Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sylabus of Ec
Uploaded by
Sanjay Singh YadavCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sylabus of Ec
Uploaded by
Sanjay Singh YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
B.
Tech (EC)
w.e.f. Session: 2012-2013
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Institute of Engineering & Technology
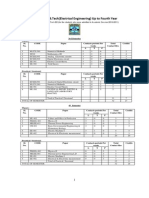
COURSE STRUCTURE
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
First Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1. AHM101 Mathematics - I 3 1 0 4 4
2. AHP101 Engineering Physics - I 2 1 0 3 3
3. CSE101
Fundamentals of Computer
& Programming
2 0 0 2 2
4.
MEE102/
EEE101
Basic Thermodynamics/
Electrical Engineering
3 1 0 4 4
5.
AHC101/
MEE101
Engineering Chemistry/
Manufacturing Process
3 1 0 4 4
6.
MEE103/
ECE101
Applied
Mechanics/Electronics
Engineering
3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
7. AHE181 Communication Skills - I 0 0 3 2 3
8.
MEE182/
MEE181
Engineering Drawing/EWS
Practice Lab
0 0 3 2 3
9.
AHC181/
AHP181
Chemistry Lab/Physics Lab 0 0 2 1 2
10. CSE181
Computer Programming
Lab
0 0 2 1 2
11.
MEE183/
EEE181
Applied Mechanics Lab/
Electrical & Electronics Lab
0 0 2 1 2
12. ECE197 General Proficiency 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 16 5 12 29 33
Second Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1. AHM102 Mathematics - II 3 1 0 4 4
2. AHP102 Engineering Physics - II 2 1 0 3 3
3. CSE102
Problem Solving using
Computers
2 0 0 2 2
4.
EEE101/
MEE102
Electrical Engineering/
Basic Thermodynamics
3 1 0 4 4
5.
MEE101/
AHC101
Manufacturing Process/
Engineering Chemistry
3 1 0 4 4
6.
ECE101/
MEE103
Electronics Engineering
/Applied Mechanics
3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
7. AHE182 Communication Skills - II 0 0 3 2 3
8.
MEE181/
MEE182
EWS Practice Lab
/Engineering Drawing
0 0 3 2 3
9.
AHP181/
AHC181
Physics Lab/Chemistry Lab 0 0 2 1 2
10. CSE182 Problem Solving Lab 0 0 2 1 2
11.
EEE181/
MEE183
Electrical & Electronics
Lab/Applied Mechanics Lab
0 0 2 1 2
12. ECE198 General Proficiency 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 16 5 12 29 33
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
Third Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1 AHM 201 Mathematics III 3 1 0 4 4
2 CEE 201/
AHE 201
Environmental Studies /
Ethics & Values
2 0 0 2 2
3 ECE 201 Electro Magnetic Field
Theory
3 1 0 4 4
4 ECE 202 Digital Electronics 3 1 0 4 4
5 ECE 205 Semiconductor Materials &
Devices
3 1 0 4 4
6 EEE 201 Network Analysis &
Synthesis
3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
1 AHE 281 Soft Skills I 0 0 2 1 2
2 ECE 281 Digital Electronics Lab 0 0 2 1 2
3 ECE 282 Electronics Lab 0 0 2 1 2
4 EEE 281 Network Lab 0 0 2 1 2
5 ECE 297 GP 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 27 30
Fourth Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1 AHM 202 CBNST 3 1 0 4 4
2
AHE 201/
CEE 201
Ethics & Values/
Environmental Studies
2 0 0 2 2
3 ECE 204 Signals & Systems 3 1 0 4 4
4 ECE 203
Electronic Devices &
Circuits
3 1 0 4 4
5 ECE 208
Electronic Measurement &
Instrumentation
3 1 0 4 4
6 ECE 206
Microprocessors &
Applications
3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
1 AHE 282 Soft Skills II 0 0 2 1 2
2
ECE 283
Electronics Workshop & PCB
Lab
0 0 2 1 2
3
ECE 288
Electronic Measurement &
Instrumentation Lab
0 0 2 1 2
4 ECE 286 Microprocessor Lab 0 0 2 1 2
5 ECE 298 GP 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 27 30
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
Fifth Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1 AHS 301/
AHS 302
Industrial Psychology/
Industrial Economics
2 0 0 2 2
2 AHE 301/
AHS 303
Technical Writing
/Principle of Management
2 1/0 0 3/2 3/2
3 ECE 301 Communication
Engineering
3 1 0 4 4
4 ECE 302 Linear Integrated Circuit 3 1 0 4 4
5 ECE 303 Antenna & Wave
Propagation
3 1 0 4 4
6 ECE 304 Control System 3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
1 AHE 381 Soft Skills III 0 0 2 1 2
2 ECE 381 Communication Lab 0 0 2 1 2
3 ECE 382 Integrated Circuit Lab 0 0 2 1 2
4 ECE 383 Control System Lab 0 0 2 1 2
5 CSE 389 Advance Programming Lab 0 0 2 1 2
6 ECE 397 GP 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 27/26 31/30
Sixth Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1
AHS 302/
AHS 301
Industrial Economics/
Industrial Psychology 2 0 0 2 2
2
AHS 303/
AHE 301
Principle of Management /
Technical Writing 2 0/1 0 2/3 2/3
3 ECE 305 Digital Communication 3 1 0 4 4
4 CSE 371
Computer Architecture and
Application 3 1 0 4 4
5 ECE 306 Microwave Engineering. 3 1 0 4 4
6 ECE 307 VLSI Technology & Design 3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
1 AHE 382 Soft Skills IV 0 0 2 1 2
2 ECE 384 Digital Communication Lab 0 0 2 1 2
3 ECE 385 Simulation Lab 0 0 2 1 2
4 ECE 386 Microwave Lab 0 0 2 1 2
5 ECE 387 CAD Lab 0 0 2 1 2
6 ECE 388 Colloquium 0 0 2 1 2
7 ECE 398 GP 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 27/28 32/33
Note: At the end of sixth semester, each student has to undergo an industrial training of minimum
04 weeks, which will be evaluated as ECE 483 in the seventh semester.
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
Seventh Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT TEACHING SCHEME CREDITS CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1 ECE 401 Data Networks 3 1 0 4 4
2 ECE 402 Digital Signal Processing 3 1 0 4 4
3 Elective-I 3 1 0 4 4
4 Elective-II 3 1 0 4 4
5 Open Elective 3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
1 ECE 481 Digital Signal Processing Lab 0 0 2 1 2
2 ECE 482 Project-I 0 0 6 3 6
3 ECE 483 Industrial Training 0 0 2 1 2
4 ECE 497 GP 0 0 0 1 0
TOTAL 26 30
Eight Semester
S.
NO.
CODE SUBJECT
TEACHING SCHEME
CREDITS
CONTACT HRS
/WEEK L T P
THEORY
1 ECE 403 Optical Communication &
Networks
3 1 0 4 4
2 ECE 404 Wireless Communication 3 1 0 4 4
3 Elective-III 3 1 0 4 4
4 Elective-IV 3 1 0 4 4
PRACTICALS
5 ECE 484 Optical Communication Lab 0 0 2 1 2
6 ECE 485 Wireless Communication
Lab
0 0 2 1 2
7 ECE 486 Project-II 0 0 14 7 14
8 ECE 498 GP 0 0 0 1 0
26 34
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
Subject Code Elective-I
ECE 406 Artificial Neural Network
ECE 407 TV & Satellite Communication
ECE 408 Radar Engineering
Subject Code Elective-II
ECE 409 Tele-communication Switching
ECE 410 Multimedia Communication
ECE 411 Mobile Computing
Subject Code Elective-III
ECE 413 Digital System Design
ECE 414 MEMS
ECE 415 Embedded Systems
Subject Code Elective-IV
ECE 416 Speech Processing
ECE 417 Multi Carrier Communication
ECE 418 Digital Image Processing
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
D
DDE
EET
TTA
AAI
IIL
LLE
EED
DD S
SSY
YYL
LLL
LLA
AAB
BBU
UUS
SS
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HM M 1 10 01 1: : M MA AT TH HE EM MA AT TI IC CS S I I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Differential Calculus: Successive Differentiation, Leibnitz theorem, Partial
Differentiation, Eulers theorem on homogeneous functions, Differentiation of
Composite and implicit functions, Total derivatives, Leibnitz rule of
differentiation under the integral sign, Jacobian, Extreme of functions of several
variables, Lagranges method of Undetermined multipliers.
14
II
Ordinary Differential Equations: Introduction, variables separable & linear
form of I order and I degree ODEs, Linear differential equations of nthorder
with constant coefficients, Euler Cauchy Equations, Simultaneous linear
differential equations. Method of variation of parameters, Applications to
Engineering problems.
14
III
Matrices: Inverse of matrix by elementary transformations, Rank of matrix,
Solution of systems of linear equations, Linear dependence and independence,
Complex matrices, Eigen values and eigen vectors, Cayley Hamilton Theorem,
Diagonalization by similarity transformation.
11
References:
Behrouz A. Forouzan and Richard F. Gilberg, Computer Science A structured Programming
Approach Using C , Cengage Learning, 2007.
K. N. King, C Programming - A Modern Approach, 2nd Edition, W. W. Norton, 2008.
Kernighan and Ritche, The C programming Language, PHI , 1996.
P. Dey, M. Ghosh, Programming in C, Oxford University Press ,2009 .
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HP P1 10 01 1: : E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G P PH HY YS SI IC CS S - - I I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. Relativistic Mechanics: Basic Concepts, Inertial & non-inertial frames,
Galilean Transformations, Michelson- Morley experiment, Einsteins postulates,
Lorentz transformation equations, Length contraction, Time dilation, Addition
of velocities, Variation of mass with velocity, Mass energy equivalence.
2. Solid State Physics : Bands in solids, Insulators, conductors and
semiconductors, electron and hole conduction, the band structure of
semiconductors, Donor and acceptor impurities, Fermi level and Fermi energy,
impurity level in N and P type semiconductors, p-n junction fabrication, effective
mass, electron and hole concentration at equilibrium, temperature dependence
of carrier concentration, conductivity and mobility, Hall effect in
semiconductors.
10
II
1. Interference: Light Fundamentals, Interference of light, Principle of
superposition and coherence of light, Interference due to division of wavefront
and division of amplitude, Theory of biprism experiment, Interference in
parallel thin films, wedge shaped films, Newtons rings and Michelsons
Interferometer.
2. Diffraction: Diffraction of light, Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction,
diffraction due to single slit and N-slits, Plane diffraction grating, absent spectra
with grating and dispersive power of grating, Rayleighs criterion and resolving
power of grating and application.
10
III
1. Polarization: Introduction to polarization fundamentals, Phenomenon of
double refraction, Nicol prism, Production and analysis of plane, circularly and
elliptically polarized light, Quarter and half wave plates, Fresnels theory of
optical activity, Specific rotation, Lorentz half shade and Biquartz polarimeters.
