Professional Documents
Culture Documents
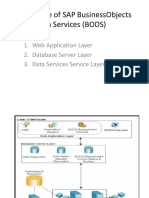
Data Services Guide for Data Integration and Quality
Uploaded by
nikkusonikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Services Guide for Data Integration and Quality
Uploaded by
nikkusonikCopyright:
Available Formats
1. What is the use of Business Objects Data Services?
Answer:
Business Objects Data Services provides a graphical interface that allows you to easily create jobs that extract data from
heterogeneous sources, transform that data to meet the business requirements of your organization, and load the data
into a single location.
2. Define Data Services components.
Answer:
Data Services includes the following standard components:
Designer
Repository
Job Server
Engines
Access Server
Adapters
Real-time Services
Address Server
Cleansing Packages, Dictionaries, and Directories
Management Console
3. What are the steps included in Data integration process?
To know the answer of this question and similar high frequency Data Services questions, please continue to,
3. What are the steps included in Data integration process?
Answer:
Stage data in an operational data store, data warehouse, or data mart.
Update staged data in batch or real-time modes.
Create a single environment for developing, testing, and deploying the entire data integration platform.
Manage a single metadata repository to capture the relationships between different extraction and access
methods and provide integrated lineage and impact analysis.
4. Define the terms Job, Workflow, and Dataflow
Answer:
A job is the smallest unit of work that you can schedule independently for execution.
A work flow defines the decision-making process for executing data flows.
Data flows extract, transform, and load data. Everything having to do with data, including reading sources,
transforming data, and loading targets, occurs inside a data flow.
5. Arrange these objects in order by their hierarchy: Dataflow, Job, Project, and Workflow.
Answer
Project, Job, Workflow, Dataflow.
6. What are reusable objects in Data Services?
Answer:
Job, Workflow, Dataflow.
7. What is a transform?
Answer:
A transform enables you to control how datasets change in a dataflow.
8. What is a Script?
Answer:
A script is a single-use object that is used to call functions and assign values in a workflow.
9. What is a real time Job?
Answer:
Real-time jobs "extract" data from the body of the real time message received and from any secondary sources used in
the job.
10. What is an Embedded Dataflow?
Answer:
An Embedded Dataflow is a dataflow that is called from inside another dataflow.
11. What is the difference between a data store and a database?
Answer:
A datastore is a connection to a database.
12. How many types of data stores are present in Data services?
Answer:
Three.
Database Datastores: provide a simple way to import metadata directly from an RDBMS.
Application Datastores: let users easily import metadata from most Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
Adapter Datastores: can provide access to an applications data and metadata or just metadata.
13. What is the use of Compace repository?
Answer:
Remove redundant and obsolete objects from the repository tables.
14. What are Memory Datastores?
Answer:
Data Services also allows you to create a database data store using Memory as the Database type. Memory Datastores
are designed to enhance processing performance of data flows executing in real-time jobs.
15. What are file formats?
Answer:
A file format is a set of properties describing the structure of a flat file (ASCII). File formats describe the metadata
structure. File format objects can describe files in:
Delimited format Characters such as commas or tabs separate each field.
Fixed width format The column width is specified by the user.
SAP ERP and R/3 format.
16. Which is NOT a datastore type?
Answer:
File Format
17. What is repository? List the types of repositories.
Answer:
The DataServices repository is a set of tables that holds user-created and predefined system objects, source and target
metadata, and transformation rules. There are 3 types of repositories.
A local repository
A central repository
A profiler repository
18. What is the difference between a Repository and a Datastore?
Answer:
A Repository is a set of tables that hold system objects, source and target metadata, and transformation rules. A
Datastore is an actual connection to a database that holds data.
19. What is the difference between a Parameter and a Variable?
Answer:
A Parameter is an expression that passes a piece of information to a work flow, data flow or custom function when it is
called in a job. A Variable is a symbolic placeholder for values.
