Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Protocol 9
Uploaded by
Roo Bee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesbiology protocol
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbiology protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesBio Protocol 9
Uploaded by
Roo Beebiology protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Yuk Yee Vuong
9. Cell Cycle, Mitosis
Questions
1. Describe division in a prokaryotic cell?
DNA replication followed by immediate cell division.
2. How many phases does the eukaryotic cell cycle consist of?
Interphase (g1,S,g2 phases) and M phase, 4 phases.
3. Name and describe three phases of interphase?
G1 RNA and protein synthesis starts, volume of the cell cytoplasm and organelles
increase rapidly. S- Nuclear DNA replication. G2- Cell growth continues.
4. Describe the centromeres, the centrioles, the mitotic spindle, and the kinetochores.
When do these structures appear during the cell cycle?
The centromere is a region in the middle of the chromosome involved in cell division
and the control of gene expression, appears during metaphase.
The kinetochore is formed on top of the centromeres. The kinetochores are the sites
where the spindles attach. Kinetochores and the spindle apparatus are responsible for
the movement of the two sister chromatids to opposite poles of dividing cell nucleus
during anaphase.
A centriole is a barrel shaped organelle found in most eukaryotic cells, though absent
in higher plants and fungi. The walls of each centriole are usually composed of nine
triplets of microtubules. Centrioles are involved in the organization of the mitotic
spindle and in the completion of cytokinesis.
The mitotic spindles function is to segregate chromosomes during cell division
(either mitosis or meiosis) to the daughter cells.
5. In what stages of the cell cycle is the cell tetraploid?
The cell is tetraploid in the stages after the S phase, after DNA replication until the
divides in cytokinesis, so it is tetraploid in the Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and
telophase.
6. Do the cells grow during the M phase?
Growth continues throughout all the phases.
7. Explain the terms sister and daughter chromosomes?
Sister chromatids are the two newly synthesized daughter chromatids derived from
the same chromosome parent.
Yuk Yee Vuong
8. Is there any difference between plant and animal cytokinesis? Describe the
cytokinesis in yeast?
Yes there is a difference between plant and animal cytokinesis. In animal cytokinesis
the membrane enfolds and forms two new identical cells. Plant cytokinesis differs
significantly from that of animal cells in that instead of forming a contractile ring,
plant cells divide by the formation of cross walls between the two daughter cells.
9. Name and describe the checkpoints of the cell cycle?
G1 Checkpoint ensures that everything is ready for DNA synthesis.
G2 Checkpoint determines if the cell can now proceed to enter M phase (mitosis)
and divide.
Metaphase Checkpoint that ensures the cell is ready to complete cell division.
10. Explain the changes in the amount of DNA in cells during the cell cycle?
The amount of DNA in the M phase is double that of the amount of DNA in the
interphase.
11. Why is it necessary to incubate the cells at 37 degrees celcius during cell staining
prior to flow cytometric analysis?
So that the cells continue cell division and activities as normal at body temperature.
12. Which phase of the cell cycle is affected by N6-dimethylaminopurine?
Affects M phase as it inhibits M phase promoting factor.
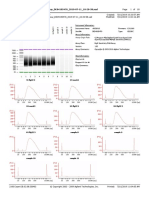
9.1 Analysis of the cell cycle using flow cytometry.
We compared these two graphs (See the next page) and saw that there was a much
lower number of cells in the second sample (treated) than the first sample. This
suggests that the chemical used to treat it suppresses the production of cells.
9.2 Mitotic Division in plant cells
Cells were observed with the 10x objective lens. Shape, size and chromosome number
of cells were seen in different stages of mitosis under the high magnification.
Yuk Yee Vuong
Fig. 3. K562 cells cultured under standard conditions for 48 h
Fig. 4. K562 cells cultured with N6-dimethylaminopurine for 48 h 39
Yuk Yee Vuong
9.3 Cell division by budding.
A specimen of suspension of yeast was prepared. Specimen was observed lower
objective first and then with the immersion objective.