2. Laser: Spontaneous and stimulated emission of radiation, Einsteins
coefficients, Principle of laser, Ruby laser, Semiconductor laser, coherence,
characteristics of laser beam and coherence property, laser applications.
3. Fiber Optics: Introduction, Principle of optical fiber, Classification of fibers,
acceptance angle and acceptance cone, Numerical aperture, Propagation
mechanism and attenuation in optical fiber.
10
References:
Aurthur Beiser, Concepts of Modern Physics, TMH.
Robert Resnick , Introduction to Special theory of relativity, Wiely & Sons
Ajoy Ghatak , Optics, TMH
Brijlal and Subramaniam , Optics, S. Chand
Anuradha De. , Optical Fibre & Laser, New Age
Resnick, Halliday and Walker , Fundamental of Physics , Wiely
S.O. Pillai , Solid State Physics , New Age International Publication , 5
th
edition
C. Kittel : Solid State Physics , Wiley Eastern, 7
th
edition.
M.A.Wahab : Solid State Physics, Narosa Publication
Credits: 03 LTP: 210 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CS SE E1 10 01 1: : F FU UN ND DA AM ME EN NT TA AL LS S O OF F C CO OM MP PU UT TE ER RS S & & P PR RO OG GR RA AM MM MI IN NG G
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction: Digital & Analog Computers, Major components of a digital
computer, Word length, processing speed, Computer classification, Batch
processing, Multiprogramming & Multi user systems, Computer network.
Number System: Binary number system, Conversion from binary number to
decimal & vice versa, Addition & subtraction of binary numbers, Use of
complements to represent negative numbers, Binary Fraction to decimal
fraction & vice versa, Hexadecimal and Octal number systems. Decimal, Binary,
Octal, Hexadecimal numbers and their inter-conversions; Representation of
information inside the computers. Integer representation, Signed 1's and signed
2's complement representation, Floating point representation.
Introduction to Programming: Programming languages: Generations of
languages, machine level, assembly and high level languages, compiler,
assembler, interpreter, Programming fundamentals, Algorithm and flow charts.
7
II
Introduction to the C Language: Structure of a C program; Standard Input-
Output in C, Data Types ,Storage classes. Operators and Expressions, Type
conversion, .Non-formatted Input and Output and Formatted Input and Output
functions.
Control Statements: Conditional Operator, The switch statement, while
Construct, Looping or iteration using for loop, do-while construct, goto
statement, special control statements, Nested loops.
7
III
Array: Representation of Single and Multidimensional Arrays, Address
calculation, Operations on arrays, Application of arrays.
Functions: Function Declaration and definition, call by value and by reference,
Scope Rules, Types: User defined and system defined, passing array to functions.
7
References:
Behrouz A. Forouzan and Richard F. Gilberg : Computer Science A structured Programming
Approach Using C ,C Language Learning ,2007
K. N. King: C Programming A Modern Approach, W. W. Norton, 2
nd
Edition, 2008.
Kernighan and Ritche :The C programming Language , PHI , 2
nd
edition, 2011
P. Dey and M. Ghosh :Programming in C, Oxford University Press 1
st
Edition , 2000
Credits: 02 LTP: 200 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EE EE E1 10 01 1: : E EL LE EC CT TR RI IC CA AL L E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G
Module
No.
Content Teaching
Hours
I
1. D C Circuit Analysis and Network Theorems:
Circuit Concepts, Active and passive elements, Electrical energy sources, linear
& non-linear network, unilateral and bilateral elements, source transformation.
Kirchhoffs laws, loop and nodal methods of analysis, star-delta transformation,
Network Theorems: Superposition Theorem, Thevenins Theorem, Nortons
Theorem, Maximum Power Transfer Theorem.
2. Steady- State Analysis of Single Phase AC Circuits:
AC Fundamentals: waveforms or wave shapes, average and effective values,
form and peak factors, concept of phasor, phasor algebra & phasor
representation. Analysis of series, parallel and series-parallel RLC Circuits:
complex power, power triangle, power factor, introduction to resonance in
series and parallel circuits (numerical problems).
13
II
1. Three Phase AC Circuits & Measuring Instruments:
Generation & advantages of three phase system, phase sequence, star and delta
connections, balanced supply and balanced load, line and phase voltage/current
relations, three-phase power and its measurement (simple numerical
problems). Classification of instruments, construction and working principles of
PMMC and MI type instruments and their range extension, single phase
dynamometer wattmeter and induction type energy meter.
2. Magnetic Circuit & Single Phase Transformer
Analogy between electric & magnetic circuits, magnetic leakage & fringing, B-H
curve, hysteresis and eddy current losses, concept of mutual and self induction
Principle of operation, construction, e .m. f. equation, equivalent circuit, power
losses, efficiency, introduction to auto transformer
13
III
Introduction to electro mechanical energy conversion, DC machines:
Construction & working principle, types, e.m.f. equation and torque equation,
applications of dc motors.
Three Phase Induction Motor: Construction & working principle, types, Principle
of operation, Concept of slip, applications. Single Phase Induction motor:
Principle of operation and introduction to methods of starting, applications.
Three Phase Synchronous Machines: Principle of operation of alternator and
synchronous motor and their applications.
2. Introduction to Power Generation & Power System:
Introduction to generation of Electrical Power (conventional and non-
conventional sources), Introduction to Wind energy and solar energy, layout of
thermal & hydro power plant, General layout of electrical power system and
functions of its elements, standard transmission and distribution voltages,
concept of grid (elementary treatment only)
14
References:
V. Del Toro , Principles of Electrical Engineering, Prentice Hall International
I.J. Nagarath , Basic Electrical Engineering, TMH
D.E. Fitzgerald and A. Grabel Higginbotham, Basic Electrical Engineering, TMH
T.K. Nagsarkar and M.S. Sukhija, Basic Electrical Engineering, Oxford University Press.
H. Cotton , Advanced Electrical Technology , Wheeler Publishing
W.H. Hayt and J.E. Kennely, Engineering Circuit Analysis, TMH.
S.N.Singh, Electrical power generation, transmission & distribution, Eastern Economy
Edition.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
M ME EE E1 10 01 1: : M MA AN NU UF FA AC CT TU UR RI IN NG G P PR RO OC CE ES SS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Engineering materials, composition, properties and their applications:
Materials composition, mechanical properties & their applications of
engineering materials-plane carbon steel, alloy steel-tool steel and stainless
steel, various non ferrous metals and alloys e.g. Cu alloy-brass, bronze, , Al alloy-
Duralumin.
Introduction to Rubber, Plastics, Composite materials and their applications.
Machining Processes: Working principles and applications of machining
processes-Lathe Machine, Drilling Machine and Grinding Machine, various tools
used in the operations of these machines.
14
II
Metal Forming Processes: Introduction to Hot & Cold working processes, eg.
Forging, Rolling, Extrusion and Drawing.
Casting Processes: Introduction to various patterns and their allowances.
Molding sand and their properties, preparation of sand moulds, basic concepts
of core, gating, runner & riser system, defects in sand casting & their remedies.
17
III
Fabrication processes: Basic concept of Welding and its classification /
operations. Introduction to Arc welding & Gas welding, types of flames.
Introduction to Soldering, Brazing and their applications.
Advanced Machining Processes: Introduction to advanced machining
processes: Ultrasonic machining, Electrochemical machining, Electric Discharge
machining, Laser Beam machining and their applications.
17
References:
Chapman WAJ, Workshop Technology, Part 1-3, Viva Books Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
Hajra Chowdhary SK and Hajra Chowdhary AK, Workshop Technology, Media Promotors &
Publishers.
Raghuwanshi RS, Workshop Technology, Dhanpat Rai and Sons, New Delhi.
Lindberg RA, Process and Materials of Manufacturing, PHI, New Delhi
Jain RK, Production Technology, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi.
Richard L and Little, Welding and Welding Technology, TMH, New Delhi.
Taylor HF, Flemming, Merton C and Wulff J, Foundry Engineering, Wiley Eastern Limited, New
Delhi.
Richard WH, Casl RL, Jr. and Philip C. Rosenthal, Principles of Metal Casting, TMH, New Delhi.
Jain V.K., Advanced Machining Processes, Allied Publishers, New Delhi.
Jain K.C. and Chitale A.K., Text book of Production Engineering, PHI , New Delhi.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E1 10 01 1: : E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC CS S E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G
Module
No.
Contents
Teaching
Hours
I
Transport phenomenon in semiconductors:
Semiconductor materials; Intrinsic and Extrinsic semiconductors; Mass-action
law, Drift and diffusion of charge carriers.
Junction diodes:
p-n junction diode: construction, operation & characteristics; Zener and
Avalanche breakdown mechanisms; Diode resistance and capacitance; Photo-
diode and LED.
Diode applications:
Rectifiers: half wave, full wave centre-tapped and bridge type.; Filters; Clippers;
Clampers; Voltage multipliers; Zener diode as voltage regulator; Regulated power
supply.
14
II
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT):
Bipolar junction transistor: construction & operation; CB ,CE, CC configurations &
their Characteristics; Operating point; Transistor as a switch; Need of biasing;
Biasing methods: fixed bias, emitter bias, potential divider bias, voltage feedback
bias; Bias stabilization; Stability factor; h-parameters; Small signal analysis of BJT
amplifier.
Field Effect Transistor (FET):
Construction, operation & characteristics of JFET; Shockleys equation; Depletion
& Enhancement type MOSFET; Biasing of JFET:-fixed bias, self bias and voltage
divider bias; Biasing of depletion type & enhancement type MOSFET.
14
III
Digital Electronics:
Number systems; Binary Addition & Subtraction; 1s and 2s complement ,
Subtraction using 2s complement; Boolean algebra; Logic gates; Implementation
of basic gates using universal gates; Realization of Boolean functions using basic
& universal gates; Canonical forms(SOP & POS); Simplification of Boolean
functions using Boolean postulates & K-map up to 4 variables with dont care
condition; Basic concept of latch.
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp):
Operational amplifier: Block diagram, ideal and practical Op-Amp characteristics;
Inverting, non-inverting and differential configurations (open loop and closed
loop); Applications of Op-Amp as buffer, adder, subtractor, integrator and
differentiator.
13
References:
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis nashelsky , Electronic devices and circuit theory , Pearson
Education/PHI, New Delhi.
Morris Mano , Digital design , Pearson Education.
R.A. Gayakwad , Op-amps & linear Integrated circuits , PHI.
R.J. Smith and R.C. Dorf , Circuits, Devices and System, Willey , 5th edition.
Jacob Millman and Christos C. Halkias , Integrated Electronics , TMH , New Delhi.
H.S. Kalsi : Electronic Instrumentation , TMH , New Delhi.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HE E1 18 81 1: : C CO OM MM MU UN NI IC CA AT TI IO ON N S SK KI IL LL L I I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. Hurdles of the Path and Route Map
Language Drills :
Singular & Plural, countable & uncountable, Parts of speech, Tense-shift
Routine Expressions :
Greeting, Introducing yourself and others, Query formal/ Informal, Replies
Positive, Neutral and Negative, Expressing surprise, regret, apology, seeking
information.
Tenses through simple presentations :
For Example:
Present : Introduction, Routine, My City, My Value System etc.
Past : Describing events marriage party, picnic, conference etc.
Experience, Process, Movie etc.
Future : Goal of my life, India of my dreams etc.
We will have to return to our roots
Cloning will make us immortal
Technological Advancement : Man is on the verge of becoming Machine/God.
2. Virtual Speaking
Extempore : 1 minute description of objects in the room.
Picture Description :
Flow of the idea, organization of the message.
Crowded Pictures
Abstract Pictures
Open ended relationship based:
(i) Mother(in Business suit) rushing outside while child is
crying, goods in home are scattered
(ii) Sibling Fight
(iii) Joint family having fun
Bars, Pie-charts, Tables
Cook a Story : Ways of developing paragraph in prose
Jumbled Pictures
One Person One Sentence
Tie up the loose threads
3. Rapid Vocabulary & its Usage:
Roots & word formation, commonly misused words, words with shades of
meaning, Phrasal Verbs, Terms used as Noun & Verb, Noun & Adjectives.
4. Speak Well
Ambiguity in conversation/ comment, Reason & ways to root it out, commonly
mispronounced words Phonetic symbols / Pronunciation Drills
5. Comprehension and Conversation
Listening: Active & Passive listening; listening with Empathy, Listening
Comprehension
Reading Comprehension (pre-discussion and post discussion)
(From Everyday English Pg. 99 103)
Telephonic Conversation :
Greetings, putting the phone on hold, inquiry about the caller.
Simple Role Play
Credits: 2 LTP: 0-0-3 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
M ME EE E1 18 81 1: : E EW WS S P PR RA AC CT TI IC CE E L LA AB B
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Machine Shop
1. To make a step turning job from mild steel round bar as per drawing.
2. To make a job for taper turning, grooving & threading from mild steel round
bar as per drawing.
3. Study of practices on Shaper.
4. Demonstration of CNC Lathe operation.
5. Demonstration of Milling Machine operation
Sheet Metal Shop
6. To make a rectangular tray as per drawing
7. To make a funnel with soldering
Carpentry Shop
8. To make a flat wooden block by using jack plane as per drawing.
9. To make a half lap corner joint as per drawing.
10. To make a wooden round block by using wood working lathe.
Welding Shop
11. To prepare a Butt-joint by electric arc welding.
12. To prepare a Lap-joint by electric arc welding.
13. To prepare a joint by gas welding.
Fitting Shop
14. To make a rectangular M.S. flat job as per drawing.
15. To make a simple and tapped hole in M.S. plate as per drawing.
16. To make a male-female joint as per drawing.
Black-smithy Shop
17. To make a nail as per sketch.
Foundry Shop
18. To make a pattern from wood for a hollow cylinder as per drawing.
19. To make a casting using a core as per given pattern.
Credits: 02 LTP: 003 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HP P1 18 81 1: : P PH HY YS SI IC CS S L LA AB B
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. To determine the wavelength of monochromatic light by Newtons rings.
2. To determine the wavelength of monochromatic light with the help of
Fresnels biprism.
3. To determine the focal length of two lenses by nodal slide and to locate the
position of cardinal points.
4. To determine the specific rotation of cane sugar solution using polarimeter.
5. To determine the wavelength of spectral lines using plane transmission
/diffraction grating.
6.Measurement of wavelength of laser (He- Ne) light using single slit
diffraction.
7. To determine the specific resistance of the material of a given wire using
Carey Fosters bridge.
8. To study the variation of magnetic field along the axis of current carrying
circular coil and then to estimate the radius of the coil.
9. To calibrate the given ammeter and voltmeter by potentiometer.
10. To study the Hall effect and determine Hall coefficient, carrier density and
mobility of a given semiconductor.
11. To determine the energy band gap of a given semiconductor material.
12 To determine E.C.E. of copper using Tangent or Helmholtz galvanometer.
13. To draw hysteresis curve of a given sample of ferromagnetic material and
then to determine the magnetic susceptibility and permeability of the given
specimen.
14. To determine the ballistic constant of a ballistic galvanometer.
15. Measurement of fiber attenuation and aperture of optical fiber.
16. To determine high resistance by leakage method.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CS SE E1 18 81 1: : C CO OM MP PU UT TE ER R P PR RO OG GR RA AM MM MI IN NG G L LA AB B
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
(1) Arithmetic operations
a. WAP to perform arithmetic operation over the variables.
b. WAP to calculate area of the circle.
c. WAP to find the sum of digits of a number.
d. WAP to find the reverse of a string..
e. WAP to implement perimeter of a rectangle
(2) Function
a. WAP to call a function by reference.
b. WAP to call a function by value.
c. WAP to calculate factorial of a number.
d. WAP to print a table of a user define number.
e. WAP to generate Fibonacci Series
(3) Pointer
a. WAP to display the contents of 2D array using pointer.
b. WAP to sort an array in ascending order using dynamic
memory allocation and pointers.
(4) Microsoft office
a. MS Word Introduction.
b. MS Excel Introduction
c. MS PowerPoint Introduction.
d. MS Paint brush Introduction.
(5) pattern
a. WAP to design the following pattern
* * * * * * * * * *
* * * * * * * *
* * * * * *
* * * *
* *
24
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EE EE E1 18 81 1: : E EL LE EC CT TR RI IC CA AL L & & E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC CS S L LA AB B
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. To verify the Thevenins theorem (DC circuits).
2. To verify the maximum power transfer theorem (DC circuits). Also draw
graph between power and load resistance.
3. To verify the Superposition Theorem (DC circuits).
4. To study the phenomenon of resonance in R-L-C series circuit and to draw
graph between frequency and current. Also show half power points.
5. To determine the V-I characteristics of a semiconductor diode. Also
calculate forward and reverse static and dynamic resistances.
6. To study the half wave and full wave (center tapped) rectifier with and
without filter. Also to calculate the ripple factor in both cases (without
filter).
7. To study single phase (induction type) energy meter.
8. To study various logic gates such as OR, AND, NOT, NAND, NOR.
9. Study of CRO and measurement of voltage and frequency using CRO.
10. V-I characteristics of Zener diode.
11. Identification of active and passive components.
12. V-I characteristics of bipolar junction transistor in common base mode.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester I
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HM M1 10 02 2: : M MA AT TH HE EM MA AT TI IC CS S - - I II I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Multiple Integrals: Double and Triple Integrals, Change of order of
integration, Change of variables, Beta and Gamma functions. Applications to
Dirichlet integrals.
Vector Calculus: Gradient, Divergence and curl ; their geometrical and
physical significance, Vector Identities, Line, surface and volume integrals,
Independence of path, Green, Gauss divergence and Stokes theorem (without
proof).
15
II
Partial Differential Equations : Solution of I order Lagranges linear PDEs,
Linear PDEs with constant coefficients, Classification of II order PDEs, Method
of separation of variables, One dimensional wave equation, DAlemberts
solution, Heat conduction equations up to two dimensions.
11
III
Laplace Transform: Properties of Laplace transform, Existence theorem,
Laplace transform of derivatives and integrals, Unit step and Dirac delta
function, periodic functions, Partial Fractions, Properties of inverse Laplace
transform, convolution theorem. Application to ODEs and integral equations.
13
References:
E. Kreyszig , Advanced Engg. Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons, 9
th
Edition.
Peter V.ONeil , Advanced Engg. Mathematics, Thomson Learning .
M.D.Greenberg , Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Pearson Education Inc.
Bali & Goyal , A Text Book of Engg. Mathematics, Infinity Science Press, U.S.A.
Allen Jeffrey , Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Academic Press, Elseveir .
B.V.Ramanna , Higher Engg. Mathematics, TMH, New Delhi.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HP P1 10 02 2: : E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G P PH HY YS SI IC CS S I II I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. Wave Mechanics: Wave model, Wave- particle duality, Photoelectric effect,
de-Broglie hypothesis, Phase and group velocities: wavepacket, Heisenbergs
uncertainty principle and its applications, Wave function and its normalisation,
Schrdingers wave equation : time dependent and time independent wave
equations, particle in one dimensional potential box.
2. X-ray Diffraction: Diffraction of X-rays by crystal planes, Braggs law, Braggs
spectrometer, Comptons effect.
10
II
1. Superconductivity: Temperature dependence of resistivity in
superconducting materials, Meissner effect, Type I and Type II superconductors,
Temperature dependence of critical field, BCS theory (qualitative), Londons
equation, Landon penetration depth, Properties and applications of
superconductors.
2. Science and Technology of Nanomaterials: Basic principle of nanoscience
and nanotechnology, Nanomaterials, creation and uses of Buckyballs. structure,
properties and uses of carbon nano-tubes (CNT), Tools to make nano-structures,
Applications of nanotechnology.
8
III
1. Electromagnetics : Inconsistency in Amperes law, Displacement current,
Equation of continuity, Maxwells equations (Integral and Differential forms),
Propagation of E-M waves in free space and in conducting media, Poynting
theorem and Poynting vector.
2. Electric Field in Matter: Dielectric materials, Dielectric polarization,
Dielectric constant, Types of Polarization, Polarizability, Clausius- Mosotti
equation, Ferro and Piezo electricity (qualitative), Dielectric losses, Applications
of dielectric materials.
3. Magnetic Field in Matter: Magnetisation, dia, para and ferromagnetism,
Langevins theory for dia and para-magnetic materials, Phenomenon of
hysteresis and its applications.
12
References:
Beiser , Concept of Modern Physics, TMH , New Delhi.
C. Kittel , Solid State Physics, Wiley Eastern, 7th edition
V. Raghavan , Materials Science and Engineering, PHI , New Delhi.
S.O. Pillai , Solid State Physics, New Age International Publication, 5th edition.
Rechard Booker and Earl Boysen, Nanotechnology, Wiley International.
David J. Griffith, Introduction to Electrodynamics, PHI, New Delhi
C.S.Liu and V.K.Tripathi , Electromagnetic Theory for Telecommunications, Cambridge
University press India.
Credits: 03 LTP: 210 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CS SE E1 10 02 2: : P PR RO OB BL LE EM M S SO OL LV VI IN NG G U US SI IN NG G C CO OM MP PU UT TE ER RS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Recursion: Mechanics of a recursive call, How recursion is implemented,
definition of recursion, Key concepts. Comparing recursion and iteration.
Structures: Declaration, initialization of. Structure, Nested structures, user
defined data types, Enumerated data types, Unions. Difference between
structure and Union.
7
II
Pointers: Introduction, Pointer variables, pointer and arrays, array of pointers,
pointers and structures, dynamic allocation.
Strings: Introduction, Declaring & Initializing string variables, String
Input/output Functions, String Manipulation Functions.
File handling in C: Data and information, File concepts, File organization, Files
in C, Files and streams, stream I/O, Sequential and Direct File organization.
Problems based on Files.
7
III
Introduction Stack, Queue & Linked List: Array Representation and
Implementation, Insertion, Deletion. Empty, Underflow.
Declarations: Storage Classes- Auto, Static, Extern, Register etc.
Low Level Programming such as Bit-level
Writing Large Programs: A simple file Program, Program by using two
Source Files, Program based on separate compilation of functions.
7
References:
Behrouz A. Forouzan and Richard F. Gilberg , Computer Science A structured Programming
Approach Using C , C Languages Learning, 2007.
K. N. King and W. W. Norton , C Programming A Modern Approach , 2nd Edition, 2008.
Kernighan and Ritchie, The C programming Language , PHI , 1996.
P. Dey, and M. Ghosh , Programming in C, Oxford University Press ,2009 .
Credits: 02 LTP: 200 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
M ME EE E1 10 02 2: : B BA AS SI IC C T TH HE ER RM MO OD DY YN NA AM MI IC CS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Basic Concepts
Thermodynamic systems, State & properties, Macroscopic & microscopic point
of view. Thermodynamic equilibrium & processes, Zeroth law of
thermodynamics, Temperature scales, Work & heat.
First Law of Thermodynamics
First law of thermodynamics, Energy equations for closed systems and open
systems under steady flow conditions, Application of first law to various
thermodynamic systems such as boiler, turbine compressor, nozzle, pump etc.
13
II
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Limitations of the first Law of thermodynamics, Concept of heat engine, Heat
pump & refrigerator, Second Law of Thermodynamics, Carnot cycle, Theorems
and Corollaries, Clausius Inequality, Concept of entropy, Principle of increase of
entropy of universe, Entropy change during various processes, Concept of
Third Law of Thermodynamics.
Properties of Steam or pure substance
Definition of pure substance, Phase change, p-T diagram and pV-T surfaces,
Formation of Steam, Classification of steam generators, Construction and
working of boilers, Concept and determination of dryness fraction of steam,
Thermodynamic properties of steam, Steam table and Mollier diagram, Various
thermodynamic processes with steam as a working medium.
Rankine cycle, layout and working of steam power plant
14
III
Gas power cycle and IC engine
Air standard cycles and efficiency, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, Concept &
classification of IC engines, Construction and working of two stroke and four
stroke engines, SI and CI engines.
Refrigeration & Air Conditioning
Elementary concept of Refrigeration & Air conditioning, Working principle and
schematic diagrams of refrigerators, air coolers, air conditioners and ice plants,
Vapour compression cycles.
13
References:
Van Wylen G.J. and Sonnlog R.E. , Fundamentals of classical thermodynamics, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc. NY.
Wark Wenneth , Thermodynamics , Mc Graw Hill book Co. NY.
Holman, J.P. , Thermodynamics, MC Graw Hill book Co. NY.
Rogers G and Mayhew Y , Engineering Thermodynamics, Pearson Education.
Jones J B and Hawkins J A , Engineering Thermodynamics, John Wiley and Sons.
Joel R. , Basic Engineering Thermodynamics, Addison Wesley.
Nag P. K. , Engineering Thermodynamics, TMH , India
Yadav R. , Thermodynamics and Heat Engines, Central Publishing House Allahabad, Vol I, 2nd
Edition.
Ballaney P.L. , Thermal Engineering, Khanna Publisher.
Arora C.P. , Engineering Thermodynamics, TMH, New Delhi.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HC C1 10 01 1: : E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G C CH HE EM MI IS ST TR RY Y
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Chemical kinetics: Order and molecularity of reactions, Zero order, first order
and second order reactions. Integrated rate equations. Theories of reaction
rates, Factors affecting rate of reaction.
Solid State: (1 lect): Types of unit cell, space lattice (only cubes), Calculation of
density of the unit cell, number of atoms per unit cell,
Chemical Bonding: M.O. theory and its applications in homo & hetero
diatomic molecules. Hydrogen bond, metallic bond and their applications.Semi-
conductor
Organic Name Reactions and Stereochemistry.
Name reactions ie.Aldol Condensation,Cannizaro reaction, Types of isomerism
(optical & geometrical), Chirality, Element of symmetry, Diastereomers,
Optically active Compounds, R-S configuration and E-Z geometrical isomers,
Conformation of ethane, n-butane
Non Conventional Energy Source: Introduction to Solar energy, Biomass and
biogas.
14
II
Introduction, Definition and Explanation of the terms: phase, component and
degree of freedom, Application of phase rule to one component system (water
& CO2 system), pH, buffer solution (Henderson equation).
Polymers: Polymerization and its classification. Thermoplastic and
Thermosetting resins. Properties of Polymers, Molecular weights of
Polymers,Elastomers. Organic conducting and biodegradable polymers
(PMMA, polystyrene, Teflon, neoprene, Buna-S, Buna-N Nylon 6, Nylon 66,
Terylene, PLA, poly hydroxy butyrate), vulcanization of rubber.
Water Treatment: Introduction, Hardness and its units, , L-S Process, Calgon
process, Zeolite and Ion-exchange resins, Treatment of Municipal Water,
reverse Osmosis, Impurities in water, Characterstics of water, Treatment
process Includes above deleted portions, boiler feed water, boiler troubles and
remedial measures
Lubrication: Introduction to lubrication, Classification, Properties & uses.
17
III
Corrosion: Introduction, Consequences, Types, Theories of Corrosion,
(galvanic, pitting, stress, water line, intergranular & soil corrosion) and
Protection of Corrosion. Electrochemical cell, Concentration cell.
Spectroscopy: Elementary ideas and simple applications of UV, visible, infra-
red and NMR spectral techniques
Fuels: Classification of fuels. Analysis of coal, determination of calorific values,
Synthetic petrol Glass: Preparation, varieties & uses.
Ceramics: Introduction, Classification, scope & application.
17
References:
Morrison Boyd , Organic Chemistry
I.L. Finar , Organic Chemistry
Y R Sharma , Elementary Organic Spectroscopy
S. S. Dara , Text Book of Engg Chemistry
Shashi Chawla , Engg Chemistry
K M Mittal , Non Conventional Energy System
Mars G Fontana , Corrosion Engg
Attkins & others , Inorganic chemistry
Attkins & others , Physical Chemistry
Puri, Sharma and Pathania : Physical Chemistry
Laidler , Chemical Kinetics
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
M ME EE E1 10 03 3: : A AP PP PL LI IE ED D M ME EC CH HA AN NI IC CS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction: Engineering Mechanics, Idealization of Bodies, concept of Rigid
Body, External Forces (Body forces & surface forces), Laws of Mechanics.
Force systems and Equilibrium: Concurrent forces in a plane, Parallel forces
in a plane, Free Body Diagram, Equation of equilibrium and their applications to
various systems of forces.
Friction: Introduction to friction, Dry friction, Laws of friction and its
application to wedge, ladder, screw, rolling friction, belt-pulley system.
14
II
Distributed Forces And Moment Of Inertia: Centroid of Composite figures,
Area Moment of Inertia, Polar Moment of Inertia, Parallel axes theorem,
Perpendicular axes theorem, Principle Moment of Inertia, Mass Moment of
Inertia of circular ring, disc, cylinder, sphere and cone about their axis of
symmetry.
Beams: Different support & load conditions, Shear Force and Bending Moment
Diagram.
Analysis Of Plane Trusses: Engineering structures, Perfect Truss,
Determination of axial forces in the members, Method of Joints, Method of
Section.
17
III
Kinematics Of Rigid Body: Plain motion of rigid body, Velocity and
acceleration under translation and rotational motion, Absolute motion, Relative
motion.
Kinetics Of Rigid Body: Force, Mass and Acceleration, Work, Power and
Energy, Impulse and Momentum, DAlemberts Principle and dynamic
equilibrium.
Principle Of Virtual Work: Principle and application of Virtual work, Stability
of equilibrium.
17
References:
I.H. Shames , Engineering Mechanics , PHI., New Delhi.
F.P. Beer and E.R. Johnston , Mechanics for Engineers (Statics and Dynamics), TMH New
Delhi.
Dr. A.K. Tayal , Engineering Mechanics Statics & Dynamics, Umesh Publications, Delhi.
V.S. Mokashi , Engineering Mechanics Statics Vol.I & Dynamics Vol-II, TMH.
J.L. Marriam and L.G. Kraig , Engineering Mechanics Statics & Dynamics, John Wiley &
Sons Ltd.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HE E1 18 82 2: : C CO OM MM MU UN NI IC CA AT TI IO ON N S SK KI IL LL LS S I II I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Communication Games(as per the level and requirement of the class) 2 truth
and 1 lie, psychological tests through pictures, Building Blind, Blind obstacle
course.
II
Discussion on Newspaper/Magazines/Comics(Underlying process), dividing
the class into small teams as per their choice- after a week one group is to ask
questions about the happenings of last week- continuing on different sides,
debate based upon counterview, narrate all the seven activities of a particular
cartoon and which one do you like the most, most important happening of the
week, analyzing headlines- appeal and attractiveness, cover pages of
magazines- comparison, upgrading vocabulary- noticing phases and popular
acronyms, Quiz from Sunday column, analyzing advertisements and their
appeal
III
Presentation Skills: Analyzing locale, audience orientation, organizing
content- Effective beginning, Development of thought and forceful/emphatic
conclusion, Visual aids- Usage of PPT- Theory & practice;
Non-Verbal clues: Significance and awareness of basics- posture & gestures,
i.e. eye contact, hand movement, gap from the audience, assessing the mood
and response of the audience.
Model presentation, Presentation on long story, Novel, Drama, Poetry e.g.- Who
moved my cheese by Spencer Johnson, The Barber's Trade Union by Mulk Raj
Anand, Jonathan Livingstone Seagull- Richard Bach, To Kill a Mockingbird-
Harper Lee, Miracles on the water- Tom Nagasaki.
IV
Debate and group discussion: Basic Theory- Difference between debate and
GD, Why GDs, Skills gauged during GD, major kinds of GDs, Dos and don'ts of
GD.
Practice of debate- Famous controversial topics to simulate the logic and free
flow of communication;
GDs- on simple factual topics, argumentative/controversial topics, Current
topics; Group Discussion/Case study on the topics with perceptual variety.
V
Role play: Simple role play- from student life(involving friends, teachers,
parents);
Advanced role plays - creating business related situations, Famous speeches
from epics(if the class is comfortable with it);
Enacting a drama popular one act play, Theme enactment (the theme is
provide to the team 1 week back, One theme to the whole batch- competition)
Credits: 02 LTP: 003 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
M ME EE E1 18 82 2: : E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G D DR RA AW WI IN NG G
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction to drawing instruments, sheet layout, types of lines and their uses,
lettering, concepts of scales in drawing and their types, types of dimensioning,
application of symbols and conventions in drawing practice, geometrical
construction.
Theory of projections, Orthographic & Oblique Projection of points, lines,
planes and solids, development of surfaces & section of solids, concepts of
isometric and perspective views.
Introduction to computer aided drawing and various softwares available in the
market. Isometric projection, conversion of pictorial views to orthographic
views and vice versa, Computer Aided drawing using Auto CAD.
