Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Changes in Cancer
Uploaded by
Ruki HartawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetic Changes in Cancer
Uploaded by
Ruki HartawanCopyright:
Available Formats
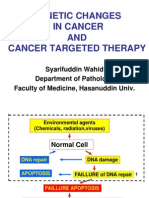
GENETIC CHANGES
IN CANCER
AND
CANCER TARGETED THERAPY
Syarifuddin Wahid
Department of Pathology
Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin Univ.
Normal Cell
DNA damage DNA repair
Environmental agents
(Chemicals, radiation,viruses)
FAILLURE of DNA repair
APOPTOSIS
FAILLURE APOPTOSIS
PERMANENT DNA DAMAGE (MUTATION)
GENETIC AND PHENOTYPIC CHANGES
1
P53 (TP53) Gene
stress of the cell
(anoxia, oncogene expression, and
DNA damage)
Activation of P53
cell cycle stop DNA repair
apoptosis
No mutation/carciogenesis
Inherited Mutation of DNA
Repair Genes and Cancer Risk
Inherited Mutation Cancer Risk
of DNA Repair Genes
DNA mismatch repair HNPCC
Nucleotid excision Skin Cancer
repair.
BRCA1 & BRCA2 Breast Ca.
Mutation in the genome of
Somatic cells
Activation of growth-
promoting oncogenes
Inactivation of
Tumor suppressor genes
Inactivation of gene
regulate apoptosis
Decreased apoptosis
Unregulated cell proliferation
Clonal Expansion
2
3
4
Activation of growth-
promoting oncogenes
INACTIVE
PROTOONCOGENE
MUTATION
(ONE ALLEL)
ACTIVE
ONCOGENE
(CELLULAR
ONCOGENE)
Oncogenes Lesion Cancer
NEU/HER2 Amplification Breast,ovary,stomach (Ad Ca)
H-RAS Point Mutation Colon, lung, pancreas
MYC Translocation Burkitts Lymphoma
RET Rearranggement Thyroid (Ca)
Daerah promoter VEGF manusia
Ket :
a. primer amplikasi dalam
kotak buram, polimorfisme
ditandai dengan angka-angka
dekat dengan tanda panah
(transciption start site). bsaHl
dan BsmFl adalah ensim
pemotong. b Haplotype gen
VEGF, (C) adalah Wild type
promoter
POINT MUTATION
ON VEGF GENE
-460T>C
+405C>G
Protooncogene
Cellular Oncogene
Viral Gene
Carcinogen
(chemical,
viral and
radiation)
Viral Oncogene
Normal production of growth factor
Normal growth
Devective immune survailance
Abnodrmal production of growth factor
Abnormal Growth
NEOPLASM
DNA
Mutation
Inactivation of
Tumor suppressor genes
and gene regulate apoptosis
Active
Genes
Inactive
Genes
MUTATION
(BOTH ALLELS , LOH)
TS Genes Function Cancer
RB Cell cycle Retinoblastoma
TP53 Cell cycle,apoptosis Sarcoma, lymphoma,
(Guardian of the genome) Adeno Ca
BRCA1 DNA repair Breast
MSH2,MLH1 Mismatch repair Colorectal (HNPCC)
DELETION
GROWTH AND
ANTIGROWTH SIGNAL
RETINOBLASTOMA (RB) GENE
RB RB homozygous (Normal)
1
st
mutation
RB rb heterozygous(N& M)
2
nd
mutation
homozygous/ loss of
rb rb heterozygosity
(Retinoblastoma)
(LOH)
(LOH)
MALIGNANT NEOPLASM
Clonal Expansion
Tumor Progression
Invasion and
metastasis
angiogenesis
Escape from immunity
Additional mutation
5
6
7
8
Metastatic subclone
Clonal expantion, growth,
Diversification, angiogenesis
Transformed Cells
Primary Tumor
INVATION
INTRAVASATION
EXTRAVASATION
Metastatic deposit
Angiogenesis
GROWTH
Tumor Cell
embolus
Ecape from imunity
transformation
progression
Proliferation
of genetically
Unstable cells
Tumor cells
variants
heterogeneity
Normal cell
Single
Tumor cell
1 gm
(10
9
cells)
1 kg
(10
12
cells)
30
doublings
10
doublings
Normal Cell
Carcinogen Induced changes
Tumor Cell
variants
Single tumor cell
Nonantigenic
Invasive
Metastatic
Requiring fewer growth factor
Metastases
Normal
Colon
cell
Increased
Cell
growth
Early
Stage
adenoma
Intermediate
Stage
adenoma
Late
Stage
adenoma
Carcinoma
Metastasis
APC gene loss
DNA loses methyl groups
RAS gene mutation
DCC gene loss
TP53 gene loss
PRL3
overexpression
MORPHOLOGIC
CHANGES
GENETIC CHANGES
MULTISTEPS CHANGES
IN COLON CANCER
CANCER TARGETED THERAPY
Tujuan utama:
Menghambat pertumbuhan dan
penyebaran sel tumor dengan
cara memblok signal
pertumbuhan sel tumor atau
menghambat layanan darah ke
jaringan tumor.
