Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Engineering Portal - Com StarDelta Motor Starter
Uploaded by
Ricardo A VergaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Engineering Portal - Com StarDelta Motor Starter
Uploaded by
Ricardo A VergaraCopyright:
Available Formats
e le ct rical-e ngine e ring-po rt al.
co m
http://electrical-engineering-po rtal.co m/star-delta-mo to r-starter
Star-Delta Motor Starter
by jiguparmar
Star-d e lta mo to r s tarte r p ane l
Introduction to Star-Delta motor starter
Most induction motors are started directly on line, but when very large motors are started that way, they cause a disturbance of voltage on the supply lines due to large starting current surges. To limit the starting current surge, large induction motors are started at reduced voltage and then have f ull supply voltage reconnected when they run up to near rotated speed. Two methods used f or reduction of starting voltage are: Star delta starting and Auto transformer starting .
Star-d e lta s tarte r p ane l
Working Principle of Star-Delta Starter
T his is the reduced voltage starting method. Voltage reduction during star-delta starting is achieved by physically reconf iguring the motor windings as illustrated in the f igure below. During starting the motor windings
are connected in star conf iguration and this reduces the voltage across each winding 3. T his also reduces the torque by a f actor of three. Af ter a period of time the winding are reconf igured as delta and the motor runs normally. Star/Delta starters are probably the most common reduced voltage starters. T hey are used in an attempt to reduce the start current applied to the motor during start as a means of reducing the disturbances and interf erence on the electrical supply. Traditionally in many supply regions, there has been a requirement to f it a reduced voltage starter on all Sc he me motors greater than 5HP (4KW). T he Star/Delta (or Wye/Delta) starter is one of the lowest cost electromechanical reduced voltage starters that can be applied.
- Wo rking Princ ip le o f Star-De lta Starte r
T he Star/Delta starter is manuf actured f rom three contactors, a timer and a thermal overload. T he contactors are smaller than the single contactor used in a Direct on Line starter as they are controlling winding currents only. T he currents through the winding are 1/root 3 (58%) of the current in the line. T here are two contactors that are close during run, of ten ref erred to as the main contractor and the delta contactor. T hese are AC3 rated at 58% of the current rating of the motor. T he third contactor is the star contactor and that only carries star current while the motor is connected in star. T he current in star is one third of the current in delta, so this contactor can be AC3 rated at one third (33%) of the motor rating.
St ar-delt a St art er Consist s f ollowing unit s
1. Contactors (Main, star and delta contactors) 3 Nos (For Open State Starter) or 4 Nos (Close Transient Starter). 2. Time relay (pull-in delayed) 1 No. 3. T hree-pole thermal overcurrent release 1 No. 4. Fuse elements or automatic cut-outs f or the main circuit 3 Nos. 5. Fuse element or automatic cut-out f or the control circuit 1No.
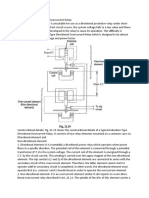
Power Circuit of Star Delta Starter
T he main circuit breaker serves as the main power supply switch that supplies electricity to the power circuit. T he main contactor connects the ref erence source voltage R, Y , B to the primary terminal of the motor U1, V1, W1. In operation, the Main Contactor (KM3) and the Star Contactor (KM1) are closed initially, and then af ter a period of time, the star contactor is opened, and then the delta contactor (KM2) is closed. T he control of the contactors is by the timer (K1T ) built into the starter. T he Star and Delta are electrically interlocked and
pref erably mechanically interlocked as well. In effect, there are four states: T he star contactor serves to initially short the secondary terminal of the motor U2, V2, W2 f or the start sequence during the initial run of the motor f rom standstill. T his provides one third of DOL current to the motor, thus reducing the high inrush current inherent with large capacity motors at startup.
Po we r c irc uit o f Star-De lta s tarte r
Controlling the interchanging star connection and delta connection of an AC induction motor is achieved by means of a star delta or wye delta control circuit. T he control circuit consists of push button switches, auxiliary contacts and a timer.
