s)
4
Estimated Pipe Dia. (mm)
5
Measured Pipe Run (m)
6
Length of Pipe Equal to Fittings Resistances (m)
7
Effective Pipe Length Col . 5 + 6 (m)
8
Pipe Pressure Loss (Pa/m)
10
11
Pressure at Start of Section (Pa)
12
13
14
Final Pipe Size (mm)
From CIBSE Tables
none
0.5
22
14
1.6
15.6
1500
Pressure Friction loss + Consumed due Static to Friction pressure loss Col. 7 x 8 = Total (Pa) Pressure Consumed (Pa)
Pressure Pressure Available at End Required of Section at End of (Pa) Section (Pa)
23,400
23,400
120,000
96,600
90,000
22
Pipe Sizing Procedure 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Reference the pipe section - section A. Calculate demand units or loading units from Tables in CIBSE guide (attached). not required Estimate flow rates in each section. Keep velocity below 2 m/s. - given Estimate pipe diameter from pipe sizing tables in CIBSE Guide C. 22mm (velocity is 1.5 m/s). Measure the pipe run from drawings. 14m Calculate length of pipe equal to resistance of fittings. 2 bends. The Total equivalent length of a fitting = Equivalent Length x Pressure Loss factor z (Zeta). See Pipe Sizing Heating Section - page 4 - pipe fitting losses. Copper pipe elbow z (Zeta) = 1.0 x 2 bends = 2.0 Determine equivalent length from CIBSE table C4.18, le = 0.8 Total equivalent length of fittings = 0.8 x 2.0 = 1.6 metres. 7. 8. Calculate effective pipe length. - 15.6m Determine pressure loss due to friction from CIBSE Tables. See Table 4.18 in Guide C (CD version).
9. Calculate pressure consumed due to friction (Pa) = effective pipe length (m) x pressure loss due to friction (Pa/m). Column 7 x 8 in Pipe Sizing Table. 10. Calculate total pressure consumed = Friction loss + Static pressure loss. There are no vertical pipe sections and therefore no static pressure loss. 11. Determine pressure at start of section. Given in drawing as 120,000 Pa.
12. Calculate pressure available at end of section = Pressure at start of section - Total pressure consumed. 120,000 23,400 = 96,600 Pa. If pressure available at end of section is less than the maximum allowable pressure drop then we can accept this pipe size. 13. Determine pressure required at end of section, this can be the minimum pressure that is required for terminal equipment. Given in drawing as 90,000Pa. 14. If the pressure available at the end of the section is more than or equal to the pressure required at the end of the section then the pipe size is correct. 22mm pipe is correct.
You might also like
- 1727 Plumbing Estimation SheetDocument1 page1727 Plumbing Estimation SheetMohammed JassimNo ratings yet
- Chilled Water and Condensor Water Pump Head CalculaitonDocument3 pagesChilled Water and Condensor Water Pump Head CalculaitonYusuf RampNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: Roof Drain Vertical Leader Requirements For Horizontal Roof Areas at Various Rainfall RateDocument1 pageDesign Calculation Sheet: Roof Drain Vertical Leader Requirements For Horizontal Roof Areas at Various Rainfall RateAhmed Handy 911No ratings yet
- Water Booster Pump Flow CalculationDocument1 pageWater Booster Pump Flow CalculationfebousNo ratings yet
- Grease Interceptor Sizing WorksheetDocument16 pagesGrease Interceptor Sizing WorksheetsamehNo ratings yet
- FAHU Cooling Load and Condensate RatesDocument4 pagesFAHU Cooling Load and Condensate RatesSundar DAACNo ratings yet
- External Static Pressure Calculation (Revision 1) 20/4/2016 SEF-B1-01 (Smoke Exhaust Fan For Compartment D Carpark SES System)Document14 pagesExternal Static Pressure Calculation (Revision 1) 20/4/2016 SEF-B1-01 (Smoke Exhaust Fan For Compartment D Carpark SES System)kkkkNo ratings yet
