Professional Documents
Culture Documents
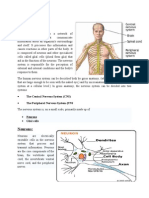
The Nervous System
Uploaded by
Kristie Becker100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
110 views8 pagesThe nervous system is the Most complex and elavorate system of biological structure in human body. There are three characteristics involved in the nerve impulse :Theshold,All or none principle and Repractory period. Neurotransmitters are chemical substances released by one neuron through then synapse and affect or influence the receiving neuron.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nervous system is the Most complex and elavorate system of biological structure in human body. There are three characteristics involved in the nerve impulse :Theshold,All or none principle and Repractory period. Neurotransmitters are chemical substances released by one neuron through then synapse and affect or influence the receiving neuron.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
110 views8 pagesThe Nervous System
Uploaded by
Kristie BeckerThe nervous system is the Most complex and elavorate system of biological structure in human body. There are three characteristics involved in the nerve impulse :Theshold,All or none principle and Repractory period. Neurotransmitters are chemical substances released by one neuron through then synapse and affect or influence the receiving neuron.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Most complex and elavorate system of biological structure in human body
Composed of central and peripheral nervous system
Neuron
Basic unit of the nervous system
Transmit and receive electrical signals
Parts of the Neuron
Dendrites
Fine and tiny hairlike structures that look like branches of a tree
Receive and send aerve impulses
Axon
Carries away the stimulus signalled by the cell body to another neuron
Myelin sheath
A fatty material that covers and protects the axon
Speeds up the conduction of nerve impulses
Nodes
They serve as a breake of the momentum of the speed of transmitting
nerve impulses
3 Types of Neuron : according to their functions
1.Sensory neurons(afferent or receptor neurons)
Receive stimuli from the environment through the sense organs
and transmits them to the central nervous system
2.Motor neurons(efferent neurons)
Carry information or messages from the central nervous system to
the muscles and glands
3.Interneurons(connecting or associating neurons)
Most numerous in the human body
Serves as integrators or coordinators of brain activities and bodily
processes.
Gial cells(neuroglia)
Smaller than neurons
They provide support to the neuron by supplying them
nutrients,releasing chemical,clearing away their waste, and helping
to separate them from other neurons
Nerve Impulse
An electro-chemical substance that passed by a dendrite inward to
a cell body, then to the axon
There are three characteristics involved in the nerve impulse
:Theshold,All or none principle and Repractory period.
Synapse
A junction or microscopic gap
Neurotransmitters
These are chemical substances released by one neuron through
then synapse and affect or influence the receiving neuron
They are responsible for sensation,perception,cognitive and motor
behavior
Some types of neurotransmitters are:
Acetycholine(cholinergic)(ACH)
Found in the limbic system
Controls muscle constraction
Dopamine(dopaminergic)
A transmitter located at the midbrain
is involved in voluntary movements,learning,memory and emotional
behaviour
Cathechollamines
composed of epinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine(non-adrenalin)
located at the hindbrain
this transmitter are involve wakefulness,learning,process,memory,eating,and
regulation of moods
Serotonin
is an inihibitory transmitter which is involved in body temperature,
sleep,moods and pain sensation
Endorphins
pain-killers synthesised by your body in response to stress and injury
GABA(Gamma-aminobutylic acid)
Is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that excites the action of the neuron
DIVISION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
I.Central Nervous System
Responsible for all mans behaviour ,the root of human behaviour
Stores and retrieves information
Composed of brain and spinal cord
A.Brain
Brain is the control system of the nervous system
It is the most intricate,complex and unique mechanism of the human body
The brain is enclosed inside the cranium(the hardest portion of the skull) to
