Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anemias
Uploaded by
doktorcoopCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anemias
Uploaded by
doktorcoopCopyright:
Available Formats
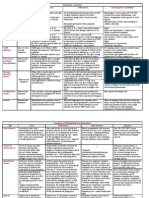
ANEMIAS
MICROCYTIC
Decreased production of Hb cell divides extra time to keep Hb concentration up
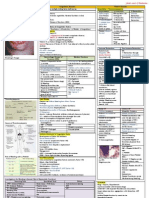
IRON DEFICIENCY
Decreased levels Hb
total iron heme Hb
microcytic anemia
Microcytic, hypochromic, RDW,
ferritin, TIBC, serum iron,
% sat
-bicycle tires!
Infants- breast feeding, Children- diet
Adults- peptic ulcer (males),
menorrhagia (females), Elderly- colon
polyps/carcinoma; esophageal web
-atrophic fissured tongue, spooning
ANEMIA CHRONIC DISEASE Assoc. w/ chronic inflamm or cancer; in
hosp. pts
available iron heme Hb
microcytic anemia
ferritin, TIBC, serum iron,
% sat
Results in production acute phase
reactants from liver, incl. hepcidin
(sequesters iron in storage sites to
prevent bacteria from getting it)
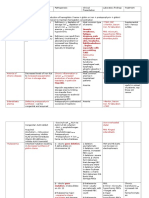
SIDEROBLASTIC ANEMIA
Defective protoporphyrin synthesis
protoporphyrin heme Hb
microcytic anemia
ferritin, TIBC, serum iron,
sat (from iron-overloaded state; iron
laden mitochondria form ring around
nucleus of erythroid precursors (ringer
sideroblasts)
-Congenital defects (ALAs)
-Acquired causes (alcoholism, lead
poisoning b/c inhibits ALAD and
ferrochelatase)
-Lead poisoning: basophilic stippling
THALASSEMIA
Decreased synthesis of globin chains
of Hg
globin Hb microcytic anemia
Microcytic, hypochromic RBCs with
target cells (incr membrane or decr
cytoplasm);
Massive erythroid hyperplasia (crew
cut X-ray, chipmunk facies)
thal = gene deletion
thal = gene mutations (point
mutations in promoter or splicing site)
MACROCYTIC
Upset in production of DNA precursors cell cant divide right amount of times
FOLATE DEFICIENCY
Deficiency in folate from diet,
increased demand, or antagonists
(methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolate
reductase)
Macrocytic RBCs and hypersegmented
neutorphils ( > 5 lobes);
homocysteine and normal
methylmalonic acid; glossitis
Develops within months because
stores limited
-treat with folate
VIT B12 DEFICIENCY
Deficiency B12 due to pernicious
anemia (autoimm destruction of
parietal cells IF deficiency),
pancreatic insuff, rarely diet
Macrocytic RBCs with
hypersegmented neutrophils;
homocysteine and methymalonic
acid; glossitis; subacute combined
degeneration of spinal cored
-Less common and takes years to
develop (large hepatic stores)
-Shilling test to test for IF
-Neuro symptoms not helped with
folatetherefore need to give B12
NORMOCYTIC WITH EXTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS
Increased peripheral destruction
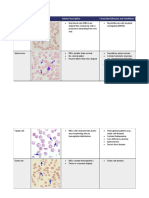
HEREDITARY SPHEROCYTOSIS
Inherited defect of RBC cytoskeleton-
membrane tethering proteins (spectrin,
ankrin, band 3.1) abnormal
blebbing; gets caught in spleen and
then eaten by macrophages anemia
Spherocytes with loss of central palor;
RDW, MCHC; splenomegaly,
jaundice with unconjugated bilirubin &
increase risk bilirubin gallstones;
Howell-Jolly bodies (small dark nuclear
remnants) in asplenic patients
-Diagnosis by osmotic fragility test
(spherocytes dont have enough room
to expand for increase in water)
-Stable course punctuated by aplastic
crisis (parvovirus B19)
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA
Auto recessive mutation in chain of
Hb; single amino acid change replaces
normal glutamic acid (hydrophilic) with
valine (hydrophobic); HbS polymerizes
when deoxygenated; continuous sickle
and de-sickle membrane damage;
(eventual intravasc. hemolysis as well)
Sickle cells
Target cells
Howell-Jolly bodies (due to
autosplenectomy)
Gamma-gandy bodies (in spleen)
-Massive erythroid hyperplasia
-Risk of aplastic crisis (parvovirus B19)
Screen with metabisulfite and
electrophoresis; increased risk for
incfection w/ encapsulated organisms
(pneumonia) must vaccinate;
increased risk of salmonella
osteomyelitis; acute chest syndrome
most common COD; fever in kids bad
HEMOGLOBIN C
Auto recessive mutation of chain of
Hb, glutamic acid replaced by lysine
-HbC crystals seen in RBCs
-Target cells
Mild anemia
NORMOCYTIC WITH INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS
Increased destruction
PAROXYSMAL NOCTURNAL
HEMOGLOBINURIA (PNH)
Acquired defect in myeloid stem cells
resulting in absent GPI; cells
susceptible to destruction by
complement (absence GPI = absence
DAF)
RBCs, WBCs and platelets lysed;
hemoglobinemia, hemoglobinuria (esp.
