Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To The Tyre Recycling World
Uploaded by
AlbertoDominaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To The Tyre Recycling World
Uploaded by
AlbertoDominaCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
Content
1. 2. 3. 4. Historical data of tyre Recycling Basic facts about Tyres Development of tyre recycling in Europe Models for the scrap recycling processing in EU
5.
6.
Function of an integrated system
Tyre Recycling World Wide
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
1. Historical data of tyre Recycling
As a rule of thumb, the scrap tire generation in industrialized countries is approximately one passenger car tire equivalent (9 kg) per population and year. The tyre recycling industry has been created virtually due to government regulations enacted to address the environmental concerns about illegally dumped or stockpiled tires. The pioneers were USA and Japan, The European model starts at 1994 in the Nordic countries.
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
1. Historical data of tyre Recycling
In the early 1900s, the average recycled content of all rubber products was over 50%.
Grinding and separation of scrap rubber of all kinds. Low rates. The largest company in the industry. Custom grinding. Specialty: hard rubber dust
Cost of natural rubber = Cost of Silver (in weight)
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
1. Historical data of tyre Recycling Cheap oil imports, the more widespread use of synthetic rubber and the development of steel belted radial tires have led to a steady decline of rubber recycling. It became increasingly difficult to grind or slice old tires.
As of 1995, the traditional tire and rubber industry used only about 2% recycled material.
Technical developments in the past decade make it very likely that the use of recycled tire materials will increase significantly. Rubber recycling not only has a long past, but also a bright future.
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
2. Basic facts about Tyres
Passenger car, lorry and off-the-road (OTR) tyres are products of complex engineering.
Tyres are made for their use on vehicles; they are not made as a recycling industry feedstock. Their composition makes them difficult to recycle.
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
2. Basic facts about Tyres
COMPOSITION OF TYRES ON THE MARKET IN THE EUROPENA UNION (by weight)
Material Rubber / Elastomers Carbon black Metal Textile Zinc oxide Sulphur Additives Passenger cars 48% 22% 15% 5% 1% 1% 8% Trucks/buses 45% 22% 25% 2% 1% 5%
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
2. Basic facts about Tyres
FOUR MATERIAL CATEGORIES
1. Natural and synthetic rubbers 2. Carbon blacks and/or silica 3. Reinforcing materials Metals Textiles 4. Facilitators 40 - 48% 22 - 27% 5 - 25% 15 - 25% 11 - 13% + 5% 8 - 0% In beads, belts and casing of a truck tyre. In casings and plies of a car tyre. Textiles are used in car tyre casings. Extender oils, waxes, and plasticizers aid processing;. Ratio of natural to synthetic rubber: 2 1 truck tyres; 4 3 car tyres. A range of carbon blacks of varying sizes, structures and characteristics are used in different parts of the tyre.
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
2. Basic facts about Tyres
COMPOSITION OF TYRES ON THE MARKET IN THE EUROPEAN UNION (by weight)
Category Passenger car tyres Vans and light utility vehicles
1Trucks
Range 7 9kg 8 11g 40 75kg 2.5 1000kg
Av.wt. 8kg 9kg 56kg
2NA
Units/t 125 111 18 -
(load index of <121 and >121
Other (bicycle, motorcycle, agriculture, construction,mining)
1 2
the average of the category trucks reflects the preponderance of smaller truck tyres. NA: Information no available.
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
3. Development of tyre recycling in Europe
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
3. Development of tyre recycling n Europe
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
3. Development of tyre recycling in Europe Consumption in Europe 2009
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
3. Development of tyre recycling n Europe
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
4. 1. Models for the scrap recycling processing in EU Tax System: The manufacturer / importer is dependent on a government tax The state is responsible for the operation of the old tire
2.
Free Market System: Each party in the chain is responsible for the fulfillment of the law All parties shall cooperate in the preparation for the market prices
3.
Producer Responsability:
The manufacturers / importers create a "contribution" in the product sold and are responsible for the management of scrap tires. Usually cares about an association that is organized by the manufacturers: an integrated system
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
4. Models for the scrap recycling processing in EU
The three models in Europe
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
5. Function of an integrated system
The tire manufacturers and / or importers are based on the integrated system
The amounts per tire may look like this (example from Norway): - Truck tires: 5.60, -
- Car tires: 0.90, - - Other than 35, -
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
5. Function of an integrated system Tire manufacturers inEurope
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
5. Function of an integrated system Responsibilities of the integrated system Management of scrap tire recycling in each country: - Certify recyclers - Distribution of used tires to recyclers (usually every two years for tenders) - Collector of contributions with the tire manufacturers - Control of inputs and outputs of waste tires in each country: everything produced or imported, must be 100% recyclable and can no longer be landfilled
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
5. Function of an integrated system Expiration of the recycling chain 1. Collection of used tires
2. Sorting of tires
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
5. Function of an integrated system Expiration of the recycling chain 3. Shredding and separation of rubber, steel and textile.