protect it from injury
It is a sponge-like organ or firm gelatin that weighs about 1,350 g(1.36 kilo
of an adult size brain)
The brain is divided into halves(cerebral hemispheres).The left hemispheres
is responsible in abstract and verbal (language) ability.The right hemispheres
Is responsible for artistic,musical spatial,visual skills and whole pattern
perception.It is also involved in the control emotions
There are 3 major subdivisions of the brain;
1.Hindbrain
It is composed of the;
a.Medulla oblongala
Then of lowest portion of the brain and is connected with the spinal
cord
b.Pons Varolii
Responsible in transmitting neurotransmitters of motor information
permitting the coordination of muscles and and integration of
movement between the right and left body
c.Cerebelum
It is responsible in control of the body movement and motor
movement
d.Reticular formation
Its function is to keep the cerebral cortex alert and conscious
2.Midbrain
Smallest division of the brain
Lies between the hindbrain and midbrain
Acts like a switchboard
Transmits neural impulses upward to the higher center of the brain and
downward to the spinal cord
Contains neurons that are important for visual and auditory functions
It also contain the reticular formation(upper portion)
3.Forebrain
The largest part of the brain
It is composed of three main parts;
a.Thalamus
Brains relay station
b. Limbic System
It receives sensory images the visceral organs and helps control their
activites
Consist of;
Amygdala
Involved in emotion and is responsible for self preservation
Hippocampus
Transforms many kinds of fleeting memories into permanent
long term memory
Hypothalamus
It controls our sleep/wake cycles,heartaction, degistion,
breathing,hunger,thirst,body temperature,water balance,blood
pressure,reproductive behavior,pleasure,hostility and pain
c.Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain
Divided into two halves called the cerebral hemispheres;
Each hemisphere is divided into 4 parts:
1.Frontal lobe
In front of the central sulcus and is the seat of personality and
movement
2.Pariental lobe
Responsible for skin senses and sense of body position
3.Occipital lobe
Involved with visual sensation and memory
4.Temporal lobe
Involve in hearing,speaking,understanding verbal and writing
materials
B.Spinal cord
A long tapering tube which occupies the hollow interior of the vertebral
column
The spinal cord is the brains link to the peripheral nervous system
Receives information from the skin and muscles and transmit them to the
brain ,and from the brain it sends message down to the muscles and glands
of the body-like a relay action
It also initiates commands for relax responses
II.The Peripheral Nervous System
It is composed of nerves.The nerves carrying sensory input to the central
nervous system are the affrenet nerves.The nerves carrying the motor output
away from the central nervous system to muscles and glands are the efferent
nerves
Its is subdivided into;
Somatic nervous system(voluntary)
Transmits sensation from the outside world to the spinal cord and
brain and relays message to skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system
Controls heart action,digestion,excretion,salvation,sexual orgasm, and
perspitation
It has 2 divisions
Sympathetic division
Operates in emergencies and stressful situation when vigorous action is
needed
Parasympathetic division
It is used in relaxed situation
CARE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
1.Protect the brain from injury
2.Avoid stress;frustration,and conflict
3.Rest and sleep are good for the mid
4.Give your body enough sunlight and fresh air
5.Eat well balanced diet.
6.Never take too much alcohol and never take prohibited and dangerous
drugs
The Endocrine Glands (Ductless Glands)
Made up of numerous glands that secrete various chemical called hormones
The various endocrine glands are the pituitary gland,pineal gland ,thyroid
gland,parathyroid gland,adrenal gland and gonads
The Connecting Mechanism- The Nervous System
A.Neuron
The basicconducting unit of the nervous system
It has 3 principal parts:
Dendrites
Are specialized signal-receiving structures where the
impulse(input)enters
Cell body(the central region)
Integregates input and output
Axon
Where the output is discharge
There are approximately 12 billion neurons in the central nervous system
Types of Neuron
1.According to speed
Impulses in the fastest neuron move at the rate of 110 m/s;in the slowest,
0.5 ./s.