in morning), hemosiderinuria (days
after hemolysis)
Sucrose test activates complement
-main cause death thrombosis of
hepatic, portal or cerebral veins;
complications include iron def anemia
and AML
GLUCOSE-6_PHOSPHATE
DEHYDROGENASE (G6PD)
DEFICIENCY
X-linked recessive disorders
reduced half-life of G6PD so cells
susceptible to oxidative stress
G6PD NADPH
glutathione oxidative injury by H2O2
intravasc. hemolysis
Heinz bodies (precipitates of denatured
Hb - need special stain) & bite cells
(splenic phagocytes pluck out Heinz
bodies); hemoglobinuria and back pain
Two variants
-African: mildly reduced half-life mild
hemolysis w/ oxidative stress
-Mediterranean: markedly reduced
half-life marked intravascular
hemolysis w/ ox stress
Ox stress caused by fava beans or
drugs (primaquine)
IMMUNE HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA (IHA)
1. Warm: IgG-mediated, extravascular
hemolysis, spherocytes, SLE
2. Cold: IgM-mediated, intravascular
hemolysis, Reynauds, cold agglutinin,
pneumaniae
Polychromasia; spheroctyes; small
fragmented red cell (triangle);
polychromatophilic red cells (big,
bluish); few red cells on smear
Coombs Test (DAT)
-Direct: confirms presence Ab-coated
RBCs
-Indirect: presence of Abs in patients
serum
MICROANGIOPATHIC HEMOLYTIC
ANEMIA
Mechanical trauma intravascular
hemolysis results from vascular
pathology; RBCs destroyed as they
pass thru circulation cheese cutter
Schistocytes (helmet cells) -Occurs with microthrombi (TTP-HUS,
DIC, HELLP), prosthetic heart valves,
and aortic stenosis
-Iron deficiency anemia can occur
MALARIA Infection of RBCs and liver with
Plasmodium transmitted by female
Anopheles mosquito; RBCs rupture as
part of the Plasmodium life cycle
intravasc hemolysis and cyclical fever
Splenomegaly, banana shape P falciparium- daily fever
P vivax and ovale- fever every other
day
ANEMIA DUE TO UNDERPRODUCTION
Decreased production of RBCs by bone marrow w/ low corrected reticulocyte count
PARVOVIRUS B19
Infects progenitor red cells and
temporarily halts erythropoiesis
significant anemia in setting of
preexisting marrow stress
Treatment supportive; is self-limiting
APLASTIC ANEMIA
Damage to hematopoietic stem cells
pancytopenia w/ low reticulocyte count
-from drugs, chemicals, viral infection,
and autoimmune damage
Empty fatty marrow (biopsy)causes=
Fanconi anemia defect in DNA repair
Diamond-Blackfan anemia congenital
erythroid aplasia
Telomerase defect
Treatment includes cessation
causative drugs, supportive care w/
transfusions and marrow-stimulating
factors; immunosuppression can be
helpful
MYELOPHTHISIC PROCESS Pathologic process (eg metastatic
cancer) that replaces bone marrow
Teardrop shaped RBCs
Epithelial cells
Hematopoeisis is impared
pancytopenia
You might also like
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chapter 14 Red Blood CellsDocument37 pagesChapter 14 Red Blood CellsCatherine LiuNo ratings yet
- Hematology SummaryDocument9 pagesHematology SummaryJovielle Hayden100% (1)
- Summary of All AnemiaDocument2 pagesSummary of All Anemiabenlarsena93% (14)
- Hematology Tables Morphology of RBCsDocument5 pagesHematology Tables Morphology of RBCsGlydenne Glaire Poncardas GayamNo ratings yet
- HAEMOPOIESISDocument6 pagesHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- H1d - Microcytic Anemias ChartDocument3 pagesH1d - Microcytic Anemias ChartqselmmNo ratings yet
- Acquired Bleeding DisordersDocument1 pageAcquired Bleeding DisordersGerardLumNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument1 pageAnemiaindriyanti natasya ayu utami kottenNo ratings yet
- RBC Morphology and InclusionsDocument3 pagesRBC Morphology and InclusionsDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- WBC Lymph Node SpleenDocument12 pagesWBC Lymph Node Spleendr brijesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Pathology p36-47Document12 pagesHematologic Pathology p36-47zeroun24No ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDocument3 pagesClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNo ratings yet
- Anemia ChartsDocument6 pagesAnemia ChartsLiz100% (1)
- RBC DisordersDocument70 pagesRBC DisordersNdor Baribolo100% (1)
- Acute and Chronic LeukemiasDocument3 pagesAcute and Chronic Leukemiaskaku100% (2)
- Decreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisDocument8 pagesDecreased Levels of Iron by Diet or Hemorrhage Impaired Heme SynthesisSamuel RothschildNo ratings yet
