Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification of CHD
Uploaded by
Prachy ShuklaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classification of CHD
Uploaded by
Prachy ShuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
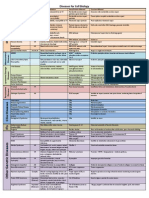
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
CLASSIFICATION:
Pulmonary
plethora
1. TGA
2. Truncus Arteriosus
3. TAPVR
4. single ventricle
5. double outlet right ventricle
6. hypoplastic left heart syndrome
CYANOTIC
Pulmonary
oligemia
1. TOF
2. TA
3. Ebsteins anomaly
4. Pulmonary atresia
Pulmonary
plethora
L > R shunts, ie
1. VSD
2. ASD
3. PDA
4. AV Canal defect
ACYANOTIC
Normal lung
vascularity
1. Coarctation
2. Congenital aortic stenosis
3. Pulmonary artery stenosis
ACYANOTIC CHD WITH PULMONARY PLETHORA:
VSD
ASD
PDA
AV canal defect
VSD:
commonest intracardiac lesion in children.
Isolated defect in about 20% of pxs with CHD.
5% associated with other lesions particularly chromosomal
abnormalities such as trisomy 13, 18, 21.
Many small VSDs close spontaneously - anatomic classification
important re expectant vs surgical management
Clinically:
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
Blowing PSM at lower sternal border
CHF, recurrent RTI, FTT
Present after 1st month of life because pulmonary vascular
resistance falls with subsequent development of interstitial
oedema.
In the older child if pulmonary vascular resistance remains high
pulm. HPT
Rarely, pulmonary vascular obstructive disease occurs reversal of
blood flow LR shunt occurs (Eisenmenger reaction)
CXR:
pulm:systolic blood flow > 2:1
Biventricular enlargement
CLASSI FI CAT I ON
M EM BRANOUS:
Anterior
Posterior
Supracristal
Gebode LV RA shunt
M USCULAR:
1/more defects
Swiss cheese
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
Increased pulmonary vascularity
Dilated pulmonary trunk
LA enlargement with posteromedial displacement of the left
mainstem bronchus
CHF signs may appear after the 1st month of life
CARDIOMEGALY, PLETHORA, ENLARGED PULM. TRUNK
ECHO:
LA hypertrophy
Colour flow Doppler demonstrates flow across the defect.
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
PERIMEMBRANOUS DEFECT IN THE
PARASTERNAL LONGAXIS PLANE
MRI:
5 YR OLD BOY: MUSCULAR VSD
ASD
2nd commonest cardiac anomaly
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
10% of all CHD
Is the commonest intracardiac shunt that persists into adulthood.
CXR:
Normal in infancy, changes noted 1
st
in childhood
RV dilation
Pulmonary trunk enlargement
Plethoric lung fields
Mild rotation of the heart and great vessels to the left.
Absent SVC contour d/t rotation over the spine
CLASSIFICATION
OST I UM
SECUNDUM :
80-90%
Midseptum (fossa ovalis)
Usually isolated
>1cm
SI NUS VENOSUS:
5%
Defect in posterior wall
close to SVC entry
Iaw PAPVD
PAT ENT FORAM EN
OVAL E
Defective approximation
of ostium secundum and
primum
ENDOCARDI AL
CUSI ON DEFECT S
5-10%
Low in atrial septum
+/or aberrant PV, PS,
Eisenmenger rx,
Clinically:
Pxs usually asymptomatic
Present in adolescence with:
Mild dyspnoea
Asymptomatic cardiac murmur
Harsh systolic murmur along
upper LSB
Loud S2 with fixed splitting
Ostium primum ASD: MR
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
ECHO: (trasnthoracic with transoesopahgeal is diagnostic)
4 chamber subcostal view
OSTIUM PRIMUM ASD Sinus Venosus defect with overriding
SVC
ASD rotated
mediastinum, prominent
RPA, absent SVC shadow
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
AV CANAL
(ENDOCARDIAL CUSHION) DEFECTS
4% of all CHD
D/t abnormal development of endocardial cushion tissue.