Control Circuit of Star-Delta Starter (Open Transition)
T he ON push button starts the circuit by initially energizing Star Contactor Coil (KM1) of star circuit and Timer Coil (KT ) circuit. When Star Contactor Coil (KM1) energized, Star Main and Auxiliary contactor change its position f rom NO to NC. When Star Auxiliary Contactor (1) (which is placed on Main Contactor coil circuit ) become NO to NC its complete T he Circuit of Main contactor Coil (KM3) so Main Contactor Coil energized and Main Contactors Main and Auxiliary Contactor Change its Position f rom NO to NC. T his sequence happens in a f riction of time. Af ter pushing the ON push button switch, the auxiliary contact of the main contactor coil (2) which is Sc he me - Co ntro l Circ uit o f Star-De lta Starte r (O p e n Trans itio n) connected in parallel across the ON push button will become NO to NC, thereby providing a latch to hold the main contactor coil activated which eventually maintains the control circuit active even af ter releasing the ON push button switch. When Star Main Contactor (KM1) close its connect Motor connects on STAR and its connected in STAR until Time Delay Auxiliary contact KT (3) become NC to NO. Once the time delay is reached its specif ied Time, the timers auxiliary contacts (KT )(3) in Star Coil circuit will change its position f rom NC to NO and at the Same Time Auxiliary contactor (KT ) in Delta Coil Circuit(4) change its Position f rom NO To NC so Delta coil energized and Delta Main Contactor becomes NO To NC. Now Motor terminal connection change f rom star to delta connection. A normally close auxiliary contact f rom both star and delta contactors (5&6)are also placed opposite of both star and delta contactor coils, these interlock contacts serves as saf ety switches to prevent simultaneous activation of both star and delta contactor coils, so that one cannot be activated without the other deactivated f irst. T hus, the delta contactor coil cannot be active when the star contactor coil is active, and similarly, the star contactor coil cannot also be active while the delta contactor coil is active. T he control circuit above also provides two interrupting contacts to shutdown the motor. T he OFF push button switch break the control circuit and the motor when necessary. T he thermal overload contact is a protective device which automatically opens the ST OP Control circuit in case when motor overload current is
detected by the thermal overload relay, this is to prevent burning of the motor in case of excessive load beyond the rated capacity of the motor is detected by the thermal overload relay. At some point during starting it is necessary to change f rom a star connected winding to a delta connected winding. Power and control circuits can be arranged to this in one of two ways open transition or closed transition.
What is Open or Closed Transit ion St art ing 1. Open Transit ion St art ers
Discuss mention above is called open transition switching because there is an open state between the star state and the delta state. In open transition the power is disconnected f rom the motor while the winding are reconf igured via external switching. When a motor is driven by the supply, either at f ull speed or at part speed, there is a rotating magnetic f ield in the stator. T his f ield is rotating at line f requency. T he f lux f rom the stator f ield induces a current in the rotor and this in turn results in a rotor magnetic f ield. When the motor is disconnected f rom the supply (open transition) there is a spinning rotor within the stator and the rotor has a magnetic f ield. Due to the low impedance of the rotor circuit, the time constant is quite long and the action of the spinning rotor f ield within the stator is that of a generator which generates voltage at a f requency determined by the speed of the rotor. When the motor is reconnected to the supply, it is reclosing onto an unsynchronized generator and this result in a very high current and torque transient. The magnitude of the transient is dependent on the phase relationship between the generated voltage and the line voltage at the point of closure can be much higher than DOL current and torque and can result in electrical and mechanical damage. Open transition starting is the easiest to implement in terms or cost and circuitry and if the timing of the changeover is good, this method can work well. In practice though it is dif f icult to set the necessary timing to operate correctly and disconnection/reconnection of the supply can cause signif icant voltage/current transients. In open transition there are four states: 1. OFF State : All Contactors are open. 2. Star State: T he Main [KM3] and the Star [KM1] contactors are closed and the delta [KM2] contactor is open. T he motor is connected in star and will produce one third of DOL torque at one third of DOL current. 3. Open State: T his type of operation is called open transition switching because there is an open state between the star state and the delta state. T he Main contractor is closed and the Delta and Star contactors are open. T here is voltage on one end of the motor windings, but the other end is open so no current can f low. T he motor has a spinning rotor and behaves like a generator. 4. Delta State: T he Main and the Delta contactors are closed. T he Star contactor is open. T he motor is connected to f ull line voltage and f ull power and torque are available