Sasaran obat
Molekul spesifik yang:
1. Terlibat dlm proses karsinogenesis,
pertumbuhan dan penyebaran
tumor.
2. Terlibat dalam angiogenesis.
3. Menjadi marker dari sel tumor
bersangkutan.
(Molecularly targeted therapy)
Transformasi: Onkogen HER2
1 = jumlah copy gen
2 = transkripsi mRNA
3 = ekspresi reseptor protein permukaan sel
4 = pelepasan reseptor dari bgn extraselluler
Normal Amplifikasi/Overekspresi
Cytoplasm
HER2 reseptor
protein
Cytoplasmic
membrane
Nukleus
HER2 DNA
HER2
mRNA
1
2
3
4
VEGF
Stem Cell Pro-B Pre-B Immature B
Mature B
Bone Marrow
Peripheral lymphoid
organ or tissue
IgM,IgD
No antigen dependence Self antigen Foreign antigen
Activated B
B CELL DEVELOPMENT
RAG-1 & RAG-2 expression
H chain
H & L chain
CD43+
CD43+
CD19+
CD10+
CD20
B220
CD43+
CD20
IgM(low)
CD43-
CD20
IgM(high)
CD20
IgM(high)
CD20
CD20 CD20 CD20 CD20 CD20
Tipe targeted therapy
1. Fokus pada molekul yang merupa-
kan komponen internal dan fungsi
sel. (Menggunakan molekul kecil yang
dapat mencapai sel dan meng-hambat
fungsi sel dan akhirnya mati).
- Single transduction inhibitor
(Imatinib mesylate, Genefitinib, Laptinib,
HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor),
- Biologic response Modifier Agent
(Denileukin diftitox), dan
- proteosome inhibitor (Bortezomib).
Tipe targeted therapy
2. Fokus pada molekul di bagian luar sel
(membran sel) misalnya reseptor atau molekul
membran lainnya.
(Menggunakan antibodi monoklonal)
mis: Anti HER2, Anti CD20
3. Fokus pada molekul (growh factor) yang ada
dalam sirkulasi
(Menggunakan antibodi monoklonal)
Mis : Anti VEGF
4. Fokus pada gen (Gene therapies).
JENIS TARGETED THERAPY
1. Menggunakan Small Molecule Drug
(SMD)
2. Menggunakan Monoclonal Antibody
(MAB)
3. Menggunakan Gene Therapy
Cara kerja MAB
Menghambat signal pertumbuhan tumor atau
yang memfasilitasi pertumbuhan tumor
Mengikat growth factor atau molekul
lainnya (mis. angiogenesis) yang ada dalam
sirkulasi sehingga tidak bisa binding
dengan reseptornya.
Binding dengan reseptor growth factor
atau angiogenesis sehingga tidak bisa
dicapai oleh growth factor atau molekul
angiogenesis.
Memicu internalisasi reseptor atau
pelepasan reseptor dari membran sel.
Cara kerja MAB
Sebagai pencari sel tumor.
Mengikat molekul yag ada di permukaan sel tumor
sehingga bahan aktip antikanker (kemoterapi atau
radioterapi) yang diikutkan di MAB dapat mencapai
dengan tepat sel tumor. (Mengantar obat
kemoterapi atau radioaktip mencapai target.
Mengefektifkan sistem imun tubuh membunuh
sel tumor (humanized MAB)
Binding dengan protein permukaan (reseptor atau
tumor marker) kemudian berinteraksi dengan
sistem imun tubuh ang akan membunuh sel target.
Memicu apoptosis sel tumor.
