Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nomenclatural: Regenerator
Uploaded by
Aitesam Ul Haq Mughal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesThis document contains definitions for various nomenclatural terms used in analyzing Stirling engines, including dimensions, volumes, temperatures, efficiencies, and other metrics. Key terms defined include basic heat input, basic power output, brake efficiency, crank angle, dead volumes, diameters, effective temperatures, fractions of gas inventory, heat exchanger lengths and temperatures, indicated efficiency, net heat input, pressures, regenerator parameters, strokes, temperatures, volumes, and wall thicknesses. Over 50 parameters are defined for evaluating Stirling engine performance and design.
Original Description:
stirling engine
Original Title
Nomenclature
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains definitions for various nomenclatural terms used in analyzing Stirling engines, including dimensions, volumes, temperatures, efficiencies, and other metrics. Key terms defined include basic heat input, basic power output, brake efficiency, crank angle, dead volumes, diameters, effective temperatures, fractions of gas inventory, heat exchanger lengths and temperatures, indicated efficiency, net heat input, pressures, regenerator parameters, strokes, temperatures, volumes, and wall thicknesses. Over 50 parameters are defined for evaluating Stirling engine performance and design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesNomenclatural: Regenerator
Uploaded by
Aitesam Ul Haq MughalThis document contains definitions for various nomenclatural terms used in analyzing Stirling engines, including dimensions, volumes, temperatures, efficiencies, and other metrics. Key terms defined include basic heat input, basic power output, brake efficiency, crank angle, dead volumes, diameters, effective temperatures, fractions of gas inventory, heat exchanger lengths and temperatures, indicated efficiency, net heat input, pressures, regenerator parameters, strokes, temperatures, volumes, and wall thicknesses. Over 50 parameters are defined for evaluating Stirling engine performance and design.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Nomenclatural
AHG: Single Annulus heater gap thickness, cm
APR: Atmospheric pressure, Pa
BHI: Basic heat input, watt
BPO: Basic Power Output from Stirling Engine before losses are deducted, watt
BRE: Brake efficiency, %
CA: Crank angle, degree
CDV: Cold dead volume, cm
3
CLV: Cold live volume, cm
3
CPR: Calculated pressure for given TAMP at given angle CA, MPa
CR: Crank radius, cm
CRL: Connecting rod length, cm
CV: Cold volume at angle CA, cm
3
DCC: Diameter of Compression Cold space, cm
DDC: Diameter of displacer cylinder, cm
DEC: Diameter of engine cylinder, cm
DEH: Diameter of expansion hot space, cm
DER: Diameter of Each regenerator, cm
DGT: Displacer Gap thickness, cm
DID: Internal Diameter of displacer, cm
DVR: Reduced dead volume
ECDC: Extra cold dead volume besides that in gas cooler, cm
3
EF: Engine frequency, cycles/sec
EFRC: Effective flow rate of gas into cold space, g/sec
EFRH: Effective flow rate of gas into hot space, g/sec
EFTC: Effective fraction of total cycle time steady flow passes in one dimension through cooler
EFTH: Effective fraction of total cycle time steady flow passes in one dimension through the heater
EFTR: Effective fraction of total cycle time steady flow passes in one dimension through the
regenerator
EFTR1: Effective fraction of cycle time steady mass flow moves out the hot space
EFTR2: Effective fraction of cycle time steady mass flow moves into the hot space
EFTR3: Effective fraction of cycle time steady mass flow moves out the cold space
EFTR4: Effective fraction of cycle time steady mass flow moves into the cold space
EHDH: Extra hot dead volume besides that in gas heater, cm
3
ERT: Effective regenerator temperature, K
ETC: Effective temperature in cold compression space, k
ETH: Effective temperature in hot expansion space, K