2. Closed Transit ion St ar/Delt a St art er
T here is a technique to reduce the magnitude of the switching transients. T his requires the use of a f ourth contactor and a set of three resistors. T he resistors must be sized such that considerable current is able to f low in the motor windings while they are in circuit. T he auxiliary contactor and resistors are connected across the delta contactor. In operation, just bef ore the star contactor opens, the auxiliary contactor closes resulting in current f low via the resistors into the star connection. Once the star contactor opens, current is able to f low round through the motor windings to the supply via the resistors. T hese resistors are then shorted by the delta contactor. If the resistance of the resistors is too high, they will not swamp the voltage generated by the motor and will serve no purpose. In closed transition the power is maintained to the motor at all time. T his is achieved by introducing resistors to take up the current f low during the winding changeover. A f ourth contractor is required to place the resistor in circuit bef ore opening the star contactor and then removing the resistors once the delta contactor is closed. T hese resistors need to be sized to carry the motor current. In addition to requiring more switching devices, the control circuit is more complicated due to the need to carry out resistor switching In close transition there are four states: 1. OFF State. All Contactors are open 2. Star State. T he Main [KM3] and the Star [KM1] contactors are closed and the delta [KM2] contactor is open. T he motor is connected in star and will produce one third of DOL torque at one third of DOL current. 3. Star Transition State. T he motor is connected in star and the resistors are connected across the delta contactor via the aux [KM4] contactor. 4. Closed Transition State. T he Main [KM3] contactor is closed and the Delta [KM2] and Star [KM1] contactors are open. Current f lows through the motor windings and the transition resistors via KM4. 5. Delta State. T he Main and the Delta contactors are closed. T he transition resistors are shorted out. T he Star contactor is open. T he motor is connected to f ull line voltage and f ull power and torque are available.
Ef f ect of Transient in Starter (Open Transient starter)
It is Important the pause between star contactor switch of f and Delta contactor switch is on correct. T his is because Star contactor must be reliably disconnected bef ore Delta contactor is activated. It is also important that the switch over pause is not too long. For 415v Star Connection voltage is ef f ectively reduced to 58% or 240v. T he equivalent of 33% that is obtained with Direct Online (DOL) starting. If Star connection has suf f icient torque to run up to 75% or %80 of f ull load speed, then the motor can be
connected in Delta mode. When connected to Delta conf iguration the phase voltage increases by a ratio of V3 or 173%. T he phase currents increase by the same ratio. T he line current increases three times its value in star connection. During transition period of switchover the motor must be f ree running with little deceleration. While this is happening Coasting it may generate a voltage of its own, and on connection to the supply this voltage can randomly add to or subtract f rom the applied line voltage. This is known as transient current. Only lasting a f ew milliseconds it causes voltage surges and spikes. Known as a changeover transient.
Size of each part of St ar-Delt a st art er 1. Size of Over Load Relay
For a star-delta starter there is a possibility to place the overload protection in two positions, in the line or in the windings.
Overload Relay in Line:
In the line is the same as just putting the overload bef ore the motor as with a DOL starter. T he rating of Overload (In Line) = FLC of Motor. Disadvantage: If the overload is set to FLC, then it is not protecting the motor while it is in delta (setting is x1.732 too high).
Overload Relay in Winding:
In the windings means that the overload is placed af ter the point where the wiring to the contactors are split into main and delta. T he overload then always measures the current inside the windings. T he setting of Overload Relay (In Winding) =0.58 X FLC (line current). Disadvantage: We must use separate short circuit and overload protections.