20. When would you use a global variable instead of a local variable?
Answer:
When the variable will need to be used multiple times within a job.
When you want to reduce the development time required for passing values between job components.
When you need to create a dependency between job level global variable name and job components.
21. What is Substitution Parameter?
Answer:
The Value that is constant in one environment, but may change when a job is migrated to another environment.
22. List some reasons why a job might fail to execute?
Answer:
Incorrect syntax, Job Server not running, port numbers for Designer and Job Server not matching.
23. List factors you consider when determining whether to run work flows or data flows serially or in parallel?
Answer:
Consider the following:
Whether or not the flows are independent of each other
Whether or not the server can handle the processing requirements of flows running at the same time (in parallel)
24. What does a lookup function do? How do the different variations of the lookup function differ?
Answer:
All lookup functions return one row for each row in the source. They differ in how they choose which of several
matching rows to return.
'
25. List the three types of input formats accepted by the Address Cleanse transform.
Answer:
Discrete, multiline, and hybrid.
26. Name the transform that you would use to combine incoming data sets to produce a single output data set with the
same schema as the input data sets.
Answer:
The Merge transform.
27. What are Adapters?
Answer:
Adapters are additional Java-based programs that can be installed on the job server to provide connectivity to other
systems such as Salesforce.com or the JavaMessagingQueue. There is also a SoftwareDevelopment Kit (SDK) to allow
customers to create adapters for custom applications.
28. List the data integrator transforms
Answer:
Data_Transfer
Date_Generation
Effective_Date
Hierarchy_Flattening
History_Preserving
Key_Generation
Map_CDC_Operation
Pivot Reverse Pivot
Table_Comparison
XML_Pipeline
29. List the Data Quality Transforms
Answer:
Global_Address_Cleanse
Data_Cleanse
Match
Associate
Country_id
USA_Regulatory_Address_Cleanse
30. What are Cleansing Packages?
Answer:
These are packages that enhance the ability of Data Cleanse to accurately process various forms of global data by
including language-specific reference data and parsing rules.
31. What is Data Cleanse?
Answer:
The Data Cleanse transform identifies and isolates specific parts of mixed data, and standardizes your data based on
information stored in the parsing dictionary, business rules defined in the rule file, and expressions defined in the
pattern file.
32. What is the difference between Dictionary and Directory?
Answer:
Directories provide information on addresses from postal authorities. Dictionary files are used to identify, parse, and
standardize data such as names, titles, and firm data.
33. Give some examples of how data can be enhanced through the data cleanse transform, and describe the benefit of
those enhancements.
Answer:
Enhancement Benefit
Determine gender distributions and target
Gender Codes marketing campaigns
Provide fields for improving matching
Match Standards results
34. A project requires the parsing of names into given and family, validating address information, and finding
duplicates across several systems. Name the transforms needed and the task they will perform.
Answer:
Data Cleanse: Parse names into given and family.
Address Cleanse: Validate address information.
Match: Find duplicates.
35. Describe when to use the USA Regulatory and Global Address Cleanse transforms.
Answer:
Use the USA Regulatory transform if USPS certification and/or additional options such as DPV and Geocode are required.
Global Address Cleanse should be utilized when processing multi-country data.
36. Give two examples of how the Data Cleanse transform can enhance (append) data.
Answer:
The Data Cleanse transform can generate name match standards and greetings. It can also assign gender codes and
prenames such as Mr. and Mrs.
37. What are name match standards and how are they used?
Answer:
Name match standards illustrate the multiple ways a name can be represented.They are used in the match process to
greatly increase match results.
38. What are the different strategies you can use to avoid duplicate rows of data when re-loading a job.
Answer:
Using the auto-correct load option in the target table.
Including the Table Comparison transform in the data flow.
Designing the data flow to completely replace the target table during each execution.
Including a preload SQL statement to execute before the table loads.
