Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electronic Circuits I (3-0-3) - 3 Credits Catalog Data
Uploaded by
أحمد السايس0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views3 pagessyllabus
Original Title
EE220
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsyllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views3 pagesElectronic Circuits I (3-0-3) - 3 Credits Catalog Data
Uploaded by
أحمد السايسsyllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Jordan University of Science and Technology
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department
EE220-Electronic Circuits I Electrical Engineering Department
EE220 Electronic Circuits I
Electronic circuits I (303) 3 credits
Semiconductor materials; intrinsic, N-type, and P-type semiconductor; carriers; density of state
and Fermi function; Distribution of carriers; conductivity and drift current; Diffusion current;
Einstein relationship; PN junction; depletion region characteristics ; forward and reverse biasing;
diode I-V characteristics; diode circuits and applications; bipolar junction transistor: theory , DC
biasing, and symmetrical swing; field effect transistor: theory, DC biasing, and symmetrical
swing.
Catalog
Data
Pre-requisites: 242100
Textbook
R. F. Pierret and G. W. Gerold, Modular series on Solid State Devices: Semiconductor
Fundamentals, Secomd edition, Addison-wesley, 1989.
G. W. Gerold and R. F. Pierret, Modular series on Solid State Devices: The PN Junction
Diode, Secomd edition, Addison-wesley, 1989.
D. Neamen, Microelectronics Circuits Analysis and Design, Third edition, McGraw-Hill,
2007.
Reference
1-D.L. Schilling and C. Belove, Electronic Circuits: Discrete and Integrated, Third Edition,
McGraw-Hill,, 1989.
2- A. S. Sedra and K.C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits, Fourth Edition, Oxford University,
1998.
3- T.L. Floyd, Electronic Devices, Second Edition,Merrill, 1988.
4- J. Millman, Microelectronics: Digital and Analog Circuits and Systems,First Edition,
McGraw-Hill, 1979.
Coordinator Dr.........................
Course
Objectives
1. Understand semiconductor fundamentals.
2. Understand the thoery and statics of PN junction diode
3. Understand small signal and large signal models of diode and ability to analyze diode
circuits.
4. Understand theory , DC models, and biasing of bipolar junction transistors.
5. Understand theory , DC models, and biasing of field effect transistors.
Pre-Requisites by Topic 1. Circuits theory
Topics
1. Semiconductor materials 4 Hours
2. intrinsic, N-type, and P-type
semiconductor
3 Hours
3. carriers 1 Hours
4. density of state and Fermi function 2 Hours
5. Distribution of carriers 2 Hours
6. conductivity and drift current 2 Hours
7. Diffusion current 2 Hours
8. PN junction 2 Hours
9. depletion region characteristics 3 Hours
10. forward and reverse biasing; diode I-V
characteristics
1 Hours
11. diode circuits and applications 6 Hours
12. bipolar junction transistor: theory ,
DC biasing, and symmetrical
swing
7 Hours
13. field effect transistor: theory, DC biasing,
and symmetrical swing.
7 Hours
Jordan University of Science and Technology
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department
EE220-Electronic Circuits I Electrical Engineering Department
Computer Usage PSpice Circuits Simulation
Engineering Science 3.0 Credits Estimated
Content
Engineering Design 0.0 Credits
Prepared by Dr. NEdal Al-Ababneh.
Date 2008.12.09
Jordan University of Science and Technology
Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department
EE220- Electronic Circuits I Electrical Engineering Department
Mapping of course (EE220) objectives to program outcomes
Program outcomes
Course Objective
Delivery
Methods
Assessment
Methods
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k)
1. Understand semiconductor fundamentals.
Lectures,
tutorials.
Homework,
quizzes,
Exams.
X X X
2. Understand the thoery and statics of PN junction diode
Lectures,
tutorials.
Homework,
quizzes,
Exams.
X X X
3. Understand small signal and large signal models of diode and ability
to analyze diode circuits.
Lectures,
tutorials.
Homework,
quizzes,
Exams.
X X X
4. Understand theory , DC models, and biasing of bipolar junction
transistors.
Lectures,
tutorials.
Homework,
quizzes,
Exams.
X X X
5. Understand theory , DC models, and biasing of field effect
transistors.
Lectures,
tutorials.
Homework,
quizzes,
Exams.
