Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antihistamine Diphenhydramine Guide
Uploaded by
Shyrra Edades PinderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antihistamine Diphenhydramine Guide
Uploaded by
Shyrra Edades PinderCopyright:
Available Formats
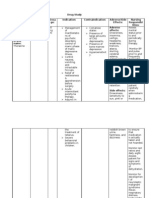
DIPHENHYDRAMINE
Drug classes
Antihistamine
Anti-motion sickness agent
Sedative-hypnotic
Antiparkinsonian
Cough suppressant
Therapeutic actions
Competitively blocks the effects of histamine at H1-receptor sites, has atropine-like, antipruritic, and sedative
effects.
Indications
Relief of symptoms associated with perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis; vasomotor rhinitis; allergic
conjunctivitis; mild, uncomplicated urticaria andangioedema; amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or
plasma; dermatographism; adjunctive therapy in anaphylactic reactions
Active and prophylactic treatment of motion sickness
Nighttime sleep aid
Parkinsonism (including drug-induced parkinsonism and extrapyramidal reactions), in the elderly
intolerant of more potent agents, for milder forms of the disorder in other age groups, and in combination with
centrally acting anticholinergic antiparkinsonian drugs
Syrup formulation: Suppression of cough due to colds or allergy
Indication for the Patient:
Contraindications and cautions
Contraindicated with allergy to any antihistamines, third trimester of pregnancy, lactation.
Use cautiously with narrow-angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy,
asthmatic attack, bladder neck obstruction,pyloroduodenal obstruction, pregnancy; elderly patients who may
be sensitive to anticholinergic effects.
IV facts
Preparation: No additional preparation required.
Infusion: Administer slowly each 25 mg over 1 min by direct injection or into tubing of running IV.
Incompatibilities: Do not combine with amobarbital, amphotericin B, cephalothin,
hydrocortisone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, thiopental.
Y-site incompatibilities: Do not mix with foscarnet.
Adverse effects
CNS: Drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness,
excitation, nervousness, tremor, headache, blurred vision,diplopia
CV: Hypotension, palpitations, bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystoles
GI: Epigastric distress, anorexia, increased appetite and weight gain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or
constipation
GU: Urinary frequency, dysuria, urinary retention, early menses, decreased libido, impotence
Hematologic: Hemolytic anemia, hypoplastic anemia,
thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia
Respiratory: Thickening of bronchial secretions, chest tightness, wheezing, nasal stuffiness, dry mouth,
dry nose, dry throat, sore throat
Other: Urticaria, rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive perspiration
Interactions
Drug-drug
Possible increased and prolonged anticholinergic effects with MAOIs
Nursing considerations
Assessment
History: Allergy to any antihistamines, narrow-angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer,
symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, asthmatic attack, bladder neck obstruction, pyloroduodenal obstruction,
third trimester of pregnancy, lactation
Physical: Skin color, lesions, texture; orientation, reflexes, affect; vision exam; P, BP; R, adventitious
sounds; bowel sounds; prostate palpation; CBC with differential
Interventions
Administer with food if GI upset occurs.
Administer syrup form if patient is unable to take tablets.
Monitor patient response, and arrange for adjustment of dosage to lowest possible effective dose.
Teaching points
Take as prescribed; avoid excessive dosage.
Take with food if GI upset occurs.
Avoid alcohol; serious sedation could occur.
These side effects may occur: Dizziness, sedation, drowsiness (use caution driving or performing tasks
requiring alertness); epigastric distress, diarrhea or constipation (take drug with meals); dry mouth (use
frequent mouth care, suck sugarless lozenges); thickening of bronchial secretions, dryness of nasal mucosa
(use a humidifier).
Report difficulty breathing, hallucinations, tremors, loss of coordination, unusual bleeding or bruising,
visual disturbances, irregular heartbeat.