39. What is the use of Auto Correct Load?
Answer:
It does not allow duplicated data entering into the target table.It works like Type 1 Insert else Update the rows based on
Non-matching and matching data respectively.
40. What is the use of Array fetch size?
Answer:
Array fetch size indicates the number of rows retrieved in a single request to a source database. The default value is
1000. Higher numbers reduce requests, lowering network traffic, and possibly improve performance. The maximum
value is 5000
41. What are the difference between Row-by-row select and Cached comparison table and sorted input in Table
Comparison Tranform?
Answer:
Row-by-row select look up the target table using SQL every time it receives an input row. This option is best if
the target table is large.
Cached comparison table To load the comparison table into memory. This option is best when the table fits
into memory and you are comparing the entire target table
Sorted input To read the comparison table in the order of the primary key column(s) using sequential read.
This option improves performance because Data Integrator reads the comparison table only once. Add a query
between the source and the Table_Comparison transform. Then, from the querys input schema, drag the
primary key columns into the Order By box of the query.
42. What is the use of using Number of loaders in Target Table?
Answer:
Number of loaders loading with one loader is known as Single loader Loading. Loading when the number of loaders is
greater than one is known as Parallel Loading. The default number of loaders is 1. The maximum number of loaders is
5.
43. What is the use of Rows per commit?
Answer:
Specifies the transaction size in number of rows. If set to 1000, Data Integrator sends a commit to the underlying
database every 1000 rows.
44. What is the difference between lookup (), lookup_ext () and lookup_seq ()?
Answer:
lookup() : Briefly, It returns single value based on single condition
lookup_ext(): It returns multiple values based on single/multiple condition(s)
lookup_seq(): It returns multiple values based on sequence number
45. What is the use of History preserving transform?
Answer:
The History_Preserving transform allows you to produce a new row in your target rather than updating an existing row.
You can indicate in which columns the transform identifies changes to be preserved. If the value of certain columns
change, this transform creates a new row for each row flagged as UPDATE in the input data set.
46. What is the use of Map-Operation Transfrom?
Answer:
The Map_Operation transform allows you to change operation codes on data sets to produce the desired output.
Operation codes: INSERT UPDATE, DELETE, NORMAL, or DISCARD.
47. What is Heirarchy Flatenning?
Answer:
Constructs a complete hierarchy from parent/child relationships, and then produces a description of the hierarchy in
vertically or horizontally flattened format.
Parent Column, Child Column
Parent Attributes, Child Attributes.
48. What is the use of Case Transform?
Answer:
Use the Case transform to simplify branch logic in data flows by consolidating case or decision-making logic into one
transform. The transform allows you to split a data set into smaller sets based on logical branches.
49. What must you define in order to audit a data flow?
Answer:
You must define audit points and audit rules when you want to audit a data flow.
50. List some factors for PERFORMANCE TUNING in data services?
Answer:
The following sections describe ways you can adjust Data Integrator performance
Source-based performance options
Using array fetch size
Caching data
Join ordering
Minimizing extracted data
Target-based performance options
Loading method and rows per commit
Staging tables to speed up auto-correct loads
Job design performance options
Improving throughput
Maximizing the number of pushed-down operations
Minimizing data type conversion
Minimizing locale conversion
Improving Informix repository performance
51. What is the purpose of database schema? Where can I find more information about this? It's not table, it's not
database, what is it?
A database schema is a way to logically group objects such as tables, views, stored procedures etc. Think of a
schema as a container of objects.
You can assign a user login permissions to a single schema so that the user can only access the objects they are
authorized to access.
Schemas can be created and altered in a database, and users can be granted access to a schema. A schema can
be owned by any user, and schema ownership is transferable.
52. Difference between database and schema.(What's the difference between a Database and a Schema in SQL Server?
Both are the containers of tables and data.If a Schema is deleted, then are all the tables contained in that schema also
deleted automatically or they are deleted when the Database is deleted?)
