Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alkanes: Saturated Each Carbon Atom Is Bonded To Four Other Atoms by Single Covalent Bonds
Uploaded by
Thuran NathanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkanes: Saturated Each Carbon Atom Is Bonded To Four Other Atoms by Single Covalent Bonds
Uploaded by
Thuran NathanCopyright:
Available Formats
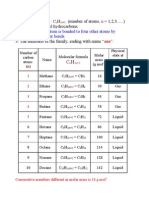
Alkanes
1. General Formula : C
n
H
2n+2
(number of atoms, n = 1,2,3......)
2. They are saturated hydrocarbons;
each carbon atom is bonded to four other atoms by
single covalent bonds.
3. The members of the family, ending with name ane.
Number of
carbon
atoms
(n)
Name
Molecular formula
C
n
H
2n+2
Molar
mass
(g mol
-1
)
Physical
state at
room
temperatu
re
1 Methane C
1
H
2x1+2
= CH
4
16 Gas
2 Ethane C
2
H
2x2+2
= C
2
H
6
30 Gas
3 Propane C
3
H
2x3+2
= C
3
H
8
44 Gas
4 Butane C
4
H
2x4+2
= C
4
H
10
58 Gas
5 Pentane C
5
H
2x5+2
= C
5
H
12
72 Liquid
6 Hexane C
6
H
2x6+2
= C
6
H
14
86 Liquid
7 Heptane C
7
H
2x7+2
= C
7
H
16
100 Liquid
8 Octane C
8
H
2x8+2
= C
8
H
18
114 Liquid
9 Nonane C
9
H
2x9+2
= C
9
H
20
128 Liquid
10 Decane C
10
H
2x10+2
= C
10
H
22
142 Liquid
Consecutive members different in molar mass is 14 g mol
-1
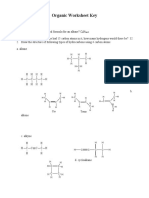
4. Structural formulae of alkanes
Name No. of
isomers
Structural formulae and Name
Methane
CH
4
0
Ethane,
C
2
H
6
0
Propane,
C
3
H
8
0
Butane,
C
4
H
10
2
H H H H
H C C C C H
H H H H
n-butane
H H H
H C C C H
H H H
H
H C H
H
H H
H C C H
H H
Pentane,
C
5
H
12
3
2 - methyl propane
H H H
H C C C H
H HCH H
H
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H H H H
n-pentane
H H H H
H C C C C H
H HCH H H
H
2-methyl butane
1 2 3 4
Hexane,
C
6
H
14
5
H
H H C H H
H C C C H
H HCH H
H
2,2-dimetyl propane
H H H H H H
H C C C C C C H
H H H H H H
n-hexane
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H HCH H H H
H
2 - methyl pentane
H
H H C H H H
H C C C C H
H HCH H H
H
2,2 - dimethyl butane
2,3 - dimethyl butane
H H H H H
H C C C C C H
H H HCH H H
H
3 - methyl pentane
H
H H H CH H
H C C C C H
H HCH H H
H
Physical Properties
Physical properties of alkanes
i. cannot conduct electrity
ii. less dense than water
iii. dissolve in organic solvents, insoluble in water
iv. low melting and boiling points
Conclusion:
- molecule held together by weak intermolecular forces
- properties of covalent compound
- gradually steady increase as the number of carbon in alkane
increases
6. Steps to name branched alkanes;
i. determined and named the long chains
ii. determined and named the branch chain
CH
3
: methyl
C
2
H
5
OR CH
2
CH
3
: ethyl
C
3
H
7
OR CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
: prophyl
iii. give number to the carbon atoms in long chain, which started
from the nearest branched
iv. The number for carbon atom which branched emerged from,
must put before/infront the alkyl
v. Named the branched first, followed by the named of long chains
The word di, tri is used if the branched chains is more than one
Chemical Properties
Pg 38
Reactivity of alkanes
1. Not reactive/unreactive because saturated hydrocarbon
2. Did not decolourized purple solution of acidified potassium
manganate(VII)
