Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class Stack: Java - Lang.Object Java - Util.Abstractcollection Java - Util.Abstractlist Java - Util.Vector
Uploaded by
durexkoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Stack: Java - Lang.Object Java - Util.Abstractcollection Java - Util.Abstractlist Java - Util.Vector
Uploaded by
durexkoCopyright:
Available Formats
java.
util
// Create a new, empty stack
Stack lifo = new Stack();
User Class Stack<E>
java.lang.Object
o java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
o
java.util.AbstractList<E>
java.util.Vector<E>
java.util.Stack<E>
All Implemented Interfaces:
Serializable, Cloneable, Iterable<E>, Collection<E>, List<E>, RandomAccess
public class Stack<E>
extends Vector<E>
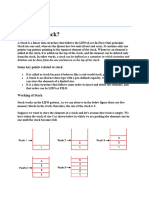
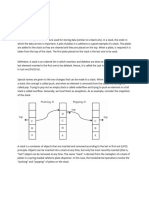
The Stack class represents a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack of objects. It extends class Vector with five
operations that allow a vector to be treated as a stack. The usual push and pop operations are provided,
as well as a method to peek at the top item on the stack, a method to test for whether the stack is empty,
and a method to search the stack for an item and discover how far it is from the top.
When a stack is first created, it contains no items.
A more complete and consistent set of LIFO stack operations is provided by the Deque interface and its
implementations, which should be used in preference to this class. For example:
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
Since:
JDK1.0
See Also:
Serialized Form
o Method Detail
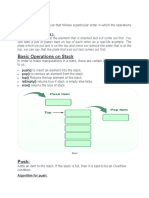
push
public E push(E item)
Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly the same effect as:
addElement(item)
Parameters:
item - the item to be pushed onto this stack.
Returns:
the item argument.
See Also:
Vector.addElement(E)
pop
public E pop()
Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that object as the value of this
function.
Returns:
The object at the top of this stack (the last item of the Vector object).
Throws:
EmptyStackException - if this stack is empty.
peek
public E peek()
Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it from the stack.
Returns:
the object at the top of this stack (the last item of the Vector object).
Throws:
EmptyStackException - if this stack is empty.
empty
public boolean empty()
Tests if this stack is empty.
Returns:
true if and only if this stack contains no items; false otherwise.
search
public int search(Object o)
Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack. If the object o occurs as
an item in this stack, this method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the
occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the stack is considered to
be at distance 1. The equals method is used to compare o to the items in this stack.
Parameters:
o - the desired object.
Returns:
the 1-based position from the top of the stack where the object is located; the return value -1 indicates
that the object is not on the stack.
You might also like
- Isa TR5.1.01 - Isa TR77.40.01-2012Document38 pagesIsa TR5.1.01 - Isa TR77.40.01-2012andr2s2cruz-1No ratings yet
- Stack Class Constructor: PublicDocument5 pagesStack Class Constructor: PublicGauri BansalNo ratings yet
- Collections APIDocument17 pagesCollections APIAlangudi BalajiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Java S Stack Class 1686837765Document10 pagesUnderstanding Java S Stack Class 1686837765Yurani CastroNo ratings yet
- Stack in JavaDocument3 pagesStack in JavaMohammed SaimNo ratings yet
- LAB # 10 Stack ADT Implementation: ObjectDocument3 pagesLAB # 10 Stack ADT Implementation: ObjectAdnan AsadNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument31 pagesCollectionBhaeathNo ratings yet
- Data Structures AssDocument11 pagesData Structures AssFiraol TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Stack Data StructureDocument30 pagesStack Data StructurenishaNo ratings yet
- Java Collection Framework-1Document15 pagesJava Collection Framework-1Thorapan ShajiNo ratings yet