Schema says what tables are in database, what columns they have and how they are related. Each database has
its own schema.
Schema is a way of categorising the objects in a database. It can be usefull if you have several applications share
a single database and while there is some common set of data that all application accesses.
A database is the main container, it contains the data and log files, and all the schemas within it. You always
back up a database, it is a discrete unit on its own.
Schemas are like folders within a database, and are mainly used to group logical objects together, which leads to
ease of setting permissions by schema.
Database is like container of data with schema, and schemas is layout of the tables there data types, relations
and stuff.
SAP DS (Data Services)
What are SAP DS (Data Services) good for? The aim SAP is pursuing with its SAP DS product is
optimize and improve your data quality with the aid of simple and efficient data integration options. As an
ETL (extract, transform, load) tool, SAP DS (former SAP BODS) lets you extract data from numerous
system- and manufacturer-independent sources. Using the SAP DS native "data profiling" functions
allows you to analyze the existing quality of your data in advance, and in the process identify and assess
problems.
The quality and integrity of your data is crucial for the quality of information and the confidence you can
have in your decisions. SAP DS helps you integrate your company-wide fragmented data and improve
your data quality.
How does SAP DS optimize your data integration and improve your data quality?
As an ETL tool (extract, transform, load), SAP DS allows you to extract data from numerous sources,
regardless of the respective systems and providers. The integrated data profiling functions help you
analyze the quality of your existing data in advance, allowing you to identify and analyze problems.
How does SAP DS operate?
You harmonize your data during the transformation phase, eliminate duplicates, standardize and
validate, and enrich it with supplementary information. This ensures that only valid data according to
predefined rules is transported into your target systems. With the help of process auditing, you can also
establish when a data transfer is to be considered successful or not beyond atomic validation rules.
Integrated metadata management supports detailed tracing of precisely how the value in a target field
was generated by your transformation process (lineage analysis) and what the effects of changes would
be (impact analysis).
Distinguishing features of SAP DS (Data Services) include its outstanding performance and intuitive
operation. All integration and data quality processes are developed and managed in a single interface,
the Data Services Designer". Centralizing functions reduce development and maintenance effort. A
uniform web interface that is separate from the development environment, the Data Services
Management Console, is used for operation and administration.
Data profiling, data integration and the improvement of data quality are key objectives when
implementing an enterprise information management (EIM) initiative. Here SAP DS (former SAP BODS)
serves as an initial and ongoing data quality gateway for your data. Whether you have problems with
duplicate customer records in your ERP system, want to validate incoming material data depending on
values, or want to load data from your CRM system and various Excel sheets into a data warehouse
after cleansing it, DS supports you with all types of data integration and data quality tasks right from the
outset. Especially in conjunction with data warehouse and master data management solutions, it makes
an important contribution towards the effectiveness and efficiency of you EIM.
