Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tissues
Uploaded by
meemansa12Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tissues
Uploaded by
meemansa12Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2
Tissues
Tissues are the group of cells that work together to perform a particular function
Cells give rise to tissues and an organ system is formed by many tissues. When
inter related organs work in a coordinated manner, they form an organ system.
Many organ systems are present in the body of an organism
Species, populations, communities, ecosystem, biome and finally biosphere are
the higher levels of organization.
Plant Tissues
On the basis of the dividing capacity, plant tissues are of two types:
Meristematic
Permanent
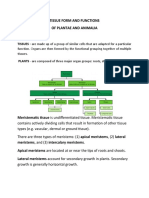
Meristematic Tissues - Consist of actively-dividing cells. Meristematic tissues
are of three types:
Apical Meristem - Present at the growing tips of stems and roots.
Their function is to increase the length of stems and roots
Intercalary Meristem - Present at the base of leaves or
internodes.They are useful for the longitudinal growth of plants
Lateral Meristem - Present on the lateral sides of the stems and roots.
they help to increase the thickness of stems and roots.
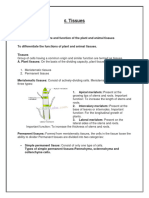
Permanent Tissues - Formed from meristematic tissues; lose the ability to
divide.
Permanent tissues are divided into two categories:
Simple Permanent - Consist of only one type of cells.Types of simple
permanent tissues:
1. Parenchyma - Composed of unspecialised living cells with
relatively thin cell walls
2. Collenchyma - Composed of living and elongated cells with cell
walls irregularly thickened at the corners
3. Sclerenchyma - Composed of long, narrow, and thick-walled
cells. This tissue is made up of dead cells and there are no
intercellular spaces.
4. Protective tissues - Epidermis and cork
Complex Permanent - Made up of more than one type of cells. Types
of complex permanent tissues:
1. Xylem Conducts water and minerals from the roots to the
different parts of the plant. It is composed of four different types
of cells Tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and fibres
2. Phloem Conducts food material from the leaves to the different
parts of the plant. It is composed of four different types of cells
Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem
fibres
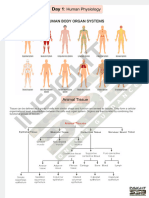
Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are classified into four types based on the functions they perform:
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
Epithelial Tissues - Form the covering of the external surfaces, internal
cavities, and organs of the animal body. Various types of epithelial tissues:
Simple Squamous Epithelium - Single layer of flat cells that are
located in Lining of the mouth, oesophagus, lung alveoli, etc.
Cuboidal Epithelium - Consists of cube-like cells that are located in
lining of kidney tubules and ducts of the salivary glands
Columnar Epithelium - Consists of elongated or column-like cells.
They are located in the inner lining of the intestine and gut.
Glandular Epithelium - Consists of multicellular glands
Connective Tissues - Specialised to connect various body organs
Various types of connective tissues:
Areolar Tissue - Found in the skin and muscles, around the blood
vessels, nerves, etc.
Adipose Tissue - Acts as the storage site of fats; found between the
internal organs and below the skin; acts as an insulator for the body
Dense Regular Connective Tissue - Main components are tendons
and ligaments; tendons connect muscles to bones, while ligaments
connect two bones together
Skeletal Tissue - Main components of skeletal tissues are cartilage and
bone. Cartilage consists of cartilage cells arranged in fluid filled space
called lacunae. In this various salts of calcium and phosphorus are
present which makes the bones hard and strong.
Fluid Tissue - Blood and lymph are the connective tissue present in
animals. Blood consists of matrix called plasma in which blood cell
(RBC, WBC, platelets). Lymph can be described as the blood without
RBCs.
Muscular Tissues - Main function of muscular tissues is to provide movement
to the body
Muscular tissues are of three types:
Striated Muscles or Skeletal Muscles or Voluntary Muscles -
Cells are cylindrical, un-branched, and multinucleate
Smooth Muscles or Involuntary Muscles - Cells are long, spindle-
shaped, and possess a single nucleus
Cardiac Muscles or Involuntary Muscles - Cells are cylindrical,
branched, and uninucleate
Nervous Tissues - Present in the brain, spinal cord, nerves
Neuron - Cells of the nervous tissue
A neuron consists of a cell body, an axon, and a dendrite
Contribute to this Revision Note:
If you find anything of importance missing from this note, email it to us at revision-notes@meritnation.com,
and well add it to this note under your name!