You might also like
- Drug Card PropofolDocument1 pageDrug Card PropofolBenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDahnel Magumpara100% (1)
- Saint Gemma Galgani EssayDocument3 pagesSaint Gemma Galgani Essayapi-3453563630% (1)
- Postconcussion SyndromeDocument16 pagesPostconcussion SyndromeonaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDocument8 pagesDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyLizeth Querubin93% (15)
- Nursing Considerations for MeropenemDocument2 pagesNursing Considerations for MeropenemKullin RainNo ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument3 pagesAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- DiphenhydramineDocument6 pagesDiphenhydramineAndrea BroccoliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesAmiodarone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Morphine SulfateDocument2 pagesMorphine SulfategreynabNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- DiphenhydramineDocument1 pageDiphenhydramineYanejoulce SacanleNo ratings yet
- Captopril Drug StudyDocument1 pageCaptopril Drug StudyRachel Mae Dente AcedillaNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Document2 pagesAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudycliffordbuenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Atenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAtenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Dutasteride 0.5mg + Tamsulosin HCL 0.4mg (Duodart)Document19 pagesDutasteride 0.5mg + Tamsulosin HCL 0.4mg (Duodart)ddandan_2No ratings yet
- AtracuriumDocument2 pagesAtracuriumFederico Andales50% (2)
- ZonisamideDocument2 pagesZonisamideRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- MinoxidilDocument4 pagesMinoxidilapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Esmolol adverse reactions and nursing implicationsDocument3 pagesEsmolol adverse reactions and nursing implicationsTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- MeperidineDocument2 pagesMeperidineNinoska Garcia-Ortiz50% (2)
- AtenololDocument3 pagesAtenololapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Multiple Injuries: Drug StudiesDocument10 pagesMultiple Injuries: Drug StudiesTarquin TomadaNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummAminah Yue100% (1)
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Pantoprazole Sodium for Gastric Acid SuppressionDocument1 pagePantoprazole Sodium for Gastric Acid SuppressionGladys SoronioNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl SublimazeDocument2 pagesFentanyl SublimazeENo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- Warfarin SodiumDocument3 pagesWarfarin SodiumAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin: A Potent Fluoroquinolone AntibioticDocument2 pagesLevofloxacin: A Potent Fluoroquinolone AntibioticEliza Rahardja100% (1)
- NSAID Parecoxib Post-Op Pain Relief RisksDocument16 pagesNSAID Parecoxib Post-Op Pain Relief RisksLeony Llanos MindoroNo ratings yet
- NystatinDocument3 pagesNystatinapi-3797941100% (3)
- AminophyllineDocument9 pagesAminophyllineZaira BataloNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Cefotaxime: Antibiotic ClassDocument2 pagesCefotaxime: Antibiotic ClassMentari AmirNo ratings yet
- SalmeterolDocument2 pagesSalmeterolapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- PlasilDocument1 pagePlasilernestjohnNo ratings yet
- Veklury (Remdesivir) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreDocument4 pagesVeklury (Remdesivir) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreRex ChanNo ratings yet
- Methylprednisolone AlphapharmDocument5 pagesMethylprednisolone AlphapharmMarthin TheservantNo ratings yet
- Regular InsulinDocument1 pageRegular InsulinKevin NelsonNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Gabapentin: Drug Class Therapeutic ActionsDocument2 pagesName of Drug: Gabapentin: Drug Class Therapeutic ActionsCecile EstebanNo ratings yet
- DiphenhydramineDocument6 pagesDiphenhydramineMiriam Defensor Santiago100% (2)
- Zine Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesZine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine MaleateDocument3 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Current Trends in ObstetricsDocument6 pagesCurrent Trends in ObstetricsShyrra Edades Pinder100% (1)