2.According to basic function
Sensory Neuron(afferent fibers)
Conduct impulses to the nervous system
Association Neuron(central or connecting)
Conduct impulses within the nervous system
Motor Neuron(efferent fibers)
Conduct impulses away from the nervous system
B.Levels of Synaptic Connections
1.Simple reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli
2.An instinct is a complex unlearned bahavior of a species set off by relatively
simple stimuli
3.The cortex level involves more neuron and may take more time before reaction or
responses takes place
C.Stimulation and homoestasis
Stimulation is the action of stimuli on nerves by which activity is evoked
Homeostatisis is the tendency of the body to maintain its natural
equilibrium
D.Nerve Impulses
Are the potencial changes moving along a nerve fiber
Two Important Principle Related to Nerve Impulses:
1.The All-or-None Law
States that the impulse is independent of the properties of the stimulus
which started it
2.The Frequency Principle
States that there are more impulses per second with stronger stimulus than
with the weaker stimulus
Varieties of Neural Circuits
1.Spatial Summation involves a many-to-one principle
Some neurons require the simultaneous stimulation of a large number of
other neurons for activation
2.Temporal Summation
In Temporal Summation repeated stimulation from one or more nearby
neurons in a short period of time may be activated
3.Recruitment
In Recruitment there is a progressive increase in the number of nerve fibers
giving nerve impulses as the exciting impulse is repeated
4.Reverberation
Neurons are frequently arranged in cuircuits in which the fiber of one neuron
comes back and ends on a neuron whose fiber stimulates the first neuron
5.Reciprocal innervation
Reciprocal innervation Depends on the way muscles are arranged and
innervated.When the extensor muscles contract ,the flexor muscles relax and
vice versa
6.Inhibition
In Inhibition reflex actions may be stopped
7.Integration
The ability of the nervous system to function as a unit
E.Division of the Human Nervous System
1.Autonomic or Sympathetic Nervous System
This system is so called becausemany of its activities are autonomous or
self regulating
It consist of two antagonist
Sympathetic System
It is active in emotion
Parasympathetic System
Composed of fibers from cranial region,some below the sympathetic
system
This division acts or affect one organ at a time
The function of these system can also be described in terms of;
Compition when both fibers are connected to the same muscle or
gland
Cooperate-both being active at once or acting in sequence
2.The Cerebro-Spinal System:
a.The Central Nervous System-The Brain
Cerebrum: For sense perception,vouluntary movements,learning,remembering,
thinking,emotion,consciousness,personality integration
Hypothalamus:Control of visceral and somatic function as temperature and
metabolism
Thalamus:The way-station for impulses coming up the spinal cord to cerebrum
Midbrain:A conduction and switching center;pupillary light reflex
Cerebellum:For muscle tone, body balance, coordination of voluntary movement
Medulla:Has control over breathing swallowing,digestion,heartabeat
Reticular Formation:For the arousal and alertness of the organism,the change
from sleep to wakefulness
Corpus Callosum:Contains fibers connecting the two brain hemisphere
Brain Areas
1.Motor Area
2.Body-sense area
3.Visual area
4.Auditory Area
5.Speech Area
6.Association Area
7.Smell Area
8.Taste Area
B.The Peripheral Nervous System
Composed of cranial nerves,the spinal nerves and the nerves of the autonomic
nervous system
Cranial nerves:There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves made up of sensory,motor
and mixed nerves
Spinal nerves:There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves
Deseases of the Nervous System
1.Infection due to bacteria,viruses,yeast,fungi, etc.