SAP BODS Training course contents
DW Concepts
Definition
Methodologies
Dimensional Modeling
DW Lifecycle
DW Challenges
ETL Overview
ETL introduction
Staging Area
Business Rules
Performance
Slowly Changing Dimensions
Surrogate Keys
Facts and Dimension Tables
Different ETL Tools
Business Objects Overview
History
Components
Architecture
Data Services
Purpose of Data Services
Data Services architecture
Define Data Services objects
Data Services Designer interface
Data Services Objects
Object Hierarchy
Jobs
Workflows
Data Flows
Source and Target Metadata
Data Stores
File formats for flat files
File formats for Excel files
File formats for XML files
Lab Exercises
Environment setup
Creating repository
Setting Job Server
Setup for realtime operation
Setting multiple datastores
Starting Job servers
Lab Exercises
Batch Jobs
Work with objects
Create a data flow
Use the Query transform
Use target tables
Execute the job
Lab Exercises
Troubleshooting Jobs
Use descriptions and annotations
Validate and tracing jobs
Use View Data and the Interactive Debugger
Use auditing in data flows
Lab Exercises
Functions, Scripts and Variables
Define built-in functions
Functions in expressions
Lookup function
Decode function
Variables and parameters
Data Services scripting language
Scripting custom functions
Lab Exercises
Important Transforms
Map Operation transform
Validation transform
Merge transform
Case transform
SQL transform
Lab Exercises
Other Transforms
Pivot transform
Hierarchy Flattening transform
Data Transfer transform
XML Pipeline transform
Lab Exercises
Error Handling
Error Handling
Recoverable work flows
Change Data Capture
Update data over time
Database native CDC mechanisms
Source-based CDC
Target Comparison
Lab Exercises
Data quality Overview
Fundamentals of DQ and Data Cleansing
Built in DQ Transformations
Data Validation
Name & Address cleansing
De duplication
Cleansing other data
Lab Exercises
Web-Services and Real-Time Integration
Real Time Jobs
SOAP Introduction
Web Services
SAP Integration
Creating datastores for SAP databases
Accessing SAP data
Running ABAP programs
R/3 Data flows
You might also like
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- SQL TutorialDocument200 pagesSQL Tutorialroamer10100% (1)
- What Is The Proper Torque To Use On A Given BoltDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Proper Torque To Use On A Given Boltes_kikeNo ratings yet
- DNV Offshore Installation OperationsDocument37 pagesDNV Offshore Installation OperationsEyoma EtimNo ratings yet
- Base SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandBase SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- How To Install SAP BODSDocument44 pagesHow To Install SAP BODSDivakar Rao Divakar100% (1)
- Change Data Capture Concepts in InformaticaDocument34 pagesChange Data Capture Concepts in InformaticasasiarchieNo ratings yet
- Bods Interview QuestionDocument10 pagesBods Interview QuestionKishore DammavalamNo ratings yet
- Performance Optimization in BODSDocument67 pagesPerformance Optimization in BODSisskumar67% (3)
- (Jeffrey K. Pinto, Jeffrey W. Trailer) EssentialsDocument216 pages(Jeffrey K. Pinto, Jeffrey W. Trailer) EssentialsMuhammad Farhan ArainNo ratings yet
- Exercise:Data Acquisition Using SAP Data ServicesDocument18 pagesExercise:Data Acquisition Using SAP Data ServicesParasaram VenkatasanjaiNo ratings yet
- Data Services-Typs of Lookup FuntionsDocument2 pagesData Services-Typs of Lookup FuntionsnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Data Services-Typs of Lookup FuntionsDocument2 pagesData Services-Typs of Lookup FuntionsnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Bods ZarantechDocument7 pagesBods ZarantechJeevan Reddy PareddyNo ratings yet
- Architecture and Components of SAP BODSDocument7 pagesArchitecture and Components of SAP BODSMurali Devarinti100% (1)
- Calling RFC From BODSDocument115 pagesCalling RFC From BODSnikkusonik0% (1)
- Calling RFC From BODSDocument115 pagesCalling RFC From BODSnikkusonik0% (1)
