Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sri Venkateswara: Institute of Science and Technology
Uploaded by
vinoth_2610Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sri Venkateswara: Institute of Science and Technology
Uploaded by
vinoth_2610Copyright:
Available Formats
SRI VENKATESWARA
INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
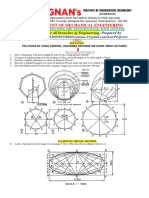
Kolundhalur 63 !"3# Th$ru%allur T&'# (D)'# GE6 *!+En,$n--r$n, Gra.h$/0 UNIT+ CONIC SECTION
1 ! # A circular wheel of 50 mm diameter rolls without slipping along a straight line. Draw the curve traced by a point P on its rim for one revolution of the wheel. Draw tangent and normal at any point revolution. Draw tangent and normal at any point on the curve. 12an !" 3 on the curve. 12an !" 3. Draw a hypocycloid of a circle of "0mm diameter that rolls inside another circle of !00mm diameter for one $he focus of a conic is 50 mm from the directri%. Draw the locus of a point P moving in such a way that its distance from the directri% is e&ual to its distance from the focus. 'ame the curve. Draw a tangent to the curve at a point (0 mm from the directri% ) 2an !" "3 " 5 ( , 1 Draw a hyperbola when the distance between its focus and directri% is 50 mm and eccentricity is #*!. Also draw the tangent and normal at a point !5 mm from the directri%. ) 2an !" "3 Draw the involute of a circle of diameter "0 mm and draw the tangent and the normal to the involute at any point on the curve. )4AY52UNE !""63 A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls on a hori+ontal line for ,5- of a revolution cloc.wise. Draw the path traced by a point P on the circumference of the circle. Also draw a tangent and normal at any point on the curve. 12AN !""63 Draw the conic curve/ if the distance of focus from the directri% is ,0 mm and e01. Also draw a tangent and normal at any point on the curve. 12AN !""63 An elastic string of 155 mm long/ has one stone end attached to the circumference of the circular disc of "0 mm diameter. Draw the curve traced out by the other end of the string/ when it is completely wound around the disc .eeping it always tight. Draw tangent and normal at any point on the curve. ) 2AN+ "3 2 10 3onstruct a cycloid curve when the diameter of the generating circle is "0 mm. Draw a tangent and normal at any point on the curve. )2ANUARY !" "3 A circle of 50 mm diameter rolls on a hori+ontal line for 4 of a revolution cloc.wise. Draw the path traced by a point P on the circumference of the circle. Also draw a tangent and normal at any point on the curve on the hyperbola. )2ANUARY !" "3'
FREE HAND SKETCHING
11 Draw the front/ top and right side views of the isometric view of the ob5ect shown in figure 1. 2ANUARY !" "
6igure 'o.1
'.7inoth 8 93:
1! Draw the front/ top and right side views of the isometric view of the ob5ect shown in figure 1. 2ANUARY !" "
6igure 'o.1 1# Draw the front/ top and side views of the isometric view of the ob5ect shown in figure 1. 2ANUARY !" "
UNIT II 7RO2ECTION OF 7OINTS
1. ar. the pro5ections of the following points on a common reference line; )i< )ii< )iii< )iv< )v< )vi< !. )i< )ii< )iii< )iv< )v< )vi< )vii< )viii< P/ #5 mm behind the 7P and !0 mm below the :P =/ "0 mm in front of the 7P and #0 mm above the :P >/ 50 mm behind the 7P and 15 mm above the :P ?/ "0 mm below the :P and in the 7P $/ #0 mm in front of the 7P and 50 mm below the :P @/ #5 mm behind the 7P and in the :P. P/ !5 mm below the :P and in the 7P =/ "0 mm behind the 7P and in the :P >/ #0 mm below the :P and #0 mm in front of the 7P ?/ !5 mm above the :P and !5 mm behind the 7P $/ !5 mm above the :P and #0 mm in front of the 7P @/ in both the 7P and the :P 7/ #5 mm below the :P and #0 mm behind the 7P A/ #0 mm above the :P and #5 mm behind the 7P
ar. the pro5ections of the following points on a common reference line;
'.7inoth 8 93:
#.