Mouse myeloma
Cell line
FUSION
Hybridomas producing
Monoclonal anti-X antibody
Antigen-X
Anti-X antibody-
producing spleen cells
In vitro selection in HAT medium
Clone cells
Screen supernatant for presence of anti-X antibody
MONOCLONAL
ANTIBODY
HUMAN/MOUSE CHIMERIC MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY (HUMANIZED MAB)
Genetic engineering
MONOCLONAL
ANYIBODY-LIKE
MOLECULE
Genetic engineering
Mouse myeloma
Cell line
FUSION
Hybridomas producing
Monoclonal anti-X antibody
Antigen-X
Screen supernatant for presence of anti-X antibody
Clone cells
In vitro selection in HAT medium
Anti-X antibody-
producing spleen cells
MONOCLONAL
ANTIBODY
Parent mouse
antibody
(cdr)
Idiotype
L-Chain
H-Chain
Antigen
Binding Site
Murine
Variable
region
(biru)
Constan
region
(merah)
-s-s-
Fab
papain
Fc
Human constant region
Human constant Fc region
HUMAN/MOUSE CHIMERIC
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
(HUMANIZED MAB)
Gambar 12. Struktur humanized
monoclonal antibody.
Constant region
a.amino manusia
(>90%)
Variable region
a.amino tikus (murin)
(<10%)
HUMAN/MOUSE
CHIMERIC MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
(HUMANIZED MAB)
Keuntungan chimeric antibody
Pembuatan antigen binding site (Fab
variable region) yang spesifik pada mencit
akan menjamin ikatan efektif dengan target
antigen.
Unsur human pada Fc constan region
memungkinkan interaksi lebih efektif dengan
human effector mechanisms dari respon
imun pasien untuk membunuh sel target.
Unsur human pada struktur antibodi di atas
90% memperkecil kemugkinan timbulnya
reaksi penolakan/allergi/syok dari pasien.
Adenoma of increasing size and
degree of dysplasia
Hyperproliperative
epithelium
Invasive carcinoma
P53 mutation
And/or LOH
DC LOH
LOH of other
Genes on 18q
K-ras mutation DNA mutation
DNA methylation
abnormalities
Mismatch repair abnormallities
GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER, 2004.
You might also like
- Genetic Changes in Cancer AND Cancer Targeted TherapyDocument44 pagesGenetic Changes in Cancer AND Cancer Targeted TherapyIcha Nadira100% (1)
- Cancer Genetics IDocument68 pagesCancer Genetics ICarlos Alonso Satornicio MedinaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of NeoplasiaDocument37 pagesMolecular Basis of NeoplasiaRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- OnkologieDocument41 pagesOnkologieNatz BatzNo ratings yet
- 2 BO3 W 2013 Lecture 11Document29 pages2 BO3 W 2013 Lecture 11aqsha.adamhNo ratings yet
- 2 The Nature of HNSCC-WayanS, DRSPBDocument29 pages2 The Nature of HNSCC-WayanS, DRSPBLeise Kestia Rosalyn LimpelehNo ratings yet
- Immunology of CancerDocument48 pagesImmunology of CancerNovia Dwi AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Cancer Perspective and Molecular BasisDocument36 pagesCancer Perspective and Molecular BasisPRAGAATHYRAJANNo ratings yet
- Neoplasma 2 (Karsinogenesis) : Mata KuliahDocument88 pagesNeoplasma 2 (Karsinogenesis) : Mata KuliahWahyu Caesar RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Moleculer Basis of NeoplasiaDocument33 pagesMoleculer Basis of NeoplasiahudaNo ratings yet
- 1 Tumorigenesis, Mutasi, Ketidakstabilan GenetikDocument44 pages1 Tumorigenesis, Mutasi, Ketidakstabilan Genetikanon_945728920No ratings yet
- Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumour Suppressor GeneDocument31 pagesCancer, Oncogenes and Tumour Suppressor GeneWinda Syahfitri HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Fusion Gene in CancerDocument26 pagesFusion Gene in CancerSajjad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Sharealike LicenseDocument49 pagesCreative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Sharealike LicenseMaria Ethel Castillo JamaolNo ratings yet
- Second 5Document7 pagesSecond 5aaajjjaaajjjaaajjjaaajjjaaajjjNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Tumor Biology 2016Document100 pagesKuliah Tumor Biology 2016izulNo ratings yet
- Tumor Markeri - Eng PDFDocument79 pagesTumor Markeri - Eng PDFdr_4uNo ratings yet