X X X
ABET a-k Engineering and Technology program outcomes
(a) An ability to apply knowledge of
mathematics, science, and engineering
(b) An ability to design and conduct
experiments, to analyze and interpret
data
(c) An ability to design a system,
component, or process to meet desired
needs
(d) An ability to function on multi-
disciplinary teams
(e) An ability to identify, formulate,
and solve engineering problems
(f) An understanding of professional and
ethical responsibility
(g) An ability to communicate effectively
(h) The broad education necessary to
understand the impact of engineering
solutions in a global and societal
context
(i) A recognition of the need for, and an
ability to engage in life-long
learning
(j) A knowledge of contemporary issues
(k) An ability to use the techniques,
skills, and modern engineering tools
necessary for engineering practice
You might also like
- EE 211 CHAPTER 2 Part1Document14 pagesEE 211 CHAPTER 2 Part1RickNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Floyd 7th Edition Solution ManualDocument171 pagesElectronic Devices Floyd 7th Edition Solution Manualعبدالرحمن المحماديNo ratings yet
- Ementa Elec2104Document5 pagesEmenta Elec2104David AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- IES - Syllabus PDFDocument3 pagesIES - Syllabus PDFGulzar AhamdNo ratings yet
- Syll 3315 Fall 18Document4 pagesSyll 3315 Fall 18gigemjuanNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering SyllabusDocument3 pagesElectronics & Telecommunication Engineering SyllabusArizulIslamNo ratings yet
- ELE 211 Fall10 SyllabiDocument4 pagesELE 211 Fall10 Syllabiahmadbashiri5135No ratings yet
- Ee1001 Basic Electrical Engineering 2013 14Document12 pagesEe1001 Basic Electrical Engineering 2013 14002Pradeep002No ratings yet
- Ies Indian Engineering Services Electronics Ece Syllabus General Ability TestDocument3 pagesIes Indian Engineering Services Electronics Ece Syllabus General Ability TestpalleshankerNo ratings yet
- Electronic Science 1Document41 pagesElectronic Science 1Vinit KhaiwalNo ratings yet
- General AbilityDocument3 pagesGeneral Abilitysanketdesai1988No ratings yet
- L01: Introduction To Course: EE510 Semiconductor Device ModellingDocument32 pagesL01: Introduction To Course: EE510 Semiconductor Device Modellingashish kumarNo ratings yet
- ECEN 2250, Introduction To Circuits & Electronics, Fall 2011 - Course Description PDFDocument4 pagesECEN 2250, Introduction To Circuits & Electronics, Fall 2011 - Course Description PDFAllen XuNo ratings yet
- Ee321 ObjectivesDocument3 pagesEe321 ObjectivesJomar DadorNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument1 pageBasic ElectronicsFarhan Ali CheemaNo ratings yet
- NEE 311 (Circuits 1 Lecture)Document6 pagesNEE 311 (Circuits 1 Lecture)Jessica Laine TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Sir Parshurambhau College, Pune (Autonomous) : Shikshana Prasaraka Mandali'sDocument13 pagesSir Parshurambhau College, Pune (Autonomous) : Shikshana Prasaraka Mandali'sprashantsheetalNo ratings yet
- Code Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices L T P C: Applied OpticsDocument6 pagesCode Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices L T P C: Applied OpticssridharchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- EDC-R10 Course TemplateDocument6 pagesEDC-R10 Course Templatekprk414No ratings yet
- IES, IAS Reference Books For GENERAL STUDIES: GeographyDocument11 pagesIES, IAS Reference Books For GENERAL STUDIES: GeographyVenkat ArunNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology, Srinagar Electrical EngineeringDocument33 pagesNational Institute of Technology, Srinagar Electrical Engineeringzahir khNo ratings yet
- Solid State DevicesDocument1 pageSolid State DevicesdeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EceDocument85 pagesSyllabus EceHemanthNo ratings yet
- Transistors by Le CroissetteDocument296 pagesTransistors by Le CroissetteDeepam kulshreshthaNo ratings yet
- 15EE103 Analysis of Electric CircuitsDocument2 pages15EE103 Analysis of Electric CircuitsDhruv KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Electrical CircuitsDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Electrical CircuitsNishant BilurkarNo ratings yet
- Tuneling Resonant DiodeDocument21 pagesTuneling Resonant DiodeYonny NovaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Electronics Engineering - SyllabusDocument2 pagesElements of Electronics Engineering - Syllabusjabefag655No ratings yet
- Course Outline PDFDocument4 pagesCourse Outline PDFMuhammad Hassan JavedNo ratings yet
- ETRX SyllabusDocument52 pagesETRX SyllabusNikhil ChavanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Electromagnetics 2: Course InformationDocument3 pagesEngineering Electromagnetics 2: Course Informationkober2124No ratings yet
