Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peters Presentation
Uploaded by
CCSMATH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views14 pagesThe document defines the inverse secant function and sketches its graph. It has a range of [0, π/2) and (π/2, π] and a domain of [-∞, -1] ∪ [1, ∞). It then evaluates various inverse trigonometric functions without a calculator by relating the inputs to angles on the unit circle based on trigonometric function restrictions established earlier.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines the inverse secant function and sketches its graph. It has a range of [0, π/2) and (π/2, π] and a domain of [-∞, -1] ∪ [1, ∞). It then evaluates various inverse trigonometric functions without a calculator by relating the inputs to angles on the unit circle based on trigonometric function restrictions established earlier.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views14 pagesPeters Presentation
Uploaded by
CCSMATHThe document defines the inverse secant function and sketches its graph. It has a range of [0, π/2) and (π/2, π] and a domain of [-∞, -1] ∪ [1, ∞). It then evaluates various inverse trigonometric functions without a calculator by relating the inputs to angles on the unit circle based on trigonometric function restrictions established earlier.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
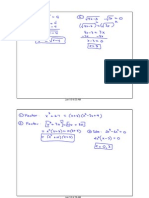
Page 420 #100
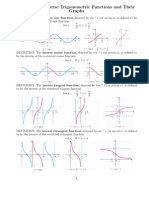
Define the inverse secant function by restricting
the domain of the secant function to the
intervals [0, π/2) and (π/2, π] and sketch its
graph.
First, to make an inverse secant function
graph, you must switch the domain and
the range of the secant function.
The range of secant is (-∞, -1] , [1, ∞)
The domain of secant is x ≠ π/2 + Nπ
You are given a restricted domain of
secant, [0, π/2) and (π/2, π]. This
becomes the range of inverse secant.
The domain of inverse secant is (-∞, -1] ,
[1, ∞)
To find the points on an inverse secant graph, make a y-
x table.
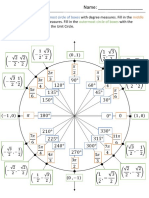
Angles on the unit circle correspond to the y values, and
the x values are the secants at each angle.
y π/6 π/4 π/3 2π/3 3π/4 5π/6 π
x (2√3)/3 √2 2 -2 -√2 -(2√3)/3 -1
This is an inverse
secant function
graph.
Y=arcsec(x) if and only if sec(y) = x
– Range: [0, π/2) and (π/2, π]
– Domain: [-∞ , -1] , [1, ∞)
#102.
Use the results of #99-101 to evaluate the
following without using a calculator.
(a) arcsec √2
(b) arcsec 1
(c) arccot (-√3)
(d) arccsc 2
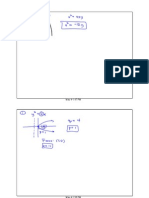
(a) arcsec√2
What angle has a secant of √2?
– Or, more simply, the cosine of 1/(√2)
1/(√2) simplifies to (√2)/2
π/4 on the unit circle has a cosine of
(√2)/2
7π/4 also has a cosine of √2/2, and
therefore a secant of √2.
Refer back to the restrictions on the range
of inverse secant: [0, π/2) and (π/2, π]
7π/4 is greater than π and so exceeds the
restriction.
(b) arcsec 1
Use the same method.
A secant of 1 means the angle also has a
cosine of 1.
0 on the unit circle has a cosine of 1.
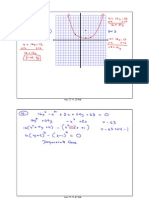
(c) arccot (-√3)
Use the same method.
A cotangent of - √3 means the angle has
a tangent of 1/(- √3).
1/(- √3) simplifies to (- √3)/3
5π/6 on the unit circle has a cotangent of
(-√3)/3.
The answer cannot be 11π/6, although it
also has a cotangent of -√3.
Referring back to problem 99, the
cotangent function is given a restriction on
its domain: (0, π). This means the inverse
cotangent function will have the same
restriction on its range, or y-values.
11π/6 is greater than π, and so exceeds
the restrictions.
(d) arccsc 2
Use the same method.
A cosecant of 2 means the angle has a sin
of ½.
π/6 has a sin of ½, and therefore a
cosecant of 2.
The answer cannot be 5π/6, although it
has a cosecant of 2.
Referring back to problem 101, the
cosecant function is given a restriction of
[- π/2, 0) and (0, π/2]. This means the
inverse cosecant function will have the
same restriction on its range.