6ig. 1. shows the pro5ections of different points. Determine the position of the points with reference to the pro5ection planes. $he distances mar.ed are in millimeters.
b b "0 !0 B !0 c #0 d/ d !5
e/ e
3" 8" a a; 8" /; 3" :
!" ,# ,9
". 6ig. 1. shows the pro5ections of different points. Determine the position of the points with reference to the pro5ection planes. $he distances mar.ed are in millimeters. & & 50 B #0 #0 s 50 r/r #5 C t/t u
3" *" . .; *" 0; 7RO2ECTION OF LINES 8" u
3" %# %9
1. A line P=/ 50 mm long is perpendicular to the :P and 15 mm in front of the 7P. $he end P/ nearer to the :P is !0 mm above it. Draw the pro5ections of the line. !. A line P=/ ,0 mm long is parallel to the :P and inclined at #0D to the 7P. $he end P is !5 mm above the :P and "0 mm in front of the 7P. Draw the pro5ections of the straight line. #. A line '/ ,0 mm long lies in the 7P and has the end in both the :P and the 7P. Et is inclined at #5D to the :P. Draw the Pro5ections of the line. ". Fne end P of a line P= is in the :P and !0 mm in front of the 7P. $he line is parallel to the 7P and inclined at "0D to the :P. $he length of the top view is "0 mm. 6ind the true length of the line. 5. A line P=/ (0 mm long has one end P/ !0 mm above the :P and #5 mm in front of the 7P. $he line parallel to the :P. $he front view has a length of 50 mm . 6ind its true inclination with the 7P. (. Fne end P of a line P= is in the :P and !0 mm in front of the 7P. $he line parallel to the 7P and inclined at "0o to the :P. $he top view has a length of "0 mm. 6ind its true length of the line. ,. Fne end P of a line P=/ 55 mm long is #5 mm in front of the 7P and !5 mm above the :P. $he line is inclined at "0D to the :P and #0o to the 7P. Draw the pro5ections of P=
'.7inoth 8 93:
. 1. A line '?/ 10 mm long has its end '/ 10 mm above the :P and 15 mm in front of the 7P. $he other end ? is (5 mm above the :P and 50 mm in front of the 7P. Draw the Pro5ections of the line and find its true inclinations with the :P and 7P. 2. A line P6/ (5 mm long has its end P/ 15 mm above the :P and 15 mm in front of the 7P. Et is inclined at 55D to the :P and #5D to the 7P. Draw its pro5ections. 10. $he end P of a line P=/ ,0 mm long is 15 mm above the :P and !0 mm in front of the 7P. = is "0 mm above the :P. Ets top view is inclined at "5D to the 7P. Draw the pro5ections of the line and find its true inclinations with the 7P and the :P. 11. A line 96/ 15 mm long has its end 9/ !5 mm above the :P and !0 mm in front of the 7P. $he top and front views of the line have lengths of 55 mm and ,0 mm respectively. Draw the pro5ections of the line and find its true inclinations with the 7P and the :P. 1!. A line P= has its end P/ 10 mm above the :P and !0 mm in front of the 7P. $he end = is #5 mm in front of the 7P. $he front view of the line measures ,5 mm. $he distance between the end pro5ectors is 50 mm. Draw the pro5ections of the line and find its true length and its true inclinations with the 7P and the :P. 1#. A straight line ?$ has its end ?/ 10 mm in front of the 7P and nearer to it. $he mid8point of the line
is 50 mm in front of the 7P and "0 mm above the :P. $he front and top views measure 100 mm and 1!0 mm respectively. Draw the pro5ections of the line. Also find its true length and true inclinations with the :P and the 7P. 1". A straight line AG/ 1" mm long is inclined at #0D to the :P and "5D to the 7P. Ets mid point is (! mm above the :P and 5! mm in front of the 7P. Draw its pro5ections. 15. A line ' has its end / 10 mm in front of the 7P and 15 mm above the :P. $he other end ' is 50
mm in front of the 7P. $he front view has a length of ,0 mm. $he distance between the end pro5ectors is (0 mm. Draw the pro5ections of the line. 6ind its true length/ true inclinations and traces by trape+oid method. 7RO2ECTION OF 7LANE SURFACES 1. A s&uare lamina of side #5 mm is parallel to the :P with one of its sides inclined at #0D to the 7P. $he lamina is !0 mm above the :P. Draw its top and front views and show its traces. !. A he%agonal plate of side #5 mm rests on the :P on one of its side perpendicular to the 7P. Draw its pro5ections when its surface is inclined at 50D to the :P. Also show its traces.
'.7inoth 8 93:
#.