- Shri G. S. Institute of Technology & Science: Department of Electronics and InstrumentationDocument4 pagesShri G. S. Institute of Technology & Science: Department of Electronics and Instrumentationakash mishra0% (1)
- Paper - I: General Ability TestDocument4 pagesPaper - I: General Ability TestMerril VincentNo ratings yet
- Rutgers University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Abet Course Syllabus COURSE: 14:332:373Document2 pagesRutgers University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Abet Course Syllabus COURSE: 14:332:373HUANG YINo ratings yet
- 15EE101 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pages15EE101 Basic Electrical EngineeringAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nasim Zafar: COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadDocument43 pagesDr. Nasim Zafar: COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus Islamabadrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument390 pagesAnalog Electronicsrashi1717100% (2)
- Lesson Plan: MagnetismDocument25 pagesLesson Plan: Magnetismjose mirandaNo ratings yet
- Ee 2112Document3 pagesEe 2112api-26484994No ratings yet
- Courses of Study: Shri Mata Vaishno Devi UniversityDocument51 pagesCourses of Study: Shri Mata Vaishno Devi UniversityMadhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Beee Theory (Eet-127)Document3 pagesBeee Theory (Eet-127)QadirNo ratings yet
- Bece203l Circuit-Theory TH 1.0 0 Bece203lDocument3 pagesBece203l Circuit-Theory TH 1.0 0 Bece203lPiranava GuruNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Ph.D. Written Test (Dec 2019) : EE1 (Communication and Signal Processing)Document4 pagesSyllabus For Ph.D. Written Test (Dec 2019) : EE1 (Communication and Signal Processing)samataNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Syllabus: GENERAL ABILITY TEST (Common For All Branches)Document3 pagesElectronics & Telecommunication Engineering Syllabus: GENERAL ABILITY TEST (Common For All Branches)pawantwrNo ratings yet
- Ies Syllabus: Part A: General EnglishDocument4 pagesIes Syllabus: Part A: General EnglishRaj RaushanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices (Book)Document243 pagesElectronic Devices (Book)Shubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- EECS 176 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEECS 176 SyllabusRubin0% (1)
- Passive and Active Metamaterial Constructs and Their Impact On Electrically Small Radiating and Scattering SystemsDocument4 pagesPassive and Active Metamaterial Constructs and Their Impact On Electrically Small Radiating and Scattering SystemsPrinlova PandaNo ratings yet
- Aim and Objective of The Course:: Course Structure Analysis Subject WiseDocument9 pagesAim and Objective of The Course:: Course Structure Analysis Subject WisepriyakanthrNo ratings yet
- Capacitors, Magnetic Circuits, and Transformers, 1964Document366 pagesCapacitors, Magnetic Circuits, and Transformers, 1964Kevin Haworth100% (1)
- Cci 4202 Electronics Course Outline September Decemeber 2022Document6 pagesCci 4202 Electronics Course Outline September Decemeber 2022Blueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Nit 3Document11 pagesNit 3Er Paramjit SinghNo ratings yet
- First-Stage AvDocument19 pagesFirst-Stage AvAbdullah A. JabberNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Notes, Example EtcDocument86 pagesElectric Circuits Notes, Example EtcDamodar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- Physical-ElectronicsDocument5 pagesPhysical-ElectronicsAlena BělaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument16 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical EngineeringBaqir Hassan ShahNo ratings yet
- EDCfinal Copy1Document69 pagesEDCfinal Copy1Andrei OleaNo ratings yet
- UGsyllabus 201819 EIDocument81 pagesUGsyllabus 201819 EINilesh MandowarNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics with Applications to Nanotechnology and Information ScienceFrom EverandQuantum Mechanics with Applications to Nanotechnology and Information ScienceNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- List of Prequalified Manufacturers Suppliers For Distribution Networks Materials - Till 5-MAY 2015Document29 pagesList of Prequalified Manufacturers Suppliers For Distribution Networks Materials - Till 5-MAY 2015أحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- Ee 537 HW 2Document1 pageEe 537 HW 2أحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- Siemens Power System Simulation For Engineers® (Pss/E)Document14 pagesSiemens Power System Simulation For Engineers® (Pss/E)Muhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Brushed DC MotorsDocument103 pagesBrushed DC Motorsأحمد السايسNo ratings yet