2. Size of Main and Delt a Cont ract or
T here are two contactors that are close during run, of ten ref erred to as the main contractor and the delta contactor. T hese are AC3 rated at 58% of the current rating of the motor. Size of Main Contactor= IFL x 0.58
3. Size of St ar Cont ract or
T he third contactor is the star contactor and that only carries star current while the motor is connected in star. T he current in star is 1/ 3= (58%) of the current in delta, so this contactor can be AC3 rated at one third (33%) of the motor rating.
Size of Star Contactor= IFL x 0.33
Motor Starting Characteristics of Star-Delta Starter
Available starting current: 33% Full Load Current. Peak starting current: 1.3 to 2.6 Full Load Current. Peak starting torque: 33% Full Load Torque.
Advantages of Star-Delta starter
T he operation of the star-delta method is simple and rugged It is relatively cheap compared to other reduced voltage methods. Good Torque/Current Perf ormance. It draws 2 times starting current of the f ull load ampere of the motor connected
Disadvantages of Star-Delta starter
1. Low Starting Torque (Torque = (Square of Voltage) is also reduce). 2. Break In Supply Possible Transients 3. Six Terminal Motor Required (Delta Connected). 4. It requires 2 set of cables f rom starter to motor. . 5. It provides only 33% starting torque and if the load connected to the subject motor requires higher starting torque at the time of starting than very heavy transients and stresses are produced while changing f rom star to delta connections, and because of these transients and stresses many electrical and mechanical break-down occurs. . 6. In this method of starting initially motor is connected in star and then af ter change over the motor is connected in delta. T he delta of motor is f ormed in starter and not on motor terminals. . 7. High transmission and current peaks: When starting up pumps and f ans f or example, the load torque is low at the beginning of the start and increases with the square of the speed. When reaching approx. 80-85 % of the motor rated speed the load torque is equal to the motor torque and the acceleration ceases. To reach the rated speed, a switch over to delta position is necessary, and this will very of ten result in high transmission and current peaks. In some cases the current peak can reach a value that is even bigger than f or a D.O.L start. . 8. Applications with a load torque higher than 50 % of the motor rated torque will not be able to start using the start-delta starter. .
9. Low Starting Torque: T he star-delta (wye-delta) starting method controls whether the lead connections f rom the motor are conf igured in a star or delta electrical connection. T he initial connection should be in the star pattern that results in a reduction of the line voltage by a f actor of 1/3 (57.7%) to the motor and the current is reduced to 1/3 of the current at f ull voltage, but the starting torque is also reduced 1/3 to 1/5 of the DOL starting torque. . 10. T he transition f rom star to delta transition usually occurs once nominal speed is reached, but is sometimes perf ormed as low as 50% of nominal speed which make transient Sparks.
Features of star-delta starting
1. For low- to high-power three-phase motors. 2. Reduced starting current 3. Six connection cables 4. Reduced starting torque 5. Current peak on changeover f rom star to delta 6. Mechanical load on changeover f rom star to delta
Application of Star-Delta Starter
T he star-delta method is usually only applied to low to medium voltage and light starting Torque motors. T he received starting current is about 30 % of the starting current during direct on line start and the starting torque is reduced to about 25 % of the torque available at a D.O.L start. T his starting method only works when the application is light loaded during the start. If the motor is too heavily loaded, there will not be enough torque to accelerate the motor up to speed bef ore switching over to the delta position.