3. Did not decolourized reddish brown solution of bromin water
4. Neutral.
Combustion of alkanes
1. In the presence of sufficient oxygen, alkanes burns to form
carbon dioxide and water. complete combustion
Chemical equation:
i. CH
4
+ O
2
CO
2
+ H
2
O
CH
4
+ 2O
2
CO
2
+ 2H
2
O
ii. C
2
H
6
+ 7/2 O
2
2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
iii. C
4
H
10
+ 13/2 O
2
4CO
2
+ 5H
2
O
iv. C
6
H
14
+ 19/2 O
2
6CO
2
+ 7H
2
O
Answers
i. CH
4
+ 2O
2
CO
2
+ 2H
2
O
ii. C
2
H
6
+ 7 O
2
2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
2
2 x C
2
H
6
+ 2 x 7 O
2
2x 2CO
2
+ 2x 3H
2
O
2
2C
2
H
6
+ 7 O
2
4CO
2
+ 6H
2
O
iii. C
4
H
10
+ 13/2 O
2
4CO
2
+ 5H
2
O
iv. C
6
H
14
+ 19/2 O
2
6CO
2
+ 7H
2
O
2. If there is insufficient oxygen, carbon monoxide or carbon
may be formed incomplete combustion
i. CH
4
+ 3/2 O
2
CO + 2H
2
O
2CH
4
+ 3 O
2
2CO + 4H
2
O
ii. CH
4
+ O
2
C + 2H
2
O
Halogenation
1. The reaction is between alkane dan chlorine.
2. Takes place under sunlight/ultra violet light.
3. Carbon-hydrogen bonds broken and new carbon-halogen bonds
are formed. One or more hydrogen atoms in alkanes molecule may be
subtituted by halogen.
4. Halogenation is substitution reaction.
Chlorination of methane
First stage;
Second stage;
H H
|
H C H +Cl-Cl H C Cl + HCl
|
H H monochloromethane
H Cl
|
H C Cl + Cl
2
H C Cl + HCl
|
H H dichloromethane
Third stage ;
Fourth stage;
Overall equation/chemical equation
CH
4
+ 4Cl
2
CCl
4
+ 4HCl
Cl Cl
|
H C Cl + Cl
2
H C Cl + HCl
|
H Cl trichloromethane
Cl Cl
|
H C Cl + Cl
2
Cl C Cl + HCl
|
Cl Cl tetrachloromethane
You might also like
- Alkanes: Saturated Each Carbon Atom Is Bonded To Four Other Atoms by Single Covalent BondsDocument10 pagesAlkanes: Saturated Each Carbon Atom Is Bonded To Four Other Atoms by Single Covalent BondsKamal Ariffin Bin SaaimNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SERIESDocument88 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY SERIESAkaNayep ApNo ratings yet
- 3 AlkenesDocument22 pages3 AlkenesEunice TangNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2Document11 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2kslpeter87No ratings yet
- 2 AlkanesDocument11 pages2 AlkanesSafina IzwaniNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 4 2017Document14 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 4 2017Shreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Chem 100 Unit 4 Organic ChemistryDocument27 pagesChem 100 Unit 4 Organic ChemistryIsah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Organic Worksheet Key: H H H H H H HDocument4 pagesOrganic Worksheet Key: H H H H H H HSoleilNo ratings yet
- Organic Worksheet KeyDocument5 pagesOrganic Worksheet KeySoleilNo ratings yet
- MEQ L (Introductory Organic Chemistry)Document62 pagesMEQ L (Introductory Organic Chemistry)Furious SKNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument11 pagesHydrocarbonsPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Organic ChemistryDocument104 pagesChapter 8 - Organic Chemistryhiu nok kwanNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument12 pagesAlkanesatomix-science100% (1)
- Alkanes: H H C H HDocument6 pagesAlkanes: H H C H HAmirah AmanNo ratings yet
- Sebatian Karbon / Carbon Compound Alkana / Alkane: N 2n N 2n+2 N 2n+1 N 2n+1Document19 pagesSebatian Karbon / Carbon Compound Alkana / Alkane: N 2n N 2n+2 N 2n+1 N 2n+1OMAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Sebatian Karbon / Carbon Compound Alkana / AlkaneDocument18 pagesSebatian Karbon / Carbon Compound Alkana / AlkaneSathya Seelan100% (1)
- 2022 H2 Alkanes Lect 1 - 4augDocument24 pages2022 H2 Alkanes Lect 1 - 4augcaseypokemon088No ratings yet
- Organic Compounds: Functional GroupsDocument34 pagesOrganic Compounds: Functional GroupsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument80 pagesNomenclature of Organic CompoundsSajjad MiraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Organic Compounds: A First LookDocument31 pagesChapter 2: Organic Compounds: A First LookLaura BeltranNo ratings yet