You might also like
- Trainee Biomedical Scientist (Immunology)Document1 pageTrainee Biomedical Scientist (Immunology)Roo Bee0% (1)
- 206BMS Epidemiology Workshop 2Document1 page206BMS Epidemiology Workshop 2Roo BeeNo ratings yet
- Joints of The BodyDocument15 pagesJoints of The BodyRoo BeeNo ratings yet
- The Paradise P1Document10 pagesThe Paradise P1Roo BeeNo ratings yet
- Blades of FireDocument3 pagesBlades of FireRoo BeeNo ratings yet
- 13 Wasted Years" vs "Period of Increasing AffluenceDocument2 pages13 Wasted Years" vs "Period of Increasing AffluenceRoo BeeNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 2100 Expert - High Sensitivity DNA Assay - DE04105470 - 2019-07-11 - 10-20-58Document18 pages2100 Expert - High Sensitivity DNA Assay - DE04105470 - 2019-07-11 - 10-20-58Pavithra MohanNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Axis Specification in DrosophilaDocument3 pagesGenetics of Axis Specification in DrosophilaJohnkevin NocheNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesLong Test in Digestive SystemThess Curayag FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction - The Nature of Drugs & Amp Drug Development & Amp RegulationDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction - The Nature of Drugs & Amp Drug Development & Amp RegulationarifpharmjuNo ratings yet
- 2 Cloning VectorsDocument25 pages2 Cloning VectorshansaborichaNo ratings yet
- C Value ParadoxDocument2 pagesC Value ParadoxRohit MaliNo ratings yet
- Southern Blotting TechniqueDocument5 pagesSouthern Blotting TechniqueVĩnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Q4 W3 4 Sci10 LawDocument8 pagesQ4 W3 4 Sci10 LawBa BengNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Prepared By, Aparna M AjayDocument46 pagesCarbohydrates: Prepared By, Aparna M AjayAparna KinginiNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 RT PCR Test Sample Type: Method UsedDocument1 pageCovid-19 RT PCR Test Sample Type: Method Usedyour mdrahamanNo ratings yet
- Tsoktouridis Et Al 2014Document9 pagesTsoktouridis Et Al 2014Francisca Beltrán GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Section A Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesSection A Multiple Choice QuestionsViola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Gen Physiology 2015Document423 pagesGen Physiology 2015cathlynjoy.marsamoloNo ratings yet
- KNHS Grade 10 Science Class Tackles BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesKNHS Grade 10 Science Class Tackles BiomoleculesMonalisa TungkagNo ratings yet
- FMGE Information BulletinDocument17 pagesFMGE Information Bulletinmahesh100% (4)
- Bacterial Growth Requirements: Growth As Defined in The Medical Dictionaries Involves An Orderly andDocument15 pagesBacterial Growth Requirements: Growth As Defined in The Medical Dictionaries Involves An Orderly andIsabelle Hazel BenemileNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone Reg of Ald SecretDocument5 pagesFunctions of The Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone Reg of Ald SecretEstellaNo ratings yet
- Physiology TransDocument8 pagesPhysiology TranschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument4 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsJonas Galeos0% (1)
- 2015 Revision Tutorial Core Topic 2 and 4 AnsDocument35 pages2015 Revision Tutorial Core Topic 2 and 4 AnsliveaqNo ratings yet
- Modern and Convensional Wound Dressing To Interleukin 1 and Interleukin 6 in Diabetic WoundDocument2 pagesModern and Convensional Wound Dressing To Interleukin 1 and Interleukin 6 in Diabetic WoundGilang yuanggaNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Swift Method For Isolating High Quality RNA From Jute (Corchorus SPP.)Document6 pagesA Simple and Swift Method For Isolating High Quality RNA From Jute (Corchorus SPP.)anasNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Chapter 8Document13 pagesBIO 101 Chapter 8mkmanNo ratings yet
- Max M: IB Questionbank Chemistry 1Document8 pagesMax M: IB Questionbank Chemistry 1HiuonManNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Factors Limiting PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesCAPE Biology Factors Limiting PhotosynthesisKashim AliNo ratings yet
- 9700 s15 QP CompleteDocument264 pages9700 s15 QP CompleteJohnNo ratings yet
- MDU4303 - Clinical Biochemistry IIDocument196 pagesMDU4303 - Clinical Biochemistry IIlamborenuNo ratings yet
- ApoptosisDocument23 pagesApoptosisLavanya Kalapala100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: Regulation and DisordersDocument15 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: Regulation and DisordersÂmoOł ÀhmdNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer PrelimsDocument10 pagesBiology Reviewer PrelimsShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet