Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm MTE111 S2014 With Solution
Uploaded by
Varij GosineOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm MTE111 S2014 With Solution
Uploaded by
Varij GosineCopyright:
Available Formats
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
1
1:
Name the primary type of bond found in the following materials:
a) Sodium chloride =>ionic
b) Silicon =>covalent
c) Gold =>metallic
d) Ice =>hydrogen / van der Waals / secondary
[2 marks]
2:
Silver has a face-centered cubic structure and an atomic radius of 0.144 nm. Calculate the
volume of its (cubic) unit cell. [4 marks]
3:
The maximum modulus of elasticity for a copper crystal is 195 GPa. What tensile stress is
required along the corresponding crystallographic direction in order to increase the interatomic
separation distance by 0.05 %? [2 marks]
Note: =E
= = ( ) (.
)
= (, ) (.
) (1 mark)
= . (1 mark)
4:
Complete the following table of intercepts and Miller indices for the lattice planes
shown below. [3 marks]
Plane #
x intercept y intercept z intercept Miller indices
1 inf. 1/2 inf. (020)
2 1 inf. 2/3 (302)
3 1 2 1 (212)
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
2
5:
Calculate the linear density of atoms along [210] in BCC iron. [5 marks]
Notes: atomic radius r =0.124 nm, linear density =1 / repeat distance.
6:
Consider a ferrous superalloy with a Youngs Modulus of 200 GPa. A 4 mm diameter bar of
this alloy is used as a structural member in an engineering design. The unstressed length of the
bar is precisely 10 m and the structural load the bar must carry is 6000 N in tension. What is the
length of the bar under this structural load? Assume no plastic deformation. For the precision of
your result use at least 5 digits. [4 marks]
Notes: =E; Neglect non-axial deformation.
=
0
1
2
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
3
7:
Calculate (a) the mass of a spherical palladium (Pd) particle of 100 nm in diameter and (b) the
number of atoms in it. The atomic mass of palladium is M =106.42 g/mol. The density of
palladium is =12.023 g/cm
3
. Avogadros number is
= 6.02 10
23
atom/mol. The volume
of a sphere with radius r is 4
3
/3. [4 marks]
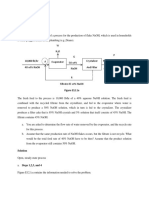
8:
The figure below shows the stress-strain curve obtained from a tensile test of iron at the three
temperatures: [3 marks]
25 C
-100 C
-200 C
Identify the corresponding curve for each temperature by writing each of the three given
temperature values in the suitable box.
_______ C
_______ C
_______ C
25 C
-100 C
-200 C
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
4
9:
A nondestructive testing program can ensure that a given 80 m diameter glass fiber will have
no atomic scale surface cracks longer than 5 m. Given that the theoretical strength of the fiber
is 5 GPa, what can you say about the expected breaking strength of this fiber? [3 marks]
Notes: The atomic scale crack has a tip radius equal to the diameter of an oxygen ion O
2
with
radius r
O2
=0.132 nm. Griffith crack model:
m
=2(c/)
1/2
.
With the crack tip radius always 2 r
O2
and the crack length always 5 m we
can say:
(1 mark)
)
.
. (2 marks)
10:
Name at least two types of point defects which influence plastic deformation and/or creep and
explain how they do it. [4 marks]
interstitial/substitutional point defects: can attach themselves to dislocations and
reduce their mobility thereby reducing the tendency for plastic deformation (by
strengthening the material) (2)
vacancy: allows for dislocation climb, a mechanism responsible for creep. The more
vacancies, the faster creep can occur by dislocation climb. (2)
11:
Name three examples of allotropes of carbon. Explain their differences with respect to
mechanical and electrical properties. [6 marks]
Diamond: hard/strong, el. insulating, transparent
Graphite: soft (van der Waals), el. conductive (aromatic rings)
graphene: strong, el. conductive, etc.