- Top 10 AnemiasDocument24 pagesTop 10 AnemiasSim M ChangNo ratings yet
- Blood FilmDocument2 pagesBlood FilmGerardLum100% (1)
- Poikilocytosis Review TableDocument5 pagesPoikilocytosis Review Tablekat100% (1)
- Interpretation of Liver Enzyme Tests - A Rapid GuideDocument3 pagesInterpretation of Liver Enzyme Tests - A Rapid Guidesserggios100% (2)
- Study Questions (Hematology)Document11 pagesStudy Questions (Hematology)tkanesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Board ReviewDocument14 pagesClinical Chemistry Board ReviewWellaBaylasNo ratings yet
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocument1 pageChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildNo ratings yet
- WBC Neoplasms Review - PathologyDocument6 pagesWBC Neoplasms Review - Pathologylas100% (6)
- Anemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDocument15 pagesAnemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDanielle FosterNo ratings yet
- Microcytic Hypochromic Macrocytic Normochromic Normocytic: Anemia HematocritDocument7 pagesMicrocytic Hypochromic Macrocytic Normochromic Normocytic: Anemia Hematocritjjjj31No ratings yet
- Endocrine Pathology p17-32Document16 pagesEndocrine Pathology p17-32zeroun24No ratings yet
- Component Therapy-Transfusion of TheDocument8 pagesComponent Therapy-Transfusion of TheGennelyn Ross Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Approach To Diagnosis of Haemolytic AnaemiasDocument2 pagesApproach To Diagnosis of Haemolytic AnaemiasGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Hematologic Pathology p48-64Document17 pagesHematologic Pathology p48-64zeroun24100% (1)
- Hematology Anemia & Bleeding Zorko2015Document6 pagesHematology Anemia & Bleeding Zorko2015Rishi Sharma100% (1)
- CBC Reviewer Anaphy LabDocument9 pagesCBC Reviewer Anaphy LabARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Anemia Table283Document2 pagesAnemia Table283Bridget ParkerNo ratings yet
- DR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistDocument68 pagesDR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistThaveeshaLindsayWhiteNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Pathology p24-35Document12 pagesHematologic Pathology p24-35zeroun24100% (6)
- Leukemia - Pathophysiology of White Cells DisordersDocument10 pagesLeukemia - Pathophysiology of White Cells DisordersJacecosmozNo ratings yet
- AUB - Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument3 pagesAUB - Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersJeanne Rodiño100% (1)
- 2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFDocument27 pages2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFAlexis Bondad100% (1)
- Urinalysis TableDocument9 pagesUrinalysis TableMegNo ratings yet
- Anti-Coagulants, Anti-Platelets, FibrinolyticsDocument1 pageAnti-Coagulants, Anti-Platelets, FibrinolyticsGerardLum100% (1)
- 33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileDocument40 pages33-Hemostasis and Coagulation ProfileOsman Mohamed MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaDocument30 pagesMicroscopic Exam 01 - RBC, WBC, BacteriaBrent LagartoNo ratings yet
- RH Blood Group SystemDocument6 pagesRH Blood Group SystemUsman ChNo ratings yet
- COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideDocument9 pagesCOMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- LN Hematology MLT FinalDocument549 pagesLN Hematology MLT FinalMahfuzur Rahman100% (3)
- Common Plating Media For Clinical Bacteriology (From Bailey & Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology, 12th Ed)Document2 pagesCommon Plating Media For Clinical Bacteriology (From Bailey & Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology, 12th Ed)Elizabeth Enjambre HernaniNo ratings yet
- Virology - Study GuideDocument5 pagesVirology - Study GuideMatt McGlothlinNo ratings yet
- Abx FinalDocument3 pagesAbx Finalyanks1120No ratings yet
- Thalassemia TableDocument2 pagesThalassemia TableMeevie ToledoNo ratings yet
- L6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Document12 pagesL6-PATHO-Neoplasia (Sept2821)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Correctly: IncorrectlyDocument70 pagesCorrectly: IncorrectlyDjdjjd Siisus100% (1)
- Blood Test ResultsDocument1 pageBlood Test ResultsnindyaNo ratings yet