5π/6 is greater than π/2, and so exceeds
the restrictions.
You might also like
- PC Sin - RuleDocument7 pagesPC Sin - RuleHector R.No ratings yet
- Antenna For All Application by John D. Kraus, 3rd Edt SolutionDocument40 pagesAntenna For All Application by John D. Kraus, 3rd Edt SolutionOmar Muñoz100% (2)
- Solutions Manual For Understanding NMR Spectroscopy 2edDocument128 pagesSolutions Manual For Understanding NMR Spectroscopy 2edscicws1133No ratings yet
- Jackson 9.10, 9.16Document13 pagesJackson 9.10, 9.16razarizvi1No ratings yet
- Filter Design TechniquesDocument124 pagesFilter Design TechniquesNarasimha Sunchu100% (2)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Their GraphsDocument5 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphssanjeev100% (1)
- Geometry Cheat Sheet 4 2d Shapes FormulasDocument2 pagesGeometry Cheat Sheet 4 2d Shapes Formulascheruma100% (1)
- Solution Agrawal Cap 2Document2 pagesSolution Agrawal Cap 2Loren Forero100% (1)
- Lognormal and Normal DistributionsDocument14 pagesLognormal and Normal DistributionsKam Fong ChanNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields Answers To Assignment 3Document5 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields Answers To Assignment 3ShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- (MWRF0012) Simplified Method Eases The Design of Bandpass FiltersDocument4 pages(MWRF0012) Simplified Method Eases The Design of Bandpass Filtersagmnm1962No ratings yet
- AP SolnDocument4 pagesAP SolnSajad VmNo ratings yet
- 4-7 Inverse Trig FunctionsDocument17 pages4-7 Inverse Trig Functionsprasarnboon0% (1)
- Derivative of Arcsecant (Why The Absolute Value)Document4 pagesDerivative of Arcsecant (Why The Absolute Value)avaquizzerNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Solutions: 1 Jackson 1.3Document5 pagesHomework 1 Solutions: 1 Jackson 1.3ahsanqauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Quantization Noise in DSPDocument31 pagesChapter 7 - Quantization Noise in DSPSarah KumakoNo ratings yet
- Study of Second Order NetworksDocument20 pagesStudy of Second Order NetworksSahilNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus-I: Note: 1. If K ( 0) Is The Curvature of A Curve at P, Then The RadiusDocument28 pagesDifferential Calculus-I: Note: 1. If K ( 0) Is The Curvature of A Curve at P, Then The RadiustechzonesNo ratings yet
- Images De-Noising With Mapshrink Estimate and Dual-Threshold in Curvelet DomainDocument5 pagesImages De-Noising With Mapshrink Estimate and Dual-Threshold in Curvelet DomainjebileeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Student ENE423Document14 pagesLecture 3 Student ENE423reraisinNo ratings yet
- Proiect AnteneDocument20 pagesProiect AnteneAndrei DuțanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Applications of Definite IntegralsDocument26 pagesChapter-2: Applications of Definite IntegralsfarihaNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Wave GuideDocument6 pagesCylindrical Wave Guidea4jabsiNo ratings yet
- Physics Quest HW 2bDocument3 pagesPhysics Quest HW 2bFuriFuriNo ratings yet
- PHY103 MidSem SolutionsDocument9 pagesPHY103 MidSem SolutionsShreyaNo ratings yet
- Learning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4Document8 pagesLearning Worksheet - Q2 - Module 4JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- MA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Document6 pagesMA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Bilguun BatboldNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2014 Paper Solutions by AakashDocument29 pagesJEE Advanced 2014 Paper Solutions by AakashAnweshaBoseNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2014 Question Paper Solutions by Aakash InstituteDocument29 pagesJEE Advanced 2014 Question Paper Solutions by Aakash InstituteAnweshaBoseNo ratings yet
- Parametric Equations of CurvesDocument20 pagesParametric Equations of CurvesCedric JosefNo ratings yet
- The Normal and Lognormal Distributions: John NorstadDocument14 pagesThe Normal and Lognormal Distributions: John NorstadkalichkoNo ratings yet
- F07 Hw02aDocument13 pagesF07 Hw02aRanjana Rani DasNo ratings yet
- Multi Scalar Multiplication For Recursive SNARKs and MoreDocument16 pagesMulti Scalar Multiplication For Recursive SNARKs and Moreeth everNo ratings yet
- Phan Tich Va Thiet Ke Giai Thuat Sanjeev Arora Lec2 Karger S Min Cut Algorithm (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Document5 pagesPhan Tich Va Thiet Ke Giai Thuat Sanjeev Arora Lec2 Karger S Min Cut Algorithm (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Trí Thức NguyenNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Beam Vibration: Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument4 pagesFinite Element Beam Vibration: Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Manufacturing EngineeringSyafiq ShaffiaiNo ratings yet
- MaxwellDocument6 pagesMaxwelljulianoeqxNo ratings yet
- Fractional Rectangular Cavity Resonator: Progress in Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 9, 69-82, 2008Document14 pagesFractional Rectangular Cavity Resonator: Progress in Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 9, 69-82, 2008Palash SwarnakarNo ratings yet
- MTH101 Grand Quiz Question Collection Grand Quiz Preparation 2021Document12 pagesMTH101 Grand Quiz Question Collection Grand Quiz Preparation 2021Abdullah Al-hijaziNo ratings yet
- Graph of Cosecant and Secant Function BY: Group 2Document13 pagesGraph of Cosecant and Secant Function BY: Group 2Lucelyn Lugas CapoyNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Beam and Laser Beam Parameters (Knife-Edge)Document14 pagesGaussian Beam and Laser Beam Parameters (Knife-Edge)Dev JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Mat1503 A05Document29 pagesMat1503 A05Duncan Jäger DMninetynineNo ratings yet
- Some Useful Integrals of Exponential Functions: Michael FowlerDocument6 pagesSome Useful Integrals of Exponential Functions: Michael FowlerSunny HungNo ratings yet
- Mmpe Smith OriDocument59 pagesMmpe Smith OriKhalif KeningganNo ratings yet
- TE Radiation ModeDocument6 pagesTE Radiation ModeLaxmanNo ratings yet
- TMM - Chapter 2Document18 pagesTMM - Chapter 2Ahmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Antennas: - Radiated Power - Radiation PatternDocument15 pagesAntennas: - Radiated Power - Radiation Patternankittripathi5No ratings yet
- Sol 1Document25 pagesSol 1Kyoung Su Lee0% (1)
- Thin Airfoil TheoryDocument10 pagesThin Airfoil TheoryAli Al-hamalyNo ratings yet
- Assignment For LecturesDocument16 pagesAssignment For LecturesDeepak JainNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 3 (Ackermanf)Document20 pagesCapitulo 3 (Ackermanf)Gabyta XikitaaNo ratings yet
- V V π 2 1 V π 2 V π 2Document3 pagesV V π 2 1 V π 2 V π 2jisteeleNo ratings yet
- A Simple Control Arithmetic of Step Wave Cascaded Multilevel Inverter With Different Voltage StepDocument5 pagesA Simple Control Arithmetic of Step Wave Cascaded Multilevel Inverter With Different Voltage StepSumit HarwaniNo ratings yet
- Exam MSC Atm09 SolnsDocument7 pagesExam MSC Atm09 SolnswhateverNo ratings yet
- 316s Answer06 PDFDocument3 pages316s Answer06 PDFjisteeleNo ratings yet
- Ua1 TN 82 24Document8 pagesUa1 TN 82 24Riyan AlviNo ratings yet
- Torus Magnetic MomentDocument6 pagesTorus Magnetic MomentBen WaterglowNo ratings yet
- Design of FIR Filters With Better Performance Using Z-WindowDocument5 pagesDesign of FIR Filters With Better Performance Using Z-WindowJoshua DusariNo ratings yet
- Jun 9 9:20 AMDocument10 pagesJun 9 9:20 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 20 10alg1Document8 pages5 20 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 18 10alg1Document8 pages5 18 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- Jun 7 8:17 AMDocument8 pagesJun 7 8:17 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- Jun 10 9:03 AMDocument12 pagesJun 10 9:03 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 19 10pc11Document5 pages5 19 10pc11CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 17 10pc11Document7 pages5 17 10pc11CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 7 10alg1Document2 pages5 7 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 7 10pc12Document4 pages5 7 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 11 10alg1Document5 pages5 11 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 28 10alg1Document3 pages4 28 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 17 10pc12Document4 pages5 17 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 13 10alg1Document3 pages5 13 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 6 10pc11Document3 pages5 6 10pc11CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 10 10pc11Document3 pages5 10 10pc11CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- May 1 10:03 AMDocument6 pagesMay 1 10:03 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 