Spectrum: common AV valves -> AV canal defect
Complete AV canal defect incl. ASD, VSD which occur less
frequently with common AV valves.
Association with asplenia/ polysplenia
Partial AV canal defect ASD and cleft mitral septal defect.
20 month old:
Septum primum ASD with
RVH
Septum secundum ASD
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
CXR:
Indistinguishable from ASD.
Complete defect- RA< RV enlargement
PDA
Persistant communication between descending aorta and LPA.
8-10% of CHD (Increased incidence in prem babies)
1 in 3000 term infants.
F:M = 2:1
Anatomic closure in 95% of infants by the 3rd month.
Remains open d/t:
low pO2 in arterial blood
increased fetal PG levels
HMD in a prem baby cxs the ductus to close
CXR: (may be normal)
Neonate:
pulmonary plethora
LA enlargement
Infant/ young child:
pulmonary plethora
Clinically:
Usually asymptomatic.
Range of symptoms from a machinery murmur in
neonate - frank CF in infancy.
Rx: sx clip
indomethacin
Clinically:
FTT
Dyspnoea
Fatigue
Pulm HPT:
- more commonly in Downs syndrome (40-50% of Downs)
have AV canal defects)
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
enlarged aortic knuckle
LA and LV enlargement
filling of AP window
Partial closure : ductus bump or diverticulum
Closed ductus : ligamentous arteriosum calcification
ECHO:
Connection between DA and LPA directly demonstrated
OBSTRUCTIVE LESIONS:
(acyanotic with normal lung vasculature):
Coarctation of the aorta
Congenital aortic stenosis
Pulmonary artery stenosis
ECHO
modality of choice and is diagnostic
functional assessment also possible
ANGIOCARDIOGRAPHY
rarely performed
CARDIAC MRI
DUCTUS BUMP
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
being used more often and allows excellent detailed visualisation of
cardiac anomalies
CXR:
Value varies tremendously.
Sometimes possible to make a diagnosis on CXR eg. aortic
coarctation in an adolescent/ adult but not in a child.
Diagnostic value is also dependent on the type of lesion.
Type of abnormality and haemodynamic consequences may be
evident on CXR eg. PDA complicated by Eisenmenger reaction.
Diagnostic features on CXR:
lung fields - normal/ increased or decreased vascularity
size and position of the heart
shape of the heart
position, size and shape of the ascending aorta, aortic arch and
MPA
assoc. skeletal anomalies
position of the viscera and main bronchi
CYANOSIS AND OLIGAEMIA:
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tricuspid atresia
Ebsteins anomaly
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
Commonest (12%) of cyanotic CHD.
4 components:
infundibular PS
RVH
high VSD
overriding of the aorta
Is the consequence of eccentric separation of the truncus
hypoplasia of the PV, MPA, RPA and LPA
Thought to be d/t aberrant development of the infundibulum.
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
If mild PS and large VSD present pink TOF as there is
sufficient pulmonary flow for oxygenation.
At the other extreme: pulmonary atresia and VSD blue TOF.
Most infants are in the middle of the spectrum.
CXR:
BOOT shaped heart (RVH with rotated heart and upturned apex)
Oligaemia
Absence of the pulmonary segment
Reticular interstitial pattern caused by collateral flow in the upper
lung fields medially
Enlarged AA
RT sided aortic arch in 25% of pxs
Pink Fallot: plethora, hollow pulmonary bay
Clinically:
Cyanosis after 3-6 months.
Exertional dyspnoea.
Hypoxic spells relieved by squatting.
Squatting increases venous systemic return.
Associated with trisomy 21, VACTERL abn., TOF
Bootshaped heart
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
ECHO:
Ant displacement of infundibular septum
excl. 2nd VSD on colour doppler
confirms large gradient over PS
SUBCOSTAL LONG AXIS
VIEW:
STENOSED RVOT BY
THICKENED INFUNDIBULAR
SEPTUM
HIGH VSD & AORTA
MRI:
High VSD with overriding aorta
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
TRICUSPID ATRESIA
1.5% of CHD
Infants cyanotic at birth and there is an obligatory ASD/VSD or
PDA (uncommon) for survival.