FIC: Fraction of gas inventory in cold space
FICMAX: Maximum in FC during cycle
FICMIN: Minimum in FC during cycle
FIF: Filler factor (fraction of regenerator volume filled with solid)
FIH: Fraction of gas inventory in hot space
FIHMAX: Maximum in FIH during cycle
FIHMIN: Minimum in FIH during cycle
g: Gravitational acceleration , m/sec
2
HDV: Hot dead volume, cm
3
HLHT: Heated length of each heater tube, cm
HLV: Hot live volume, cm
3
HSIT: Heat sink metal temperature, K
HSOT: Heat source metal temperature, K
HV: Hot volume at angle CA, cm
3
IEF: Indicated efficiency, %
INR: Intermediate ratio
IPO: Indicated Power, watt
LD: Length of displacer, cm
LEC: Length of expansion cylinder, cm
LOR: Length of regenerator, cm
M: Molecular weight of working gas
m: Working gas inventory, grams
MCP: Minimum cycle pressure, MPa
MEP: Maximum Engine pressure, MPa
MPC: Mean pressure for cycle, MPa
MS: Mesh size, wires per cm
n: Constant
NHI: Net heat input, watt
NN: Nusselt Number
NPO: Net power, watt
NR: No. of regenerator per unit
NSL: No. of screen layers
ODE: Outer diameter of expansion cylinder, cm
PA: Phase Angle, degree
PR: Pressure at angle CA for MR=1, MPa
R: Universal gas constant, J/ (K*mole)
RDV: Regenerator dead volume
RT: Ratio of temperature
RV: Ratio of volume
SCC: Stroke of compression cold piston, cm
SEA: Angle used in Schmidt Equation
SEH: Stroke of expansion hot piston, cm
SOD: Stroke of displacer, cm
TAMP: Time average mean pressure
TDV: Total Dead volume, cm
3
THWS: Thickness of wires in screen, cm
TLV: Total Live volume, cm
3
TV: Total gas volume at angle CA
WI: Work for one increment, J
WT1: Wall thickness of displacer, cm
WT2: Wall thickness of cylinder, cm
You might also like
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Technical Dairy: 1-Boiler and Auxillaries Main BoilerDocument59 pagesTechnical Dairy: 1-Boiler and Auxillaries Main Boilersuleman247No ratings yet
- Fired Heater - 2013 FW TalkDocument38 pagesFired Heater - 2013 FW TalkSong Hoe100% (2)
- Date Time: Technical Audit Study of Old Power Plants at BangladeshDocument3 pagesDate Time: Technical Audit Study of Old Power Plants at BangladeshASHUTOSH RANJANNo ratings yet
- Understanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersFrom EverandUnderstanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Heat Exchanger Design Aircooled V7.1: File: Untitled - Edr Date: 8/15/2011 Time: 12:00:35 PMDocument26 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Aircooled V7.1: File: Untitled - Edr Date: 8/15/2011 Time: 12:00:35 PMEhsan MoemeniNo ratings yet
- Test Sheet For Fresh Water GeneratorDocument1 pageTest Sheet For Fresh Water GeneratorBHASKAR HALDAR100% (1)
- Process Calculations For DesignDocument26 pagesProcess Calculations For DesignOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Heating Coil Sizing For Fuel Oil TankDocument2 pagesHeating Coil Sizing For Fuel Oil TankAhmed Mujtaba93% (14)
- Calculated Primary AirDocument1 pageCalculated Primary AirBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab - NGS (1) (2) - YathinDocument48 pagesHeat Transfer Lab - NGS (1) (2) - Yathinswaroopdash.201me256No ratings yet
- Air Cooler - DesignDocument7 pagesAir Cooler - Designkarthipetro100% (1)
- Service PerformanceDocument1 pageService PerformancewalleyranNo ratings yet
- Jord1v BNBF NDocument1 pageJord1v BNBF NkamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Air Pipe SizeDocument6 pagesCalculation of Air Pipe SizePhyu Mar Thein Kyaw100% (1)
- Ariel Performance Software DescriptionDocument8 pagesAriel Performance Software Descriptionmichaelxiao100% (2)
- Thermal Relief Therm - VTDocument6 pagesThermal Relief Therm - VTRafael ReyesNo ratings yet
- MTU 20V4000 L33 Technical Data SheetDocument8 pagesMTU 20V4000 L33 Technical Data SheetB-ENERGY INVESTMENTNo ratings yet
- Aircool AnalysisDocument7 pagesAircool AnalysisFilipus JulianNo ratings yet
- Ac Test RigDocument7 pagesAc Test Riggopal dasNo ratings yet
- Burner CalculationDocument6 pagesBurner CalculationAnonymous 3ESYcrKP100% (4)