References:
Bhatt N.D. and Panchal V.M. , Elementary Engineering Drawing , Charothar Publishing,
Gujarat.
Dhawan R.K. , A Text book of Engineering Drawing, S. Chand.
Gopalkrishna K.R. , Engg. Graphics, Subhash Publishers, Banglore.
Trymbaka Murty.S , Computer Aided Engineering Drawing , T.K. International Publishing
House Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
Luzadder Warren J. and Duff John M. , Fundamentals of Engineering Drawing with an
introduction to Interactive Computer Graphics for Design and Production, PHI, New
Delhi.
Singh Ajit , Machine Drawing, TMH, New Delhi.
Credits: 02 LTP: 003 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HC C1 18 81 1: : C CH HE EM MI IS ST TR RY Y L LA AB B
Any TEN Experiments are to be performed
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. Preparation and Standardization of solutions.
2. To determine the constituents and amount of alkalinity of the supplied
water sample.
3. To determine the percentage of available chlorine in given sample of
bleaching powder.
4. To determine pH of a solution using a pH-meter and titration of such
solution pH-metrically.
5. Determination of free CO2 in a given sample of water.
6. To determine the Ferrous ion content in given iron ore by titrimetric
analysis against standard K2Cr2O7 solution using K3[Fe(CN)]6 as an external
indicator.
7. To determine iron concentration in the sample of water by colorimetric
method. The method involves use of KCNS as color developing agent and the
measurements are carried out at max 480nm.
8. To determine the viscosity of an addition polymer like polystyrene sample
by using Ostwald viscometer relative to water.
9. To determine the temporary and permanent hardness of water by using
EDTA or complexometry.
10. To determine the equivalent weight of iron by chemical displacement
method. The equivalent weight of copper is 63.5.
11. To determine chloride ion in a given water sample by Argentometric
method (Mohrs Method).
12. To determine the moisture content in a given sample of coal.
13. To determine the calorific value of a solid fuel by bomb calorimeter.
14. Show that inversion of cane sugar is the example of first order reaction by
polarimeter.
Credits: 01
LTP: 002 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CS SE E1 18 82 2: : P PR RO OB BL LE EM M S SO OL LV VI IN NG G L LA AB B
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
(1) Recursion
a. WAP to calculate factorial of a number.
b. WAP to generate table of any number.
c. WAP to find GCD of two numbers.
d. WAP to calculate nth term of Fibonacci Series 1,1,2,3,5,8
e. WAP to find the sum of digits of a number.
f. WAP to find the reverse of a string.
g.
(2) Structure
a. WAP to enter 10 records of student .Structure fields are Name, Roll no,
Marks. Calculate the average of their marks.
b. Declare a structure which will contain the following data for three
employees.
i. Emp_code 3 characters,
ii. First_name 20 characters,
iii. Middle_initial 1 character,
iv. Last_name 20 characters.
v. The employee code to be stored in the structure are
E01,E02,E03. Write a program to input names for 3 employees
and printout initials of each.(e.g. Anil K Nehra will be printed as
AKN) along their codes.
c. WAP to demonstrate, how structure is passed to a function.
d. WAP to perform arithmetic operations using functions and switch
case and enumeration.
(3) Pointer
a. WAP to display the contents of 2D array using pointer.
b. WAP to sort an array in ascending order using dynamic memory
allocation and pointers.
(4) File handling
a. WAP to copy the contents of a given file into another file.
b. WAP to read the characters from a file and display the uppercase on a
console.
(5) Introduction to Data Structure
a. WAP to demonstrate various operations (create, push, pop, overflow,
underflow, peek, display) of STACK using array implementation.
b. WAP to demonstrate various operations (create, enqueue, dequeue,
overflow, underflow, peek, display) of Queue using array
implementation.
c. WAP to demonstrate various operations [(create, Traversing,
Searching, Inserting an element (at beginning, at end, after a given
element), Deleting an element (from beginning, from end, after a given
element)] of a linked List.
d. WAP to demonstrate various operations (create, Traversing,
Searching, Inserting an element at beginning, Deleting an element
from end) of a doubly linked List.
24
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
M ME EE E1 18 83 3: : A AP PP PL LI IE ED D M ME EC CH HA AN NI IC CS S L LA AB B
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
1. To conduct the tensile test and determine the ultimate tensile strength,
percentage elongation for a steel specimen.
2. To determine the compression test and determine the ultimate compressive
strength for a specimen.
3. To conduct the Impact-tests (Izod/Charpy) on Impact-testing machine to
find the toughness.
4. To determine the hardness of the given specimen using Brinell/Rockwell
hardness testing machine.
5. Friction experiment on inclined plane.
6. Simple & compound gear-train experiment.
7. Worm & worm-wheel experiment for load lifting.
8. Belt-Pulley experiment.
9. Bending of simply-supported beams for theoretical & experimental
deflection.
10. Torsion of rod/wire experiment.
11. Experiment on Trusses.
12. Experiment on Moment of Inertia.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester II
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
A AH HM M 2 20 01 1: : M MA AT TH HE EM MA AT TI IC CS S I II II I
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Solution Of Cubic and Biquadratic Equations : Cardons Method of solving
Cubic equations, Descartes and Ferraris method of solving Biquadratic
equations.
Fourier Series : Fourier series of Period 2_ , Even and Odd functions, Fourier
series for discontinuous functions, Half range sine and cosine series, Change of
interval.
13
II
Fourier transform: Fourier sine and cosine integrals, Complex Fourier
transform, Fourier sine and cosine transforms, Applications to heat conduction
equations.
Z- Transform : Properties of Z transform, Inverse Z transform, Partial
fractional and Residue method, applications of Z transform in solving
difference equations.
13
III
Functions of a complex variable: Analytic functions, Cauchy - Reimann
equations , Harmonic function, Milnes Thomson method, Cauchy integral
theorem, Taylors, Maclaurins and Laurents series ( without proof ), Zeros and
Singularities, Residue, Cauchy Residue theorem, Contour integration involving
unit circle.
14
References:
E. Kreyszig , Advanced Engg. Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons, 9th edition.
Bali & Goyal , A Text Book of Engg. Mathematics, Infinity Science Press.
Peter V.ONeil , Advanced Engg. Mathematics, Thomson Learning.
M.D.Greenberg , Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Pearson Education Inc.
Allen Jeffrey , Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Academic Press.
B.V.Ramanna , Higher Engg. Mathematics, TMH New Delhi.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CE EE E2 20 01 1: : E EN NV VI IR RO ON NM ME EN NT TA AL L S ST TU UD DI IE ES S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Basics Of Environmental Studies:
Environmental Studies: Introduction, Scope and Importance Environment:
Concept, Natural and Anthropogenic Environment Natural Environment:
Structure & Function of Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Lithosphere and Biosphere
Ecology and Ecosystem: Definitions Types, Structure & Functions of Ecosystem.
7
II
Natural Resources:
Natural Resources: Introduction, Classification, Concept of Conservation
Present Status and Major Issues Related to Water Resources, Forest Resources
and Mineral Resources Energy Resources: Introduction, Classification, Energy
Use Patterns, Energy Crisis, Alternative Energy Resources Present Status and
Major Issues Related to Fossil Fuels, Hydroelectricity, Nuclear Energy, Solar
Energy and Biomass Energy.
6
III
Current Environmental Problems:
Effects of Human Activities on Environment: Effect of Agriculture, Housing,
Mining, Transportation and Industries Environment Pollution: Causes, Effects
and Control of Air Pollution, Water Pollution, Land Pollution and Noise
Pollution Introduction and Management of Solid Wastes and Hazardous Wastes
Global Environmental Challenges: Global Warming, Ozone Layer Depletion,
Acid Rain, Urbanization, Overpopulation and Biodiversity Depletion.
7
IV
Environmental Protection:
Environmental Protection: Role of Citizens, Role of Government, Initiatives by
NGOs, Contribution of International Agencies and Conventions Approaches to
Environmental Protection: Public Awareness, Environmental Education,
Environmental Ethics, Environmental Laws and Environmental Economics
Tools and Strategies: Environmental Impact Assessment, Life Cycle
Assessment, Ecological Footprints and Sustainable Development Efforts
towards Environmental Protection in India.
6
References:
Benny Joseph , Environmental Studies.
Deswal & Deshwal , Textbook on Environmental Studies.
AK De , Environmental Studies.
Shashi K Singh and Anisha Singh , Environmental Science & Ecology.
Agarwal and Sangal , Environment & Ecology.
Credits: 02 LTP: 200 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 20 01 1: : E EL LE EC CT TR RO OM MA AG GN NE ET TI IC C F FI IE EL LD D T TH HE EO OR RY Y
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Review of vector algebra
Scalar & vectors, Unit vectors, Vector addition & subtraction, Position vector,
Vector Multiplications, Components of Vector.
Coordinate System & Transformation
Cartesian, cylindrical and Spherical coordinates & their transformation.
Vector Calculus
Line, Surface and Volume Integrals, Gradient of a scalar, Divergence of a Vector,
Curl of a Vector, Divergence Theorem , Stokess Theorem.
Electrostatics-I
Coulombs law & field intensity, Electric fields due to continuous charge
distributions. Electric flux density, Gausss law, Electric potential.
13
II
Electrostatics-II
Electric Dipole, Energy density in electrostatic field, Conductors and current,
Polarization in dielectrics, Continuity equation and relaxation time, Boundary
conditions, Poissons and Laplaces equation, Capacitance, Method of Images.
Magnetostatics
Biot-savarts law, Amperes Circuit law, Magnetic flux density, The scalar and
vector magnetic potential, Maxwells equations for static field, Forces due to
magnetic field, Magnetic torque and moment, Magnetization in materials,
Magnetic boundary conditions, Inductance, Magnetic energy.
14
III
Maxwells Equations
Faradays law, Displacement current, Maxwells equations in point and integral
forms, Retarded potential
E M Wave Propagation
Wave propagation in lossy dielectrics, Plane wave in lossless dielectrics, Plane
wave in free space, Plane wave in good conductors, Power and the Poynting
vector, Reflection of a plane wave at normal and oblique incidence, wave
polarization.
Transmission Lines
Transmission line parameters, Transmission line Equation, Lossless and low
loss propagation, Wave reflection and VSWR, transmission line of finite length,
Reflection Coefficient, Standing wave ratio, Stub Matching, Smith chart and
measurement of inductance, capacitance and resistance with the help of smith
chart.
14
Text Book:
1. Jordan E.C. and Balmain K.G., Electromagnetic wave and radiating Systems, PHI Second
edition.
2. W.H. Hayt and J.A. Buck, Electromagnetic Field Theory, 7th TMH.
Reference Books:
1. M.N.O. Sadiku, Elements of Electromagnetics, 4th Ed, Oxford University Press
2. Kraus, F Electromagnetics Tata Mc Graw Hill fifth edition.
3. Ramo S, Whinnery T.R. and Vanduzer T, Field and Waves in communication
electronics John Wiley and sons third edition.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 20 02 2: : D DI IG GI IT TA AL L E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC CS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Logic Families, Diode, BJT & MOS as a switching element, concept of transfer
characteristics, Input characteristics and output characteristics of logic gates,
Fan-in, Fan-out, Noise margin, circuit concept and comparison of various logic
families: TTL, CMOS Tri-state logic, open collector output, packing density,
power consumption & gate delay.