- Sap Bods FaqsDocument4 pagesSap Bods Faqssai krishnaNo ratings yet
- PP MFG End UserDocument92 pagesPP MFG End Userprasadpandit123No ratings yet
- SAP BODS Latest Interview Questions by GarudatrainingsDocument28 pagesSAP BODS Latest Interview Questions by GarudatrainingsZakir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Crew Tasks on WatchDocument10 pagesCrew Tasks on WatchmytnameNo ratings yet
- SAP BODS Concatenate Rows Using Custom FunctionDocument5 pagesSAP BODS Concatenate Rows Using Custom FunctionLakshmi PNo ratings yet
- Define Pricing Procedure StepsDocument3 pagesDefine Pricing Procedure Stepsashokkumar1979No ratings yet
- 00 Top 20 Best Data Science Books You Should ReadDocument8 pages00 Top 20 Best Data Science Books You Should ReadCristian MendesNo ratings yet
- Data Services ComponentsDocument25 pagesData Services ComponentsACBNo ratings yet
- Data Services Guide for Data Integration and QualityDocument17 pagesData Services Guide for Data Integration and QualitynikkusonikNo ratings yet
- SAP BODS Interview QuestionsDocument12 pagesSAP BODS Interview QuestionsVenkat Raman Gajjala100% (2)
- BODS Match TrasnformDocument1 pageBODS Match Trasnformisskumar0% (1)
- Gapura Company Profile - 17mar17Document43 pagesGapura Company Profile - 17mar17als izmiNo ratings yet
- SAP-BODS Integration Using IDOCSDocument7 pagesSAP-BODS Integration Using IDOCSsathishNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Performance of Sap Bods JobsDocument2 pagesHow To Improve Performance of Sap Bods JobssatishNo ratings yet
- Connect BODS and SAP in 4 StepsDocument10 pagesConnect BODS and SAP in 4 StepsMurali Devarinti100% (1)
- SAP BODS Data Services overview and implementationsDocument5 pagesSAP BODS Data Services overview and implementationsajayc50No ratings yet
- 2 - BODS ErrorsDocument19 pages2 - BODS ErrorsSubhadip Das Sarma100% (1)
- Designing and Optimizing Side-View Mirrors: Martin OlssonDocument97 pagesDesigning and Optimizing Side-View Mirrors: Martin OlssonAndrei StoicescuNo ratings yet
- 25+ Tricky SAP BODS Interview Questions with SMART ANSWERSDocument1 page25+ Tricky SAP BODS Interview Questions with SMART ANSWERSpattabhikvNo ratings yet
- BODS - Job Control TableDocument8 pagesBODS - Job Control Tablevenkat143786No ratings yet
- SAP BODI Sample Resume 1Document7 pagesSAP BODI Sample Resume 1Raouhi El MehdiNo ratings yet
- BODS Introduction and ArchitectureDocument9 pagesBODS Introduction and Architecturetuliplily2109No ratings yet
- Sap BodsDocument46 pagesSap Bodstuliplily210950% (2)
- BODS Overview and Components GuideDocument94 pagesBODS Overview and Components GuideOwais KhokharNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Some Rules of ThumbDocument6 pagesRevisiting Some Rules of Thumbhamidrezaee008No ratings yet
- BODS Training SessionDocument18 pagesBODS Training SessionDeweshChandraNo ratings yet
- Sap Bods 4.2 Sap Bods 4.2 Sap Bods 4.2: Course Content 2015 Course Content Course ContentDocument5 pagesSap Bods 4.2 Sap Bods 4.2 Sap Bods 4.2: Course Content 2015 Course Content Course ContentShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- SQL Transform Customized SQL QueriesDocument7 pagesSQL Transform Customized SQL QueriesnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- SQL Transform Customized SQL QueriesDocument7 pagesSQL Transform Customized SQL QueriesnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Row Generation TransformDocument7 pagesRow Generation TransformnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Row Generation TransformDocument7 pagesRow Generation TransformnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- BodsDocument19 pagesBodsSugguna Viswanadth100% (1)
- SAP Data Services 4.x Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument35 pagesSAP Data Services 4.x Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (2)
- BC670 PDFDocument225 pagesBC670 PDFMailin1981No ratings yet
- Sap Bods FaqsDocument38 pagesSap Bods FaqsrajuNo ratings yet