2.Tumurs
3.Heredity disorders
4.Degenerative diseases
5.Congenital abnormalities
6.Convulsive disorders
7.Poison and toxins
8.Reflex disorder
ON BRAIN STUDIES
Doubtful researches:
1.That all brain areas are equipotential
2.taht special neutral processes of the brain are meant for specific function
Researches that have firmly established some truths which were considered
doubtful:
1.That all areas of the brain are not equipotential
2.In the higher mental processes like reasoning and problem solvinf,many,and not
only a few areas are involved in the process
3.While some functions of the brain are localized in certain fixed areas,many
function of the brain are duplicated in more than one brain area
Four methods popular among physiological psychologist and
neurophysicist in studying the brain are the ff:
1.Injury or Surgical ablation
2.Electrical or chemical stimulation
3.The use of the Electroencephalogram(EEG)
4.The use of refined microelectrodes
ALZHEIMER-A SLOW DEATH OF THE MIND
Is a degenerative brain disorder named after Alios Alzheimer,a German
neurologist,and is a cruel,incurable disease killing a person twice-firstthe
brain and then his body
Recent clues to the pathology of Alzheimer are the ff:
1.Tangles and Plaques
2.Hippocampus Blockage
3.Reduced RNA
4.Genetics
5.Slow Viruses
6.Interlocking causes
Cure:
1.They use drugs to raise the level of this neuro-transmitter.The most effective is
physostigmine
2Believing that not enough drug gets into the brain when taken orally,.A small
pump is implanted under the skin of the abdomen.Then a catheter inserts
acetylcholine drug(bethanechol) thru a hole in the skull and is continuously flowed
directly into the brains ventricles
You might also like
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemananthNo ratings yet
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemSumaira Noreen100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesNervous SystemkenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System LectureDocument234 pagesNervous System Lecturealyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System AnatomyDocument10 pagesAutonomic Nervous System AnatomyghalyNo ratings yet
- CVS FullDocument32 pagesCVS FullLianne PalinsadNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemAltaf Hussain Khan50% (2)
- The Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedDocument24 pagesThe Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- The Nervous SystemDocument54 pagesThe Nervous Systemeleldev100% (2)
- Study Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesStudy Guide QuestionszaidaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy LectureDocument20 pagesAnatomy Lectureshiba ngujo100% (1)
- Endocrine System Practice TestDocument10 pagesEndocrine System Practice TestFarrah Turner Matthews0% (1)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument46 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyBegumHazinNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesStructure and Function of The Endocrine Systemwalt65No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endocrine System NotesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To The Endocrine System NotesJulioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesEndocrine SystemDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemKimberly Anne SP Padilla100% (2)
- The Endocrine System Study GuideDocument4 pagesThe Endocrine System Study Guideapi-2776680980% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument75 pagesEndocrine Systemneri_pearl100% (1)
- The Nervous System - NotesDocument12 pagesThe Nervous System - NotesLol lol100% (2)
- Chapter 1 The Human OrganismDocument12 pagesChapter 1 The Human OrganismJenny AnneNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System Bio FactsheetDocument4 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Bio FactsheetEleanor WilliamsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahDocument24 pagesThe Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahAzhar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument5 pagesDigestive System NotesRavenApigoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- L23 The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesL23 The Nervous SystemGemma Wrigley100% (2)
- General Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyDocument4 pagesGeneral Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyChristine Rose EmNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument55 pagesEndocrine SystemMatt OñaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE Nervous SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors: ExteroreceptorsDocument10 pagesSensory Receptors Sensory Receptors: ExteroreceptorsMikhail CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- 7-Nervous SystemDocument69 pages7-Nervous SystemCarl Vincent VingnoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemDocument38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemBrantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Body and Its ConstituentsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 The Body and Its ConstituentsmadisonNo ratings yet
