Professional Documents
Culture Documents
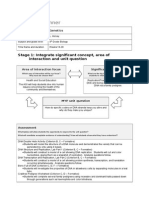
Digital Unit Plan Template
Uploaded by
api-249566512Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digital Unit Plan Template
Uploaded by
api-249566512Copyright:
Available Formats
Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Growth, Development, and Reproduction of Organisms Content Area: Science CA Content
Standard(s)/Common Core Standard(s): LS1.B: Growth and Development of Organisms Organisms reproduce, either sexually or asexually, and transfer their genetic information to their offspring. (secondary to MS-LS3-2) Animals engage in characteristic behaviors that increase the odds of reproduction. (MS-LS1-4) Plants reproduce in a variety of ways, sometimes depending on animal behavior and specialized features for reproduction. (MS-LS1-4) Genetic factors as well as local conditions affect the growth of the adult plant. (MS-LS1-5) Name: Iris Lee Grade Level: 8th
LS3.A: Inheritance of Traits Genes are located in the chromosomes of cells, with each chromosome pair containing two variants of each of many distinct genes. Each distinct gene chiefly controls the production of specific proteins, which in turn affects the traits of the individual. Changes (mutations) to genes can result in changes to proteins, which can affect the structures and functions of the organism and thereby change traits. (MS-LS3-1) Variations of inherited traits between parent and offspring arise from genetic differences that result from the subset of chromosomes (and therefore genes) inherited. (MS-LS3-2)
LS3.B: Variation of Traits In sexually reproducing organisms, each parent contributes half of the genes acquired (at random) by the offspring. Individuals have two of each chromosome and hence two alleles of each gene, one acquired from each parent. These versions may be identical or may differ from each other. (MS-LS3-2) In addition to variations that arise from sexual reproduction, genetic information can be altered because of mutations. Though rare, mutations may result in changes to the structure and function of proteins. Some changes are beneficial, others harmful, and some neutral to the organism. (MS-
LS3-1)
LS4.B: Natural Selection In artificial selection, humans have the capacity to influence certain characteristics of organisms by selective breeding. One can choose desired parental traits determined by genes, which are then passed on to offspring. (MS-LS4-5)
Big Ideas: Organisms reproduce to pass on their genetic information to the next generation Chromosomes carry genetic information that will be used to make up an individual Inherited traits from parents to offspring are varied due to the sexual reproduction; there is no variation in genetic information when asexual reproduction occurs Artificial selection can be used to choose desired parental traits to be passed on to offspring
Unit Goals and Objectives: MS-LS1-4. Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively. MS-LS1-5. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how environmental and genetic factors influence the growth of organisms. MS-LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result in harmful, beneficial, or neutral effects to the structure and function of the organism. MS-LS3-2. Develop and use a model to describe why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation. MS-LS4-5. Gather and synthesize information about the technologies that have changed the way humans influence the inheritance of desired traits in organisms.
Unit Summary: All living organisms grow, develop, and reproduce in different ways. In this unit, we will learn the differences between organisms' life cycles and their ability to reproduce and pass on their genetic information to their offspring. We will also learn about genes and different variations of inherited traits. This information is located on chromosomes of our DNA. And finally, we will end this unit by discussing how we, as humans, can selectively breed organisms by choosing traits we believe are desirable.
Assessment Plan: Entry-Level: Brainstorm What does growth and development mean to you?
Formative: Quiz Vocabulary Quickwrite What is DNA and why is it important? Flow chart Steps involved in mitosis Venn diagram Similarities and differences of sexual and asexual reproduction
Summative: Unit Exam Poster Draw out each step in mitosis and add a description to each picture using key words from the unit
Lesson 1 Student Learning Objective: By the end of this lesson, students will know the concepts that are involved in the growth and development of organisms. Students will have a further understanding of the role in DNA, as well as get a brief overview of the processes that it is involved in. We will also
Acceptable Evidence: Students will be able to complete guided notes that accompany the teacher lecture. Be able to explain how behaviors in organisms increase successful reproduction
Instructional Strategies: Communication Collection Collaboration Presentation Organization Interaction
Lesson Activities: A presentation on the growth and development of organisms with guided notes. It includes a short video on mitosis. We will pause in some parts of the lesson so students will be able to answer questions (with their group members) that have been included in the lecture. Afterwards, I will call on some students to respond to them.
touch briefly in the reproduction cycle of plants. Content Standard LS1.B Growth and Development Lesson 2 Student Learning Objective: Students will be learning through various digital interactives to reinforce what they have learned. After this lesson, students will be able to discuss the various internal and external factors affecting plant growth. Content Standard: MSLS1-5 Lesson 3 Student Learning Objective: Students will be creating two graphic organizers that will be used as an introduction to why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and why sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation. Content Standard: MSLS3-2
Acceptable Evidence: Students will be able to fill out the webercise with the appropriate answers. They will be introduced to heredity in this activity and their answers to what did you learn in this portion after watching a movie will determine how much they learned from it.