4 10pc12Document7 pages5 4 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 6 10pc12Document4 pages5 6 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 5 10pc12Document7 pages5 5 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- Apr 29 9:40 AMDocument5 pagesApr 29 9:40 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 4 10pc11Document7 pages5 4 10pc11CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 5 5 10alg1Document4 pages5 5 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 26 10alg1Document6 pages4 26 10alg1CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 27 10pc12Document6 pages4 27 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 28 10pc12Document5 pages4 28 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 27 10pc11Document3 pages4 27 10pc11CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- Apr 24 10:06 AMDocument6 pagesApr 24 10:06 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 26 10pc12Document4 pages4 26 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- Apr 27 9:57 AMDocument6 pagesApr 27 9:57 AMCCSMATHNo ratings yet
- 4 20 10pc12Document4 pages4 20 10pc12CCSMATHNo ratings yet
- First of All Draw The Space Diagram, To Some Suitable Scale As Shown in Fig. (A)Document28 pagesFirst of All Draw The Space Diagram, To Some Suitable Scale As Shown in Fig. (A)Surjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- 34 Trigonometry II (MSS)Document28 pages34 Trigonometry II (MSS)Srinivas VamsiNo ratings yet
- Elementary Calculus SMN1014Document3 pagesElementary Calculus SMN1014Arvind RaveeNo ratings yet
- LO: I Can Find The Volume of A CylinderDocument13 pagesLO: I Can Find The Volume of A CylinderNaz OmarNo ratings yet
- Rotation Solution: EXAMPLE 14: A 1200 LB Sled Is Pulled Along ADocument4 pagesRotation Solution: EXAMPLE 14: A 1200 LB Sled Is Pulled Along AJamael AbulaisNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5Document3 pagesProblem Set 5GURUDUTTA PALNo ratings yet
- AdvancedDocument173 pagesAdvancedHein SanNo ratings yet
- Euler Angles 123Document3 pagesEuler Angles 123Rahul KooraNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument16 pagesMotion in A Straight Lineuniverse2010No ratings yet
- Speed QuizDocument2 pagesSpeed QuizKhairi SharifuddinNo ratings yet
- S&L - Lesson 16. Introduction To Setting of CurvesDocument6 pagesS&L - Lesson 16. Introduction To Setting of CurvesEr Jogendra SorenNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 11 FormulaDocument8 pagesPhysics Class 11 FormulaSarthak Kamli100% (1)
- Eotvos EffectDocument5 pagesEotvos Effectjoff_grNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsDocument17 pagesRD Sharma Class 11 Maths Chapter 11 Trigonometric EquationsBhushan kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2peehutyagi06No ratings yet
- Rectangular Pyramid Easy 1Document2 pagesRectangular Pyramid Easy 1Meaza BeleteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Book AnswersDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Book Answersapi-247437524No ratings yet
- Introduction To Trigonometry Class Test - I: Example 9: SolutionDocument1 pageIntroduction To Trigonometry Class Test - I: Example 9: SolutionSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- SAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesSAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric Functionstomcantyyy100% (1)
- Area Activity Sheet - Higher AbilityDocument8 pagesArea Activity Sheet - Higher AbilityJyoti NahataNo ratings yet
- Compound AnglesDocument14 pagesCompound AnglesChainarong TaepanichNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Measurement 063812Document29 pagesChapter 9 Measurement 063812ellenmaejulio280No ratings yet
- Pure Maths Formula SheetDocument20 pagesPure Maths Formula SheetSaifur Rahman Raffael100% (1)
- Degrees & Radians Conversion Practice: Convert Each Degree Measure Into RadiansDocument2 pagesDegrees & Radians Conversion Practice: Convert Each Degree Measure Into Radianscaclubindonesia0% (1)
- Color Unit Circle Quiz KeyDocument1 pageColor Unit Circle Quiz KeyskscribdNo ratings yet
- Kids Math - Finding The Volume of A Cube or BoxDocument6 pagesKids Math - Finding The Volume of A Cube or Boxsathish11407144No ratings yet
- Time Distance and TrainDocument15 pagesTime Distance and Trainimd mdlNo ratings yet
- Worksheet TRGO NB8 Without AnswersDocument2 pagesWorksheet TRGO NB8 Without AnswersathulNo ratings yet