Fullerenes (buckyballs/-tubes/-etc, CNTs): strong, el. conductive or semiconductive
12:
Describe (a) the concept of x-ray diffraction and (b) what it is used for. [5 marks]
Re (a): A coherent (single wavelength) x-ray is directed onto a crystalline or
polycrystalline sample (material to be tested) and diffracted (reflected) by the
crystallographic planes into various directions. The directions (reflection angles)
depend on the distance between the individual planes of one plane type. Braggs Law is
used to derive interplanar spacing from the observed diffraction angles. (3)
Re (b): By use of a database, the set of diffraction angles (diffraction pattern) can be
assigned to a certain crystal structure and thereby a certain material (elemental or
intermetallic compound), i.e. the material can be identified via its crystal structure. If
the material type is known (chemically), it can help identify the crystal structure. (2)
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
5
13:
Tensile test of a metallic sample: (a) Describe how the onset of plastic deformation can be
explained using microstructural and micromechanical features and concepts. (b) Name two
methods to strengthen a metal and describe the underlying mechanism of strengthening.
[5 marks]
Re (a): For plastic deformation, dislocations are moving. Dislocations move along slip
directions on slip planes (slip systems). For the plastic deformation to start, the applied
stress must be large enough so the resolved shear stress is above the critical resolved
shear stress in most/all of the grains (Schmids Law). (3)
Re (b): smaller grain (grain refinement), cold working (work or strain hardening),
solution hardening, dispersion (2nd phase) strengthening are all methods to
strengthen a metal. The underlying mechanism is to introduce obstacles to dislocation
motion (reduce dislocation mobility). (2)
14: BONUS
The table below lists the atomic weight, density, and atomic radius for three hypothetical
elements with cubic crystal structure. For each element, determine whether its crystal structure
is FCC, BCC, or simple cubic and then justify your answer.
N
A
=6.022 10
23
atom/mol. [6 marks]
Element Atomic Weight (g/mol) Density (g/cm
3
) Atomic Radius (nm)
A 43.1 6.40 0.122
B 184.4 12.30 0.146
C 91.6 9.60 0.137
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
6
Solutions midterm MTE111 S2014
7
You might also like
- Mechanical Phase Separations Chapter Explains Particle Separation DevicesDocument36 pagesMechanical Phase Separations Chapter Explains Particle Separation DevicesIvan MarmilichNo ratings yet
- Brackish WaterDocument35 pagesBrackish WaterChemsys SunnyNo ratings yet
- Optimally Economic Design of Flare Systems PDFDocument5 pagesOptimally Economic Design of Flare Systems PDFMedaculoNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.3 Material Balance: 3.1 Fluidized Bed ReactorDocument14 pagesChapter No.3 Material Balance: 3.1 Fluidized Bed Reactorsagar dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Projects Can Be Divided Into Three TypesDocument25 pagesChemical Engineering Projects Can Be Divided Into Three Typestrungson1100% (1)
- Separating Liquids and Gases in Process EquipmentDocument22 pagesSeparating Liquids and Gases in Process Equipmentعبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Flow Rate Calculations for Venturi Meters and Orifice PlatesDocument4 pagesFlow Rate Calculations for Venturi Meters and Orifice PlatesSC TagleNo ratings yet
- MNT Design 2520of 2520equipmentsDocument32 pagesMNT Design 2520of 2520equipmentsshamsabbasNo ratings yet
- Iron and SteelDocument6 pagesIron and SteelkhansaaaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactors: FoglerDocument34 pagesChemical Reactors: FoglerMike PoulinNo ratings yet
- Design of packed absorber column for multi-component gas scrubbingDocument104 pagesDesign of packed absorber column for multi-component gas scrubbingNana kwadwoNo ratings yet
- Lumped Parameter Model Reaction Group Conservation of MassDocument16 pagesLumped Parameter Model Reaction Group Conservation of MassPrayogo KuntoroNo ratings yet
- Sizing StrippingDocument14 pagesSizing StrippingEka trisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Design & Simulation of Nitrobenzene Manufacturing Process: Name of Student: Kasar Khanadal MheDocument23 pagesDesign & Simulation of Nitrobenzene Manufacturing Process: Name of Student: Kasar Khanadal Mheکبری ادریس رسولNo ratings yet