Instructional Strategies: Communication Collection Collaboration Presentation Organization Interaction
Lesson Activities: Students will be working independently to fill out the webercise that is provided on the website. This activity is important because it will bridge prior knowledge to a new lesson on heredity and genetics. By using a short movie clip on heredity and giving students to write freely on what they have learned, it will give me an idea of where I need to start and how much more information that theyll need when we start genetics and variation of traits.
Acceptable Evidence: Students will be able to correctly fill out their graphic organizers in concordance to what we have learned thus far. Students will be able to understand that there are different ways organisms reproduce and pass their genetic information to their offspring.
Instructional Strategies: Communication Collection Collaboration Presentation Organization Interaction
Lesson Activities: Students are asked to fill out two graphic organizers that will further their knowledge on our lecture. Allowing students to discuss their answers amongst themselves will also increase what they have taken in because it reinforces what was just learned. Examples and a grading rubric will be available to the students to model what I want from them. This activity is important because it will bridge what we have learned to what we will be learning next.
Unit Resources: Videos Learn with Tim and Moby at BrainPOP: DNA (After watching the video, take the quiz here) Heredity (After watching the video, take the quiz here) Simulations Characters of Inheritance at Learn.Genetics: What is a trait? Genetic Variation at Learn.Genetics: Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Natural vs. Artificial Selection Activities Additional help to master Punnet Squares at Education Development Center, INC: Punnet Squares After finishing the unit, try this Mendelian activity and breed wrinkled peas: Mendelian Pea Lab And if you have time, work in the Crazy Plant Shop to breed plants for customers and learn more about artificial selection: Crazy Plant Factory
Useful Websites: Plant Growth Plant Reproduction
You might also like
- 10th Life Science Carol Lilliam Muñoz Avila 2: Identify Desired Results (Stage 1)Document8 pages10th Life Science Carol Lilliam Muñoz Avila 2: Identify Desired Results (Stage 1)Carol LilliamNo ratings yet
- MYP Genetics unit plannerDocument5 pagesMYP Genetics unit plannerashokNo ratings yet
- Developmental Human Behavioral Epigenetics: Principles, Methods, Evidence, and Future DirectionsFrom EverandDevelopmental Human Behavioral Epigenetics: Principles, Methods, Evidence, and Future DirectionsLivio ProvenziNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan 304Document4 pagesDigital Unit Plan 304api-300436413No ratings yet
- Bruton Strategy Lesson 1Document27 pagesBruton Strategy Lesson 1api-489727615No ratings yet
- Teacher Preparation Notes For Genetics and Genetics SupplementDocument16 pagesTeacher Preparation Notes For Genetics and Genetics SupplementMary Ann DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Grade 07: Inheritance and Variations of Traits: Stage 1: Desired ResultsDocument7 pagesGrade 07: Inheritance and Variations of Traits: Stage 1: Desired ResultsVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- 10th Life Science Carol Lilliam Muñoz Avila 2: Identify Desired Results (Stage 1)Document8 pages10th Life Science Carol Lilliam Muñoz Avila 2: Identify Desired Results (Stage 1)Carol LilliamNo ratings yet
- Mutation Inquiry Activity SequenceDocument9 pagesMutation Inquiry Activity Sequenceapi-251753669No ratings yet
- Ngss Dup Goals Objectives and Assessments - TemplateDocument5 pagesNgss Dup Goals Objectives and Assessments - Templateapi-549667596No ratings yet
- Module Overview 1 1Document10 pagesModule Overview 1 1api-302379243No ratings yet
- Annotated Unit PlansDocument8 pagesAnnotated Unit Plansapi-249804589No ratings yet
- AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument26 pagesAaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaGlen Mark MacarioNo ratings yet
- Tran Digital Unit Plan - Goals Objectives and AssessmentsDocument3 pagesTran Digital Unit Plan - Goals Objectives and Assessmentsapi-289524714No ratings yet
- Assessment PlanDocument11 pagesAssessment PlanmattwegleyNo ratings yet
- Stage 1 - Desired Results: Title of Unit Grade Level Curriculum Area Time FrameDocument29 pagesStage 1 - Desired Results: Title of Unit Grade Level Curriculum Area Time FramemkirbypowersNo ratings yet
- Skin UbdDocument3 pagesSkin Ubdapi-275510930No ratings yet