A circular lamina of diameter (0 mm is held vertical with its surface inclined at "5D to the 7P. Ets centre is "0 mm above the :P and #0 mm in front of the 7P. Draw its top and front views as also its traces.
".
A pentagon of side #0 mm rests on the ground on one of its corners with the sides containing the corner being e&ually inclined to the ground. $he side opposite to the corner on which it rests is inclined at #0D to the 7P and is parallel to the :P. $he surface of the pentagon ma.es 50D with the ground. Draw the top and front views of the pentagon.
5.
A s&uare lamina P=>? of side "0 mm rests on the ground on its corner P in such a way that the diagonal P> is inclined at "5D to the :P and apparently inclined at #0D to the 7P. Draw its pro5ections.
(.
A rectangular plate ,0 % "0 mm has one of its shorter edges in the 7P inclined at "0D to the :P. Draw its top view if its front view is a s&uare of side "0 mm.
,.
A :e%agonal plate of side !0 mm rests on the :P on one of its sides inclined at "5D to the 7P. $he surface of the plate ma.es an angle of #0D with the :P. Draw the front and top views of the plate. UNIT III 7RO2ECTION OF SOLIDS
1. A cube of side "0 mm rests on the :P on one of its ends with a vertical face inclined at "0 o to the 7P. Draw its pro5ections. !. Draw the top/ front/ right side and left side views of a s&uare pyramid of base of side #0 mm and altitude "0 mm when it is resting on the ground on its base with one of the edges of the base inclined at (0D to the 7P. #. A s&uare prism of base edge 50 mm and a%is length 10 mm is lying on the :P on one of its longer edges with its faces e&ually inclined to the :P. Draw its top and front views when the a%is is perpendicular to the 7P. ". A pentagonal pyramid of base of side #0 mm and a%is (0 mm rests on the :P on one corner of the base/ one of the base edges containing which ma.es "0D with the :P. Draw its pro5ections when the a%is is perpendicular to the 7P and the base is touching the 7P. 5. A he%agonal prism of base side !0 mm/ a%is length 50 mm lies on the ground on one of its rectangular faces with the a%is parallel to both the :P and the 7P. Draw its pro5ections. (. A pentagonal prism of base side "0 mm and a%is length (0 mm lies on the :P on one of its longer edges with its a%is parallel to both the :P and the 7P. Fne of the rectangular faces containing the resting edge is inclined at #0D to the :P. Draw its top and front views.
'.7inoth 8 93:
,.
Draw the pro5ections of a he%agonal prism of base side !0 mm and a%is length 50 mm when it is lying on the ground on one of its rectangular faces and the a%is is inclined at #5D to the 7P.
1.
A s&uare prism of base side #5 mm and a%is length (0 mm lies on the :P on one of its longer edges with its faces e&ually inclined to the :P. Draw its pro5ections when its a%is is inclined at #0D to the 7P.
2.
A cylinder of diameter #0 mm and a%is length 50 mm is resting on the :P on a point so that its a%is is inclined at "5D to the :P and parallel to the 7P. Draw its top and front views.
10. A cone of base diameter "0 mm and altitude 10 mm rests on the :P with its a%is inclined at #0D to the :P and parallel to the 7P. Draw its front and top views. 11. A cone of base side 50 mm and altitude ,0 mm is freely suspended by means of a string from one of its base point with its a%is parallel to 7P. Draw its pro5ections. 1!. A cylinder of base side 50 mm and altitude ,0 mm is freely suspended by means of a string from one of its base point with its a%is parallel to 7P. Draw its pro5ections. UNIT IV SECTION OF SOLIDS 1. A cube of side !5 mm rests on the :P on one of its faces with a vertical face inclined at #5D to the 7P. A plane perpendicular to the :P and parallel to the 7P cuts the cube 10 mm away from the a%is and farther away from the 7P. Draw the top view and sectional front view. !. A cube of side !5 mm rests on the :P on one of its faces with a vertical face inclined at #5D to the 7P. A plane perpendicular to the :P and inclined at 50D to the 7P cuts the cube/ # mm away from the a%is. Draw the top view and the sectional front view. Also draw the true shape of the section. #. A cube of side "0 mm is placed and cut by a plane in such a way that the true shape of the section is a regular he%agon. Draw the front and top views of the cube and determine the inclination of the plane with the :P. ". A s&uare prism of base side #0 mm and height (0 mm rests on the :P on one of its ends with two of its rectangular faces e&ually inclined to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at (0D to the :P meeting the a%is at 15 mm from the top. Draw its front view/ sectional top view and the true shape of the section.