You might also like
- Wye Delta Starter MotorDocument12 pagesWye Delta Starter MotorCharles NunezNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction To Star-Delta Motor StarterDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Star-Delta Motor StarterKudzie Maphy MasaireNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Star-Delta Motor StarterDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Star-Delta Motor StarterBala SrivasNo ratings yet
- Star-Delta Motor Starter PDFDocument9 pagesStar-Delta Motor Starter PDFWrya Saeed0% (1)
- Star-Delta Motor Starter Explained in DetailsDocument10 pagesStar-Delta Motor Starter Explained in DetailsFrenzy TaherNo ratings yet
- Star DeltaDocument15 pagesStar DeltaAbdul HaleemNo ratings yet
- Star Delta StarterDocument40 pagesStar Delta Startersupermannon100% (1)
- Star-Delta Starter: Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument25 pagesStar-Delta Starter: Electrical Notes & Articlesprabhanshu241991100% (1)
- Star-Delta Starter - Electrical Notes & Articles PDFDocument30 pagesStar-Delta Starter - Electrical Notes & Articles PDFNikhil Chakravarthy Vatsavayi100% (1)
- y D Starter PDFDocument13 pagesy D Starter PDFnazar750No ratings yet
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrinciplePrasant Kumar100% (5)
- EELabReport@#7 WDSC AbajenzaDocument6 pagesEELabReport@#7 WDSC Abajenzaปุลื้ม ปุริมNo ratings yet
- Industrial Installation Contactors Magnetic Contactors Are Electromagnetically Operated Switches That Provide A Safe andDocument11 pagesIndustrial Installation Contactors Magnetic Contactors Are Electromagnetically Operated Switches That Provide A Safe andDemisKebedeNo ratings yet
- EE6504-Electrical Machines - II-306544629-Em II Unit 4Document20 pagesEE6504-Electrical Machines - II-306544629-Em II Unit 4Rajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- EE6504-Electrical Machines - II-306544629-Em II Unit 4Document20 pagesEE6504-Electrical Machines - II-306544629-Em II Unit 4Rajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Star DeltaDocument6 pagesStar DeltaNurain XuNo ratings yet
- Automatic Star Delta Starter Using Relay and Adjustable Electronic Timer For 3 Phase Induction MotorDocument8 pagesAutomatic Star Delta Starter Using Relay and Adjustable Electronic Timer For 3 Phase Induction MotorNoushz channelNo ratings yet
- Open Transition and Closed Transition Star Delta Wye Delta Starters For Induction MotorsDocument30 pagesOpen Transition and Closed Transition Star Delta Wye Delta Starters For Induction Motorsshahadat08No ratings yet
- Lab 6 Kawalan MotorDocument20 pagesLab 6 Kawalan MotorMohd FiqrieNo ratings yet
- Motors: Principles of A MotorDocument11 pagesMotors: Principles of A MotorAbishek AbiNo ratings yet
- Direct On Line DOL Motor StarterDocument6 pagesDirect On Line DOL Motor StarterFebrian Nugroho WinartoNo ratings yet
- Motor StartersDocument9 pagesMotor Startersanon_896479742No ratings yet
- Unit Iv Starting and Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument19 pagesUnit Iv Starting and Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorVamshiNo ratings yet
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working Principle: Descriptions: ADocument2 pagesSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working Principle: Descriptions: Alcmscheid9954No ratings yet
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleJabir QuadriNo ratings yet
- Motor STAR - DELTA Starter Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsDocument3 pagesMotor STAR - DELTA Starter Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsTEUKUNo ratings yet
- Motor Starter Ac Motor StartersDocument6 pagesMotor Starter Ac Motor StartersShukor Az100% (1)
- Star Delta Starter of Induction Motor: © 2014 IJIRT - Volume 1 Issue 6 - ISSN: 2349-6002Document2 pagesStar Delta Starter of Induction Motor: © 2014 IJIRT - Volume 1 Issue 6 - ISSN: 2349-6002Umer AyazNo ratings yet
- Automatic Star DeltaDocument3 pagesAutomatic Star DeltaAbisheik Rishi100% (1)
- Eia Micro ProjectDocument5 pagesEia Micro ProjectMeezan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Direct On Line DOL Motor Starter PDFDocument7 pagesDirect On Line DOL Motor Starter PDFVasudev AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Star Delta Starter For Three Phase - Formatted PaperDocument4 pagesStar Delta Starter For Three Phase - Formatted PaperOm PandeyNo ratings yet