- Constipation Clinical ManifestationDocument1 pageConstipation Clinical ManifestationShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- HTP Ineffective BreathingDocument2 pagesHTP Ineffective BreathingShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- PA FINDINGS Body Part Exam Summary and AnalysisDocument16 pagesPA FINDINGS Body Part Exam Summary and AnalysisShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- HTP Ineffective BreathingDocument2 pagesHTP Ineffective BreathingShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- HTP ScabiesDocument3 pagesHTP ScabiesShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Cultural Criteria and NaturalDocument4 pagesCultural Criteria and NaturalShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- DisorderDocument6 pagesDisorderShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- HTP Oral FungalDocument2 pagesHTP Oral FungalShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Abarintos Family GenoGram Shows Pulmonary RisksDocument1 pageAbarintos Family GenoGram Shows Pulmonary RisksShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- HTP Oral FungalDocument2 pagesHTP Oral FungalShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Pcap Pedriatric Community PneumoniaDocument1 pagePcap Pedriatric Community PneumoniaShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Edades, Shyrra L. BSN305Document1 pageEdades, Shyrra L. BSN305Shyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and PreventionDocument1 pagePneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and PreventionShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and PreventionDocument1 pagePneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and PreventionShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- HTP Ineffective BreathingDocument3 pagesHTP Ineffective BreathingShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Institute of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFar Eastern University Institute of Nursing Nursing Care PlanShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Roxithromycin TabletDocument13 pagesRoxithromycin Tabletno debedeNo ratings yet
- Viral Myositis in Children: Child Health UpdateDocument3 pagesViral Myositis in Children: Child Health UpdateMark Christian GlindroNo ratings yet
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and The CDCDocument24 pagesChronic Fatigue Syndrome and The CDCArvi Jansen100% (1)
- Nursing assessment essentialsDocument5 pagesNursing assessment essentialsFay DalanonNo ratings yet
- Fine Tuning the Nutrition Care ProcessDocument13 pagesFine Tuning the Nutrition Care ProcessRacquel Jahn CorderoNo ratings yet
- Miopati - Referensi MiopatiDocument25 pagesMiopati - Referensi MiopatiKelvin Theandro GotamaNo ratings yet
- HSN101Document3 pagesHSN101Raha RajabigamasaeiNo ratings yet
- Positive Language Guide - 0Document22 pagesPositive Language Guide - 0Xristos BeretisNo ratings yet
- Cardio CaseDocument21 pagesCardio CaseJan Rae Y. BattungNo ratings yet
- World Hunger Web QuestDocument5 pagesWorld Hunger Web Questapi-313403351No ratings yet
- Captopril Sublingual Vs OralDocument8 pagesCaptopril Sublingual Vs OralTa RaNo ratings yet
- WC BPR - Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1573r4e FinalDocument68 pagesWC BPR - Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1573r4e FinalArumDesiPratiwiNo ratings yet
- Herbal PlantsDocument14 pagesHerbal Plantsapi-3739910100% (2)
- Ms. Ann Female 48 Years Old Diabetes Mellitus Foot/diabetes Mellitus Joseph MDocument10 pagesMs. Ann Female 48 Years Old Diabetes Mellitus Foot/diabetes Mellitus Joseph MFielMendozaNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiaDocument25 pagesArrhythmiad_94No ratings yet
- Thyroid Autoimmune DiseasesDocument21 pagesThyroid Autoimmune Diseasesmicheal1960No ratings yet
- Health TipsDocument102 pagesHealth Tipsgurkirt100% (1)
- Kripps Newsletter 5Document135 pagesKripps Newsletter 5suckerxNo ratings yet
- Gyn 9 - All Gynecology 5 2021Document22 pagesGyn 9 - All Gynecology 5 2021Menna Kamal100% (3)
- Test Bank Chapter 6: Older Adults: Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 7 EditionDocument11 pagesTest Bank Chapter 6: Older Adults: Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 7 EditionBriseidaSolisNo ratings yet
- Severe Nausea and Vomiting in PregnancyDocument14 pagesSevere Nausea and Vomiting in Pregnancyamelina0% (1)
- Daftar Kode BPJSDocument2 pagesDaftar Kode BPJSlilik agustinNo ratings yet
- IM Written Report Diabetes Case ReportDocument10 pagesIM Written Report Diabetes Case ReportJessa Mateum VallangcaNo ratings yet
- An Essay On Yoga and HealthDocument2 pagesAn Essay On Yoga and HealthGentleStrength100% (1)
- Expository ParagraphDocument4 pagesExpository ParagraphLaura PalacioNo ratings yet
- Uworld QuestionsDocument17 pagesUworld Questionsmoped00No ratings yet
- MCI Screening Test (FMGE) Question Paper - 2002Document678 pagesMCI Screening Test (FMGE) Question Paper - 2002Anbu Anbazhagan100% (1)
- A Topic Presentation ON: Emerging Communicable DiseasesDocument52 pagesA Topic Presentation ON: Emerging Communicable DiseasesGiri SivaNo ratings yet