Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Happy New Year 2005 Happy New Year 2005: Free Issue
Uploaded by
mam73Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Happy New Year 2005 Happy New Year 2005: Free Issue
Uploaded by
mam73Copyright:
Available Formats
Free issue Free issue
PAPERWORK
2 10 W A R B I R D S S E R I E S
Happy New Year 2005
Scale 1/48 design by NOBI
For individual use only, under no circumstances can this document be distributed without permission. Copyright 2003-2004
1 / 4
PAPERWORK
2 10 W A R B I R D S S E R I E S
Hawker Seafury
The Hawker Sea Fury Carrier borne fighter-bomber was the British Fleet Air
Arm's last piston-engined fighter, developed during WWII it did not see
service with the Fleet Air Arm until after the war. It was arguably the
fastest piston powered aircraft ever manufactured
.
It was a development from the Hawker Tempest, itself a development of the
Hawker Typhoon. Originally, the Hawker Fury was designed by Sidney Camm in
1942 under F.2/43 specification, to provide the RAF with a lightweight
replacement for the Tempest II.
On 23 June, 1942, Luftwaffe Pilot Oberleutnant Arnim Faber erroneously
landed his Focke-Wulf Fw 190A-3 fighter at RAF Pembrey, apparently having
mistaken this airfield for a Luftwaffe channel coast airfield. The British were
thereby presented with a working example of the Fw 190 fighter, which had
been giving the RAF an extremely difficult time. The Hawker Fury design was
a direct result of the examination of Faber's Fw 190A-3. Examination of
Faber's aircraft was largely responsible for the preparation of Specification
F.6/42, which called for a new, high-performance fighter.
The design was modified in 1943 to meet a Royal Navy specification (N.7/43)
for a carrier-based interceptor and named the Hawker Sea Fury. Hawker was
designated to work on the land-based version, and responsibility for the naval
conversion was assigned to Boulton-Paul Aircraft Ltd. of Wolverhampton.
Early in 1944, a revised naval specification, N.22/43, supplanted N.7/43. and
in April 1944 contracts were placed for 200 F.2/43 planes for the RAF and
200 N.22/43 planes for the Fleet Air Arm. The first Sea Fury prototype,
SR661, flew on 21 February, 1945. It was powered by a Centaurus XII engine
driving a four-bladed propeller. This airplane had a deck arrester hook under
the rudder, but retained fixed wings. The second Sea Fury prototype, SR666,
was powered by a Centaurus XV driving a five-bladed propeller and was a
fully navalized aircraft with folding wings. The prototype Sea Fury SR661 was
subsequently tested for its suitability as a naval fighter, and in deck landing
trials, at the A&AEE Boscombe Down in May 1945. Tests were still underway
as the Japanese surrendered in August 1945.
With the end of the Second World War, the RAF cancelled all production
contracts for the Fury, deciding to concentrate all of its future efforts on
jet fighters. The Royal Navy reduced its order for Sea Furies to 100 aircraft,
and canceled the Boulton-Paul contract in its entirety.
The first production aircraft - a Mark 10 which was a carrier-based version,
with folding wings- did not make its initial flight until September 1946.
Although originally intended to serve with both the RAF and FAA, the RAF
order was cancelled at the end of the war. The first deck trials with Sea Fury
TF898 began aboard HMS Victorious during the winter of 1946-47. The Mark
10 was approved for carrier operations in Spring 1947, and five Fleet Air Arm
squadrons were then equipped with the Sea Fury. The Mark 10 was followed
by the Mark 11 fighter-bomber - 615 of these were eventually delivered to the
Navy. It became the Fleet Air Arm's principal single-seat fighter and remained
so until the introduction of the Sea Hawk jet fighter in 1953.
The Sea Fury served throughout the Korean War, replacing the Seafire, which
was not really built for carrier operations, being too fragile.
The Sea Fury was used by the FAA, Canada, Holland, Australia, and other
countries including the Iraq Air Force. A total of 75 Sea Furies served with
the Royal Canadian Navy(R.C.N.) between 1948 and 1956. All flew from the
Aircraft Carrier HMCS Magnificent in 871 squadron.
Versions
Mk.X 50 built, first production variant powered by Centaurus XV
FB.MK 11 First widespread variant, 615 built including 31 for the RAN and
53 for the RCN.
T.Mk 20 60 trainers, 10 of which were later converted to target tugs for
West Germany.