'.7inoth 8 93:
5.
A he%agonal prism of base side #0 mm and a%is length ,0 mm rests on one of its ends on the :P with two base sides parallel to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at #0D to the :P. $he cutting plane meets the a%is at #0 mm from the top. Draw the front view/ sectional top view and true shape of the section.
(.
A pentagonal prism of base side "0 mm and a%is length 10 mm is lying no the :P on one of its rectangular faces with its a%is parallel to both the :P and the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the :P and inclined at #0D to the 7P. $he cutting plane meets the a%is at 1( mm from one of its ends. Draw the top view sectional front view and the true shape of the section.
,.
A he%agonal pyramid of base of side !0 mm and altitude 50 mm rests on its base on the :P with two edges of the base perpendicular to the 7P. A cutting plane parallel to the :P cuts the pyramid at a height of !0 mm above the base. Draw the front view and sectional top view.
1.
A pentagonal pyramid of base side !0 mm and altitude 55 mm rests on its base on the :P with one of the base edges perpendicular to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane inclined at 50D to the base. $he cutting place meets the a%is at 15 mm above the base. Draw the front view/ sectional top view and the true shape of the section.
2.
A he%agonal pyramid of base side !5 mm and a%is 55 mm rests on its base on the :P with two base edges perpendicular to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at #0D to the :P meeting the a%is at !0 mm from the verte%. Draw the front view/ sectional top view and the true shape of the section.
10. A cone of base diameter "0 mm and height 50 mm rests on its base on the :P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at "0D to the :P. $he cutting plane meets the a%is at !0 mm from the verte%. Draw the sectional top view and the true shape of he section. DEVELO74ENT OF SURFACES 11. A he%agonal prism of base side !0 mm and height "5 mm is resting on one of its ends on the :P with two of its lateral faces parallel to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at #0D to the :P. $he plane meets the a%is at a distance of !0 mm above the base. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the lower portion of the prism.
'.7inoth 8 93:
1!. A cylinder of diameter "0 mm and height 50 mm is resting vertically on one of its ends on the :P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at #0D to the :P. $he plane meets the a%is at # point #0 mm from the base. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the lower portion of the truncated cylinder. 1#. A pentagonal pyramid of base of side !5 mm and height (0 mm is resting vertically on its base on the ground with one of the sides of the base parallel to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and parallel to the :P at a distance of !5 mm above the base. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the frustum of the pyramid. Also show the top view of the cut surface. 1". A right circular cone of base diameter (0 mm and height ,0 mm is resting on its base on the ground. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and inclined at #0D to the :P. $he cutting plane bisects the a%is of the cone. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the truncated cone. 15. A cone of base diameter (0 mm and height ,0 mm is resting on its base on the ground. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and parallel to the :P at a distance !0 mm from the verte%. Et is also cut by a plane inclined at "0D to the base and meeting the a%is at a point !0 mm above base. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the cut cone. 1(. A he%agonal prism of base edge !5 mm and height (0 mm rests on one of its ends on the :P with a vertical face parallel to the 7P. A hori+ontal hole of diameter #( mm is drilled centrally right through the prism with its a%is perpendicular to the 7P. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the prism with the hole. UNIT V ISO4ETRIC 7RO2ECTIONS 1. A he%agonal prism of base side #0 mm and a%is length ,0 mm rests on one of its ends on the :P with two base sides parallel to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and $n/l$n-d a) 3"< )o )hH7. $he cutting plane meets the a%is at #0 mm from the top. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection. !. A pentagonal prism of base side "0 mm and a%is length 10 mm is lying no the :P on one of its rectangular faces with its a%is parallel to both the :P and the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the :P and $n/l$n-d a) 3"< )o )h- V7 . $he cutting plane meets the a%is at 1( mm from one of its ends. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection. #. A pentagonal pyramid of base side !0 mm and altitude 55 mm rests on its base on the :P with one of the base edges perpendicular to the 7P. Et is cut by a .lan- $n/l$n-d a) *"< )o )h- =a0- . $he cutting place meets the a%is at 15 mm above the base. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection.
'.7inoth 8 93:
".