Transposition of the great vessels in 30%.
PS in 50%.
May be assoc with RT sided aortic arch or TAPVR
The obligatory R L shunt at atrial level leads to LVH.
CXR:
Normal to diminished pulmonary blood flow.
LVH (rounded apex)
prominent RA contour.
Concave pulmonary artery segment.
May have RT sided aorta.
EBSTEINS MALFORMATION
<1% of CHD
Tricuspid valve tx displaced into RV severe incompetence
RA enlarged
RV partially atrialised
ASD always present
TRICUSPID ATRESIA:
ROUNDED LT HEART
BORDER &
HOLLOW PULMONARY
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
CXR Findings:
Box shaped heart
Oligaemia
RA enlargement with rounding of SVC/ RA junction
Clinically:
Palpitations, cyanosis
Usually present in 1st month of life.
Poorly fxning RV flow backup increased cyanosis
because of R to L shunting via ASD.
Severe pulmonary HPT
LARGE HEART, CURVED LT
HEART BORDER,
SQUARED APEX, SMALL
AORTIC ARCH, OLIGAEMIA
EBSTEIN
MALFORMATION IN A 1
MONTH OLD INFANT
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
CYANOSIS AND PLETHORA:
TGA
CONGEN. CORRECTED TGA
PERSISTENT TA
ANOMALOUS PULM VENOUS RETURN
DOUBLE OUTLET RV
SINGLE VENTRICLE
TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT ARTERIES
5% OF CHD
Aorta arises from RV and MPA from LV
Aorta comes to lie anterior to the pulmonary artery.
deoxygenated blood circulates to the body and oxygenated blood
circulates to the lungs.
Incompatible with life if no ASD/ VSD/ PDA
4 CHAMBER VIEW- REDUNDANT
TRICUSPID LEAFLETS EXT. INTO RV
Clinically:
Intensely cyanotic at birth.
Unresponsive to 100% O2 if no VSD
Degree of pulmonary blood flow determines the degree of
cyanosis
Admixture of oxygenated and non oxygenated blood - less
cyanosis
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
CXR:
At birth normal cardiac size, mild cardiomegaly later
Hyperinflated and plethoric lung fields
Lack of normal thymic outline due to stress
Egg on the side/ apple on a string shaped heart
Rx: Jantene procedure or palliative if large VSD
EGG SHAPED HEART, NARROW SUP.
MED., PLETHORA
TGA IN 1 DAY OLD BABY: EGG
ON SIDE APP.,
LOSS OF THYMIC CONTOUR IN
SUPERIOR MEDIASTINUM
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
CONGENITALLY CORRECTED TGA
Occurs when there is inversion of the ventricles with normal atrial
relationship.
Aorta lies to the left of the MPA
Coexisting lesions: VSD, single ventricle, PS, TR
Clinical findings depend on the severity of intracardiac lesions.
CXR:
Often normal
Varying pulmonary vascularity but usually normal/ decreased
Abn. bulge in left upper cardiac border and mediastinum d/t
ascending aorta arising from the left side and being border
forming.
TGA: PARASTERNAL SHORT
AXIS PLANE-
MPA POST. TO AORTA
CONGEN.CORRECTED TGA-
DOUBLE INLET LV
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
PERSISTENT TRUNCUS ARTERIOSUS
Due to developmental failure of septation of the primitive truncus
arteriosus into the aorta and MPA.
<2% of CHD; 1:10 000 live births
There is an obligatory shunt at the ventricular level.
Collett Edwards Classification (based on origin of MPA)
I Originate from aortic trunk
II Origin of PA from ascending aorta
III Separate orifices
IV MPA originates from the descending aorta
CxR:
Mild oval cardiomegaly
Plethora which may be asymmetrical
35% RT side aortic arch
Pulmonary artery waist d/t thymic stress
Clinically:
Present in early infancy with cyanosis, FTT, dyspnoea, CHF
High association with Di Georges syndrome with TA occurring in
10% of these pxs and coarctation of the aorta in 30%.