4. Fine grinding of the rubber tire and sale of various products produced.
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
6. Tyre Recycling World Wide
The scrap tire industry is driven by regulation. Timing of regulatory introduction dictates the current state of development. USA and Japan have the more developed end product market, but Europe is rising quickly . Russia and Australia seems to start on regulation programs, incipient industry. South America, Asia and Africa are in developing stages
Profitability of the industry remains the most immediate concern.
USA: http://www.rma.org/scrap_tires/state_issues/ Australia: http://www.environment.gov.au/settlements/waste/tyres/index.html Japan: http://www.j-sra.jp/ Report 2003 http://www.irevna.com/pdf/Industry%20report.pdf
Introduction to the tyre recycling world
Thank you for your attention!
JORDI HUGUET jordi.huguet@comsaemte.com
You might also like
- Project Plan Tyre RecyclingDocument4 pagesProject Plan Tyre RecyclingAjit Chauhan100% (3)
- Old Report by US Env TiresDocument119 pagesOld Report by US Env Tiressunilkrawal9778No ratings yet
- Tyre ProcessingDocument6 pagesTyre ProcessingapplesbyNo ratings yet
- Waste Management: Maciej Sienkiewicz, Justyna Kucinska-Lipka, Helena Janik, Adolf BalasDocument10 pagesWaste Management: Maciej Sienkiewicz, Justyna Kucinska-Lipka, Helena Janik, Adolf BalasGina MoraNo ratings yet
- Study On End-Of-Life Tires ELTs Recycling StrategyDocument11 pagesStudy On End-Of-Life Tires ELTs Recycling StrategyFrancesco PiccinonnaNo ratings yet
- Tyre Chips RecyclingDocument14 pagesTyre Chips RecyclingtarunNo ratings yet
- Tire Recycling - Tural Ahmedli, Kamala HajiyevaDocument19 pagesTire Recycling - Tural Ahmedli, Kamala HajiyevaEziz IskenderovNo ratings yet
- Ts-4 Scrap Tires To Crumb Rubber Feasibility Analysis For Processing FacilitiesDocument19 pagesTs-4 Scrap Tires To Crumb Rubber Feasibility Analysis For Processing Facilities陳0鴻50% (2)
- Stone Paper vs. Real PaperDocument2 pagesStone Paper vs. Real PaperSappi HoustonNo ratings yet
- Tyre Industry: Presentation By: Mukesh Kumar M.B.A. IBDocument19 pagesTyre Industry: Presentation By: Mukesh Kumar M.B.A. IBMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Waste Tyre Reycling Project Report BriefDocument10 pagesWaste Tyre Reycling Project Report BriefVijay SinghNo ratings yet
- KRUPA Falcon Tyre ProjectDocument59 pagesKRUPA Falcon Tyre ProjectIsmail DesaiNo ratings yet
- Study On Auto Bricks Bangladesh Perspect PDFDocument26 pagesStudy On Auto Bricks Bangladesh Perspect PDFMohiminul Khan100% (1)
- Keshav Enterprise MailDocument11 pagesKeshav Enterprise MailSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cement ManufacturingDocument4 pagesCement Manufacturinghijzain100% (1)
- Technical Report For Tyre Crumb and ShredDocument47 pagesTechnical Report For Tyre Crumb and ShredMurugan ManiNo ratings yet
- Indian Infrastructure FinancingDocument30 pagesIndian Infrastructure FinancingHilly ObscureNo ratings yet
- Ginning From LummusDocument8 pagesGinning From LummusGizachew ZelekeNo ratings yet
- Package Cement Fugitive EmissionDocument192 pagesPackage Cement Fugitive EmissionJay KumarNo ratings yet
- LafargeDocument7 pagesLafargeSrashti SuneriyaNo ratings yet
- Study On Retreaders Attitude Towards Midas Treads in Terms of Marketing Mix".Document59 pagesStudy On Retreaders Attitude Towards Midas Treads in Terms of Marketing Mix".anju100% (4)
- Bestway Cement IndustryDocument11 pagesBestway Cement IndustrySaadQureshi0% (1)
- Tire RecyclingDocument7 pagesTire RecyclingAbu BakrNo ratings yet
- Tyre Manufaturing ProcessDocument15 pagesTyre Manufaturing ProcessSyama TripathyNo ratings yet
- Mining, Communities and Sustainable Development - Case Study Hima CementDocument16 pagesMining, Communities and Sustainable Development - Case Study Hima CementAfrican Centre for Media Excellence100% (1)
- Presentation On Ambuja CementDocument47 pagesPresentation On Ambuja CementParesh BhuriaNo ratings yet
- Refuse Disposal Management in PCMCDocument6 pagesRefuse Disposal Management in PCMCGRD JournalsNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument4 pagesProfileAsanga HarshanNo ratings yet