- ArrayList and IteratorDocument28 pagesArrayList and Iteratornurul aqilah fauzanNo ratings yet
- Stacks and QueuesDocument21 pagesStacks and QueuesDhivya NNo ratings yet
- Stacks and QueuesDocument21 pagesStacks and QueuesRavi Teja PallapoluNo ratings yet
- Java Collection Cheatsheet - v1.1Document20 pagesJava Collection Cheatsheet - v1.1donepong kingsNo ratings yet
- Lists, Stacks, and QueuesDocument29 pagesLists, Stacks, and QueuessNo ratings yet
- Cmu EduDocument6 pagesCmu EduRatulNo ratings yet
- Collection in JavaDocument18 pagesCollection in JavaAkshay KhankeNo ratings yet
- Hadoop Bigdata UNIT-1Document18 pagesHadoop Bigdata UNIT-1PiyushNo ratings yet
- Answers For AdsDocument16 pagesAnswers For Adsrajaprasad2No ratings yet
- DSA With Java - Unit 3Document14 pagesDSA With Java - Unit 3Sabin MaharjanNo ratings yet
- LinkedList (Java Platform SE 6)Document18 pagesLinkedList (Java Platform SE 6)Ayunda TimmyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 StackDocument7 pagesUnit 3 StackShrijeshNo ratings yet
- DSD Unit 2 Stacks QueuesDocument52 pagesDSD Unit 2 Stacks QueuesMaha LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Stack Compiled NoteDocument9 pagesStack Compiled NotesyabseeshoesNo ratings yet
- StackDocument18 pagesStackadiraihajaNo ratings yet
- Java Collection FrameworkDocument34 pagesJava Collection Frameworkanon_860045317No ratings yet
- Linkedlist in JavaDocument49 pagesLinkedlist in Javasindhu4sindNo ratings yet
- Collection FrameworkDocument4 pagesCollection FrameworkSaurabh KothariNo ratings yet
- ELEE28706D StacksandQues S5Document37 pagesELEE28706D StacksandQues S5Ehtisham MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4. Stack & QueueDocument26 pagesChapter-4. Stack & QueueQuazi Hasnat IrfanNo ratings yet
- I B.SC CS DS Unit IiDocument9 pagesI B.SC CS DS Unit Iiarkaruns_858818340No ratings yet
- Collections: Inconveniencies of ArraysDocument5 pagesCollections: Inconveniencies of ArraysPraneeth MutnuruNo ratings yet
- Stacks and QueuesDocument32 pagesStacks and QueuesNavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-List (Sequential List) Arraylist Class: Edited by Miss Nafisah AminDocument29 pagesTopic 2-List (Sequential List) Arraylist Class: Edited by Miss Nafisah AminsofiaNo ratings yet
- Stacks and Queues Queues COS3711Document27 pagesStacks and Queues Queues COS3711JohannesNo ratings yet
- A Micro Project On Dsu1111Document10 pagesA Micro Project On Dsu1111shaikhnumn22No ratings yet
- Linked List and CursorsDocument7 pagesLinked List and CursorsSourav Kumar BiswalNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument15 pagesCollectionGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 - StacksDocument5 pages2 - Stacksyotopia horoor gameNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro StacksDocument10 pages01 Intro StacksChetan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Class Linkedlist: Overview Package Use Tree Deprecated Index Help JavaDocument13 pagesClass Linkedlist: Overview Package Use Tree Deprecated Index Help JavaMaajith MarzookNo ratings yet
- LinkedList in Java - JavatpointDocument11 pagesLinkedList in Java - JavatpointmanojNo ratings yet
- VB Data StructureDocument39 pagesVB Data StructureVínãy KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample - Bank Management SystemDocument9 pagesSample - Bank Management SystemRizwan UllahNo ratings yet
- JEDI Course Notes DataSt Chapter02 StacksDocument19 pagesJEDI Course Notes DataSt Chapter02 Stacksmhonique_21No ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument11 pagesData StructuresThe Invincible'sNo ratings yet
- Stacks and Queues: Saurav Karmakar Spring 2007Document32 pagesStacks and Queues: Saurav Karmakar Spring 2007mb08026No ratings yet
- HCT 108 Handout5Document14 pagesHCT 108 Handout5Gerald KapinguraNo ratings yet
- Stack QueueDocument62 pagesStack QueuedmumminaNo ratings yet
- Collec in JavaDocument13 pagesCollec in JavaShubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledTanvi KakadNo ratings yet
- Lab 07 PDFDocument16 pagesLab 07 PDFApoorv SinghNo ratings yet
- Stacks Queues DequesDocument28 pagesStacks Queues Dequesviswanath12No ratings yet