Fleet Air Arm history
Total FAA 1939-1945: 1 (a total 725 built post-war)
First delivered to RN: May 1945 to A&AEE only
First squadron 1939-1945: None 1939-1945
Operational squadron: None in 1939-1945. Saw trials in Oct 1945 and
service from 1947
Last served with RN 1955 - last Sea Fury squadron disbanded
Serials of the Sea Fury 11 were TF956-TF973, TF985-TF999, TG113-TG129, VR918-VR952,
VW224-VW243, VW541-VW590, VW621-VW670, VW691-VW718, VX608-VX643, VX650-
VX696, VX707-VX711, VX724-VX730, VX748-VX764, WF590-WF595, WF610-WF627, WE673-
WE694, WE708-WE736, WE785-WE806, WM472-WM482, WM487-WM495, WG564-WG575,
WG590-WG604, WG621-WG630, WH581-WH594, WH612-WH623, WJ221-WJ248, WH276-
WJ292, WJ294-WJ297, WJ299-WJ301, WN474-WN479, WN484-WN487, and WX627-
WX656.
Scale 1/48 design by NOBI
For individual use only, under no circumstances can this document be distributed without permission. Copyright 2003-2004
2 / 4
PAPERWORK
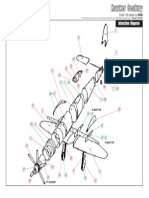
2 10 W A R B I R D S S E R I E S
29
6
5
4
3
2
1
26
27
28
37
8
29
7
29
35
36 32
33
34
Scale 1/48 design by NOBI
For individual use only, under no circumstances can this document be distributed without permission. Copyright 2003-2004
3 / 4
PAPERWORK
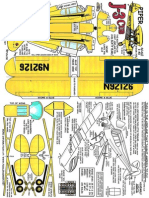
2 10 W A R B I R D S S E R I E S
9*
17
29
29
30
38
21
24
4a* 2a*
11
1a*
25
Scale 1/48 design by NOBI
For individual use only, under no circumstances can this document be distributed without permission. Copyright 2003-2004
4 / 4
PAPERWORK
2 10 W A R B I R D S S E R I E S
Join of part 12
1b*
10
19
31
20*
22
6b*
7b*
16*
15*
14*
13*
18
12*
23*
You might also like
- World War II Nose Art in Color ( PDFDrive )Document51 pagesWorld War II Nose Art in Color ( PDFDrive )BraunGergelyGáborNo ratings yet
- Ing Swin Gar M 1/8" Lite-PlyDocument1 pageIng Swin Gar M 1/8" Lite-Plymam73100% (1)
- Air Forces International 013Document32 pagesAir Forces International 013José Fernandes Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- North American P-51B Mustang's extra fuel tank and increased rangeDocument4 pagesNorth American P-51B Mustang's extra fuel tank and increased rangecastropereira100% (1)
- Fokker DR1 Plans (Parts Templates Non-Tiled)Document1 pageFokker DR1 Plans (Parts Templates Non-Tiled)mam73No ratings yet
- Naval War OOB Battle of Midway 1942Document14 pagesNaval War OOB Battle of Midway 1942Ian IskandarNo ratings yet
- Fokker DR1 Plans (Parts Templates Tiled)Document25 pagesFokker DR1 Plans (Parts Templates Tiled)mam73No ratings yet
- Me 262Document3 pagesMe 262mam73100% (2)
- Me 262Document3 pagesMe 262mam73100% (2)
- Me 262Document3 pagesMe 262mam73100% (2)
- Me 262Document3 pagesMe 262mam73100% (2)
- Me 262Document3 pagesMe 262mam73100% (2)
- German Seaplane Fighters of WWIDocument151 pagesGerman Seaplane Fighters of WWIFrancisco Alvarez100% (4)
- Profile Publications Aircraft 160 - Mitsubishi G3m NellDocument17 pagesProfile Publications Aircraft 160 - Mitsubishi G3m NellMilch&HonigNo ratings yet
- Mustang!: Air ForceDocument7 pagesMustang!: Air ForceJan Gądek100% (1)
- CAC-13 Boomerang ModelDocument8 pagesCAC-13 Boomerang ModelMalyNo ratings yet
- Osprey - Combat Aircraft 118 - He 162 Volksjager Units-36-47 - RotatedDocument12 pagesOsprey - Combat Aircraft 118 - He 162 Volksjager Units-36-47 - Rotatedjose luisNo ratings yet