Digital system and binary numbers: Signed binary numbers, binary codes,
Cyclic Codes, Error Detecting and Correcting Codes, Hamming Codes. Floating
point representation.
Gate-level minimization : Five variable K-Map, dont care conditions, POS
simplification, NAND and NOR implementation, Quine Mc- Clusky method
(Tabular method)
13
II
Combinational Logic : Combinational circuits, analysis procedure, design
procedure, Binary Adder-Subtractor, Decimal Adder, Binary Multiplier,
Magnitude Comparator, Decoders, Encoders, Multiplexers
Synchronous sequential logic: Sequential Circuits, Storage Elements : Latches,
Flip Flops, Analysis of Clocked Sequential Circuits, State Reduction and
Assignments, Design Procedure
Register and counters: Shift Registers, Ripple Counter, Synchronous Counter,
Other Counters.
14
III
Registers and Counters: Shift Registers, Ripple Counter, Synchronous Counter,
Other Counters.
Memory and programmable logic : RAM, ROM, PLA, PAL, FPGA, PROM, EPROM,
EEPROM
Asynchronous Sequential Logic : Analysis procedure, circuit with latches, Design
procedure, Reduction of state and flow table, Race free state assignment,
hazards.
14
Text Book:
1. M. Morris Mano and M. D. Ciletti, Digital Design 4th Edition, Pearson Education
2. S. Salivahanan & S. Asivazhagan, Digital Circuit & Design, IInd Edition
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 20 03 3: : E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC C D DE EV VI IC CE ES S & & C CI IR RC CU UI IT TS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Review of transistors: all configurations of BJTs and FETs with their
characteristics. High frequency equivalent circuits of BJTs, MOSFETs, Miller
effect, Short circuit current gain, s-domain analysis and amplifier transfer
function. Low and high frequency response of BJTs and FETs in all
configurations.
12
II
Feedback Amplifiers: Classification of amplifiers, the feedback concept, The
transfer gain with feedback, General characteristics of negative feedback
amplifiers, input resistance, output resistance, Method of analysis of feedback
amplifier, voltage series feedback, voltage shunt feedback, current series,
current shunt feedback.
Oscillators: Conditions for oscillations, Sinusoidal oscillators, the phase shift
oscillators, resonant circuit oscillators, a general form of oscillator circuit, the
Wein Bridge oscillators, crystal oscillators, frequency stability
14
III
Output stages and Power amplifiers: Power amplifiers, Power Transistors,
Class A, Class B, Class AB, Class C operation, Design Application.
Power Devices: The p-n-p-n Diode, Semiconductor Controlled Rectifier,
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, DIAC, TRIAC.
14
Text Books:
1. Neamen D A, Electronics Circuits, 3rd Ed TMH
2. Ben G. Streetman, Sanjay Banerjee, Solid State Electronic Devices , 5th Ed.PHI
Reference Books:
1. Jacob Millman, Christos Halkias, Satyabrata Jit, Electronic Devices and Circuits, TMH
2. Sedra S., Smith K., Micro-electronics ,5th edition, OXFORD
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EE EE E 2 20 01 1: : N NE ET TW WO OR RK K A AN NA AL LY YS SI IS S & & S SY YN NT TH HE ES SI IS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
A1: Network Theorems (Applications to ac networks):
Super-position theorem, Thevenins theorem, Nortons theorem, Maximum
power transfer theorem, Millmans theorem, Compensation theorem,
Tellegens theorem, Reciprocity Theorem.
A2: Graph Theory:
Graph of a Network, concept of tree, co-tree, link, basic loop and basic cut set,
Incidence matrix, cut set matrix, Tie set matrix; Duality; Loop and Nodal
methods of analysis..
14
II
B1: Two Port Networks:
Characterization of LTI two port networks: ZY, ABCD and h parameters,
reciprocity and symmetry. Inter-relationships between the parameters, inter-
connections of two port networks, Ladder and Lattice networks. T &
Representation.
B2: Transient Analysis:
RL, RC and RLC circuits classical approach.
B3: Network Functions:
Concept of Complex frequency, Transform Impedances, Network functions of
one port and two port networks, properties of driving point immittance and
transfer functions.
14
III
C1: Network Synthesis:
Positive real function; definition, properties of LC, RC and RL driving point
functions, synthesis of LC, RC and RL driving point immittance, functions using
Foster and Cauer first and second forms.
C2: Filters:
Image parameters and characteristics impedance, low pass, highpass, (constant
K type) filters, and introduction to active filters.
14
Text Books:
1 D.Roy Choudhary, Networks and Systems 2
nd
Ed., New Age International (P) Ltd. Publishers.
2 C.L Wadhwa, Network Analysis and Synthesis (Including Linear System Analysis) 3
rd
Ed., New
Age International Publishers.
3 A.Chakrabarti, Network Analysis & Synthesis, Dhanpat Rai & Co.
Reference Books:
4 M.E. Van Valkenburg, An Introduction to Modern Network Synthesis, Wiley Eastern Ltd.
5 Sudhakar, Circuits & Networks: Analysis and Synthesis, TMH Education Pvt. Ltd.
6 K.S. Suresh Kumar, Electric Circuits and Networks Pearson Education.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 28 81 1: : D DI IG GI IT TA AL L E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC CS S L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. Realization of 4-bit even / odd parity checkers using Ex-OR gate.
2. Realization of 4-bit binary decoder/ demultiplexer.
3. Realization of 4-bit / 3-bit multiplexer.
4. Realization of full-adder & full subtractor using logic gates and using Boolean
expression.
5. Realization of decimal to BCD encoder using IC 74147.
6. Realization and implementation of RS, JK, T and D flip-flop using logic gates.
7. Realization and implementation serial in parallel out and parallel in serial out
shift register.
8. Realization and implementation 4-bit binary ripple counter using JK flip-flop.
9. Realization and implementation of 2-bit up/down synchronous counter.
10. Realization and implementation of Arithmetic logic unit.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 28 82 2: : E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC CS S L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. To study application of CRO and function generator.
2. To study application of diode as (a) clipper ckt (b) clamper ckt.
3. To study application of Zener diode as a voltage regulator.
4. To study V-I characteristic of JFET and MOSFET.
5. Realization of BJT as a buffer amplifier.
6. Realization of multistage amplifier using BJT and calculation of current gain
7. Realization of JFET as amplifier and determine various parameters.
8. Realization of MOSFET as a switch.
9. Realization of Op-Amp as integrator & differentiator.
10. Realization of tuned amplifier and its application in Hartley and Collpit oscillator.
11. Realization of Wien Bridge oscillator.
12. Realization of crystal oscillator.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EE EE E 2 28 81 1: : N NE ET TW WO OR RK K L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. Verification of principle of superposition with dc sources.
2. Verification of Thevenin, Norton and Maximum power transfer theorems in ac
circuits.
3. Verification of Tellegins theorem for two networks of the same topology.
4. Determination of transient response of current in RL and RC circuits with step
voltage input.
5. Determination of transient response of current in RLC circuit with step voltage input
for underdamp, critically damp and overdamp cases.
6. Determination of frequency response of current in RLC circuit with sinusoidal ac
input.
7. Determination of z and h parameters (dc only) for a network and computation of Y
and ABCD parameters.
8. Determination of driving point and transfer functions of a two port ladder network
and verify with theoretical values.
9. Determination of frequency response of a Twin T notch filter.
10. To determine attenuation characteristics of a low pass / high pass active filters.
11. Implementation of Pre-emphasis and De-emphasis circuits.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester III
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 20 06 6: : MICROPROCESSORS AND APPLICATIONS
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Microprocessor and Microprocessor Development Systems: Evolution of Microprocessor,
Microprocessor architecture and its operations, memory, inputs-outputs (I/Os), data transfer
schemes interfacing devices, architecture advancements of microprocessors, typical
microprocessor development system.
8-bit Microprocessors
8085 microprocessor: pin configuration, internal architecture. Timing & Signals: control
and status, interrupt: ALU, machine cycles, Instruction Set of 8085, Addressing Modes,
Instruction format, op-codes, mnemonics, no. of bytes, RTL, variants, no. of machine cycles
and T states
Instruction Classification: Data transfer, arithmetic operations, logical operations,
branching operation, machine control; Writing assembly Language programs, Assember
directives.
13
II
16-bit Microprocessors
8086 microprocessor: pin configuration, internal architecture. Timing & Signals: control
and status, interrupt: ALU, machine cycles, Instruction Set of 8086, Addressing Modes,
Instruction format, op-codes, mnemonics, no. of bytes, RTL, variants, no. of machine cycles
and T states
Interrupts: Hardware and software interrupts, responses and types.
13
III
Peripheral Interfacing:
I/O programming: Programmed I/O, Interrupt Driven I/O, DMA I/O interface: serial and
parallel communication, memory I/O mapped I/Os. Peripheral Devices: 8237 DMA
controller, 8255- Programmable peripheral interface, 8253/8254 Programmable
timer/counter. 8259 programmable Interrupt Controller, 8279-keyboard display controller,
ADC/DAC interfacing.
Introduction to Advanced Microprocessors and Microcontrollers.
13
Text Books:
1. Gaonkar, Ramesh S, Microprocessor Architecture, programming and applications with the 8085 Pen ram International
Publishing
5
th Ed.
2. Ray, A.K. & Burchandi, K.M., Advanced Microprocessors and Peripherals: Architecture, Programaming and
Interfacing Tata Mc. Graw Hill.
Reference Books:
3. Uffenbeck, John, Microcomputers and Microprocessors PHI/
3
rd Edition 5. Brey, Barry B. INTEL Microprocessors
Prentice Hall ( India)
4. M. Rafiquzzaman, Microprocessors- Theory and applications PHI
5. B. Ram, Advanced Microprocessor & Interfacing Tata McGraw Hill
6. Renu Singh & B.P. Singh, Microprocessor and Interfacing and applications New Age International
7. Hall D.V., Microprocessors Interfacing Tata Mc Graw Hill
8. Liu and Gibson G.A., Microcomputer Systems: The 8086/8088 Family Prentice Hall (India)
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 20 05 5: : SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIALS AND DEVICES
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
EXCESS CARRIERS IN SEMICONDUCTORS.
Optical Absorption. Luminescence. Photoluminescence. Electroluminescence.
Carrier Lifetime and Photoconductivity. Direct & Indirect Band gap Semiconductor,
Direct & Indirect Recombination, Steady State Carrier Generation, Quasi-Fermi
Levels. Photoconductive Devices. Diffusion & Drift of Carriers. The Continuity
Equation. Steady State Carrier Injection. The Haynes-Shockley Experiment.
Gradients in the Quasi-Fermi Levels.