- Final Report Cement Industry PakistanDocument126 pagesFinal Report Cement Industry PakistanAdeeba Hussam100% (10)
- TKM Sustainability Report 2011Document86 pagesTKM Sustainability Report 2011naz-92No ratings yet
- Organizational Structure in Textile SectorDocument15 pagesOrganizational Structure in Textile SectorMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- A Report On The Winter Internship at Apollo Tyre1Document17 pagesA Report On The Winter Internship at Apollo Tyre1Krishnakumar ErattemparambilNo ratings yet
- CementDocument18 pagesCementrazanymNo ratings yet
- Cement Industries in PakistanDocument20 pagesCement Industries in PakistanAli Imran Jalali100% (1)
- Tire Recycling IndustryDocument110 pagesTire Recycling IndustryBen GuhmanNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of Pakistan Cement IndustryDocument42 pagesCritical Analysis of Pakistan Cement Industrytanseer_0493% (15)
- The Impact of Energy Crisis On Textile SectorDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Energy Crisis On Textile SectorAymen SaeedNo ratings yet
- 3ton Tire Recycling Rubber Powder Plant Xinda 170713Document3 pages3ton Tire Recycling Rubber Powder Plant Xinda 170713William Gómez SuárezNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of DG Khan Cement FactoryDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of DG Khan Cement FactoryMuhammad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Cement Industry PakistanDocument23 pagesCement Industry Pakistansyed usman wazir100% (27)
- Extrusion Equipment: Tire and Rubber IndustryDocument36 pagesExtrusion Equipment: Tire and Rubber Industrythiagorep17No ratings yet
- Topic: "A Study On Productivity Efficiency of Textile Industry of India"Document5 pagesTopic: "A Study On Productivity Efficiency of Textile Industry of India"Divya SinghNo ratings yet
- A Look Into The Indian Cement Industry PresentationDocument27 pagesA Look Into The Indian Cement Industry PresentationsumitkumareceNo ratings yet
- Project of Waste Tyre RecycleDocument17 pagesProject of Waste Tyre RecycleAkbar RazaNo ratings yet
- Fauji CementDocument3 pagesFauji CementHaroon RashidNo ratings yet
- Lafarge Ravena Modernization FEISDocument97 pagesLafarge Ravena Modernization FEISLafargeRavenaFactsNo ratings yet
- Cement ManualDocument52 pagesCement Manualemad sabriNo ratings yet
- Alternative Fuels For The Cement Industry PDFDocument6 pagesAlternative Fuels For The Cement Industry PDFPopovac NetNo ratings yet
- Leather Exporting PDFDocument20 pagesLeather Exporting PDFAyman BrohiNo ratings yet
- Disposal of Waste Tyres For Energy Recovery and Safe Environment-ReviewDocument18 pagesDisposal of Waste Tyres For Energy Recovery and Safe Environment-ReviewshlogonNo ratings yet
- Deliverable 2.1.1 ROADTIREDocument66 pagesDeliverable 2.1.1 ROADTIREImml TasbiNo ratings yet
- Locale of The Work Conducted: PreludeDocument26 pagesLocale of The Work Conducted: PreludeAshira GordhanNo ratings yet
- Tyres As An Alternative PDFDocument2 pagesTyres As An Alternative PDF1977julNo ratings yet
- Tyre Recycling in The European Union: Dr. Valerie L. Shulman Secretary General, ETRADocument42 pagesTyre Recycling in The European Union: Dr. Valerie L. Shulman Secretary General, ETRAAnmol GuptaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of TyreDocument20 pagesLife Cycle of TyreDarshal Nahar100% (1)
- Tire RecyclingDocument16 pagesTire RecyclingDeepak KewatNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Rubber TIre Recycling MachineDocument31 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Rubber TIre Recycling Machinerynsasa191No ratings yet
- The Automobile Industry - : Environmental IssuesDocument33 pagesThe Automobile Industry - : Environmental IssuesArnika KarekarNo ratings yet
- Tyre Flows Recycling AnalysisDocument27 pagesTyre Flows Recycling AnalysisMohammed AlnahhalNo ratings yet
- Tyre Recycling. 2 ENGDocument18 pagesTyre Recycling. 2 ENGsbyketNo ratings yet