- Engine Room Ventilation - Calculation PDFDocument2 pagesEngine Room Ventilation - Calculation PDFSarawut Jae100% (1)
- Turbine Heat Rate and EfficiecyDocument48 pagesTurbine Heat Rate and EfficiecyPralay Raut100% (6)
- Chapter 5 - Equipment Sizing and CostingDocument21 pagesChapter 5 - Equipment Sizing and CostingHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- Half Pipe CalculationDocument3 pagesHalf Pipe CalculationCaptainTonies0% (1)
- Turbo Calc SDocument13 pagesTurbo Calc Spartha6789No ratings yet
- Radiation and Convection Heat TransferDocument5 pagesRadiation and Convection Heat TransfergsdaundhNo ratings yet
- HVAC AcroymnsDocument6 pagesHVAC AcroymnsglenlcyNo ratings yet
- Fan Heat Sink OptimizationDocument6 pagesFan Heat Sink Optimizationrobert s wilsonNo ratings yet
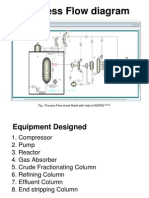
- Process Flow Diagram: Fig: Process Flow Sheet Made With Help of ASPENDocument42 pagesProcess Flow Diagram: Fig: Process Flow Sheet Made With Help of ASPENSwarnim RajNo ratings yet
- Compressors Course-Chapter 3Document19 pagesCompressors Course-Chapter 3Abdallah SayedNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications Scania 176 Kva Natural GasDocument6 pagesTechnical Specifications Scania 176 Kva Natural GasTomas Leon JuliaNo ratings yet
- 920 KVA Data SheetDocument3 pages920 KVA Data SheetPriyanathan ThayalanNo ratings yet
- DEWALT HVACR Professional Reference Master EditionDocument24 pagesDEWALT HVACR Professional Reference Master EditionLorenc Hysa100% (1)
- Refer This Lab Manual For Preparing Your Experimental Work.Document22 pagesRefer This Lab Manual For Preparing Your Experimental Work.Prem ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument13 pagesBoilerEDUARDONo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredDocument5 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredkarthickNo ratings yet
- Boilers Chimney Draft and Breeching CalculationDocument15 pagesBoilers Chimney Draft and Breeching Calculationjoabjim8392No ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Daftar SimbolDocument12 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Daftar SimbolAnggiRaymondPardedeNo ratings yet
- Transportasi Fluida (Compressible Fluid-Fan Blower)Document36 pagesTransportasi Fluida (Compressible Fluid-Fan Blower)Evia Salma ZauridaNo ratings yet
- 8.assessment of CompresorsDocument14 pages8.assessment of CompresorsPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Lesson 16 Combustor Design ConsiderationsDocument45 pagesLesson 16 Combustor Design ConsiderationsRicardo Carpio OssesNo ratings yet
- Vessel - Vertical Sizing - IPunitsDocument25 pagesVessel - Vertical Sizing - IPunitsAnders FTNo ratings yet
- Tube Calculation: Cylinder DataDocument1 pageTube Calculation: Cylinder DataMamank Ira SudrajatNo ratings yet
- GE Cycles Lecture Info 2009Document18 pagesGE Cycles Lecture Info 2009Sayantan Datta Gupta100% (1)
- Process Design ConditionsDocument8 pagesProcess Design ConditionsGerald RahanraNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument22 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignRupack HalderNo ratings yet
- 1000 KVA-datasheetDocument4 pages1000 KVA-datasheetPriyanathan ThayalanNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ake Int Absolute Stage Last of Pressure e Arg Disch AbsoluteDocument8 pagesPressure Ake Int Absolute Stage Last of Pressure e Arg Disch Absolutemasih tadayonNo ratings yet
- Design HeatexchangerDocument15 pagesDesign HeatexchangerMayurMahajan100% (1)
- HE Design CalculationDocument4 pagesHE Design CalculationkishoreprithikaNo ratings yet
- HVAC Calculation Engine Room Airflow CapacityDocument2 pagesHVAC Calculation Engine Room Airflow Capacityiqbal_syawalNo ratings yet
- PressorsDocument8 pagesPressorsManoj MisraNo ratings yet
- FW HeaterDocument93 pagesFW HeateridigitiNo ratings yet
- MeteringDocument38 pagesMeteringm.shehreyar.khan100% (1)