- Villa Cold Water Pipe SizingDocument32 pagesVilla Cold Water Pipe SizingHem SopheapNo ratings yet
- Estimate Load CalculationDocument2 pagesEstimate Load Calculationmeeng2014No ratings yet
- ESP Calculation for Multiple Duct RunsDocument11 pagesESP Calculation for Multiple Duct RunsJitheesh Sahadevan100% (1)
- List of cable nomenclature and ratingsDocument4 pagesList of cable nomenclature and ratingssmcsamindaNo ratings yet
- Water Heater Calculation Rev ADocument1 pageWater Heater Calculation Rev AalvinchuanNo ratings yet
- A. Load Values, in Water Supply Fixture Units (Wsfu) For All AreasDocument4 pagesA. Load Values, in Water Supply Fixture Units (Wsfu) For All AreasIbrahim A. HameedNo ratings yet
- Noise Calculation Procedure - Simple MethodDocument7 pagesNoise Calculation Procedure - Simple MethodZiyad AwaliNo ratings yet
- ClimateMaster Pool SizingDocument5 pagesClimateMaster Pool SizingNghiaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Bank Al Ehsaa Chilled Water Pumps Hydraulic CalculationDocument6 pagesAgricultural Bank Al Ehsaa Chilled Water Pumps Hydraulic CalculationMohammed TanveerNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chiller System VS VRF Syatem PDFDocument1 pageComparison Chiller System VS VRF Syatem PDFfakir mohammadNo ratings yet
- Project: Doha Metro - Major Station Pump Friction Loss AnalysisDocument5 pagesProject: Doha Metro - Major Station Pump Friction Loss AnalysisAdnan AttishNo ratings yet
- Hap Calculations - Etr-1Document10 pagesHap Calculations - Etr-1jobees7850No ratings yet
- Rainwater Calculation - Dar ElhandasaDocument2 pagesRainwater Calculation - Dar ElhandasaPhyomaungNo ratings yet
- BMW showroom plumbing and fire fighting water demandDocument9 pagesBMW showroom plumbing and fire fighting water demandJohnson SambranoNo ratings yet
- DesignCompilation (De Jesus)Document13 pagesDesignCompilation (De Jesus)loureniel de jesusNo ratings yet
- DUCT LOSS CALCULATION TABLEDocument6 pagesDUCT LOSS CALCULATION TABLETanveerNo ratings yet
- Cold Water Tank (Plumbing)Document3 pagesCold Water Tank (Plumbing)Jin FongNo ratings yet
- B+G+20 Residential Building, Kolkata PlumbingDocument4 pagesB+G+20 Residential Building, Kolkata Plumbingvignesh msNo ratings yet
- Drainage Pipe SizingDocument7 pagesDrainage Pipe SizingMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Drainage CalculationDocument2 pagesDrainage CalculationΒΑΓΓΕΛΗΣ ΑΝΤΩΝΙΟΥNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop Calculation Combined Steel and Mesonery Duct PDFDocument3 pagesPressure Drop Calculation Combined Steel and Mesonery Duct PDFsmcsamindaNo ratings yet
- Code BS en 12056 2-2000-Pipe SizingDocument16 pagesCode BS en 12056 2-2000-Pipe SizingsenghouNo ratings yet
- 00 BLANK - Hot and Cold Water LU Calculation SheetDocument14 pages00 BLANK - Hot and Cold Water LU Calculation SheetrNo ratings yet
- Domestic CaculatorDocument10 pagesDomestic CaculatorAnonymous BJ9omONo ratings yet
- ESP Calculation For FAHU: Section Air Flow Duct Size L/S CFM W (MM) X H (MM) W (In) X H (In) L (M) FPM M/s 983.20 4.99Document11 pagesESP Calculation For FAHU: Section Air Flow Duct Size L/S CFM W (MM) X H (MM) W (In) X H (In) L (M) FPM M/s 983.20 4.99Mohammed Abdul MoiedNo ratings yet
- Load Check FiguresDocument2 pagesLoad Check FiguresAaron Etzkorn100% (1)
- Preparation of HVAC Ducting LayoutDocument6 pagesPreparation of HVAC Ducting Layoutarunima04No ratings yet