A he%agonal pyramid of base side !5 mm and a%is 55 mm rests on its base on the :P with two base edges perpendicular to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and $n/l$n-d a) 3"< )o )hH7 meeting the a%is at !0 mm from the verte%. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection.
5.
A cylinder of diameter "0 mm and height 50 mm is resting vertically on one of its ends on the :P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and $n/l$n-d a) 3"< )o )h- H7. $he plane meets the a%is at a point #0 mm from the base. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection.
(. Draw the isometric view of a cylinder of diameter "( mm and height (0 mm when it is resting on one of its ends on the :P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and $n/l$n-d a) 8*< )o )h- H7. $he plane passes through a point on the a%is located at 15 mm from the top. ,. Draw the isometric view of a frustum of cone of bottom base diameter (0 mm and top face diameter "0 mm and a%is height (0 mm. 1. Draw the isometric view of frustum of a he%agonal pyramid when it is resting on its base on the :P with two of the base edges parallel to the 7P. $he side of the base is !0 mm and top 1 mm. $he height of the frustum is 55 mm. 2. A pentagonal pyramid of base of side !5 mm and height (0 mm is resting vertically on its base on the ground with one of the sides of the base parallel to the 7P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and .arall-l )o )h- H7 at a distance of !5 mm above the base. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection of the frustum of the pyramid. 10. A he%agonal pyramid of base of side !0 mm and altitude 50 mm rests on its base on the :P with two edges of the base perpendicular to the 7P. A cutting plane .arall-l )o )h- H7 cuts the pyramid at a height of !0 mm above the base. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection. 11. A right circular cone of base diameter (0 mm and height ,0 mm is resting on its base on the ground. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and $n/l$n-d a) 3"< )o )h- H7 . $he cutting plane bisects the a%is of the cone. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection of the truncated cone. 1!. A cone of base diameter "0 mm and height 50 mm rests on its base on the :P. Et is cut by a plane perpendicular to the 7P and $n/l$n-d a) 8"< )o )h- H7. $he cutting plane meets the a%is at !0 mm from the verte%. Draw the isometric view and isometric pro5ection.
'.7inoth 8 93:
7ERS7ECTIVE 7RO2ECTIONS 1#. A regular he%agonal pyramid of base edge !0 mm and height #5 mm rests on its base on the ground plane with one of its base edges touching the picture plane. $he station point is #0 mm above the ground plane and "0 mm in front of the PP. $he central plane is #0 mm to the right of the a%is. Draw the perspective pro5ection of the pyramid by visual ray method. @se the top view and the front view. 1". Draw the perspective view of a pentagonal prism of base side !0 mm and height "0 mm when it rests on its base on the ground plane with one of its rectangular faces parallel to and !0 mm behind the picture plane. $he station point is "5 mm in front of the PP and (0 mm above the HP. $he observer is !0 mm to the left of the a%is. @se the top view and the end view to draw the perspective by visual ray method. 15. A s&uare prism of base !5 % !5 mm and height "0 mm rests on the HP on one of its ends with a rectangular face receding away from the PP towards right ma.ing (0D with PP. $he corner nearest to the PP is "0 mm to the left of the station point and !0 mm behind the PP. Draw the perspective view of the prism by visual ray method. @se the top view and front view. 1(. A cylinder of diameter "0 mm and height "0 mm rests on the HP on one of its ends with its a%is #5 mm behind the picture plane. $he station point is "5 mm to the right of the a%is. $he station point is (5 mm above the HP and "0 mm in front of the PP. Draw the perspective view of the cylinder by visual ray method. 1,. A s&uare pyramid of base side #0 mm and a%is length 55 mm rests on its base edges e&ually inclined to the PP and behind it. $he station point is 50 mm in front of the PP and (0 mm above the ground. $he central plane is 15 mm to the left of the a%is of the solid. Draw the perspective pro5ection of the pyramid.
10
'.7inoth 8 93:
You might also like
- Fly Can Be Pretty Too: Wire & Jewelry Making Tutorial Series T99From EverandFly Can Be Pretty Too: Wire & Jewelry Making Tutorial Series T99Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- JAN 2013-FN AKeyDocument13 pagesJAN 2013-FN AKeysnvijayanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics QB PDFDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics QB PDFKarthi SanNo ratings yet
- Ellipses, parabolas, hyperbolas & engineering graphics questionsDocument6 pagesEllipses, parabolas, hyperbolas & engineering graphics questionsDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics Question BankSriram JNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesKings: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrammit2007No ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankflorenceprasadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question Bank on Plane Curves, Freehand Sketching and ProjectionsDocument15 pagesEngineering Graphics Question Bank on Plane Curves, Freehand Sketching and ProjectionsimamuddeenNo ratings yet
- Engg. Drawing QuestionsDocument9 pagesEngg. Drawing QuestionsdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Qus PaperDocument6 pagesQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument11 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankRajkumarNo ratings yet
- First Sem Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument11 pagesFirst Sem Engineering Graphics Question BankPRIYA RAJINo ratings yet
- R7100107 Engineering GraphicsDocument2 pagesR7100107 Engineering GraphicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument12 pagesQuestion BankBalaChandarNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Bombay Department of Mechanical Engineeringashwinagrawal1995No ratings yet
- Question Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand SketchingDocument14 pagesQuestion Bank Engineering Graphics (GE6152) : Unit-I Plane Curves & Free Hand Sketchingnandhu20No ratings yet
- GE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankDocument11 pagesGE6152 EngineeringGraphicsquestionbankNatarajan AgoramNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Engg Graphics 1Document15 pagesQuestion Bank Engg Graphics 1yuvashreesharmiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Subjective Questions On Engineering Graphics (B.Tech. 1 Year)Document5 pagesUnit-1: Subjective Questions On Engineering Graphics (B.Tech. 1 Year)nirmalkrNo ratings yet
- Ed Mid-1 Question Bank With Answers Viit 2022-23 by SsraoDocument14 pagesEd Mid-1 Question Bank With Answers Viit 2022-23 by SsraoSANYASIRAO SURADANo ratings yet
- Engg. Drawing - Lab MannualDocument16 pagesEngg. Drawing - Lab Mannualanandsohan916No ratings yet
- GE6152 Engineering GraphicsDocument13 pagesGE6152 Engineering GraphicspsvnccNo ratings yet
- Eg QPDocument5 pagesEg QPSurulivelrajantNo ratings yet
- Dr.NGP Institute of Technology Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument18 pagesDr.NGP Institute of Technology Engineering Graphics Question BankPraveen MathiNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument14 pagesAssignmentAdel AwadNo ratings yet
- Eg Question Bank - 2013Document18 pagesEg Question Bank - 2013kgmaheswaranNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Lab ManualDocument11 pagesEngineering Graphics Lab ManualPatel AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Ge 6152 Engineering Graphics Anna University Question Bank - I Plane Curves & Freehand SketchingDocument14 pagesGe 6152 Engineering Graphics Anna University Question Bank - I Plane Curves & Freehand SketchingArul JothiNo ratings yet
- Drawing AssignmentDocument6 pagesDrawing AssignmentJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering GraphicsDocument15 pagesEngineering GraphicsvpsraviNo ratings yet
- EGDocument11 pagesEGvivekselvan2No ratings yet
- Drawing Curves and Projections of Planes and LinesDocument8 pagesDrawing Curves and Projections of Planes and Linesjuber_nriNo ratings yet
- 9a03101c Engineering DrawingDocument7 pages9a03101c Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Register No and Engineering Graphics Class Test II Question PaperDocument3 pagesRegister No and Engineering Graphics Class Test II Question PaperelangandhiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics QuestionDocument6 pagesEngineering Graphics QuestionScience SpiritNo ratings yet
- Vivekananda Institute of Technology & Science:Karimnagar: Engineering DrawingDocument1 pageVivekananda Institute of Technology & Science:Karimnagar: Engineering DrawingideepujNo ratings yet
- Egd GraphicDocument2 pagesEgd GraphicAmaan DastanNo ratings yet
- EG Question - Final - PrintDocument9 pagesEG Question - Final - PrintgandhiramNo ratings yet
- ED Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesED Important QuestionsNitin NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics Question BankSivakumar LNo ratings yet