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
Rx:
Ratselli procedure- valved conduit between RV and PA, VSD closed.
ANOMALOUS PULMONARY VENOUS RETURN
Is the return of pulmonary venous blood not to the LA.
Total/ Partial
TAPVR:
1% of CHD
2X commoner in males
CXR:
With obstruction:
Congested pulmonary vessels and a normal cardiac silhouette in
obstruction.
Without obstruction:
TAPVR
!% of CHD
2 x commoner in males
Supracardiac
50%
Cardiac
30%
Infracardiac
15%
Obstruction to
venous return occurs
Mixed
5%
Clinically:
Present in the first week of life.
High pulmonary flow and good admixture mild cyanosis
More severe pulmonary venous obstruction severe cyanosis
A third of pxs have other abnormalities eg. truncus
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
Cardiomegaly (RV and RA enlargement)
Enlarged pulmonary artery segment
Increased pulmonary blood flow.
In older pxs- classic snowman/ figure 8
PAPVR
Only part of venous drainage is anomalous.
Assoc with sinus venosus ASD.
Most drain to SVC or left sided SVC.
Best example is the scimitar syndrome
SINGLE VENTRICLE
Present with early cyanosis and CHF.
Aorta and pulmonary trunk are transposed.
Invariably associated with asplenic syndrome.
CXR: cardiomegaly and CHF
DOUBLE OUTLET RV
Aorta and pulmonary trunk arise from RV.
VSD almost always persists
Great arteries may be transposed.
PS may be present.
HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART SYNDROME
Commonest cause of CF in the neonate.
Presents at birth.
Hypoplasia/ atresia of aortic and mitral valves.
TAPVR: SNOWMAN/ FIG 8/
COTTAGE LOAF HEART-
CONVEXITY OF SUP. MED., RVH
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
Obligatory L R shunt at atrial level most common
CXR: globular heart, pulmonary congestion in 24 hours
EISENMENGER REACTION
Occurs in L R shunts (ASD, VSD, PDA)
Development of obliterative pulmonary arteriosclerosis
pulmonary vascular occlusive dx
progressive increase in pulmonary resistance and decrease in the LR
shunt until pulmonary resistance exceeds systemic resistance
preferential RV flow into systemic circulation
shunt reversal of R L
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com)
You might also like
- Child With Bruises 00Document36 pagesChild With Bruises 00Awatef AbushhiwaNo ratings yet
- Littmann Cardiac AuscultationDocument1 pageLittmann Cardiac AuscultationSri Wahyuni100% (1)
- Pediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsDocument22 pagesPediatric Hematooncology Alarm SymptomsMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- NEPHROTIC SYNDROME - HamidDocument20 pagesNEPHROTIC SYNDROME - HamidAbdul Hamid OmarNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument29 pagesPericarditisPavin KumarNo ratings yet
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Document18 pagesPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015)Ars MoriendiNo ratings yet
- Cell InjuryDocument23 pagesCell InjuryFiori MedNo ratings yet
- UW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesDocument41 pagesUW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesUsama BilalNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease GuideDocument43 pagesValvular Heart Disease Guideurmila prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Neurology Rule of 4Document2 pagesNeurology Rule of 4achantihariNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Pediatric Diseases Chapter SummaryDocument16 pagesGenetic and Pediatric Diseases Chapter SummaryJustine HungNo ratings yet
- Cyanosis in The NewbornDocument32 pagesCyanosis in The Newbornimma_2014No ratings yet
- Congenital Development of Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesCongenital Development of Urinary SystemRinxas VerinxtNo ratings yet
- PnemoniaDocument4 pagesPnemoniadhavalNo ratings yet
- Hem-Onc: AnswerDocument3 pagesHem-Onc: AnswerAman Raj KNo ratings yet
- ECG Clinical TeachingDocument21 pagesECG Clinical TeachingSumi SajiNo ratings yet
- Two Transcripts From The Holistic Oral SummitDocument28 pagesTwo Transcripts From The Holistic Oral SummitSilambarasu KaruppiahNo ratings yet
- Oral Cases Study Guide - PediatricsDocument68 pagesOral Cases Study Guide - PediatricsJohn100% (1)