- CHILLER Vs VRF - Commercial Comparison - 03.03.2021Document3 pagesCHILLER Vs VRF - Commercial Comparison - 03.03.2021Azher IrfanNo ratings yet
- Basement Sump Pit CalculationDocument12 pagesBasement Sump Pit CalculationRajkishore NayakNo ratings yet
- Hvac For AuditoriumDocument15 pagesHvac For AuditoriumkomalNo ratings yet
- Generator Room LouverDocument1 pageGenerator Room LouverKarthy Ganesan50% (2)
- Project Name: North Dagon Hospitsl 10/21/2020Document2 pagesProject Name: North Dagon Hospitsl 10/21/2020codefinderNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Check Figure: (Based On The AIRAH Handbook 3rd Edition)Document5 pagesCooling Load Check Figure: (Based On The AIRAH Handbook 3rd Edition)KaushikNo ratings yet
- Stairwell pressurization design calculation sheetDocument3 pagesStairwell pressurization design calculation sheetMohd Najeeb Ali FathaanNo ratings yet
- Proposed Sethsiripaya Office Project Water Demand CalculationDocument6 pagesProposed Sethsiripaya Office Project Water Demand CalculationThilanka NuwanNo ratings yet
- Non Pressurised Cold Water Pipe SizingDocument5 pagesNon Pressurised Cold Water Pipe SizingZiaullah BiyabaniNo ratings yet
- APERFECTHEATLOADDocument1 pageAPERFECTHEATLOADselva.uae8207No ratings yet
- 230313-MEP Client RequirementDocument19 pages230313-MEP Client RequirementSelcen yeniçeriNo ratings yet
- TCVN 2622-1995 Fire Prevention Standards - enDocument49 pagesTCVN 2622-1995 Fire Prevention Standards - enCity Boy100% (3)
- Proposed Residential Building Pressure Relief Damper CalculationsDocument1 pageProposed Residential Building Pressure Relief Damper CalculationsKarthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Mep Questionnaire HospitalDocument7 pagesMep Questionnaire HospitalRaju KsnNo ratings yet
- Green Oasis Mall Water Pump CalculationsDocument19 pagesGreen Oasis Mall Water Pump CalculationsKashif SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- S&W CalculationDocument10 pagesS&W CalculationSameera LakmalNo ratings yet
- Regulation DD-9.0: Drainage: 9.1 Domestic Drainage 9.2 Water Supply 9.3 Rainwater Drainage 9.4 A/C DrainDocument10 pagesRegulation DD-9.0: Drainage: 9.1 Domestic Drainage 9.2 Water Supply 9.3 Rainwater Drainage 9.4 A/C DrainSarathNo ratings yet
- TCVN 7336-2003 Fire Protection Automatic Sprinkler System (En)Document24 pagesTCVN 7336-2003 Fire Protection Automatic Sprinkler System (En)canniumNo ratings yet
- HVAC Thermal Storage - Practical Application and Performance Issues - SampleDocument12 pagesHVAC Thermal Storage - Practical Application and Performance Issues - SamplePhan YhNo ratings yet
- Elegantry: Water Storage Tank Hydraulic Calculations: 1Document3 pagesElegantry: Water Storage Tank Hydraulic Calculations: 1zshehadehNo ratings yet
- Balancing Circuits for Optimal FlowDocument75 pagesBalancing Circuits for Optimal Flowmaxmorek100% (1)
- Masterclass duct frictionDocument11 pagesMasterclass duct frictionT Satheesh Kumar100% (1)
- Basic Calculations PDFDocument14 pagesBasic Calculations PDFJean-Noël LerouxNo ratings yet
- ch2 p2 PDFDocument31 pagesch2 p2 PDFYahya Abdulsalam0% (1)
- Pipe Sizing GuideDocument4 pagesPipe Sizing GuideorganicspolybondNo ratings yet
- EXAMPLE 5.2-1: Filling A Watering Tank: Table 1: Data From The Manufacturer's Pump CurveDocument4 pagesEXAMPLE 5.2-1: Filling A Watering Tank: Table 1: Data From The Manufacturer's Pump CurveRohit Gadekar100% (1)