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFDocument8 pagesGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics ProblemsDocument3 pagesEngineering Graphics ProblemsBALAMUGUNDAN50% (2)
- Tutorial – Lettering & Dimensioning PracticeDocument20 pagesTutorial – Lettering & Dimensioning PracticeSubramanian ManivelNo ratings yet
- Code: 9A03101 B.Tech I Year (R09) Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015Document1 pageCode: 9A03101 B.Tech I Year (R09) Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015Ramu VenkatNo ratings yet
- 3110013_EGD MANUAL-2023-24Document16 pages3110013_EGD MANUAL-2023-24devambanugariya2803No ratings yet
- GE8152 EG Consolidated Question BankDocument13 pagesGE8152 EG Consolidated Question BankGnaneswaran NarayananNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics QPDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics QPgandhiramNo ratings yet
- Projection of LineDocument3 pagesProjection of LineSuyog ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Code: 9a03101a B.Tech I Year (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, June 2013Document8 pagesCode: 9a03101a B.Tech I Year (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, June 2013sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- GE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5Document7 pagesGE2111 QB Unit 1 To 5meckup123No ratings yet
- Important Questions For MidDocument2 pagesImportant Questions For MidBalaji BaluNo ratings yet
- SELVAM COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DOCUMENTDocument13 pagesSELVAM COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GRAPHICS DOCUMENTRichard S DavidsonNo ratings yet
- R13 - JNTU B.Tech I Year Engineering Drawing Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesR13 - JNTU B.Tech I Year Engineering Drawing Exam QuestionsSiddharth ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Engg. Graphics-QnsDocument7 pagesEngg. Graphics-QnsstmuruganNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5Document7 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question Bank Unit1 Unit5florenceprasadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Sheet Problems 2019-20 First SemdocxDocument5 pagesEngineering Drawing Sheet Problems 2019-20 First SemdocxRohan DharpawarNo ratings yet
- Projection of LinesDocument2 pagesProjection of LinesanandandmeenaNo ratings yet
- Ed Most Important Questions With Answers by SsraoDocument16 pagesEd Most Important Questions With Answers by SsraoSANYASIRAO SURADANo ratings yet
- Babies Are Such Fun to Dress: Sizes 6 Months to 4 Years Knit & CrochetFrom EverandBabies Are Such Fun to Dress: Sizes 6 Months to 4 Years Knit & CrochetNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing Implementation in a Malaysian Auto Components CompanyDocument9 pagesLean Manufacturing Implementation in a Malaysian Auto Components Companyvinoth_2610No ratings yet
- 5S PrincipleDocument53 pages5S PrincipleAmir M. VillasNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fuel CycleDocument63 pagesNuclear Fuel Cyclevinoth_2610No ratings yet
- FDTP Final Selected List13Document9 pagesFDTP Final Selected List13jebileeNo ratings yet
- B.E. Mech PDFDocument113 pagesB.E. Mech PDFarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- PhDRegulations 2010Document45 pagesPhDRegulations 2010Rag RagavanNo ratings yet
- Tnea - Annauniv.edu Tanca2014 Eligibility (Tanca)Document19 pagesTnea - Annauniv.edu Tanca2014 Eligibility (Tanca)avenashaNo ratings yet
- Vit List of Journals - With Snip and If - EngineeringDocument79 pagesVit List of Journals - With Snip and If - Engineeringvinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Syllabus R2013 PDFDocument105 pagesSyllabus R2013 PDFlogeshboy007No ratings yet
- Elshaddai Engineering Company ProfileDocument6 pagesElshaddai Engineering Company Profilevinoth_2610No ratings yet
- ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Getting Started GuideDocument28 pagesANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Getting Started Guidevinoth_2610No ratings yet
- ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Getting Started GuideDocument28 pagesANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Getting Started Guidevinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Unit-3 (Eg)Document3 pagesUnit-3 (Eg)vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Unit-3 (Eg)Document3 pagesUnit-3 (Eg)vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Maintenance QuestionDocument9 pagesMaintenance Questionvinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Unit-3 (Eg)Document3 pagesUnit-3 (Eg)vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Maintanance & Repair of Two Wheelers & Three Wheelers - IIDocument110 pagesMaintanance & Repair of Two Wheelers & Three Wheelers - IIihikochiNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 (Eg)Document3 pagesUnit-3 (Eg)vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- ReflectionsDocument8 pagesReflectionsvinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes and Instructional ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLearning Outcomes and Instructional Objectivesvinoth_2610100% (1)