- Cancer: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument42 pagesCancer: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarM.PRASAD NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cell BiologyDocument36 pagesMolecular Cell BiologyEda BasarirNo ratings yet
- 13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Document17 pages13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Kw ChanNo ratings yet
- Conceptos Básicos en Biología Tumoral (1) : Dra. Cristina Nadal Oncología Médica Hospital Clínic BarcelonaDocument57 pagesConceptos Básicos en Biología Tumoral (1) : Dra. Cristina Nadal Oncología Médica Hospital Clínic BarcelonarafatrujNo ratings yet
- Cancer CytogeneticsDocument70 pagesCancer CytogeneticsAlina MocanuNo ratings yet
- OncogenesDocument77 pagesOncogenesAnand Reghuvaran100% (3)
- 10ECMDocument49 pages10ECMrameshvibhin poosarlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16-JnuCancer - 複本Document42 pagesChapter 16-JnuCancer - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 CarcinogenesisDocument84 pagesLecture 20 CarcinogenesisMohammad_Islam87100% (1)
- K1-Perspectife, Blok Onk DefiDocument35 pagesK1-Perspectife, Blok Onk Defiparik2321No ratings yet
- OncologyDocument73 pagesOncologymark barcelonaNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument12 pagesReviewapi-3700537No ratings yet
- 59 Genetics of Cancer II Tumor Suppressors and ApoptosisDocument68 pages59 Genetics of Cancer II Tumor Suppressors and ApoptosisLunaLureNo ratings yet
- Review Questions: Cell Cycle Regulation &Document100 pagesReview Questions: Cell Cycle Regulation &jassiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 38 - Neoplasia IVDocument49 pagesLecture 38 - Neoplasia IVapi-3703352100% (1)
- Tumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneDocument61 pagesTumor Suppressor Gene & Proto-OncogeneKartthik ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Genetic Factors in CarcinogenesisDocument40 pagesEnvironmental and Genetic Factors in CarcinogenesisBatool SherbiniNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument51 pagesNeoplasia: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DGokul PoudelNo ratings yet
- Boll Et Al-2023-Scientific ReportsDocument14 pagesBoll Et Al-2023-Scientific ReportsJoy IsmailNo ratings yet
- 10-17-2006 - Tsg-Ym03Document60 pages10-17-2006 - Tsg-Ym03api-3696530No ratings yet
- 4 CarcinogenesisDocument48 pages4 CarcinogenesisDipo Mas SuyudiNo ratings yet
- Current Diagnostic Tests For Colorectal Cancer: Evlina Suzanna, MD, PathDocument87 pagesCurrent Diagnostic Tests For Colorectal Cancer: Evlina Suzanna, MD, PathFaulina Yosia PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Mdfund Unit16chapter14Document43 pagesMdfund Unit16chapter14Abigail LausNo ratings yet
- Lecture #10. The Biology of Cancer, p53Document49 pagesLecture #10. The Biology of Cancer, p53cafemedNo ratings yet
- Cancer: When Good Cells Go BadDocument62 pagesCancer: When Good Cells Go BadEpi Panjaitan100% (1)
- Gene Therapy Where We Are: and Where To Go?Document60 pagesGene Therapy Where We Are: and Where To Go?Faisal GhairatNo ratings yet
- Biology of CancerDocument62 pagesBiology of CancerSavitaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Cancer: Nethravathi R GN113011Document51 pagesMolecular Basis of Cancer: Nethravathi R GN113011manuel1788No ratings yet
- Mecanismos de Resistencia.Document31 pagesMecanismos de Resistencia.Sosígenes Souza. ́.No ratings yet
- Anti-Cancer Drugs : DR - DR Muh Darwin P.SPPD, Khom FK Unlam / Rsud UlinDocument147 pagesAnti-Cancer Drugs : DR - DR Muh Darwin P.SPPD, Khom FK Unlam / Rsud UlinM Iqbal Hisyam QNo ratings yet
- AnticancerDocument78 pagesAnticancerRajkishor GogoiNo ratings yet
- Cancer Genetics and GenomesDocument98 pagesCancer Genetics and GenomesAnonymous HNTNhspNo ratings yet
- Ch7 NeoplasmDocument96 pagesCh7 Neoplasmmormor80No ratings yet
- 12 Biochemical Markers Cancer DetectionDocument17 pages12 Biochemical Markers Cancer DetectionPaulina PaskeviciuteNo ratings yet
- Genetics, Reproduction & Female HealthcareDocument30 pagesGenetics, Reproduction & Female Healthcareronwest1990No ratings yet