- Uow009702 Electronic Monitoring and Access Control Commissioning StandardDocument29 pagesUow009702 Electronic Monitoring and Access Control Commissioning StandardstarykltNo ratings yet
- Private Water Supply GuidelinesDocument40 pagesPrivate Water Supply GuidelinesstarykltNo ratings yet
- Aqua 1Document324 pagesAqua 1staryklt100% (1)
- CCTV and Lighting Upgrade Commissioning StandardDocument19 pagesCCTV and Lighting Upgrade Commissioning Standards_morrissey_consulting100% (1)
- Power System Sizing Form: G G G GDocument4 pagesPower System Sizing Form: G G G GstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009694 Hydraulic Services Design StandardsDocument37 pagesUow009694 Hydraulic Services Design StandardsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009698 Building Monitoring and Control Systems Design StandardsDocument23 pagesUow009698 Building Monitoring and Control Systems Design StandardsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009701 Electrical Services Commissioning StandardDocument26 pagesUow009701 Electrical Services Commissioning StandardstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009699 Building Elements Commissioning StandardDocument28 pagesUow009699 Building Elements Commissioning StandardstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009693 Fire Services Design StandardsDocument20 pagesUow009693 Fire Services Design StandardsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009695 Landscaping Design StandardsDocument43 pagesUow009695 Landscaping Design StandardsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Res StreetsDocument50 pagesRes StreetsVas SteelNo ratings yet
- Uow009696 Mechanical Services Design StandardsDocument19 pagesUow009696 Mechanical Services Design StandardsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Uow009695 Landscaping Design StandardsDocument43 pagesUow009695 Landscaping Design StandardsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Ts Join GuideDocument1 pageTs Join GuidestarykltNo ratings yet
- Floor Waste Installation OverviewDocument2 pagesFloor Waste Installation OverviewstarykltNo ratings yet
- Enclosed Shower BaysetDocument2 pagesEnclosed Shower BaysetstarykltNo ratings yet
- Residential Electric Service InstallationDocument56 pagesResidential Electric Service InstallationJ Hevesi100% (1)
- Concrete Path GuidelinesDocument6 pagesConcrete Path GuidelinesKipegoNo ratings yet
- Ds05 DrivewaysDocument15 pagesDs05 DrivewaysstarykltNo ratings yet
- BUILDING IN ALASKA CLIMATEDocument15 pagesBUILDING IN ALASKA CLIMATEstarykltNo ratings yet
- Guide To Concrete RepairDocument168 pagesGuide To Concrete Repairhansen_zinck4751100% (11)
- Floor Waste Installation OverviewDocument2 pagesFloor Waste Installation OverviewstarykltNo ratings yet
- Purlin Mounted AnchorDocument2 pagesPurlin Mounted AnchorstarykltNo ratings yet
- 0621 SIKA Waterproofing - Wet AreasDocument12 pages0621 SIKA Waterproofing - Wet AreasstarykltNo ratings yet
- 7123AF Aquatherm Fusiotherm Hot & Cold Water System 2010Document9 pages7123AF Aquatherm Fusiotherm Hot & Cold Water System 2010starykltNo ratings yet
- 0118 Texture Coating For Interior Concrete and MasonryDocument4 pages0118 Texture Coating For Interior Concrete and MasonrystarykltNo ratings yet
- 75mm Lab TestsDocument19 pages75mm Lab TestsstarykltNo ratings yet
- 100mm Lab TestsDocument17 pages100mm Lab TestsstarykltNo ratings yet
- Lancashire Residential Road Design GuideDocument42 pagesLancashire Residential Road Design Guidesweptpath2012No ratings yet