- BO Data Integrator Architecture, Management Tools and Core ConceptsDocument8 pagesBO Data Integrator Architecture, Management Tools and Core ConceptsNarender Reddy0% (1)
- BODS Vs SDI Vs SLTDocument4 pagesBODS Vs SDI Vs SLTVeera TNo ratings yet
- Business Objects Data Services (BODS) - Training MaterialDocument53 pagesBusiness Objects Data Services (BODS) - Training Materialsundhar_v0% (2)
- Bods ScriptingDocument3 pagesBods ScriptingLakshmi PNo ratings yet
- SAP Data Services: Integrate, Transform, Deliver Trusted DataDocument4 pagesSAP Data Services: Integrate, Transform, Deliver Trusted Dataharryharsan0% (1)
- Remove special characters and truncate strings in SQL queriesDocument7 pagesRemove special characters and truncate strings in SQL queriesnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Sap Bods: - Vijaya PolisettyDocument51 pagesSap Bods: - Vijaya PolisettykadalidurgaprasadNo ratings yet
- Resuse objects in SAP BODS ETLDocument5 pagesResuse objects in SAP BODS ETLanilNo ratings yet
- Bods InterviewDocument61 pagesBods InterviewKishore Dammavalam100% (3)
- Sap Bods DetailsDocument2 pagesSap Bods DetailsKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- BODS Scripting: SelectDocument5 pagesBODS Scripting: Selectyella reddyNo ratings yet
- SAP BO Data Integrator and Data ServicesDocument5 pagesSAP BO Data Integrator and Data ServicesshinyvasuNo ratings yet
- SAP BusinessObjects Data Services Setup GuideDocument35 pagesSAP BusinessObjects Data Services Setup GuideVenkatesh DevathiNo ratings yet
- Bods 2Document385 pagesBods 2kishoreNo ratings yet
- Data Profiling With SAP Business Objects Data ServicesDocument9 pagesData Profiling With SAP Business Objects Data Services1j1j1jNo ratings yet
- Beginner's guide to SAP BODSDocument85 pagesBeginner's guide to SAP BODSprasadgvkNo ratings yet
- Scheduling BODS Jobs Sequentially and ConditionallyDocument18 pagesScheduling BODS Jobs Sequentially and Conditionallymatzprivie100% (1)
- Data MigrationDocument5 pagesData MigrationLaxmi Ganesh MNo ratings yet
- SAP BO Admin QuestionsDocument4 pagesSAP BO Admin QuestionsKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Sap BodsDocument38 pagesSap BodsTrishul SampathNo ratings yet
- SAP BO Data Services TransformsDocument27 pagesSAP BO Data Services TransformsLakshmi PNo ratings yet
- DataStage MatterDocument81 pagesDataStage MatterShiva Kumar0% (1)
- Top 50 SAP Business Objects Data Services (BODS) Interview Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesTop 50 SAP Business Objects Data Services (BODS) Interview Questions With Answerssatishsapbiw100% (1)
- SAP BO Errors GuideDocument738 pagesSAP BO Errors GuideReddy100% (1)
- CASE AssignmentDocument1 pageCASE AssignmentnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- DWH BasicDocument6 pagesDWH BasicnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- How To Execute Single Workflow in A JobDocument4 pagesHow To Execute Single Workflow in A JobnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Dat MigDocument1 pageDat MignikkusonikNo ratings yet
- EIM ChangetheRowDelimiterDocument1 pageEIM ChangetheRowDelimiternikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Fake Companies ListDocument13 pagesFake Companies ListNikhil KarkraNo ratings yet
- DW BasicsDocument8 pagesDW BasicsnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Is There Elseif Condition in BODSDocument2 pagesIs There Elseif Condition in BODSnikkusonik100% (1)
- Load The Data Into A Flat File and Atleast Leave First 4 Rows BlankDocument5 pagesLoad The Data Into A Flat File and Atleast Leave First 4 Rows BlanknikkusonikNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Course Syllabus OverviewDocument2 pagesSAP HANA Course Syllabus OverviewnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- JD of DS-ISDocument2 pagesJD of DS-ISnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- There Is Different Conversion Function Which Used To Convert One Form of Data Into Another FormatDocument6 pagesThere Is Different Conversion Function Which Used To Convert One Form of Data Into Another FormatnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- XML SchemaDocument7 pagesXML SchemanikkusonikNo ratings yet