JUNCTIONS.
Equilibrium Conditions. The Contact Potential. Equilibrium Fermi Levels. Space
Charge at a Junction. Steady State Conditions. Reverse Bias. Reverse-Bias
Breakdown. Transient and A.C. Conditions. Time Variation of Stored Charge. The
Varactor Diode. Effects of Contact Potential on Carrier Injection. Graded Junction.
13
II
Type of Junctions
Metal-Semiconductor Junctions. Schottky Barriers. Rectifying Contacts. Ohmic
Contacts. Typical Schottky Barriers. Heterojunctions.
OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICES.
Photodiodes. Solar Cells. Photodetectors. Light-Emitting Diodes. Light-Emitting
Materials. Multilayer Heterojunctions for LEDs. Lasers. Semiconductor Lasers.
Population Inversion at a Junction. Emission Spectra for p-n Junction Lasers..
Heterojunction Lasers. Materials for Semiconductor Lasers.
HIGH FREQUENCY AND HIGH POWER DEVICES.
Tunnel Diodes: Degenerate Semiconductors. Tunnel diode Operation. Circuit
Applications. Transit Time Devices: The IMPATT Diode. Gunn Effect and
Related Devices: Transferred Electron Mechanism. Formation and Drift of Space
Charge Domains. Fabrication.
13
III
BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS.
Solution of the Diffusion Equation in the Base Region. Charge Control Analysis.
The Switching Cycle. Drift in the Base Region. Base Narrowing. Avalanche
Breakdown. Injection Level; Thermal Effects. Base Resistance and Emitter
Crowding.
Gummel-Poon Model. Kirk Effect. High-Frequency Transistors. Heterojunction
Bipolar Transistors.
FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS
The Metal-Semiconductor FET. The GaAs MESFET. The High Electron Mobility
Transistor (HEMT). Short Channel Effects. The Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor
FET. Basic Operation. The Ideal MOS Capacitor. Threshold Voltage. MOS
Capacitance-Voltage Analysis. Time-dependent Capacitance Measurements.
13
Text Books:
1. Ben.G.Streetman & Sanjan Banerjee Solid State Electronic Devices (5th Edition) PHI Private
Ltd, 2003
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 20 04 4: : SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Signals:
Definition, types of signals and their representations, commonly used
signals (in continuous-time as well as in discrete-time), operations on
continuous-time and discrete-time signals (including transformations of
independent variables).
Systems:
Classification, linearity, time-invariance and causality, impulse response,
characterization of linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, unit sample
response, convolution summation, step response of discrete time systems,
stability.
convolution integral, co-relations, signal energy and energy spectral density,
signal power and power spectral density, properties of power spectral
density.
13
II
Fourier series
Trigonometric & Exponential Fourier Series Analysis, Sampling Theorem,
Nyquist criteria for sampling theorem
Fourier Transforms (FT):
(i) Definition, conditions of existence of FT, properties, magnitude and
phase spectra, Some important FT theorems, Parsevals theorem, Inverse
FT, relation between LT and FT
(ii) Discrete time Fourier transform (DTFT), inverse DTFT, convergence,
properties and theorems, Comparison between continuous time FT and
DTFT
13
III
Laplace-Transform (LT) and Z-transform (ZT):
(i) One-sided LT of some common signals, important theorems and
properties of LT, inverse LT, solutions of differential equations using LT,
Bilateral LT, Regions of convergence (ROC)
(ii) One sided and Bilateral Z-transforms, ZT of some common signals,
ROC, Properties and theorems, solution of difference equations using one-
sided ZT, s- to z-plane mapping
Application of Signals and Systems in MATLAB
13
Text Books:
P. Ramakrishna Rao, `Signal and Systems 2008 Edn., Tata MGH, New Delhi
Reference Books:
1. Chi-Tsong Chen, `Signals and Systems, 3
rd
Edition, Oxford University Press,
2004
2. V. Oppenheim, A.S. Willsky and S. Hamid Nawab, signals & System, PEARSON Education,
Second Edition, 2003.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EE EE E 2 20 02 2: : E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC C M ME EA AS SU UR RE EM ME EN NT TS S A AN ND D I IN NS ST TR RU UM ME EN NT TA AT TI IO ON N
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Theory of Measurement
Introduction, Performance Characteristics: Static & Dynamic, Standards, Error
analysis; Sources, Type and Statistical Analysis
Transducers
Passive transducers : resistive, Inductive and Capacitive.
Bridge : Direct Current and Alternating Current Bridges, LCR bridge.
13
II
Analog Meters
AC analog meters: Average, Peak and RMS responding Voltmeters, Sampling
Voltmeters.
Electronics Analog meters: Electronics Analog DC and AC Voltmeter and
Ammeters, Electronic Analog Ohmmeter and Multimeter.
Digital Meters
Analog to digital converter: Transfer Characteristics, A/D conversion techniques:
Simple Potentiometric & servo method, Successive Approximation, Ramp type,
Integrating & Dual-slop Integrating method.
Digital to Analog Converter: Transfer characteristics, D/A conversion techniques,
Digital mode of operation, performance characteristics of D/A converters.
Specification of Digital meters: display digit & counts resolution, sensitivity,
accuracy, speed & settling time etc.
13
III
Oscilloscopes & RF Measurements
Types of Oscilloscopes, Controls, Measurements of Voltage, Frequency, Time &
Phase, High Frequency Measurements.
Probes: Types of Probes, Probe Loading & Measurement Effect, Probe
Specifications.
Signal Generators & Analyzers
Signal Generators: Sinusoidal, Non-Sinusoidal & Function Generators, Frequency
Synthesis Techniques.
Signal Analyzers: Distortion Wave and Network Spectrum Analyzers.
13
Text Books:
1. Electronic Instruments & Instrumentation Technology by MMS Anand, PHI Pvt.
Ltd.
2. Electronics Instrumentation by H.S. Kalsi TMH.
Reference Books:
1. Electronic & Electrical measurement and Instrumentation by A.K. Sawhney,
Dhanpat Rai publication.
2. Electronics Instrumentation & Measurement Techniques by W.D. cooper & A.D.
Helfrick, PHI 3
rd
Ed.
3. Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation by Oliver & Cage Mc-Graw Hill.
4. Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements by David A. Bell, 2
nd
Ed., PHI
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 28 83 3: : E EL LE EC CT TO OR RN NI IC CS S W WO OR RK KS SH HO OP P & & P PC CB B L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. Introduction to Electronics Workshop & PCB fabrication process.
2. To make a layout diagram/ artwork of Op-Amp based Simple circuit /BJT as a switch
3. To study the process of transferring of Artwork on Cu-cladded sheet i.e. printing.
4. To perform the etching operation of printed cu-cladded sheet.
5. To perform drilling operation of PCB.
6. To study the mounting of component on the PCB and its soldering.
7. Testing of fabricated PCB for its function.
8. To design and winding of step down transformer for given parameters.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 2 28 86 6: : M MI IC CR RO OP PR RO OC CE ES SS SO OR R L LA AB B
List of Experiments
8085/8086 Based Experiments
1. Recursive routine for finding Factorial N.
2. Assembly Language Programs for 8086.
3. Assembly Language Programs for 8086 to address and data transfer.
4. Assembly Language Programs for 8086 to addition, subtraction.
5. Assembly Language Programs for 8086 to block transfer.
6. Assembly Language Programs for 8086 to find greatest numbers.
7. Look up table method for finding the ASCII of an alphanumeric code.
8. Interfacing with 8255 in I/O mode/BSR mode to 8085/8086 based system.
9. Interfacing with 8253 to 8085/8086 based system.
10. To 8085/8086 based system verification of Interrupts.
11. Interfacing with ADC/DAC to 8085/8086 based system.
12. Serial communication between two kits through RS-232C using 8251.
13. Signed Multiplication using Booth's Algorithm.
14. To perform microprocessor based stepper motor operation through 8085 kit.
15. Mini Project on some interfacing applications.
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EE EE E 2 28 82 2: : E EL LE EC CT TR RO ON NI IC C M ME EA AS SU UR RE EM ME EN NT T& & I IN NS ST TR RU UM ME EN NT TA AT TI IO ON N L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. Study of semiconductor diode voltmeter and its use as DC average responding AC voltmeter.
2. Measurement of low resistance by Kelvins double bridge.
3. Measurement of inductance by Maxwells bridge.
4. Measurement of inductance by Hays bridge.
5. Measurement of capacitance by De Sautys bridge.
6. Study of distortion factor meter and determination of the % distortion of the given oscillator.
7. Study of the transistor tester and determination of the parameters of the given transistors.
8. Study of the following transducer (i) PT-100 (ii) J-type (iii) K-type (iv) Pressure.
9. Measurement of phase difference and frequency using CRO (lissajous figure).
10. Radio Receiver Measurements.
11. Calibration of single-phase energymeter with the help of standard wattmeter.
`
Credits: 01 LTP: 002 Semester IV
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 02 2: : L LI IN NE EA AR R I IN NT TE EG GR RA AT TE ED D C CI IR RC CU UI IT TS S
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Circuit Mirror Circuits : Current Mirrors using BJT and MOSFETs, Simple
current Mirror, Base Current compensated current Mirror, Wilson and
Improved Wilson Current Mirrors, Widlar Current source and Cascode current
Mirror.
Operational Amplifier : Basic Information of Op-Amp, The ideal Operational
Amplifier, Operational Amplifier Internal Circuit, FET Operational Amplifier
Operational Amplifier Characteristics and Applications : DC and AC
Characteristics, Instrumentation Amplifier, V to I and I to V converter, Op-Amp
Circuits using diodes, Sample and Hold Circuit, Log and Antilog Amplifier,
Multiplier and Divider, Differentiator, Integrator, Electronic Analog
Computation.
13
II
Comparators and Waveform Generators : Comparator, Regenerative
Comparator (Schmitt Trigger), Square Wave Generator (Astable Multivibrator),
Monostable Multivibrator, Triangular Wave Generator, Basic Principle of Sine
Wave Oscillators.
Voltage Regulator : Series Op-Amp Regulator, IC Voltage Regulators, 723
General Purpose Regulator, Switching Regulator.
Active Filters : First and Second order LP, HP, BP, BS and All pass active
Filters, State Variable Filter, Switched Capacitor Filters.
14
III
555 Timer : Description of Functional Diagram, Monostable Operation, Astable
Operation, Schmitt Trigger
Phase-Locked Loop : Basic Principles, Phase Detector/Comparator, Voltage
Controlled Oscillator (VCO), Low Pass Filter, Monolithic Phase-Locked Loop,
PLL Applications
D-A and A-D Converters : Basic DAC Techniques, A-D Converters, DAC/ADC
Specifications
13
References :
1. D. Roy Choudhury, Shail B. Jain Linear Integrated Circuits, 4
th
Edition, New Age
International Publishers.
2. Ramakant A. Gayakwad, Op-Amps & Linear Integrated Circuits, 3
rd
Edition, PHI.
3. Sedra and Smith, Microelectronics Circuits 4
th
Edition, Oxford University Press.