- 2017 Postgraduate Convocation ListDocument11 pages2017 Postgraduate Convocation ListCheckNo ratings yet
- Aisi S901-13Document18 pagesAisi S901-13Edison BecerraNo ratings yet
- Availability 99 999Document6 pagesAvailability 99 999Luis Jesus Malaver GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Standard Welded Beams Dimensions and PropertiesDocument35 pagesStandard Welded Beams Dimensions and PropertiesKmt_Ae100% (2)
- UKTI Innovation ReportDocument34 pagesUKTI Innovation ReportNETParkNetNo ratings yet
- Ansi Asabe S366.2 May2004 (Iso 5675-1992) (R2009)Document3 pagesAnsi Asabe S366.2 May2004 (Iso 5675-1992) (R2009)StephanNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing SteelDocument5 pagesReinforcing SteelStraus WaseemNo ratings yet
- FRC Guide: Properties & Uses of Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocument17 pagesFRC Guide: Properties & Uses of Fiber Reinforced ConcretePallav Paban BaruahNo ratings yet
- Limitless Innovation With Limited Space: Parking Simpli EdDocument7 pagesLimitless Innovation With Limited Space: Parking Simpli EdAbudo PaixaoNo ratings yet
- Inspection Engineer 1691669896Document3 pagesInspection Engineer 1691669896ArhamNo ratings yet
- ArchiTalk Series 1 Attendees BreakdownDocument6 pagesArchiTalk Series 1 Attendees Breakdownfachrin anugrahNo ratings yet
- North Territory Occupation ListDocument7 pagesNorth Territory Occupation ListHariza Jaya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- ECE104Document6 pagesECE104Angelo Gabriel E. AzucenaNo ratings yet
- CCE Certification FlowchartDocument1 pageCCE Certification FlowchartonixexenNo ratings yet
- Semester 2 Final ReflectionDocument6 pagesSemester 2 Final Reflectionapi-202153663No ratings yet
- CE-102, Civil Engg MaterialDocument3 pagesCE-102, Civil Engg MaterialSALAHBIN NAEEMNo ratings yet
- 1936 4261 1 SMDocument5 pages1936 4261 1 SMErick Reyna ChirinosNo ratings yet
- RISK ElevatorDocument4 pagesRISK ElevatordashNo ratings yet
- ND MechatronicsDocument260 pagesND MechatronicsaniaffiahNo ratings yet
- Software MeasurementDocument38 pagesSoftware MeasurementBilal BaberNo ratings yet
- List of books and standards on vibratory machine foundationsDocument5 pagesList of books and standards on vibratory machine foundationsMiminoRusNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Dynamic and Static Pile Load TestingDocument11 pagesComparison Between Dynamic and Static Pile Load TestingMOST PASONNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Prototype Projects of Aeronautical Engineering Students of Philippine State College of AeronauticsDocument119 pagesOptimization of Prototype Projects of Aeronautical Engineering Students of Philippine State College of AeronauticsDerik RoqueNo ratings yet
- 50 1 323-1-Base Isolation and Dampers 2022Document121 pages50 1 323-1-Base Isolation and Dampers 2022elidstone@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- All Branch Time TableDocument10 pagesAll Branch Time TableUday hpNo ratings yet
- 2 - المحاضرة الثانية 2020Document21 pages2 - المحاضرة الثانية 2020سجاد عباسNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document91 pagesClass 1meenasundarNo ratings yet
- 31295015251746Document181 pages31295015251746Mani KandanNo ratings yet
- University of MauritiusDocument28 pagesUniversity of MauritiusAdrian StănilăNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Testing, Adjusting & Balancing of CHW SystemsDocument10 pagesMethod Statement For Testing, Adjusting & Balancing of CHW SystemsAbdülhamit KAYYALİNo ratings yet