- ISDocument1 pageISnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- CachingDocument7 pagesCachingnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Syllabus: 1. HANA Introduction 2. Look & FeelDocument3 pagesSAP HANA Syllabus: 1. HANA Introduction 2. Look & FeelnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Consultant - Course Content - 30 Hours: Self Learning SAP CenterDocument3 pagesSAP HANA Consultant - Course Content - 30 Hours: Self Learning SAP CenternikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Lets Assume We Have A Job With A ScriptDocument2 pagesLets Assume We Have A Job With A ScriptnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- RepositoryDocument1 pageRepositorynikkusonikNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Syllabus: 1. HANA Introduction 2. Look & FeelDocument3 pagesSAP HANA Syllabus: 1. HANA Introduction 2. Look & FeelnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- DOP-learning Purpose OnlyDocument2 pagesDOP-learning Purpose OnlynikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Files As Data SourcesDocument25 pagesFiles As Data SourcesnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- DWBI Error Handling Reccovery FlatfilesTipsDocument8 pagesDWBI Error Handling Reccovery FlatfilesTipsnikkusonikNo ratings yet
- Intel Case StudyDocument22 pagesIntel Case Studyshweta_sgupta50% (2)
- Warranty ManualDocument23 pagesWarranty ManualSamuel AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- GE 8077 - TQM Principles and ToolsDocument36 pagesGE 8077 - TQM Principles and ToolsmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Bayes Rule Related ProblemsDocument2 pagesBayes Rule Related ProblemsMuhammad Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- The Top 200 International Design Firms - ENR - Engineering News Record - McGraw-Hill ConstructionDocument4 pagesThe Top 200 International Design Firms - ENR - Engineering News Record - McGraw-Hill ConstructiontarekhocineNo ratings yet
- Ceridust® 6721: Polypropylene Wax / Amide WaxDocument2 pagesCeridust® 6721: Polypropylene Wax / Amide Waxمحمد عزتNo ratings yet
- NR467 - Rules For Steel Ships - PartAVol01Document262 pagesNR467 - Rules For Steel Ships - PartAVol01Meleti Meleti MeletiouNo ratings yet
- Quality Manual - Super Rock 2012 - PublishedDocument40 pagesQuality Manual - Super Rock 2012 - PublishedTracy BranderNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment Questionnaire B: and Attestation of ComplianceDocument20 pagesSelf-Assessment Questionnaire B: and Attestation of Compliancemustafaanis786No ratings yet
- Hybrid IDEF0 IDEF03 HoustonDocument3 pagesHybrid IDEF0 IDEF03 HoustonHouston Mandar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Grand Stands RequirementsDocument8 pagesGrand Stands RequirementsJonathan Marvin Bacares DueNo ratings yet
- CRM Final Ppt-6Document21 pagesCRM Final Ppt-6Niti Modi ShahNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems ER ModelDocument30 pagesDatabase Management Systems ER ModelsupriyaNo ratings yet
- ARC Tech Talk Vol 5 Why Rack Flue Spaces Are Important enDocument3 pagesARC Tech Talk Vol 5 Why Rack Flue Spaces Are Important enBaoDuongTranNo ratings yet
- PENGENALAN RobotikDocument44 pagesPENGENALAN Robotikwan alifNo ratings yet
- DWS Carbon Slicklines Physical Properties and SpecificationsDocument1 pageDWS Carbon Slicklines Physical Properties and Specificationserwin atmadjaNo ratings yet
- Franchising Chapter 1Document16 pagesFranchising Chapter 1Nguyên BùiNo ratings yet
- Panwater Proposal 11309Q3Document4 pagesPanwater Proposal 11309Q3WahidCesarR100% (1)
- Module6-Detailed Project Report and EPCDocument10 pagesModule6-Detailed Project Report and EPCJames K. BitokNo ratings yet