- ReproductivestrategiesDocument21 pagesReproductivestrategiesapi-241062194No ratings yet
- Natural Selection and The Evidence For Evolution Digital Unit Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesNatural Selection and The Evidence For Evolution Digital Unit Plan Templateapi-267645354No ratings yet
- Agriculture ProjectDocument18 pagesAgriculture ProjectRita BekeredjianNo ratings yet
- Teacher Preparation Notes For Meiosis and Fertilization - Understanding How Genes Are InheritedDocument9 pagesTeacher Preparation Notes For Meiosis and Fertilization - Understanding How Genes Are InheritedQueen1982 KNo ratings yet
- Genetics Webquest2Document3 pagesGenetics Webquest2api-366982317No ratings yet
- Genetics student's activity reportDocument3 pagesGenetics student's activity reportSerenio, CharimaeNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lesson Plan RevisionDocument3 pagesGenetics Lesson Plan RevisionJaqueline Kaye Tivoli KalawNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Template: Objectives/OutcomesDocument4 pagesUnit Plan Template: Objectives/Outcomesapi-546993307No ratings yet
- Sciencelp 4Document3 pagesSciencelp 4api-243035462No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11th EditionDocument7 pagesSolution Manual For Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Editionlardavileou0No ratings yet
- 5e Heredity Genetics Unit Portfolio CrespoDocument6 pages5e Heredity Genetics Unit Portfolio Crespoapi-247308630No ratings yet
- Carrillo e Castleberry T Engaged Learning Project FinalDocument3 pagesCarrillo e Castleberry T Engaged Learning Project Finalapi-284877281No ratings yet
- Motor Development Research PaperDocument8 pagesMotor Development Research Paperepfdnzznd100% (1)
- Hs Sexlinked InheritanceDocument14 pagesHs Sexlinked InheritanceMarcelo Pessoa NetoNo ratings yet
- SSC Gr8 Biotech Q4 Module 1 WK 1 - v.01-CC-released-09May2021Document22 pagesSSC Gr8 Biotech Q4 Module 1 WK 1 - v.01-CC-released-09May2021Ivy JeanneNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Stages 1 2 and 3Document11 pagesUnit Plan Stages 1 2 and 3api-709290948No ratings yet
- Lessonplan 1-19-17Document5 pagesLessonplan 1-19-17api-346184496No ratings yet
- Blended Learning Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBlended Learning Lesson Planapi-510705933No ratings yet
- Unitplan Honda EvolutionDocument48 pagesUnitplan Honda Evolutionapi-287211281No ratings yet
- Study Guide - Docx 3Document20 pagesStudy Guide - Docx 3scottNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Docx 1Document17 pagesStudy Guide - Docx 1scottNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Docx 2Document17 pagesStudy Guide - Docx 2scottNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Exploring Evolution Name: C. Jordan Abney Content Area: Science-Biology Grade Level: 9 GradeDocument6 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Exploring Evolution Name: C. Jordan Abney Content Area: Science-Biology Grade Level: 9 Gradeapi-355641109No ratings yet
- LAS - Biotech (Grade 8) - MELC - 3 - Q2 - Week-3Document10 pagesLAS - Biotech (Grade 8) - MELC - 3 - Q2 - Week-3Sharon CordovaNo ratings yet
- NGSS & Common Core 5E Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesNGSS & Common Core 5E Lesson Planapi-300263583No ratings yet
- Human Biology Y11 Syllabus ATAR - GDDocument25 pagesHuman Biology Y11 Syllabus ATAR - GDparty100% (1)
- Dup - Genetics Heredity and InheritanceDocument8 pagesDup - Genetics Heredity and Inheritanceapi-492431821No ratings yet
- Los Grade 2Document60 pagesLos Grade 2Omar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Unit PlanDocument4 pagesUnit Planapi-301973984No ratings yet
- Life Span Development 15th Edition Santrock Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesLife Span Development 15th Edition Santrock Solutions Manualjaundicecrincum05ba2100% (22)
- Dwnload Full Life Span Development 15th Edition Santrock Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Life Span Development 15th Edition Santrock Solutions Manual PDFjaydens5a100% (12)
- BCL SBLA Science 9-12 GeneticdisordersDocument6 pagesBCL SBLA Science 9-12 GeneticdisordersbmhshNo ratings yet
- Sed 482 Final Unit Plan 2Document5 pagesSed 482 Final Unit Plan 2api-273094447No ratings yet
- Educ100 Prelim MidtermDocument40 pagesEduc100 Prelim MidtermJanessa Jones GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction LPDocument15 pagesSexual Reproduction LPKATRINA MARIE AmayNo ratings yet