- IB Organic Chemistry Note SL (Note Cards)Document31 pagesIB Organic Chemistry Note SL (Note Cards)陳定均No ratings yet
- Erica Jane L. Sulit Rhoyelle D. Mag-IsaDocument28 pagesErica Jane L. Sulit Rhoyelle D. Mag-IsaErica Jane SulitNo ratings yet
- Naming of AlkanesDocument10 pagesNaming of Alkanesrudi_zNo ratings yet
- Cyclohexane Cyclohexene Lab AnswersDocument6 pagesCyclohexane Cyclohexene Lab AnswersTingYuan HoiNo ratings yet
- OCI Lecture6-7Document18 pagesOCI Lecture6-7Baga DagaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro To Organic ChemistryDocument144 pages1 - Intro To Organic ChemistryDANIEL ORTAÑEZNo ratings yet
- Alcohol: Hydroxide Ion, OHDocument20 pagesAlcohol: Hydroxide Ion, OHKamal Ariffin Bin SaaimNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Reactions NotesDocument14 pagesAlkenes Reactions NotesMartin AlvinNo ratings yet
- Addition ReactionsDocument18 pagesAddition ReactionsPanmati DeviNo ratings yet
- Organic - Chemistry HandoutsDocument34 pagesOrganic - Chemistry HandoutsVernice OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Solutions To In-Chapter ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Solutions To In-Chapter ProblemsRome Erwin Manalo FestinNo ratings yet
- Note On AlkenesDocument8 pagesNote On Alkenes1danfammy1No ratings yet
- Addition ReactionsDocument18 pagesAddition ReactionswidodoNo ratings yet
- Visit For 100's of Free Powerpoints: Decane (What Is The Formula? - )Document18 pagesVisit For 100's of Free Powerpoints: Decane (What Is The Formula? - )ayiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction SchemeDocument19 pagesChemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction Schemehelixate94% (16)
- Alkena (Alkenes) Dan Alkuna (Alkynes) : Puji Astuti Ibrahim, M.SiDocument33 pagesAlkena (Alkenes) Dan Alkuna (Alkynes) : Puji Astuti Ibrahim, M.SiNadia Elvansa PutriNo ratings yet
- CH 2 (Crude Oil Characterisation) 2018 BDocument63 pagesCH 2 (Crude Oil Characterisation) 2018 Bnafisa afariNo ratings yet
- Visit For 100's of Free Powerpoints: Decane (What Is The Formula? - )Document18 pagesVisit For 100's of Free Powerpoints: Decane (What Is The Formula? - )Toto SudaryantoNo ratings yet
- 5 AlcoholDocument10 pages5 AlcoholfadhlinamNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1&2Document142 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1&2Kennedy ChitayiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Representation: Lewis' FormulasDocument63 pagesMolecular Representation: Lewis' FormulasnegarNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC ChemistryDocument150 pagesORGANIC ChemistryAhmad AlShahrourNo ratings yet
- 15 - Thai Ha - Cong Thuc Cau TaoDocument3 pages15 - Thai Ha - Cong Thuc Cau TaoNguyễn Thái HàNo ratings yet
- Answers Chapter 17 Summary QuestionsDocument4 pagesAnswers Chapter 17 Summary QuestionsNada HadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document1 pageChapter 27Tehzeeb Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- 2 IsomerismDocument4 pages2 IsomerismInshira Malik DansalNo ratings yet
- 2023 Alkanes Tutorial Ans SchemeDocument14 pages2023 Alkanes Tutorial Ans SchemeJun JieNo ratings yet
- Alkane Theory Eng. Module-4Document16 pagesAlkane Theory Eng. Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Names of CompoundsDocument5 pagesNames of CompoundsSonaliNo ratings yet
- Xkis Organic Chemistry 18-19 - Abhishek KumarDocument7 pagesXkis Organic Chemistry 18-19 - Abhishek KumarSwastik Dutta RoyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Chapter 14 ReviewDocument27 pagesOrganic Chemistry Chapter 14 ReviewĐỗ Minh HuânNo ratings yet
- CHEM 100 Lecture 1-6Document35 pagesCHEM 100 Lecture 1-6shuang maNo ratings yet
- Organic Naming RulesDocument50 pagesOrganic Naming Rulesjg2No ratings yet
- Organic ReactionsDocument6 pagesOrganic Reactionssiyamthandabuthelezi71No ratings yet