- Java Collections QueueDocument3 pagesJava Collections QueueAditya Chandra FebriawanNo ratings yet
- Unit01 QueueDocument42 pagesUnit01 QueueKareem Abbas DawoodNo ratings yet
- Stack and Queue-ClassDocument85 pagesStack and Queue-ClassRising ShineeNo ratings yet
- StackDocument18 pagesStackGayathri ValivetiNo ratings yet
- Python StacksDocument4 pagesPython StacksAlvaro OcolaNo ratings yet
- Viva Final DS - LabDocument30 pagesViva Final DS - LabAsquare FoundationNo ratings yet
- Java Package Mastery: 100 Knock Series - Master Java in One Hour, 2024 EditionFrom EverandJava Package Mastery: 100 Knock Series - Master Java in One Hour, 2024 EditionNo ratings yet
- Car Audio DEH-X5Document2 pagesCar Audio DEH-X5Jairo Enciso OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Hera - PND Lab: User ManualDocument17 pagesHera - PND Lab: User ManualSaw GyiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Azmat Ullah Baig. Hamza IdreesDocument26 pagesCloud Computing: Azmat Ullah Baig. Hamza IdreesAzmat Ullah BaigNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument11 pagesDX DiagNeil HendricksNo ratings yet
- M2000 Basic Skill Training Compress - PART1Document24 pagesM2000 Basic Skill Training Compress - PART1iqbalcanNo ratings yet
- Competency ChartDocument12 pagesCompetency ChartSUBODHHNo ratings yet
- Digital Printing PressesDocument65 pagesDigital Printing PressesLessie556No ratings yet
- K2 User Manual 1509Document39 pagesK2 User Manual 1509Ghofur Al MusthofaNo ratings yet
- Asst Prof. Essaid Meryam Department of Robotics EngineeringDocument20 pagesAsst Prof. Essaid Meryam Department of Robotics EngineeringkyungmunNo ratings yet
- Stata Cheat Sheet: Command in "User" Menu Useful For What? Additional Options More InfoDocument2 pagesStata Cheat Sheet: Command in "User" Menu Useful For What? Additional Options More InfoAbdel KadirNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: Lesson 1: Configuring, Managing, and Troubleshooting Resource AccessDocument53 pagesTopic 5: Lesson 1: Configuring, Managing, and Troubleshooting Resource AccessarivsNo ratings yet
- Proxmox Backup Datasheet V2.0Document4 pagesProxmox Backup Datasheet V2.0WilfredoNo ratings yet
- EAM Modeling GuidelinesDocument13 pagesEAM Modeling GuidelinesAli AkbarNo ratings yet
- MCS 043 Q-1 (2014) SolutionDocument4 pagesMCS 043 Q-1 (2014) Solutionnikhu_shuklaNo ratings yet
- LakshmiinrusimhaprapattiDocument3 pagesLakshmiinrusimhaprapattiRadhe GovindaNo ratings yet
- Sap Workflow TipsDocument3 pagesSap Workflow TipsBro Jeff100% (1)
- Q1W2Document42 pagesQ1W2JENNEFER ESCALANo ratings yet
- System Configuration PDFDocument990 pagesSystem Configuration PDFEmmanuel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Developed by Whatsapp: Telegram ID: Support Website:: Egyfixlab 00201283689946 @egyfixlabDocument28 pagesDeveloped by Whatsapp: Telegram ID: Support Website:: Egyfixlab 00201283689946 @egyfixlabview starNo ratings yet
- PDF Hacks: 100 Industrial-Strength Tips & ToolsDocument4 pagesPDF Hacks: 100 Industrial-Strength Tips & ToolsBen YungNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer ICDocument4 pages555 Timer ICtajju_121No ratings yet
- Stock CategoriesDocument5 pagesStock Categoriesharshita kaushikNo ratings yet
- Generating Summery Risk Scores For Mobile Applications: Master of Computer ApplicationsDocument67 pagesGenerating Summery Risk Scores For Mobile Applications: Master of Computer ApplicationsVirinchi RachakondaNo ratings yet
- Resume of Jmclarke55Document1 pageResume of Jmclarke55api-24783078No ratings yet
- Madison Wiley ResumeDocument1 pageMadison Wiley Resumeapi-350528326No ratings yet
- Success Story VTWealth SSC InteractiveDocument2 pagesSuccess Story VTWealth SSC InteractiveSebastian SchnurNo ratings yet
- Resource Description Framework: A Small Case Study On Educational DomainDocument17 pagesResource Description Framework: A Small Case Study On Educational DomainKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Databases DiagramsDocument34 pagesDatabases DiagramsSam BaitsiNo ratings yet
- OTM 21C ReleaseDocument24 pagesOTM 21C ReleaseRahul KumarNo ratings yet