- 06.2 Inborn Error of Metabolism - Iii B - Trans PDFDocument10 pages06.2 Inborn Error of Metabolism - Iii B - Trans PDFAshim AbhiNo ratings yet
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument69 pagesAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisJirran CabatinganNo ratings yet
- PMKP Indikator International Library The JCI Library of MeasuresDocument2 pagesPMKP Indikator International Library The JCI Library of MeasuresMustafidzAlAbror100% (6)
- Clinical Neurocardiology PDFDocument505 pagesClinical Neurocardiology PDFadnanNo ratings yet
- PaediatricEMQsAAMallick PDFDocument7 pagesPaediatricEMQsAAMallick PDFMuzhaffar Abdullah100% (1)
- 9-13 1 PM Structure, Classification & ReplicationDocument26 pages9-13 1 PM Structure, Classification & ReplicationsepuluhtigaNo ratings yet
- Heart MurmursDocument48 pagesHeart MurmursAhmed T Al-MomtinNo ratings yet
- POLYCYTHEMIADocument29 pagesPOLYCYTHEMIAFaizan KhanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Antepartum Haemorrhage (APHDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Antepartum Haemorrhage (APHSanaNo ratings yet
- Transplantation: Presented by Santhiya K II M.SC Biotechnology 18PBT014Document54 pagesTransplantation: Presented by Santhiya K II M.SC Biotechnology 18PBT014AbiNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics SamplexDocument6 pagesPediatrics SamplexThea SansonNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology and Sexual DifferentiationDocument11 pagesReproductive Physiology and Sexual DifferentiationAbeebs SalahouNo ratings yet
- Approach To Cyanotic Heart Disease Christopher Cheung Santokh Dhillon PDFDocument13 pagesApproach To Cyanotic Heart Disease Christopher Cheung Santokh Dhillon PDFsuckeydluffyNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument24 pagesBleeding Disorderskholoud220No ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of The AortaDocument15 pagesCoarctation of The AortaNadiyaSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- MED - Finals 1.5 - Asthma PDFDocument12 pagesMED - Finals 1.5 - Asthma PDFYestin Reece Corpus ArcegaNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument43 pagesAtelectasismulan557100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Malaria: How Parasite Infection Affects the BodyDocument20 pagesPathophysiology of Malaria: How Parasite Infection Affects the Bodymelia100% (1)
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Glycogen Storage Disease, Type II (Pompe Disease) : BackgroundDocument7 pagesGlycogen Storage Disease, Type II (Pompe Disease) : Background201111000No ratings yet
- Exam 1 DiseasesDocument1 pageExam 1 DiseasesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- TURP Procedure ExplainedDocument36 pagesTURP Procedure ExplainedRight VentricleNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease 2017 and IeDocument59 pagesRheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease 2017 and IeLipi GautamNo ratings yet
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDocument5 pagesDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPENo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument25 pagesAcute Rheumatic Heart DiseaseArun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDocument1 pageDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (1)
- Pathology of the Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesPathology of the Digestive SystemDianNursyifaRahmahNo ratings yet
- Uworld GI NotesDocument17 pagesUworld GI NotesAyodeji SotimehinNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument14 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseasePernel Jose Alam MicuboNo ratings yet
- Pulmonic Valve DiseaseDocument22 pagesPulmonic Valve Diseasesarguss14No ratings yet
- The Most CommonsDocument80 pagesThe Most CommonsJmee8No ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inDocument13 pagesGenetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inQworld100% (1)
- Sheehan SyndromeDocument6 pagesSheehan SyndromeArvie TagnongNo ratings yet
- Respiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)Document4 pagesRespiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)PkernNo ratings yet
- Respi PhysioDocument7 pagesRespi PhysioAmal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel BakyDocument8 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel Bakyahmed gabrNo ratings yet
- Stevens Johnson DiseaseDocument5 pagesStevens Johnson DiseaseShammy RNNo ratings yet
- Medical MnemonicsDocument65 pagesMedical MnemonicsMIRZA MUHAMMAD ADNAN100% (1)
- Approach To The Child With Anemia - UpToDateDocument41 pagesApproach To The Child With Anemia - UpToDateDaniel Enrique CardenasNo ratings yet
- Signs of Respiratory Distress in Your Child: Signs To Look ForDocument2 pagesSigns of Respiratory Distress in Your Child: Signs To Look ForMa GynNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument3 pagesAtelectasisLouis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Anti FungalsDocument5 pagesAnti FungalskakuNo ratings yet
- Kidney NewDocument4 pagesKidney NewParth BhayanaNo ratings yet
- PD 17 To 21Document148 pagesPD 17 To 21Loai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Fetal AssessmentDocument52 pagesIntrapartum Fetal AssessmentAditya TejabaswaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 011Document10 pagesChapter 011api-281340024No ratings yet
- The History of Ecg MachineDocument4 pagesThe History of Ecg MachineAshley Nicole LimNo ratings yet
- Culture Illness and CareDocument9 pagesCulture Illness and CareIncaOreNo ratings yet
- Nstemi and Stemi, The Ups and Downs: Juan I. Irizarry Medical Intern San Cristobal HospitalDocument27 pagesNstemi and Stemi, The Ups and Downs: Juan I. Irizarry Medical Intern San Cristobal HospitalJuanchi INNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument14 pagesAntianginal DrugsDRABHIJITNo ratings yet
- 3 Statins (Atorvastatin & Rosuvastatin)Document15 pages3 Statins (Atorvastatin & Rosuvastatin)Thet Su LwinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Quick and Easy Medical Terminology 9th Edition by LeonardDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Quick and Easy Medical Terminology 9th Edition by Leonardamyrileyixgnaoqjmt100% (22)
- PDA Case StudyDocument5 pagesPDA Case StudyDiana Andrea AyongaoNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Statin Therapy in Ischemic Post Stroke PatientsDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Statin Therapy in Ischemic Post Stroke Patientsvhania baniNo ratings yet
- Procedural Outcomes of Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument9 pagesProcedural Outcomes of Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary InterventionsarahNo ratings yet
- PPT Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy REVISEDDocument43 pagesPPT Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy REVISEDAdhe SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Blok 8Document50 pagesFarmakologi Blok 8Syarah Mutia DewiNo ratings yet
- Supliment-2022 RJC PDFDocument320 pagesSupliment-2022 RJC PDFSimona IonitaNo ratings yet
- NICE Afib GuidelinesDocument49 pagesNICE Afib GuidelinestomlehrerlunaticNo ratings yet
- RUNDOWN West Borneo Cardiovascular Annual Meeting (WeBCAM) 2023Document3 pagesRUNDOWN West Borneo Cardiovascular Annual Meeting (WeBCAM) 2023Bayu Zeva WirasaktiNo ratings yet
- Ccu Guideline Nicvd-1Document9 pagesCcu Guideline Nicvd-1Farhan AnikNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease Classification and TypesDocument27 pagesCongenital Heart Disease Classification and TypesIda WilonaNo ratings yet
- Suresh 1998Document5 pagesSuresh 1998Andi Tiara S. AdamNo ratings yet
- Ecg CompiledDocument65 pagesEcg CompiledVstreamhdNo ratings yet
- 7.2023 HSIC Vietnam DCB Complex LHB Draft3 FDocument32 pages7.2023 HSIC Vietnam DCB Complex LHB Draft3 FR&D DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Heart Valve ClinicDocument5 pagesHeart Valve ClinicYohanes DemonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Emergencies (Autosaved)Document30 pagesCardiac Emergencies (Autosaved)Sakshi RaturiNo ratings yet
- Farmacology Del Paro CardiacoDocument14 pagesFarmacology Del Paro CardiacoNicoSwtifNo ratings yet
- Vivid 2Document5 pagesVivid 2Iqra ChuhanNo ratings yet