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- Physical Organic Chemistry—Ii: Specially Invited Lectures Presented at the Second IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry Held at Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 29 April–2 May 1974From EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry—Ii: Specially Invited Lectures Presented at the Second IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry Held at Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 29 April–2 May 1974Th. J. De BoerNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Halogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesFrom EverandHalogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesAri L. HorvathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Notes Form 4 KSSM Bio BM 28 Sept 2021Document54 pagesNotes Form 4 KSSM Bio BM 28 Sept 2021Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 5 - StudentDocument15 pagesForm 5 Physics Chapter 5 - StudentPavithiranNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry 2012 PDFDocument2 pagesSPM Chemistry 2012 PDFThuran Nathan100% (1)
- A Math Formula ListDocument8 pagesA Math Formula Listacsbr4science1100% (1)
- Module 10 Graf FunctionDocument10 pagesModule 10 Graf FunctionHelen PappuNo ratings yet
- Latihan Masa Cuti f4Document1 pageLatihan Masa Cuti f4Amalina KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Heymanya Nathan: Cempaka International School Persiaran Awana Taman Cheras Permata Dua 43200 Cheras SelangorDocument1 pageHeymanya Nathan: Cempaka International School Persiaran Awana Taman Cheras Permata Dua 43200 Cheras SelangorThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- NLP StatsDocument5 pagesNLP StatsThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Registration Information: Managing Projects Today (MPT) Date: 5 To7 April 2010Document1 pageRegistration Information: Managing Projects Today (MPT) Date: 5 To7 April 2010Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Page Cover BRIGHTmINDSDocument1 pagePage Cover BRIGHTmINDSThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- New Economic Model For Malaysia: WWW - Neac.gov - MyDocument209 pagesNew Economic Model For Malaysia: WWW - Neac.gov - MyThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Shiva Mahimna Stotram - English Lyrics (Text)Document6 pagesShiva Mahimna Stotram - English Lyrics (Text)Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Awards Won by Multimedia University ITEX Malaysia 2013 Awards Won by Multimedia UniversityDocument7 pagesAwards Won by Multimedia University ITEX Malaysia 2013 Awards Won by Multimedia UniversityThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Repeated Bright Minds contact informationDocument22 pagesRepeated Bright Minds contact informationThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- June 2013 Intake: Programmes OfferedDocument2 pagesJune 2013 Intake: Programmes OfferedThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- IHT SC No 2014Document1 pageIHT SC No 2014Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Nota Ekpress PMR SainsDocument10 pagesNota Ekpress PMR SainsThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Checkpoint Maths P1 Specimen 2012Document12 pagesCambridge Checkpoint Maths P1 Specimen 2012Maryam Rai80% (10)
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document17 pagesChapter 7Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Bright Minds Dad Ads A As PM 2014Document1,472 pagesBright Minds Dad Ads A As PM 2014Thuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Sukatan Pelajaran Maths T STPMDocument23 pagesSukatan Pelajaran Maths T STPMKar Wai NgNo ratings yet
- NLPDocument1 pageNLPThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Hierarchy in The Classification of OrganismsDocument2 pagesBiodiversity: Hierarchy in The Classification of OrganismsKesha623No ratings yet