- Nandpur: Gas Field, OgdclDocument5 pagesNandpur: Gas Field, OgdclAsad Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Tle Reviewer LDocument5 pagesTle Reviewer LmaryjeandolinoNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter: Encotec Energy (India) Pvt. LTDDocument5 pagesCover Letter: Encotec Energy (India) Pvt. LTDmalhi16001No ratings yet
- Electronic Controlled Fuel SystemDocument34 pagesElectronic Controlled Fuel SystemMohamed ZakiNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Surface TensionDocument104 pagesCeramic Surface TensionIvan RodrigoNo ratings yet
- CIFOZ Congress 2018: Presentation by Infrastructure Development Bank of Zimbabwe (IDBZ)Document20 pagesCIFOZ Congress 2018: Presentation by Infrastructure Development Bank of Zimbabwe (IDBZ)eddinsonNo ratings yet
- Wall Panel SystemsDocument19 pagesWall Panel SystemsLaura Sacdalan94% (17)
- STEAG Presentation 29Document30 pagesSTEAG Presentation 29vamsiklNo ratings yet
- ExtrusionDocument12 pagesExtrusionNitesh YadavNo ratings yet
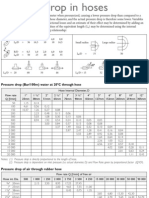
- Pressure Drop Table For HosesDocument1 pagePressure Drop Table For Hosesparthasarathyk69@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Get Back To Balance: Unbalanced Rotors Can Damage More Than Just BearingsDocument2 pagesGet Back To Balance: Unbalanced Rotors Can Damage More Than Just BearingsAnonymous PVXBGg9TNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6 7 8 Water TurbinesDocument69 pagesExperiment No. 6 7 8 Water TurbinesMilon MirdhaNo ratings yet
- 3 Band Graphic Equalizer CircuitDocument3 pages3 Band Graphic Equalizer CircuitNur Bazilah NordinNo ratings yet
- Seminar PPT On Green ConcreteDocument16 pagesSeminar PPT On Green ConcreteSandeep Meena75% (8)
- In Ar Y: LCD Monitor CCFL Inverter ControllerDocument11 pagesIn Ar Y: LCD Monitor CCFL Inverter ControlleraladinthewizardNo ratings yet
- How Does Variable Turbine Geometry WorkDocument3 pagesHow Does Variable Turbine Geometry WorkRowan CorneliusNo ratings yet
- XFEM Analysis of A Plate With An Edge Crack PDFDocument14 pagesXFEM Analysis of A Plate With An Edge Crack PDFNagaraj RamachandrappaNo ratings yet
- Philips Professional Lighting Solutions SouthAfrica 2012 PDFDocument89 pagesPhilips Professional Lighting Solutions SouthAfrica 2012 PDFMilica LolićNo ratings yet
- HIPOT TestingDocument4 pagesHIPOT Testingparuchurivenkat5272100% (1)
- Sour Water Stripper: Our ExperienceDocument2 pagesSour Water Stripper: Our Experiencevarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Brochure 2023Document2 pagesBrochure 2023SuganthiVasanNo ratings yet
- Kvc-Uv: Capture Jet Hood With Supply Air and UV TechnologyDocument9 pagesKvc-Uv: Capture Jet Hood With Supply Air and UV Technologying_ballesterosNo ratings yet
- Drill LineDocument16 pagesDrill Linemech133No ratings yet
- Impact of Industrialization On Region and Community WelfareDocument7 pagesImpact of Industrialization On Region and Community WelfareTejaswini RastogiNo ratings yet
- INSPECT AND SERVICE COOLING SYSTEMS - QuizDocument8 pagesINSPECT AND SERVICE COOLING SYSTEMS - QuizbalalaNo ratings yet
- Plant Location, Its Selection Criteria, and Factors Affecting Plant LocationDocument5 pagesPlant Location, Its Selection Criteria, and Factors Affecting Plant LocationEngr Muhammad Ehsan100% (1)
- Sony Kdl-40nx710 - kdl40nx711 & Kdl-46nx710 - kdl46nx711 Ch. Az1-H LCD TV SMDocument40 pagesSony Kdl-40nx710 - kdl40nx711 & Kdl-46nx710 - kdl46nx711 Ch. Az1-H LCD TV SMedsel72No ratings yet
- Direct To HomeDocument22 pagesDirect To HomeShashank DubeyNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Pure and Applied PhysicsDocument383 pagesDictionary of Pure and Applied PhysicsInam Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Summary: American Prometheus: The Triumph and Tragedy of J. Robert Oppenheimer by Kai Bird & Martin J. Sherwin: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: American Prometheus: The Triumph and Tragedy of J. Robert Oppenheimer by Kai Bird & Martin J. Sherwin: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (159)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)