- IBM-Tandy Guide for Secret Weapons of the LuftwaffeDocument41 pagesIBM-Tandy Guide for Secret Weapons of the Luftwaffetestinghb100% (1)
- Operacion Thesis 1943Document6 pagesOperacion Thesis 1943Anonymous dMF0fis0No ratings yet
- Aero SeriesDocument55 pagesAero Seriesboon1961100% (2)
- Fairey Swordfish MK II ManualDocument42 pagesFairey Swordfish MK II Manualcatdude01100% (1)
- Schiffer Military History - Gabby - A Fighter Pilot's LifeDocument175 pagesSchiffer Military History - Gabby - A Fighter Pilot's LifeNickiedeposieNo ratings yet
- Modeller's Guide To Early P-51 Mustang VariantsDocument10 pagesModeller's Guide To Early P-51 Mustang Variantsseafire47100% (3)
- Safo 150Document36 pagesSafo 150Panos ThalassisNo ratings yet
- ScaleAircraft-Drawings WWII PartBDocument73 pagesScaleAircraft-Drawings WWII PartBAmrutraj Benahal100% (3)
- Fokker DR1 Plans (Assembly Drawing)Document2 pagesFokker DR1 Plans (Assembly Drawing)mam73No ratings yet
- Marek - Grumman F6F 3 Hellcat 2Document4 pagesMarek - Grumman F6F 3 Hellcat 2Sam AE100% (1)
- High Flew The FalconsDocument144 pagesHigh Flew The FalconsАлександр Гуменюк100% (1)
- JAS 39 Park Jet Construction ManualDocument17 pagesJAS 39 Park Jet Construction Manualmam73No ratings yet
- Aeromodelo f15 - Planos para DepronDocument1 pageAeromodelo f15 - Planos para Depronmam73100% (1)
- Vol28 No4Document36 pagesVol28 No4Panos ThalassisNo ratings yet
- Seversky P-35 in DetailDocument10 pagesSeversky P-35 in Detailseafire47100% (1)
- Albatros Productions - Windsock - Datafile No26 - Sopwith F1 CamelDocument40 pagesAlbatros Productions - Windsock - Datafile No26 - Sopwith F1 CamelNickiedeposie100% (1)
- Kampfflieger Blohm Voss BV P.170 1x48Document10 pagesKampfflieger Blohm Voss BV P.170 1x48dandolea75100% (1)
- Warpaint No23 - Fairey GannetDocument46 pagesWarpaint No23 - Fairey GannetNickiedeposieNo ratings yet
- Harry CobbyDocument11 pagesHarry Cobbya1sdfghjklNo ratings yet
- A 36Document8 pagesA 36mam73No ratings yet
- Warbird Profile 1 A-26 B-C InvaderDocument44 pagesWarbird Profile 1 A-26 B-C Invaderamarok61100% (7)
- F-14 Park Jet Construction GuideDocument23 pagesF-14 Park Jet Construction Guidemam73100% (1)
- (ModelArt) XF5U-1 Flying Pancake (1-32)Document24 pages(ModelArt) XF5U-1 Flying Pancake (1-32)cerasella91100% (1)
- The War at Sea 1939-45: Wargaming Rules For WW2 Naval BattlesDocument32 pagesThe War at Sea 1939-45: Wargaming Rules For WW2 Naval BattlesGrumpyOldManNo ratings yet
- VU-7 Provided Services For The Fleet With Navy FJ-4 Fury JetsDocument10 pagesVU-7 Provided Services For The Fleet With Navy FJ-4 Fury JetstrojandlNo ratings yet
- Modelart 1 32 Messerschmitt BF 109Document13 pagesModelart 1 32 Messerschmitt BF 109burtNo ratings yet
- X-15 300 DpiDocument5 pagesX-15 300 Dpimam73100% (1)
- Fighting Colors N 6561 - Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress in Color 86Document33 pagesFighting Colors N 6561 - Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress in Color 86Nathan Blyth100% (1)
- British Airplane - Supermarine SpitfireDocument3 pagesBritish Airplane - Supermarine SpitfireStefan NitulescuNo ratings yet
- FFVS J 22 in DetailDocument3 pagesFFVS J 22 in Detailseafire47100% (1)
- Sea Fury Korean OperationsDocument9 pagesSea Fury Korean Operationshowlettalexander100% (2)
- CA15Document5 pagesCA15mam73No ratings yet
- Aero SeriesDocument55 pagesAero Seriesboon1961100% (1)
- Albatros Productions - Windsock - Datafile Special - Albatros FightersDocument61 pagesAlbatros Productions - Windsock - Datafile Special - Albatros FightersNickiedeposieNo ratings yet
- Re200 Waging Neutrality FlyРаst - May 2016Document5 pagesRe200 Waging Neutrality FlyРаst - May 20165768asd100% (2)
- B 17 Flying Fortress Camo MarkingsDocument24 pagesB 17 Flying Fortress Camo Markingslucylokins100% (4)
- Build a 1/32 Scale P-39F Airacobra Model in 12 StepsDocument15 pagesBuild a 1/32 Scale P-39F Airacobra Model in 12 StepsCristian LacánNo ratings yet
- Small Forces Observer: Vol. 20 No. 3 October 1996Document34 pagesSmall Forces Observer: Vol. 20 No. 3 October 1996Panos ThalassisNo ratings yet
- Messerschmitt 262a-1a and 262B: AVSIM Commercial Aircraft ReviewDocument18 pagesMesserschmitt 262a-1a and 262B: AVSIM Commercial Aircraft ReviewCraciun CosminNo ratings yet
- FlugRevue - Hawker Tornado - TyphoonDocument4 pagesFlugRevue - Hawker Tornado - TyphoonStargazer100% (1)
- Fiat CR 42Document20 pagesFiat CR 42seafire47No ratings yet
- SAMOLOTYDocument28 pagesSAMOLOTYstuleeNo ratings yet
- (Airlife Publishing) (Combat Legend) Ju 87 StukaDocument98 pages(Airlife Publishing) (Combat Legend) Ju 87 Stukazkarlos100% (13)
- Bismarck3den PDFDocument19 pagesBismarck3den PDFi_kostadinovic100% (1)
- Sharkmouth Typhoon: Special EditionDocument4 pagesSharkmouth Typhoon: Special EditionsharkmouthNo ratings yet
- Buffalo 03 PDFDocument4 pagesBuffalo 03 PDFRuben Dario50% (2)
- Russian Battleship Sevastopol (1911)Document5 pagesRussian Battleship Sevastopol (1911)Andrea MatteuzziNo ratings yet
- Desert PreludeDocument18 pagesDesert PreludeOtto Heinrich WehmannNo ratings yet
- MMPBooks LeafletDocument4 pagesMMPBooks LeafletCasemate PublishersNo ratings yet
- Spitfire EE853Document5 pagesSpitfire EE853John Engelsted100% (1)
- 2012 WildEagles June 2012Document17 pages2012 WildEagles June 2012MuazNo ratings yet
- All Ahead Full: World War II Memoirs of an Lsm 215 VeteranFrom EverandAll Ahead Full: World War II Memoirs of an Lsm 215 VeteranNo ratings yet
- Curtiss SB2C HelldiverDocument8 pagesCurtiss SB2C HelldiverAviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Messerschmitt BF 109 The Yugoslav Story Sample PagesDocument18 pagesMesserschmitt BF 109 The Yugoslav Story Sample PagesWerk UdrugaNo ratings yet
- Air Forces International 015Document32 pagesAir Forces International 015José Fernandes Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Tigers Taming The: Force Report Sri Lanka Air ForceDocument5 pagesTigers Taming The: Force Report Sri Lanka Air ForceBharat TailorNo ratings yet
- Dassault Mirage IIIDocument24 pagesDassault Mirage IIIHarry BerryNo ratings yet
- Warbirds Series: Scale 1/48 Design by NOBIDocument1 pageWarbirds Series: Scale 1/48 Design by NOBImam73No ratings yet
- SPM6600 Manual DX6iDocument71 pagesSPM6600 Manual DX6iFelipe Osmar de AvizNo ratings yet
- Aeromodelo Extra 300lxDocument25 pagesAeromodelo Extra 300lxmam73No ratings yet
- Manual Futaba 6exapDocument24 pagesManual Futaba 6exapmam73No ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Instruction Manual For Futaba 6EXAP For Futaba 6EXAP 6-ChannelDocument24 pagesInstruction Manual Instruction Manual For Futaba 6EXAP For Futaba 6EXAP 6-ChannelbarnetladNo ratings yet
- J3cub RGDocument1 pageJ3cub RGmam73No ratings yet
- Gripen Park Jet (Assembly Drawing Tiled)Document2 pagesGripen Park Jet (Assembly Drawing Tiled)mam73No ratings yet
- LiL Lightnin InstructionsDocument12 pagesLiL Lightnin Instructionsmam73No ratings yet
- Hydro FoamyDocument21 pagesHydro Foamymam73No ratings yet
- P-40 29 Inch WSDocument15 pagesP-40 29 Inch WSmam73No ratings yet
- P-38 Plans 8x11Document20 pagesP-38 Plans 8x11mam73No ratings yet
- Gripen GuideDocument16 pagesGripen Guidemam73No ratings yet
- Howard CarpenterDocument1 pageHoward Carpentermam73No ratings yet
- Gripen Park Jet (Assembly Drawing Tiled)Document2 pagesGripen Park Jet (Assembly Drawing Tiled)mam73No ratings yet
- JW E0 OYF9 Ez 0 RIb 91 AZb P3 VC 2 RDocument31 pagesJW E0 OYF9 Ez 0 RIb 91 AZb P3 VC 2 RАлександр 123No ratings yet
- Document summary generatorDocument109 pagesDocument summary generatorMiguel ChavezNo ratings yet
- First Merged8 PDFDocument190 pagesFirst Merged8 PDFAndreea NecutaNo ratings yet
- Q Wawa SQXBDocument109 pagesQ Wawa SQXBMiguel ChavezNo ratings yet
- Entrega 1 - Semana 4 - Fundamentos PsicologiaDocument1,927 pagesEntrega 1 - Semana 4 - Fundamentos Psicologiajoana caterin ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Lamp IranDocument218 pagesLamp IranMuhammad FatihNo ratings yet
- DriverPack Offline PDFDocument929 pagesDriverPack Offline PDFMahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 222Document25 pages222Александр 123No ratings yet
- (HorribleSubs) Kimetsu No Yaiba - 04 (720p) .MKV (1) .TorrentDocument120 pages(HorribleSubs) Kimetsu No Yaiba - 04 (720p) .MKV (1) .TorrentFrizky100% (1)
- M WQXH GN VZGIDocument109 pagesM WQXH GN VZGIMiguelangel ChávezNo ratings yet
- Flight Theory Airframes Engines Hardware Avionics PDFDocument384 pagesFlight Theory Airframes Engines Hardware Avionics PDFcollinsNo ratings yet
- ZR UdncDocument286 pagesZR UdncGrauspn CasselNo ratings yet
- Dparos Iy, Co - Mstfml.Document264 pagesDparos Iy, Co - Mstfml.MocerNo ratings yet
- DHJSWPVGDocument285 pagesDHJSWPVGBiblioteca ICEL Cuautitlán IzcalliNo ratings yet
- XepnbyykcffixjtiitfwDocument124 pagesXepnbyykcffixjtiitfwjeenmathew26No ratings yet
- EsktfgxopusofwqquiipDocument178 pagesEsktfgxopusofwqquiiptbekapsqfnlpmkqddaNo ratings yet
- Alfa BetDocument18 pagesAlfa BetFadhilGhazyNo ratings yet
- BwzuqboxklspcqqmnemyDocument145 pagesBwzuqboxklspcqqmnemydownloader20No ratings yet
- 317 British Aircraft Carriers 1945-2010Document49 pages317 British Aircraft Carriers 1945-2010juanNo ratings yet
- Yuyuigvafaxylm PJ, TrcutuuDocument264 pagesYuyuigvafaxylm PJ, TrcutuuMocerNo ratings yet
- FUzmcf ISWBTDocument109 pagesFUzmcf ISWBTMiguelangel ChávezNo ratings yet
- TXDN JWH DVC HDocument109 pagesTXDN JWH DVC HMiguelangel ChávezNo ratings yet
- IibfzuqfpbvbujjplmzgDocument59 pagesIibfzuqfpbvbujjplmzgkhsfzgndNo ratings yet
- Document title generatorDocument109 pagesDocument title generatorMiguel ChavezNo ratings yet
- LscfktnhqwomrmuzlfsyDocument131 pagesLscfktnhqwomrmuzlfsyj17uag5rtNo ratings yet
- gqptyhqtqqzxofbomdixDocument41 pagesgqptyhqtqqzxofbomdixMarijan KovačNo ratings yet
- ZLV LDR JwgikDocument109 pagesZLV LDR JwgikMiguelangel ChávezNo ratings yet