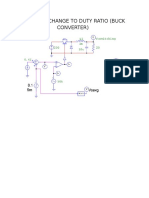
- 0.1 V Step Change To Duty Ratio (Buck Converter)Document2 pages0.1 V Step Change To Duty Ratio (Buck Converter)أحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- CommSys Revision FirstDocument11 pagesCommSys Revision Firstأحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture (9-2 Monday)Document4 pages1st Lecture (9-2 Monday)أحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- Exp 0Document2 pagesExp 0أحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- ABET Syllabus EE531-SummerDocument3 pagesABET Syllabus EE531-Summerأحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- Power MetersDocument8 pagesPower Metersأحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- Book 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitDocument566 pagesBook 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitMAT JIBRUD100% (3)
- This Quiz About The Conventional Single Phase Transformer 1. Fill in The BlankDocument1 pageThis Quiz About The Conventional Single Phase Transformer 1. Fill in The Blankأحمد السايسNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IX (Semiconductor Devices)Document20 pagesUNIT-IX (Semiconductor Devices)mitakar7868No ratings yet
- Eee 2002 Lecture Notes PDFDocument148 pagesEee 2002 Lecture Notes PDFSatadru DasNo ratings yet
- Major Project ReportDocument46 pagesMajor Project ReportAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Semiconductor Diodes: Capacitor Circuit Circuit Test Diode Circuit Electronics Circuits Zener Diode Power DiodeDocument10 pagesMcqs in Semiconductor Diodes: Capacitor Circuit Circuit Test Diode Circuit Electronics Circuits Zener Diode Power DiodeDonna JoveroNo ratings yet
- 2020-10-30SupplementaryEC203EC203-I - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2020-10-30SupplementaryEC203EC203-I - Ktu QbankFayaz aliNo ratings yet
- Eight Practicals Class 12Document27 pagesEight Practicals Class 12Priyanshu jhaNo ratings yet
- IGBT Models PDFDocument52 pagesIGBT Models PDFAris Sid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) of ElectronicsDocument64 pagesMultiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Electronicskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document31 pagesLecture 5Ali MustafaNo ratings yet
- WB WB WB WBD D D D1 1 1 130 30 30 300 0 0 03 3 3 3D D D D: Highvoltagefast-SwitchingnpnpowertransistorDocument5 pagesWB WB WB WBD D D D1 1 1 130 30 30 300 0 0 03 3 3 3D D D D: Highvoltagefast-SwitchingnpnpowertransistorAkmal FirdausNo ratings yet
- Makalah KomputerDocument17 pagesMakalah KomputerMatludin100% (1)
- LED and Photo DiodesDocument12 pagesLED and Photo Diodessarthak MongaNo ratings yet
- Classnotes Chapter 5 Microwavedevices1Document29 pagesClassnotes Chapter 5 Microwavedevices1M Ramesh GowdaNo ratings yet
- Quick Start GuideDocument128 pagesQuick Start GuidePavan KumarNo ratings yet
- AP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusDocument17 pagesAP Eamcet 2019 SyllabusbbbbbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Thermionic EmissionDocument22 pagesThermionic EmissionHazel LawNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics 10ec73 NotesDocument264 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics 10ec73 NotesBhakti KalyankastureNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Solar Power Producing EfficiencyDocument8 pagesCase Study of Solar Power Producing EfficiencyYna San AgustinNo ratings yet
- A 243 MT Exam 20202021 CDocument1 pageA 243 MT Exam 20202021 CIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Diode XPDocument4 pagesDiode XPKaasamHarishKumarNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronic Materials and DevicesDocument16 pagesOptoelectronic Materials and DevicesMar'i MuchammadNo ratings yet
- SimbolDocument26 pagesSimboldrion67No ratings yet
- Chemistry ConceptsDocument60 pagesChemistry ConceptsElla Jean LanoteNo ratings yet
- B.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument87 pagesB.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualSwastika sainNo ratings yet
- Me2255 Electronics and Microprocessor Anna University Question BankDocument6 pagesMe2255 Electronics and Microprocessor Anna University Question BankMayakannan RNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodesDocument26 pagesSemiconductor DiodesAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 PN Junction TutorialDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 PN Junction TutorialasiffarookiNo ratings yet
- Photodiode Investigatory ProjectDocument25 pagesPhotodiode Investigatory ProjectHarshdeep Singh100% (1)