- Rental FlyersDocument1 pageRental FlyersThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Add Maths FormulaeDocument9 pagesAdd Maths FormulaeThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- SPM ENGLISH Form 5 Step by Wicked StepDocument113 pagesSPM ENGLISH Form 5 Step by Wicked StepThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Order Science and Maths SoftwareDocument1 pageOrder Science and Maths SoftwareThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Tests For Categorizing Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument7 pagesTests For Categorizing Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesFaye ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Espectros de RMN PDFDocument47 pagesEspectros de RMN PDFJéssicaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry by Perkin and KippingDocument373 pagesOrganic Chemistry by Perkin and KippingSanjayShirodkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Activity AnswersDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Activity AnswersSF MasturahNo ratings yet
- CHEM 210 Exam 1 QuestionsDocument3 pagesCHEM 210 Exam 1 QuestionsRamez AnaniNo ratings yet
- A Safe Simple Halogenation ExperimentDocument1 pageA Safe Simple Halogenation ExperimentCarlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document25 pagesModule 6ABIGAIL OLAJUMOKE JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Electron Counting: Understanding Structure and ReactivityDocument48 pagesElectron Counting: Understanding Structure and ReactivityrizukiseptiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sheppard CHEM 4201 Fall 2014 Exam I Study Guide: Max MaxDocument4 pagesDr. Sheppard CHEM 4201 Fall 2014 Exam I Study Guide: Max MaxIbrahim MNo ratings yet
- Pestalotiopsin A synthesis and key reactionsDocument2 pagesPestalotiopsin A synthesis and key reactionsPercival GalahadNo ratings yet
- 7 - Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers (2014-22)Document4 pages7 - Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers (2014-22)bv7353651No ratings yet
- Chap 10 Chem c-12Document14 pagesChap 10 Chem c-12Pratham VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Module-2:: Metal Complexes and OrganometallicsDocument75 pagesModule-2:: Metal Complexes and OrganometallicsAshutosh100% (2)
- Upper Sixth Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesUpper Sixth Organic ChemistryBaninla NerusNo ratings yet
- Chem 153 Problem Set 1Document2 pagesChem 153 Problem Set 1wanglixiangNo ratings yet
- Astm 54DDocument11 pagesAstm 54DjarjarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-I (For Odd SEMESTER), CY-101: By: Prof. Vandana SrivastavaDocument59 pagesChemistry-I (For Odd SEMESTER), CY-101: By: Prof. Vandana SrivastavaHoly GrailNo ratings yet
- Oh, C6h5ohDocument3 pagesOh, C6h5ohSjhsjsjNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9 Chap 1 Long QADocument17 pagesChemistry 9 Chap 1 Long QAAkbar Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Broadbent ResumeDocument1 pageBroadbent Resumescott8323No ratings yet
- Thermal Transitions of Homopolymers - Sigma-Aldrich PDFDocument3 pagesThermal Transitions of Homopolymers - Sigma-Aldrich PDFYee Kin WengNo ratings yet
- Activity No.6: Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument7 pagesActivity No.6: Notre Dame of Dadiangas Universitydenshang 10No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Questionsdaniday1977100% (1)
- US 2010 patent for natural disinfecting cleanersDocument26 pagesUS 2010 patent for natural disinfecting cleanersEnrique Franco ArizaNo ratings yet
- 11 Dec 2012 USP DailycatalogDocument163 pages11 Dec 2012 USP DailycatalogramaiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 7th Edition (2013) Chapter23 PDFDocument44 pagesBiochemistry 7th Edition (2013) Chapter23 PDFAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Department of Chemistry, IIT BombayDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Department of Chemistry, IIT BombaySandipan Saha100% (1)
- Color Reactions Intact Protein (Gluten) Basic HydrolysisDocument6 pagesColor Reactions Intact Protein (Gluten) Basic HydrolysisJennifer CamaNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-4 SET-2 Chapter-12 PDFDocument42 pagesCLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-4 SET-2 Chapter-12 PDFRitik RajNo ratings yet
- Test - D18 Dec 2022Document9 pagesTest - D18 Dec 2022PrinceNo ratings yet