- Feaqpupto Apr2010Document16 pagesFeaqpupto Apr2010vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Xms-MBAAssignmnt 2Document11 pagesXms-MBAAssignmnt 2vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Ce1211 Solid and Fluid Mechanics1Document17 pagesCe1211 Solid and Fluid Mechanics1m_k_tripathyNo ratings yet
- Xms-MBAAssignmnt 2Document11 pagesXms-MBAAssignmnt 2vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Anna University Chennai SyllabusDocument95 pagesAnna University Chennai SyllabusRAAM MECHNo ratings yet
- Ce 1262 Strength of Materials d07Document3 pagesCe 1262 Strength of Materials d07vinoth_2610No ratings yet
- Design of Electrical Apparatus 2 Marks by Mr. M.SureshDocument38 pagesDesign of Electrical Apparatus 2 Marks by Mr. M.SureshMr.M.SureshNo ratings yet
- Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge Tuesday 13th June 2017 Organised by The United Kingdom Mathematics TrustDocument4 pagesJunior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge Tuesday 13th June 2017 Organised by The United Kingdom Mathematics TrustAdd UpNo ratings yet
- 430-C-1 - Maths (Basic)Document19 pages430-C-1 - Maths (Basic)pranjal kunwar0% (1)
- STRAIGHT LINESDocument6 pagesSTRAIGHT LINESGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Cadet enDocument2 pagesCadet enMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Document5 pages2nd Mid-Term Test (Add Maths f4)Jarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- 10.trigonometry MS P4Document169 pages10.trigonometry MS P4LingNo ratings yet
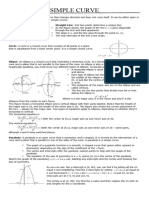
- Simple CurveDocument2 pagesSimple CurvefillosheenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Worked SolutionsDocument65 pagesChapter 4 Worked SolutionsAnshdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Questions - Introduction To Trigonometry - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF DownloadDocument9 pagesVery Short Answer Questions - Introduction To Trigonometry - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Downloadkrishnatsharma5432No ratings yet
- 2015 Circular Measure NotesDocument5 pages2015 Circular Measure NoteskarpeoNo ratings yet
- Geometric Designs Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesGeometric Designs Practice Problemsrichard reyesNo ratings yet
- LONGQUIZ Answer GaldoEdmalyA BEED3ADocument6 pagesLONGQUIZ Answer GaldoEdmalyA BEED3AEdmaly Abonacion GaldoNo ratings yet
- Peak IB Maths Applications Interpretation Answer SupplementDocument21 pagesPeak IB Maths Applications Interpretation Answer SupplementطارقبنزيادالعجوريNo ratings yet
- Director CircleDocument2 pagesDirector CirclecatalinatorreNo ratings yet
- Maths Important QuestionDocument16 pagesMaths Important QuestionSai PrajitNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Teaching Guide and CurriculumDocument276 pagesPre-Calculus Teaching Guide and CurriculumaoakkNo ratings yet
- Circle SolutionDocument18 pagesCircle SolutionSushil MeshramNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Textbook For Class IXDocument10 pagesMathematics: Textbook For Class IXRishu DwivediNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and Integration Formulas SheetDocument7 pagesDifferentiation and Integration Formulas SheetnirobNo ratings yet
- Classify Quadrilaterals WorksheetDocument4 pagesClassify Quadrilaterals WorksheetMarie SarenNo ratings yet
- Philippine Education Dept Tables of Specs for Math III 3rd GradingDocument4 pagesPhilippine Education Dept Tables of Specs for Math III 3rd Gradingnorvel_19No ratings yet
- Summative Test. (Parallel and Perpendicular) DocxDocument2 pagesSummative Test. (Parallel and Perpendicular) DocxRuth Matriano100% (1)
- CBSE Class 5 Mathematics Worksheet - FractionsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 5 Mathematics Worksheet - FractionsVijay SunderNo ratings yet
- 4-Galang-Whlp-Quarter 3 Week 4Document14 pages4-Galang-Whlp-Quarter 3 Week 4Andrea GalangNo ratings yet
- CIT 101 Py Lesson 6 FinalDocument9 pagesCIT 101 Py Lesson 6 FinalYasara MadanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations: Open SentencesDocument57 pagesLinear Equations: Open SentencesEpoditmas SeyerNo ratings yet
- Line Bisector Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLine Bisector Lesson Planapi-258989443No ratings yet
- Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Let's Check Your Understanding! Grade 5 MathematicsDocument28 pagesProperties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Let's Check Your Understanding! Grade 5 MathematicsAnggia PramithasariNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Formula in A3Document20 pagesClass 12 Formula in A3Tshering TashiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Eucld's GeometryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Eucld's Geometryvision2010jobNo ratings yet