- Block-1 Communication IGNOUDocument81 pagesBlock-1 Communication IGNOUr kumarNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis Enzymes Maths and Write Up Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesDiffusion Osmosis Enzymes Maths and Write Up Exam QuestionsArooj AbidNo ratings yet
- Mudbound: Virgil Williams and Dee ReesDocument125 pagesMudbound: Virgil Williams and Dee Reesmohan kumarNo ratings yet
- Posterior Cranial Fossa Anesthetic ManagementDocument48 pagesPosterior Cranial Fossa Anesthetic ManagementDivya Rekha KolliNo ratings yet
- Methods in Enzymology - Recombinant DNADocument565 pagesMethods in Enzymology - Recombinant DNALathifa Aisyah AnisNo ratings yet
- DentinogenesisDocument32 pagesDentinogenesisNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Planificare 3 FairylandDocument6 pagesPlanificare 3 FairylandBulf Adela MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cooking MethodsDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Cooking MethodsAizelle Guerrero Santiago100% (1)
- Unleash Your Inner Millionaire: Achieve Wealth, Success, and Prosperity by Reprogramming Your Subconscious MindDocument20 pagesUnleash Your Inner Millionaire: Achieve Wealth, Success, and Prosperity by Reprogramming Your Subconscious MindMariana PopaNo ratings yet
- MigrationDocument6 pagesMigrationMaria Isabel PerezHernandezNo ratings yet
- Provisional DismissalDocument1 pageProvisional DismissalMyra CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Klarna: Klarna A Company Valued To Be 5.5 Billion and 8 Most Valued Fintech Company in The WorldDocument1 pageKlarna: Klarna A Company Valued To Be 5.5 Billion and 8 Most Valued Fintech Company in The WorldChetan NarasannavarNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Requirements of Special Land Use PermitDocument1 pageChecklist of Requirements of Special Land Use PermitAnghelita ManaloNo ratings yet
- Romeuf Et Al., 1995Document18 pagesRomeuf Et Al., 1995David Montaño CoronelNo ratings yet
- (Nand Flash Memory) HY27 (U - S) S (08 - 16) 121M (Rev0.6)Document43 pages(Nand Flash Memory) HY27 (U - S) S (08 - 16) 121M (Rev0.6)jituelectNo ratings yet
- Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesDocument5 pagesSpaces For Conflict and ControversiesVistalNo ratings yet
- Brief For Community Housing ProjectDocument5 pagesBrief For Community Housing ProjectPatric LimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Microeconomics - Group 10Document13 pagesAssignment 1: Microeconomics - Group 10Hải LêNo ratings yet
- Ode To The West Wind Text and AnalysisDocument7 pagesOde To The West Wind Text and AnalysisAbdullah HamzaNo ratings yet
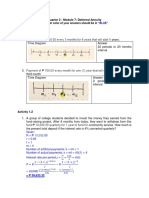
- What's More: Quarter 2 - Module 7: Deferred AnnuityDocument4 pagesWhat's More: Quarter 2 - Module 7: Deferred AnnuityChelsea NicoleNo ratings yet
- Network Monitoring & Forensics: Jim IrvingDocument102 pagesNetwork Monitoring & Forensics: Jim IrvingKarel GoldmannNo ratings yet
- Easy Pork Schnitzel: With Apple Parmesan Salad & Smokey AioliDocument2 pagesEasy Pork Schnitzel: With Apple Parmesan Salad & Smokey Aioliclarkpd6No ratings yet
- Rapidjson Library ManualDocument79 pagesRapidjson Library ManualSai Kumar KvNo ratings yet
- 47 Vocabulary Worksheets, Answers at End - Higher GradesDocument51 pages47 Vocabulary Worksheets, Answers at End - Higher GradesAya Osman 7KNo ratings yet
- Building Envelop Design GuidDocument195 pagesBuilding Envelop Design GuidCarlos Iriondo100% (1)
- HSG 9 Tienganh 2019Document7 pagesHSG 9 Tienganh 2019Bảo HoàngNo ratings yet
- The Role of Religion in The Causation of Global Conflict & Peace and Other Related Issues Regarding Conflict ResolutionDocument11 pagesThe Role of Religion in The Causation of Global Conflict & Peace and Other Related Issues Regarding Conflict ResolutionlorenNo ratings yet
- Manuel Vs AlfecheDocument2 pagesManuel Vs AlfecheGrace0% (1)
- NURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubricDocument7 pagesNURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubriccmpNo ratings yet
- Literature StudyDocument20 pagesLiterature StudyAnn NambiaparambilNo ratings yet