- Tumor Suppressor Gene TherapyDocument10 pagesTumor Suppressor Gene TherapyMuhammad Ikram RabbaniNo ratings yet
- CarcinogenesisDocument3 pagesCarcinogenesiskishorkumarn8212No ratings yet
- Tumor Suppressor GenesDocument8 pagesTumor Suppressor GenesamaraadhithiyaNo ratings yet
- A - Murine Cancer ModelsDocument31 pagesA - Murine Cancer ModelsJong de CastroNo ratings yet
- NEOPLASIADocument15 pagesNEOPLASIADr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Dasar Onkologi 27 MeiDocument26 pagesDasar Onkologi 27 MeiSuciLestari LubisNo ratings yet
- 10 SEPT 20 Prof YOGIARTO FINALDocument42 pages10 SEPT 20 Prof YOGIARTO FINALSurya RajNo ratings yet
- Pet Spect MRCCC Siloam Semanggi 26mei2012Document49 pagesPet Spect MRCCC Siloam Semanggi 26mei2012Ruki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Ards PDFDocument20 pagesArds PDFRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Bill Gite Harly 2013Document41 pagesKuliah Bill Gite Harly 2013aisyahmayangwulanNo ratings yet
- DR - Dedi Alita Why Do We Need de ResuscitationDocument31 pagesDR - Dedi Alita Why Do We Need de ResuscitationRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Changes in CancerDocument44 pagesGenetic Changes in CancerRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- 2009 Anesthesia Outside The OpDocument167 pages2009 Anesthesia Outside The Opshinta.shintaNo ratings yet
- Presentation VentiDocument41 pagesPresentation VentiRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- P HighDocument12 pagesP HighRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- 12 Practical Regional Anesthes PDFDocument20 pages12 Practical Regional Anesthes PDFRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Neuralgia Keynote PDFDocument21 pagesCranial Neuralgia Keynote PDFRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Akmal M. Hanif - Atrial Fibrillation GuidelineDocument74 pagesAkmal M. Hanif - Atrial Fibrillation GuidelinesigaretNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Sendi Degenaratif Dan InflamatifDocument36 pagesPenyakit Sendi Degenaratif Dan InflamatifSnakeeyes NonganNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati, DR - DiahDocument42 pagesPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati, DR - DiahYuliana LatifNo ratings yet
- Pedoman Nasional Penanggulangan Tuberkulosis 2007Document168 pagesPedoman Nasional Penanggulangan Tuberkulosis 2007inesia_90210100% (27)
- Dyspnea Prof Menaldi CompressedDocument48 pagesDyspnea Prof Menaldi CompressedRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Pain 2Document106 pagesPain 2She JocelynNo ratings yet
- Persistent Asthma - Prof DR SidhartaniDocument18 pagesPersistent Asthma - Prof DR SidhartaniRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Syndrome DR Hemi SinoritaDocument32 pagesMetabolic Syndrome DR Hemi SinoritaRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Non-Western Medicine Inclusion National Health PlanDocument27 pagesNon-Western Medicine Inclusion National Health PlanRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Laparoscopic Surgery - Najmaldin, GuillouDocument163 pagesA Guide To Laparoscopic Surgery - Najmaldin, GuillougoodforamenNo ratings yet
- Cedera Kepala Presentasi....Document49 pagesCedera Kepala Presentasi....Johan HeriNo ratings yet
- 3 - Guidelines Pleural Effusions UnilateralDocument11 pages3 - Guidelines Pleural Effusions UnilateralRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Buku Bedah UmumDocument126 pagesBuku Bedah UmumSilvia Kamal100% (7)
- MRI From A To ZDocument271 pagesMRI From A To ZGizelle Valim Dos Santos100% (11)
- Hand Book Gastro Ardy MoeftyDocument57 pagesHand Book Gastro Ardy MoeftyRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PicturesDocument474 pagesAnatomy PicturesRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Imaging Techniques and Findings for Head TraumaDocument82 pagesImaging Techniques and Findings for Head TraumaRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- CT BasicsDocument112 pagesCT BasicsPhilippe Q GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Applications in TextilesDocument10 pagesBiotechnology Applications in TextilesDaksh Kumar14% (7)