- CHE656 2010 Homework2 SolutionsDocument20 pagesCHE656 2010 Homework2 Solutionsdinesh1989novemberNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Degradation of Remazol Red RB 133 Using Sacrificial ElectrodesDocument23 pagesElectrochemical Degradation of Remazol Red RB 133 Using Sacrificial ElectrodesGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Database CP Delta H Delta GDocument18 pagesDatabase CP Delta H Delta GsafinaNo ratings yet
- Densitas WaterDocument3 pagesDensitas WaterFathur Deka ApriandaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL-on Absorption - 2018 - SolutionDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL-on Absorption - 2018 - SolutionMayank Prasad100% (1)
- Soln Sa Adsorption PDFDocument2 pagesSoln Sa Adsorption PDFRee ValeraNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design Equations and ExamplesDocument25 pagesReactor Design Equations and ExamplesTÍN Phạm Nguyễn TrọngNo ratings yet
- Fluid Fluid Reaction KineticsDocument27 pagesFluid Fluid Reaction KineticsIlyas AzmanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 CompiledDocument29 pagesLab 4 CompiledFakhrulShahrilEzanieNo ratings yet
- MATLAB ProjectsDocument2 pagesMATLAB ProjectsNidhi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ch8551 Mass Transfer-I Unit I - (Diffusion) C303.1: Department of Chemical Engineering, VSBECDocument12 pagesCh8551 Mass Transfer-I Unit I - (Diffusion) C303.1: Department of Chemical Engineering, VSBECSaravanan SundaramNo ratings yet
- Design of Production 2-Ethylhexanol From Propylene and Synthesis GasDocument11 pagesDesign of Production 2-Ethylhexanol From Propylene and Synthesis Gasعلی محمد قادر خضرNo ratings yet
- Lampiran ADocument2 pagesLampiran ApittsuhermanNo ratings yet
- Ads or PtionDocument18 pagesAds or PtionBlessy GabaynoNo ratings yet
- Qeee Solution DocumnetDocument9 pagesQeee Solution DocumnetAkshay B100% (1)
- Something Related To Catalysts.Document2 pagesSomething Related To Catalysts.Deepro BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Rr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IIDocument8 pagesRr410802 Chemical Reaction Engineering IISrinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- Convergence Hints (Aspen)Document13 pagesConvergence Hints (Aspen)Saurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Simulasi OptimasiDocument3 pagesTugas Simulasi Optimasidimas wNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid Equilibria. Ethylene Oxide - Acetaldehyde and Ethylene Oxide - Water SystemsDocument5 pagesVapor-Liquid Equilibria. Ethylene Oxide - Acetaldehyde and Ethylene Oxide - Water SystemsGie0% (1)
- Impor Dimethyl Ether (DME)Document3 pagesImpor Dimethyl Ether (DME)Savannah Yonita CNo ratings yet
- XDocument2 pagesXXxxNo ratings yet
- Wo 2014185872 A 1Document11 pagesWo 2014185872 A 1Shahid AliNo ratings yet
- Design and analysis of waste water treatment processesDocument53 pagesDesign and analysis of waste water treatment processesMuddasar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- PBRDocument19 pagesPBRdarvyneeNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations II Rr320801Document8 pagesMass Transfer Operations II Rr320801Nagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Checker X analyzes report on advance stop line designDocument22 pagesPlagiarism Checker X analyzes report on advance stop line designMuhamad Ichsan YogaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document4 pagesLecture 9Asif AliNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A Sudah FinalDocument20 pagesLampiran A Sudah FinalBayu Handika PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Heat of Solution and Mixing PDFDocument33 pages2 - Heat of Solution and Mixing PDFshifa veronicaNo ratings yet
- PRESENTASI ATK MUHAMMAD RAIS ZAINDocument8 pagesPRESENTASI ATK MUHAMMAD RAIS ZAINMuhammad RaisNo ratings yet
- Chaper 4 Non-Reactive Multi Units ProcessDocument48 pagesChaper 4 Non-Reactive Multi Units Processجنات الغبيراءNo ratings yet
- Problem with Gas AnalysisDocument2 pagesProblem with Gas AnalysisKyle LabastillaNo ratings yet
- Basic Integration Formulas ExercisesDocument1 pageBasic Integration Formulas ExercisesJWAN RA YA3QOBNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem #5Document10 pagesSample Problem #5DozdiNo ratings yet
- Cyanide Treatment TechnologiesDocument3 pagesCyanide Treatment Technologiesdei_sandeep7994No ratings yet
- Neraca MassaDocument15 pagesNeraca MassaFrengky Akmil PutraNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of CSTR For Manufacture of Propylene GlycolDocument6 pagesModeling and Simulation of CSTR For Manufacture of Propylene Glycolantoojacome100% (1)