- 21EE44 Module 4Document18 pages21EE44 Module 4AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Induction Generator Starting MethodsDocument5 pagesInduction Generator Starting MethodsChathuranga NagasingheNo ratings yet
- Motor Control DOLDocument3 pagesMotor Control DOLAvid LearnerNo ratings yet
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleKsr AkhilNo ratings yet
- Unit-4-Electrical Machines: Lecture-3 Starting methods of 3-Φ Induction MotorDocument13 pagesUnit-4-Electrical Machines: Lecture-3 Starting methods of 3-Φ Induction MotorPratik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Study of DOL Starter: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesStudy of DOL Starter: Objectivevivek soniNo ratings yet
- Starter MotorDocument15 pagesStarter MotorfieraminaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Direct - On - Line - DOL - Motor - StarterDocument7 pages2.2 Direct - On - Line - DOL - Motor - StarterEdison EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Star Delta StarterDocument4 pagesStar Delta StarterAmey TanawadeNo ratings yet
- DC Motor StarterDocument25 pagesDC Motor StarterSrinivasan PrakashNo ratings yet
- Working of DOL StarterDocument7 pagesWorking of DOL Starteralekya100% (1)
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleDocument2 pagesSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrinciplePradeepChandraVarmaMandapatiNo ratings yet
- Hapter I: NtroductionDocument41 pagesHapter I: NtroductionGadhi LadkiNo ratings yet
- Direct On Line DOL Motor StarterDocument6 pagesDirect On Line DOL Motor StarterEdwin Cob GuriNo ratings yet
- Work Shop MoterDocument23 pagesWork Shop Moterbelacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- Direct On LineDocument9 pagesDirect On LineShanti NaiduNo ratings yet
- Lab 14 - 3-Phase AlternatorDocument7 pagesLab 14 - 3-Phase AlternatorjalilemadiNo ratings yet
- IJRPR3553Document4 pagesIJRPR3553everhealthlifesciencesNo ratings yet
- Direct On Line DOL Motor StarterDocument6 pagesDirect On Line DOL Motor StarterPierre Enrique Carrasco FuentesNo ratings yet
- Direct On Line Starter MotorDocument10 pagesDirect On Line Starter MotorCharles NunezNo ratings yet
- Types of Motor StarterDocument10 pagesTypes of Motor StarterEngr. CasmirNo ratings yet
- Star Delta Starter - Working Principle, Theory, Circuit DiagramDocument10 pagesStar Delta Starter - Working Principle, Theory, Circuit DiagramNaveen SinghNo ratings yet
- New Star Delta Forward ReverseDocument9 pagesNew Star Delta Forward ReverseBasuki Ikhy100% (1)
- DocumentDocument26 pagesDocumentPurbita ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab Star DeltaDocument8 pagesOpen Ended Lab Star Deltaali hamzaNo ratings yet
- ABB Cyberwave DC Charger Single Phase 080515Document4 pagesABB Cyberwave DC Charger Single Phase 080515Ricardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- The Role of Medium Voltage Switchgear in Power SystemDocument2 pagesThe Role of Medium Voltage Switchgear in Power SystemRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Power Distribution SystemsDocument120 pagesPower Distribution SystemscarlosmandopintoNo ratings yet
- Ferroresonance Occurrence in Power TransformerDocument3 pagesFerroresonance Occurrence in Power TransformerRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Applications and Characteristics of Differential Relays ANSI 87Document6 pagesApplications and Characteristics of Differential Relays ANSI 87Ricardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares EnglishDocument5 pagesVerbos Irregulares EnglishRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Scott and L Brance TransformersDocument9 pagesScott and L Brance TransformersRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Resonance Phenomena - EEPDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Resonance Phenomena - EEPRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lighting Circuits Connections For Interior Electrical Installations 2Document7 pagesLighting Circuits Connections For Interior Electrical Installations 2Ricardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lighting Circuits Connections For Interior Electrical InstallationsDocument8 pagesLighting Circuits Connections For Interior Electrical InstallationsRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Do You Understand What Is Electric ShockDocument3 pagesDo You Understand What Is Electric ShockRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Ground Fault Protection - EEPDocument3 pagesGround Fault Protection - EEPRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Protection and Control Guide - EEPDocument4 pagesProtection and Control Guide - EEPRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- Consider Typical Robots Consider Typical RobotsDocument16 pagesConsider Typical Robots Consider Typical RobotsOthers ATBP.No ratings yet
- People Vs CorreaDocument2 pagesPeople Vs CorreaRmLyn Mclnao100% (1)
- Banking Adbl EnglishDocument74 pagesBanking Adbl Englishdevi ghimireNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - VLSM Design and Implementation Practice TopologyDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer - VLSM Design and Implementation Practice TopologyBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Awareness On Stock MarketDocument11 pagesAwareness On Stock MarketBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- E. What Was The Chinese POW Death Rate in WW2 and The Second Sino-Japanese WarDocument3 pagesE. What Was The Chinese POW Death Rate in WW2 and The Second Sino-Japanese WarPamela SantosNo ratings yet
- Comprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire TruckDocument79 pagesComprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire Truckbhupendra singh sengarNo ratings yet
- Concept of InsuranceDocument4 pagesConcept of InsuranceNazrul HoqueNo ratings yet
- GSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFDocument27 pagesGSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFAbdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems FYBCom PDFDocument41 pagesEcosystems FYBCom PDFShouvik palNo ratings yet
- Ventilation WorksheetDocument1 pageVentilation WorksheetIskandar 'muda' AdeNo ratings yet
- 2015.15009.fundamental Principles of Physical Chemistry - Text PDFDocument782 pages2015.15009.fundamental Principles of Physical Chemistry - Text PDFAnoif Naputo Aidnam100% (1)
- 2-Amino-5-Aryl-2-Oxazolines.: (,ee TableDocument7 pages2-Amino-5-Aryl-2-Oxazolines.: (,ee TableChristopher HowellNo ratings yet
- Definition of Surface Texture and Stylus InstrumentDocument5 pagesDefinition of Surface Texture and Stylus InstrumenthosseinNo ratings yet
- KC CVDocument2 pagesKC CVVishal KeshriNo ratings yet
- OXE Training - Complete (2011)Document94 pagesOXE Training - Complete (2011)Dhexter Villa75% (4)
- Civil Engineering Construction Manager in ST Louis MO Resume Mark JensenDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering Construction Manager in ST Louis MO Resume Mark JensenMark JensenNo ratings yet
- Fractal Approach in RoboticsDocument20 pagesFractal Approach in RoboticsSmileyNo ratings yet
- Debit Note and Credit NoteDocument2 pagesDebit Note and Credit Noteabdul haseebNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument46 pagesComputer Architecturejaime_parada3097100% (2)
- Thinking Out LoundDocument2 pagesThinking Out LoundExita ConiaNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Selection Of: MaterialsDocument22 pagesFactors Influencing The Selection Of: MaterialsMaulik KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument6 pagesMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNo ratings yet
- Lotte Advanced Materials Co., LTD.: ISO 9001:2015, KS Q ISO 9001:2015Document2 pagesLotte Advanced Materials Co., LTD.: ISO 9001:2015, KS Q ISO 9001:2015Tayyab KhanNo ratings yet
- Stonecoal v3 Guidelines 2023-03-22Document71 pagesStonecoal v3 Guidelines 2023-03-22Esha RamaswamiNo ratings yet
- Relativity Space-Time and Cosmology - WudkaDocument219 pagesRelativity Space-Time and Cosmology - WudkaAlan CalderónNo ratings yet
- Sri Anjaneya Cotton Mills LimitedDocument63 pagesSri Anjaneya Cotton Mills LimitedPrashanth PB50% (2)
- Marketing Plan Potato Food TruckDocument25 pagesMarketing Plan Potato Food TruckAhasan h. ShuvoNo ratings yet
- ShowimgDocument76 pagesShowimgROSHAN ROBERTNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Type: P25-34/0DDocument1 pageProduct Data Sheet: Type: P25-34/0DAlejandro RustrianNo ratings yet
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceFrom EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power System Control and ProtectionFrom EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)From EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Digital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionFrom EverandDigital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)