- Cep Lesson Plan-BiotechDocument6 pagesCep Lesson Plan-Biotechapi-318020619No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and ReproductionDocument10 pagesCell Cycle and ReproductionJean May Pajila CabagayNo ratings yet
- Genetic Traits InventoryDocument10 pagesGenetic Traits InventorymarisakendallNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Lifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual PDFDocument12 pagesDwnload Full Lifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual PDFquatchristabelfa55hd100% (11)
- Sed 482 Final Unit Plan 2Document4 pagesSed 482 Final Unit Plan 2api-273094447No ratings yet
- Dev Psych - Module 2Document4 pagesDev Psych - Module 2The Lyric ListsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Biology (II) Continuity of LifeDocument18 pagesAssignment Biology (II) Continuity of Life秋秋No ratings yet
- Anatomy For Beginners - Reproduction WorksheetDocument4 pagesAnatomy For Beginners - Reproduction WorksheetJames Dauray100% (1)
- Bioekologi HamaDocument53 pagesBioekologi HamaMatcha LatteNo ratings yet
- Microscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeDocument4 pagesMicroscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeLouie Jane EleccionNo ratings yet
- Writing Hooks For EssaysDocument4 pagesWriting Hooks For Essaysb72hvt2d100% (2)
- Diagnostic Test in Science Grade 5 SY 2019-2020 Name: Grade/Section: Direction: Shade The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science Grade 5 SY 2019-2020 Name: Grade/Section: Direction: Shade The Letter of The Correct AnswerMEERA JOY BLANCONo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Embryology - Randel PDFDocument399 pagesVertebrate Embryology - Randel PDFrandelNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument2 pagesRevision Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of AdolescenceArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Al-Khair Higher Secondary School.: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesAl-Khair Higher Secondary School.: ObjectiveTariq MuneerNo ratings yet
- Paper 5 - CH - 7 Q. 1 HERIDITY AND ENVIRONMENTDocument3 pagesPaper 5 - CH - 7 Q. 1 HERIDITY AND ENVIRONMENTnoorjhan dosaniNo ratings yet
- Sci8 q4 Mod2 v4Document31 pagesSci8 q4 Mod2 v4Jay-ar RiosNo ratings yet
- Fundal height measurement: Assessing fetal growth and gestational ageDocument29 pagesFundal height measurement: Assessing fetal growth and gestational ageMary Ann G. CorsanesNo ratings yet
- Terminologia Embryologica - 2 (FIPAT к НИР2023)Document329 pagesTerminologia Embryologica - 2 (FIPAT к НИР2023)Sadyk MerdanowNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Module KSSR (Semakan 2017) Science Year 6Document116 pagesTeaching and Learning Module KSSR (Semakan 2017) Science Year 6LING KUOK LIMNo ratings yet
- Kara Rogers The Reproductive SystemDocument266 pagesKara Rogers The Reproductive Systemharcaian_cristinaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument3 pagesMitosis and Meiosisfghvfhf50% (2)
- Question Paper Unit A161 02 Modules b1 b2 b3 Higher TierDocument16 pagesQuestion Paper Unit A161 02 Modules b1 b2 b3 Higher TierAnonymous QFkCS837bNo ratings yet
- Nagpur Gynecologist ListDocument46 pagesNagpur Gynecologist ListsreevidyaNo ratings yet
- HUMREP35 Suppl1 ESHRE 2020 - V4 PDFDocument522 pagesHUMREP35 Suppl1 ESHRE 2020 - V4 PDFIoana Adina RugescuNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 5 Q2 COT 1 Ni Ama. 12.7.2022Document196 pagesScience Grade 5 Q2 COT 1 Ni Ama. 12.7.2022Amabelle Pagalunan AcletaNo ratings yet
- NEET Biology Weightage AnalysisDocument9 pagesNEET Biology Weightage AnalysisNEET 2022100% (2)
- 1-20 Mock Tests CATDocument872 pages1-20 Mock Tests CATTanmay GargNo ratings yet
- Biology SSC-II Exam Answer SheetDocument9 pagesBiology SSC-II Exam Answer SheetMahwishbukhariNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Unit Lesson in ScienceDocument14 pages3rd Grade Unit Lesson in Scienceapi-611895095No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Final DemoDocument9 pagesLesson Plan For Final DemoJunjun Caoli50% (2)
- BIO 3:plant ClassificationDocument5 pagesBIO 3:plant ClassificationTers MedinaNo ratings yet
- Support MaterialDocument267 pagesSupport MaterialIshvarya100% (1)
- Stages of Lactation ExplainedDocument35 pagesStages of Lactation ExplainedIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- Alexander 2022 Deceptively Aligned MesaoptimizersDocument92 pagesAlexander 2022 Deceptively Aligned MesaoptimizersStamnumNo ratings yet
- Expectations as an Egg DonorDocument2 pagesExpectations as an Egg DonorNini LekishviliNo ratings yet
- SEMEN ANALYSIS GUIDEDocument9 pagesSEMEN ANALYSIS GUIDEMartin Clyde100% (1)