- Solvay TowerDocument10 pagesSolvay Towerraspati19No ratings yet
- HimmelblauDocument17 pagesHimmelblauadilla nitaaNo ratings yet
- Philipp Louis D#2docxDocument8 pagesPhilipp Louis D#2docxEymann Jala100% (3)
- Sample ProblemsDocument18 pagesSample ProblemsEggy ThreekingsNo ratings yet
- 4 2020 Pap Menara DistilasiDocument48 pages4 2020 Pap Menara DistilasiAlwan Al AzharNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 WastewaterDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 WastewaterAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nNo ratings yet
- Assignment - #2 GeotechDocument16 pagesAssignment - #2 GeotechÅbhîshęķ ĂryąNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/Undertakingdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Astm A510mDocument7 pagesAstm A510mÖZGÜRNo ratings yet
- Benzocaine Syntheisi Via Fischer EsterificationDocument7 pagesBenzocaine Syntheisi Via Fischer EsterificationXiang Yu100% (7)
- Pre-Final Examination Feb 2023Document1 pagePre-Final Examination Feb 2023Arun AchalamNo ratings yet
- Practical ElectricityDocument104 pagesPractical Electricityray davis100% (1)
- Xampler HFDocument8 pagesXampler HFAnil ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water - S PDFDocument6 pages3 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water - S PDFJon CranNo ratings yet
- Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders: The International Pharmacopoeia - Ninth Edition, 2019Document4 pagesBulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders: The International Pharmacopoeia - Ninth Edition, 2019Khaled ZEMNINo ratings yet
- B Pharmacy 2015Document114 pagesB Pharmacy 2015GalataNo ratings yet
- G.6 Q.1 SCIENCE Lesson 2 Homogeneous MixtureDocument35 pagesG.6 Q.1 SCIENCE Lesson 2 Homogeneous MixturemeguiNo ratings yet
- ExperimentDocument2 pagesExperimentParth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- HEC Past PaperDocument21 pagesHEC Past PaperTalha Aslam100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Design Lecture - 07Document24 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Lecture - 07Mohmmad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Industria1 C o M B U S T I o N Pollution and C o N T R o L PDFDocument890 pagesIndustria1 C o M B U S T I o N Pollution and C o N T R o L PDFAfzaal AshrafNo ratings yet
- Oxidation States of ManganeseDocument4 pagesOxidation States of ManganesexbokyxNo ratings yet
- 1 What - Are - Enzymes PDFDocument16 pages1 What - Are - Enzymes PDFtmlNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 8Document1 pageSyllabus 8harrypaswan87No ratings yet
- Buthelezi, Olaniran, Pillay. 2009. Turbidity and Microbial Load Removal From River Water Using Bioflocculants From Indigenous Bacteria IDocument7 pagesButhelezi, Olaniran, Pillay. 2009. Turbidity and Microbial Load Removal From River Water Using Bioflocculants From Indigenous Bacteria IAzb 711No ratings yet
- Granta EduPack ReleaseingDocument8 pagesGranta EduPack ReleaseingAshwary Sheel Wali Research Scholar, Dept of Mech Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- The Elegant UniverseDocument2 pagesThe Elegant UniverseNarasoma P. FeynmanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Paint Formulated Using SecondaDocument8 pagesCharacterization of Paint Formulated Using SecondasiaNo ratings yet
- Hilts 105Document277 pagesHilts 105Wesley CheungNo ratings yet
- Astm D 6583 00 - Ensaio Padronizado Porosidade Camada de TintaDocument2 pagesAstm D 6583 00 - Ensaio Padronizado Porosidade Camada de TintaNara CamargoNo ratings yet
- En 13237-2003 Terms and Definitions For Equipment and Protective Systems Intended For Use in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresDocument26 pagesEn 13237-2003 Terms and Definitions For Equipment and Protective Systems Intended For Use in Potentially Explosive AtmospheresGargiulo AnitaNo ratings yet
- k30 Euroline BisDocument16 pagesk30 Euroline BiscyberquasitNo ratings yet
- The Design of Network Arches: SynopsisDocument11 pagesThe Design of Network Arches: SynopsisProjesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Amines Amino Acids ProteinsDocument13 pagesAmines Amino Acids ProteinsClifford Dwight RicanorNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Rate For Standard Stock Materials Common SR 2021-22 (11 KV System)Document161 pagesSchedule of Rate For Standard Stock Materials Common SR 2021-22 (11 KV System)sagar mukulNo ratings yet