- Hematology Lectures 1 5 DR - TuyDocument10 pagesHematology Lectures 1 5 DR - TuyMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument5 pagesAnemia SGps PandetteNo ratings yet
- USMLE - Heme & Lymph PathologyDocument21 pagesUSMLE - Heme & Lymph PathologyMatt McGlothlinNo ratings yet
- Anemia EngDocument49 pagesAnemia EngingritfuryNo ratings yet
- FBC Analysers and FBC InterpretationDocument63 pagesFBC Analysers and FBC InterpretationNikkole PhalulaNo ratings yet
- 7.1. Anemia 2023Document30 pages7.1. Anemia 2023MichellyTjoaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia and JaundiceDocument8 pagesNeonatal Hyperbilirubinemia and JaundiceAndreea GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: Client Code: Client'S Name and AddressDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Report: Client Code: Client'S Name and AddressKhurram Shadab IqbalNo ratings yet
- ISBB CompilationDocument6 pagesISBB CompilationElla SalesNo ratings yet
- Haematology Assignment 1Document4 pagesHaematology Assignment 1KINGSCOMPUTERS CYBERNo ratings yet
- Table of Blood Group Systems v. 9.0 03-FEB-2021Document3 pagesTable of Blood Group Systems v. 9.0 03-FEB-2021AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Wa0038.Document9 pagesWa0038.Sambhu Nath DeyNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis AlgorithmDocument1 pageHereditary Hemochromatosis AlgorithmS6b2No ratings yet
- A Study of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice About Sickle Cell Anaemia in Patients With Positive Sickle Cell Status in Bardoli TalukaDocument4 pagesA Study of Knowledge, Attitude and Practice About Sickle Cell Anaemia in Patients With Positive Sickle Cell Status in Bardoli TalukaManisa ParidaNo ratings yet
- Scales and Arpeggios FingeringsDocument2 pagesScales and Arpeggios FingeringsJames RileyNo ratings yet
- Blood Component TherapyDocument13 pagesBlood Component TherapyMohamed ElgayarNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping and RH TypingDocument4 pagesBlood Grouping and RH TypingJeevs MusicNo ratings yet
- Blood BankingDocument10 pagesBlood BankingSheen AmboyNo ratings yet
- Blood Type Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesBlood Type Review WorksheetSofa100% (2)
- Accu-Temp® Cautery: Specialty CauterizationDocument2 pagesAccu-Temp® Cautery: Specialty CauterizationrhymenNo ratings yet
- Schwartz's Hemostasis, Surgical BleedingDocument33 pagesSchwartz's Hemostasis, Surgical BleedingArifHidayat100% (4)
- ThrombocytopeniaDocument1 pageThrombocytopeniaanum786110No ratings yet
- Coombs TestDocument6 pagesCoombs TestjnsenguptaNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping Brochure 2013 - Priced PDFDocument8 pagesBlood Grouping Brochure 2013 - Priced PDFmwenyeweNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion PolicyDocument6 pagesBlood Transfusion PolicyTanisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guide To Transfusion - Preoperative Autologous Donation (Chapter 16)Document4 pagesClinical Guide To Transfusion - Preoperative Autologous Donation (Chapter 16)Ahmed ZeyadNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anaemia: DR Mrs Stella Kanu Bmls Mbbs MSCDocument17 pagesIron Deficiency Anaemia: DR Mrs Stella Kanu Bmls Mbbs MSCDavid KanuNo ratings yet
- Collection TubeDocument6 pagesCollection TubeChristiane ReaNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Kadar Hematokrit Dan Hemoglobin Pada Kejadian Infark Miokard Akut (Ima) Di Rsup Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado Periode Januari - Agustus 2014Document7 pagesGambaran Kadar Hematokrit Dan Hemoglobin Pada Kejadian Infark Miokard Akut (Ima) Di Rsup Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado Periode Januari - Agustus 2014Elma CantikaNo ratings yet
- Types of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesTypes of AnaemiaSuhaila NaemaNo ratings yet
- LP 10 Anemia 3Document43 pagesLP 10 Anemia 3Anonymous elq7jZiSNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination For Pregnant WomanDocument31 pagesPhysical Examination For Pregnant WomanFrancia ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Pathology Consultation On Hba Methods and Interferences: Jeanne M. Rhea, PHD, and Ross Molinaro, PHDDocument12 pagesPathology Consultation On Hba Methods and Interferences: Jeanne M. Rhea, PHD, and Ross Molinaro, PHDyosefinNo ratings yet
- PDF TextDocument1 pagePDF TextBoss GuptaNo ratings yet