You might also like
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesvaidika.soni12009No ratings yet
- NCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)Document4 pagesNCERT Chapter 6: Tissues (Plant Tissue and Animal Tissue)Chetan Gautam100% (1)
- TissuesDocument16 pagesTissuesDiya sashiniNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 TissuesDocument20 pagesChapter 06 TissuesManushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: TissuesDocument20 pagesChapter - 6: TissuesMadhuriNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument74 pagesTissuesMonica Sree100% (1)
- Tissue Class 9Document40 pagesTissue Class 9Extra AccountNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesChapter 6 Tissues Class 9anmolmuskan2020No ratings yet
- (Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesDocument20 pages(Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- IX 6 TissuesDocument20 pagesIX 6 Tissuesvaishnav.shrot777No ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 - Tissues - Class Ix - ScienceDocument20 pagesChapter - 6 - Tissues - Class Ix - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: TissuesDocument20 pagesChapter - 6: Tissueskrista leeNo ratings yet
- Tip Growth Girth: Is Stem Bark ForDocument4 pagesTip Growth Girth: Is Stem Bark ForSarvesh SinghNo ratings yet
- RudrakshDocument3 pagesRudrakshAmartyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesAbhishek100% (1)
- Tissue SystemDocument41 pagesTissue Systemrahul royNo ratings yet
- 6 TissuesDocument20 pages6 TissuesSarika NiranjaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Cell Types and TissuesDocument36 pagesLesson 4 Cell Types and TissuesKathline Joy DacilloNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- Cell TissuesDocument28 pagesCell TissuesStifany Dianne VillasNo ratings yet
- TISSUE FORM AND-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesTISSUE FORM AND-WPS OfficeBasser EsmaelNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9Document13 pagesTissues Class 9Richa Nawani KaushikNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues NotesHarshitNo ratings yet
- Different Kind of Tissues in Plant and AnimalsDocument15 pagesDifferent Kind of Tissues in Plant and AnimalsKeerti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1Document6 pagesPlant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1PawanNo ratings yet
- Tissues NTBDocument39 pagesTissues NTBAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissue 6 MARCH 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument11 pagesPlant and Animal Tissue 6 MARCH 2013: Lesson Descriptiondeepa100% (1)
- 642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueDocument11 pages642020112334AM-Class 9 Biology Notes-Chapter-6 Plant TissueL Sri Madhi100% (1)
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Tissue Systems - STD 9Document14 pagesTissue and Tissue Systems - STD 9Syamala Natarajan100% (1)
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues Noteskapil100% (1)
- Plant & Animal TissueDocument39 pagesPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Tissues: M.Daisy PrasanthiDocument39 pagesTissues: M.Daisy PrasanthiDinakarKonda100% (1)
- General Biology IIDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument13 pagesTissuesAvika Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Tissues: Facts That Matter TissuesDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Tissues: Facts That Matter TissuesmarioNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Tissues NotesDocument6 pagesTissues NotesYashvi PatelNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument3 pagesTissues NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of TissuesDocument24 pagesDifferent Types of Tissuesneha_asNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument18 pagesTissueSatyam PrakashNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document44 pagesGen Bio 2Reymark Dao-anNo ratings yet
- Tissue Form & FunctionDocument14 pagesTissue Form & FunctionLi KimNo ratings yet
- Tissues Just NotesDocument20 pagesTissues Just NotesSudesh Sharma100% (1)
- 9 SC TissueDocument8 pages9 SC Tissuevishesh1997No ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- MoreDocument6 pagesMoreLenovoNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsDocument10 pagesBiology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsFatima Zulqarnain100% (1)
- Study of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifDocument60 pagesStudy of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifEntirety 4uNo ratings yet
- Organization of Living BeingsDocument6 pagesOrganization of Living BeingsSanhitha RameshNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of AnimalsDocument41 pagesParts and Functions of AnimalsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Tissue Notes 9Document7 pagesTissue Notes 9Priyad MundadaNo ratings yet
- Cell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesCell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationSyuri MustikaNo ratings yet