- Capillarys ImmunotypingDocument62 pagesCapillarys ImmunotypingAbdel Razzak Mikati100% (1)
- Plant Cell CultureDocument8 pagesPlant Cell Culturenurul9535No ratings yet
- Appl Sartobind Virus Purification Removal SL-4038-e06012Document4 pagesAppl Sartobind Virus Purification Removal SL-4038-e06012Yaser WazirNo ratings yet
- 2.03.14 Newcastle DisDocument20 pages2.03.14 Newcastle DisErman Satya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument14 pagesMonoclonal AntibodiesBrigitte ReyesNo ratings yet
- Davis ProjectDocument76 pagesDavis ProjectMuhammad SameerNo ratings yet
- Kim, Minjung Bioen 315 Last HomeworkDocument5 pagesKim, Minjung Bioen 315 Last Homeworkapi-281990237No ratings yet
- Extractables Studies For Single-Use Systems Used in Antibody-Drug Conjugate ManufacturingDocument9 pagesExtractables Studies For Single-Use Systems Used in Antibody-Drug Conjugate ManufacturingAsif MohammedNo ratings yet
- Insert - Elecsys CA 15-3 II.03045838500.V22.enDocument5 pagesInsert - Elecsys CA 15-3 II.03045838500.V22.enLILI DARMAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Design and Production of Bispecific AntibodiesDocument30 pagesDesign and Production of Bispecific AntibodiesAndrei TatomirNo ratings yet
- Sterile Filtration of Highly Concentrated Protein FormulationsDocument11 pagesSterile Filtration of Highly Concentrated Protein FormulationsMohammed Zakiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9A23605 ImmunologyDocument4 pages9A23605 ImmunologysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ImmDocument44 pagesImmMuhammad AdnanNo ratings yet
- One Step HCG Strip Revised 20-8-09Document2 pagesOne Step HCG Strip Revised 20-8-09sabina3163No ratings yet
- BioFactura-CBMS VRP ProposalDocument218 pagesBioFactura-CBMS VRP ProposalpabloNo ratings yet
- Schedule and Abstract CollectionDocument17 pagesSchedule and Abstract CollectionintermountainasmNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal Antibodies The Next Generation April 2010Document10 pagesMonoclonal Antibodies The Next Generation April 2010Al ChevskyNo ratings yet
- The Advent and Rise of Antibody MonoclonalDocument3 pagesThe Advent and Rise of Antibody MonoclonalsarijuicyNo ratings yet
- Biotech Drugs - Biological Therapeutic Agents PDFDocument4 pagesBiotech Drugs - Biological Therapeutic Agents PDFRenan Vieira Zaffanelli SallesNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Project on MedicineDocument14 pagesRecombinant DNA Project on MedicineAyush Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal AntibodyDocument40 pagesMonoclonal AntibodyTamilarasi Sasivarnam100% (1)
- Glycoengineered Antibodies - Towards The Next-Generation of Immunotherapeutics PDFDocument38 pagesGlycoengineered Antibodies - Towards The Next-Generation of Immunotherapeutics PDFAndrei TatomirNo ratings yet
- Centrifuges in Pharmaceutical Plants GEA Tcm11 18046Document44 pagesCentrifuges in Pharmaceutical Plants GEA Tcm11 18046N.SRINUVASARAO0% (1)
- Full Download Basic and Applied Concepts of Immunohematology 2nd Edition Blaney Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Basic and Applied Concepts of Immunohematology 2nd Edition Blaney Test Bankjosephefwebb100% (23)
- MSDSDocument4 pagesMSDSkomite k3rsNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Pharmacology: Gayathri Krishna, Vinod Soman Pillai, Mohanan Valiya VeettilDocument11 pagesEuropean Journal of Pharmacology: Gayathri Krishna, Vinod Soman Pillai, Mohanan Valiya VeettilautomationenggNo ratings yet
- H088Document2,013 pagesH088Rodrigo Mansilla OjedaNo ratings yet
- MCQS of BiotechnologyDocument16 pagesMCQS of BiotechnologyMuhammad Bilal Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 30 - Evaluation of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Membrane Test Assays For The Forensic Identification of Seminal Fluid PDFDocument4 pages30 - Evaluation of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Membrane Test Assays For The Forensic Identification of Seminal Fluid PDFMN IrshadNo ratings yet