- Pre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyDocument5 pagesPre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyGlenice Joy SenocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4 The Anatomy of The Nervous System and Neural TransmissionDocument47 pagesChapter 3 & 4 The Anatomy of The Nervous System and Neural Transmissionjohn rey adizNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: The Central Processing UnitDocument85 pagesThe Nervous System: The Central Processing UnitGeoffrey MilesNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesOrgans of The Digestive SystemBrandon HunterNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesNervous System NotesAlex Whitwam100% (3)
- Nervous System Reviewer!Document5 pagesNervous System Reviewer!Madelle Capending DebutonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesIntegumentary Systemkuroko tetsuya100% (2)
- Chapter 2.0 Cell Signalling and Endocrine RegulationDocument93 pagesChapter 2.0 Cell Signalling and Endocrine RegulationNurarief AffendyNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle: Hina Karim NES InstructorDocument19 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle: Hina Karim NES InstructorshahinaNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 - Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesNCM 104 - Nervous Systembabeepny807076100% (5)
- EE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLDocument29 pagesEE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLtmkiran100% (1)
- The Human Nervous Syste1Document10 pagesThe Human Nervous Syste1taytay321No ratings yet
- Principles of Neural and Hormonal CommunicationDocument56 pagesPrinciples of Neural and Hormonal Communicationlynn.dargham2No ratings yet
- Overview of Nervous SystemDocument63 pagesOverview of Nervous SystemMAHARANI100% (1)
- Endocrine System QuizDocument2 pagesEndocrine System QuizDr. Atif Hassan KhirelsiedNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument12 pagesNervous System WorksheetLeamae ObinaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemC H ♥ N T Z0% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemEllanny GloriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Inflammation, Tissue Repair, and Wound HealingDocument5 pagesChapter 14: Inflammation, Tissue Repair, and Wound Healingbdelvalle3100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument33 pagesDrugs Acting On The Immune SystemAnonymous iG0DCOf100% (1)
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument29 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum Marie50% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocument25 pagesEndocrine Systemangel_maui100% (13)
- Peripheral Nervous System NotesDocument9 pagesPeripheral Nervous System NotesSaoirseNo ratings yet
- As-Built Commercial BLDG.1Document11 pagesAs-Built Commercial BLDG.1John Rom CabadonggaNo ratings yet
- Fear of God-3Document50 pagesFear of God-3Duy LêNo ratings yet
- List of Olympic MascotsDocument10 pagesList of Olympic MascotsmukmukkumNo ratings yet
- Lifting PermanentmagnetDocument6 pagesLifting PermanentmagnetShekh Muhsen Uddin Ahmed100% (1)
- Navi-Planner User ManualDocument331 pagesNavi-Planner User ManualRichard KershawNo ratings yet
- Route Clearence TeamDocument41 pagesRoute Clearence Teamctenar2No ratings yet
- April 2021 BDA Case Study - GroupDocument4 pagesApril 2021 BDA Case Study - GroupTinashe Chirume1No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument10 pagesSickle Cell DiseaseBrooke2014No ratings yet
- CL200 PLCDocument158 pagesCL200 PLCJavierRuizThorrensNo ratings yet
- Brochure GM Oat Technology 2017 enDocument8 pagesBrochure GM Oat Technology 2017 enArlette ReyesNo ratings yet
- Statistical Techniques EE 532Document1 pageStatistical Techniques EE 532AdnanNo ratings yet
- SAP HR - Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW)Document5 pagesSAP HR - Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW)Bharathk KldNo ratings yet
- Current Surgical Therapy 13th EditionDocument61 pagesCurrent Surgical Therapy 13th Editiongreg.vasquez490100% (41)
- Bathinda - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesBathinda - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBhuwan GargNo ratings yet
- Asu 2019-12Document49 pagesAsu 2019-12janineNo ratings yet
- MPT EnglishDocument5 pagesMPT Englishkhadijaamir435No ratings yet
- Four Hour Body Experiment Tracker TemplateDocument4 pagesFour Hour Body Experiment Tracker Templatechanellekristyweaver100% (1)
- SXV RXV ChassisDocument239 pagesSXV RXV Chassischili_s16No ratings yet
- FDD Spindle Motor Driver: BA6477FSDocument12 pagesFDD Spindle Motor Driver: BA6477FSismyorulmazNo ratings yet
- Qualitrol 900 910Document6 pagesQualitrol 900 910chennupati999No ratings yet
- Simon Fraser University: Consent and Release FormDocument1 pageSimon Fraser University: Consent and Release FormpublicsqNo ratings yet
- PR Earth Users Guide EMILY1Document2 pagesPR Earth Users Guide EMILY1Azim AbdoolNo ratings yet
- Nse 2Document5 pagesNse 2dhaval gohelNo ratings yet
- Ward 7Document14 pagesWard 7Financial NeedsNo ratings yet
- XU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Document5 pagesXU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Harold John LaborteNo ratings yet
- Em FlexicokingDocument8 pagesEm FlexicokingHenry Saenz0% (1)
- IbmautomtiveDocument38 pagesIbmautomtiveMeltz NjorogeNo ratings yet
- MiddleWare Technology - Lab Manual JWFILESDocument171 pagesMiddleWare Technology - Lab Manual JWFILESSangeetha BajanthriNo ratings yet
- Perturbation MethodsDocument29 pagesPerturbation Methodsmhdr100% (1)
- Beautiful SpotsDocument2 pagesBeautiful SpotsLouise Yongco100% (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainFrom EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (95)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)