4. Michal Jacob, Applications and Design with Analog Integrated Circuits, 2
nd
Edition, PHI 2006
5. Jacob Milliman and Arvin Grabel, Microelectronics, 2
nd
Edition, TMH, 2008.
Semester - V LTP: 310 Credits: 04
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 01 1 : : C CO OM MM MU UN NI IC CA AT TI IO ON N E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Amplitude Modulation
Frequency translation, amplitude modulation, double side band suppressed
carrier (DSB-SC) modulation, double side band with carrier (DSB-C), single-
sideband modulation (SSB), vestigial-sideband modulation.
Angle -Modulation
Angle modulation, phase and frequency modulation, tone modulated FM signal,
arbitrary modulated FM signal, FM modulators and demodulators, radio
transmitter and receiver.
14
II
Noise in Communication Systems
Sources of noise, frequency-domain representation of noise, superposition of
noises, linear filtering of noise, quadrature components of noise, representation of
noise using orthonormal coordinates, single-sideband suppressed carrier, double-
sideband suppressed carrier, double sideband with carrier, FM receiving system,
calculation of signal to noise ratio, comparison of FM and AM, preemphasis and
deemphasis, noise in phase modulation, threshold in frequency modulation.
14
III
Pulse Modulation and Digital Transmission of Analog Signal
Analog to digital : noisy channel and role of repeater, pulse amplitude modulation
and concept of time division multiplexing, pulse width modulation and pulse
position modulation, digital representation of analog signal, differential pulse code
modulation and delta modulation, noise in PCM transmission, noise in delta
modulation transmission.
12
References :
1. Principles of Communication Systems,Third Edition by Herbert Taub, Donald L Schilling, Goutam
Saha, TMH.
2. B.P. Lathi and Zhi Ding, Modern Digital and Analog Communication systems, International fourth
edition, Oxford University Press.
3. S. Haykins, Communication Systems, 5th ed., John wiley.
Semester - V LTP: 310 Credits: 04
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 04 4 : : C CO ON NT TR RO OL L S SY YS ST TE EM M
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction to control system: Industrial Control examples. Transfer function
models of mechanical, electrical system. Control hardware and their models:
potentiometers, synchros, dc and ac servomotors, tachogenerators, Closed-loop
systems. Block diagram and signal flow graph analysis, transfer function.
State-space model:Concepts of state, state variable, state model, state models for
linear continuous time functions, diagonalization of transfer function, solution of
state equations, concept of controllability & observability.
15
II
Time domain Analysis of Control Systems: Time response of continuous
datasystems, typical test signals for the time response of control systems, the unit
step response and time-domain specifications, Steady-State error and error
constants time response of a first order system, transient response of a prototype
second order system. Basic modes of feedback control: proportional, integral and
derivative.
Stability in time domain:stability concept, relative stability, Routh stability
criterion. Concept of Root locus technique. Root locus method of design.
14
III
Frequency domain analysis:Relationship between time & frequency
response,Performance specifications in frequency-domain. Polar plots, Bodes plot,
stability in frequency domain, Nyquist plots. Nyquist stability criterion. Frequency-
domain methods of design, Compensation & their realization in time & frequency
domain. Lead and Lag compensation.
12
References :
1 B.C. Kuo & Farid Golnaraghi, Automatic Control Systems, 8th Edition, John Wiley India, 2008.
2 I. J. Nagrath & M. Gopal, Control System Engineering, New Age International Publishers
3 William A. Wolovich, Automatic Control Systems, Oxford University Press, 2010.
4 Joseph J. Distefano III, Allen R. Stubberud, Ivan J. Williams, Control Systems Schaums Outlines
Series, 3
rd
Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, Special Indian Edition 2010.
Semester - V LTP: 310 Credits: 04
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 03 3 : : A AN NT TE EN NN NA A & & W WA AV VE E P PR RO OP PA AG GA AT TI IO ON N
Module
No.
Content
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction: Basic Antenna parameters: Patterns, Beam Area ( Beam solid angle),
Radiation Intensity, Beam efficiency, Directivity & Gain, Directivity & Resolution,
Antenna Apertures, Effective height, Radio Communication link , Retarded
Potential, Power Radiation by small Current element.
Antenna Arrays: Introduction. Arrays of two isotropic point sources, Non isotropic
but similar point sources, Principle of pattern multiplication, Linear arrays of n
isotropic point sources of equal amplitude and spacing, Linear broadside arrays
with non uniform Amplitude distributions: General consideration, Example of
Dolph-Tchebyscheff(D-T) distribution for an array of eight sources
13
II
Horizontal Antennas above plane ground, Vertical Antenna above plane ground,
Folded dipole antenna, Yagi-Uda antenna, The small loop, comparison of Far fields
of small loop and short dipole, Radiation resistance of loops, slot antenna,
Babinets principle of complementary antennas, Impedance of slot antenna, Patch
or micro-strip antennas, Horn Antennas, the rectangular Horn antenna, Helical
Antenna, Reflector antennas: Flat sheet reflector, corner reflector and design,
Paraboloid Reflector, Comparison between parabolic and corner reflector,
Broadband and frequency independent antenna: Basics, log periodic Antenna
Balun, Balun Types I, II and III and choke baluns, matching stubs.
14
III
Antenna Measurements: Gain, Directional pattern, Phase, polarization
Wave propagation: Electromagnetic or radio waves, modes of propagation,
Structure of atmosphere, Ground waves or surface wave propagation, Ground
wave attenuation factor A, Sky wave or ionosphere wave propagation, space wave
propagation , Propagation of radio waves through ionosphere or expression for the
refractive index of the ionosphere, Mechanism of radio waves bending by the
ionosphere, critical frequency, virtual height, maximum usable frequency,
calculation of MUF, LUF, skip distance, range of space wave propagation or Line of
sight, effective earth radius, Duct propagation
13
References :
1. Antenna for all Applications 3rd edition Krauss, Marhefka & Ahmed S khan, TMH publication.
2. Antenna & Wave Propagation by K.D. Prasad, Satya Publication
Semester - V LTP: 310 Credits: 04
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 82 2: : I IN NT TE EG GR RA AT TE ED D C CI IR RC CU UI IT T L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. To verify characteristics of op-Amp. 741, 381 and TL 084.
2. Realization of compartor and zero crossing detector using op-Amp.
3. Realization of 2
nd
order active low pass and high pass filter.
4. Realization of Astable and Monostable multivibrator using IC 555.
5. Realization of voltage controlled oscillator using IC 8038/2206.
6. Realization of triangular and sine wave generator using op-Amp.
7. Realization of adder and subtractor using op-Amp.
8. Realization of CMOS and TTL inverter to obtain transfer characteristics.
9. Realization of V to I and I to V convertor.
10. Realization of voltage regulator using IC 723.
11. Realization of Inverting and non inverting amplifier using op-Amp.
12. To study PLL and analyze the locking and capturing frequency range.
Semester V LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 81 1: : C CO OM MM MU UN NI IC CA AT TI IO ON N L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. Realization of amplitude modulation using transistors and find modulation Index.
2. Realization of Linear envelop detector for demodulation of AM ware and observe diagonal
peak clipping effect.
3. Realization of frequency modulation and determine its modulation index.
4. To study demodulation of FM wave.
5. To study Pulse amplitude modulation and realize on bread board using discrete components.
6. To study Pulse width modulation and realize on bread board using discrete components.
7. To study transmission line and measure its characteristics impedance.
8. To study Yagi-Uda, antenna. Plot radiation pattern and find beam width.
9. To study parabolic antenna. Plot radiation pattern and find beam width.
10. To study super heterodyne receiver and to analyze selectivity, sensitivity and fidelity of
analog communication system.
11. To realize FM system using VCO and PLL.
Semester V LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 83 3: : C CO ON NT TR RO OL L S SY YS ST TE EM M L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. DC SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
(a) To study D.C. speed control system on open loop and close loop.
(b) To study of Transient performance, another time signal is added at the input of control Circuit.
(c) To study how eddy current breaking is being disturbance rejected by close and open loop.
2. DC MOTOR POSITION CONTROL
(a) To study of potentiometer displacement constant on D.C. motor position control.
(b) To study of D. C. position control through continuous command.
(c) To study of D.C. position control through step command.
(d) To study of D.C. position control through Dynamic response.
3. AC MOTOR POSITION CONTROL
(a) To study of A.C. motor position control through continuous command.
(b) To study of error detector on A.C. motor position control through step command.
(c) To study of A.C. position control through dynamic response.
4. AC SERVOMOTOR
(a) To study speed-torque characteristic of an AC Servomotor.
5. SYNCHRO TRANSMITTER / RECEIVER
(a) To study of Synchro Transmitter in term of Position v/s Phase and voltage magnitude with respect to
Rotor Voltage Magnitude/Phase.
(b) To study of remote position indication system using Synchro-transmitter/receiver.
6. PID CONTROLLER
(a) To observe open loop performance of building block and calibration of PID Controls.
(b) To study P, PI and PID controller with type 0 system with delay.
(c) To study P, PI and PID controller with type 1 system.
7. LEAD LAG COMPENSATOR
(a) To study the open loop response on compensator.
(b) Close loop transient response.
8. LINEAR SYSTEM SIMULATOR
(a) Open loop response (i) Time constant, (iii) Integrator
(b) Close loop system (I) First order system (II) Second order system
9. Introduction to MATLAB (Control System Toolbox), Implement at least two experiment in
MATLAB.
a. Different Toolboxes in MATLAB, Introduction to Control Systems Toolbox.
b. Determine transpose, inverse values of given matrix.
c. Plot the pole-zero configuration in s-plane for the given transfer function.
d. Determine the transfer function for given closed loop system in block diagram representation.
e. Plot unit step response of given transfer function and find peak overshoot, peak time.
f. Plot unit step response and to find rise time and delay time.
g. Plot locus of given transfer function, locate closed loop poles for different values of k.
h. Plot root locus of given transfer function and to find out S, Wd, Wn at given root & to discuss stability.
i. Plot bode plot of given transfer function.
j. Plot bode plot of given transfer function and find gain and phase margins
k. Plot Nyquist plot for given transfer function and to compare their relative stability
l. Plot the Nyquist plot for given transfer function and to discuss closed loop stability, gain and phase
margin.
Semester V LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CS SE E 3 38 89 9: : A AD DV VA AN NC CE ED D P PR RO OG GR RA AM MM MI IN NG G L LA AB B
List of Experiments
C- Program
Q1. Write a C Program to check primality of a number using:
(I)Recursion (II)Without Recursion
Q2. Write a C Program without using semicolon to output Hello.
Q3. Write a Crogram to swap two numbers without using third variable.
Q4. Write a program to generate the Fibonacci series up to user specified limit using
recursive function
Q5. Write a program to generate the following pattern.
INDIAIDNI
INDI IDNI
IND DNI
IN NI
I I
Q6. Write a program to find whether a given string is palindrome or not
Q7. Write a program which removes all the white spaces and new line character from a
file.
Q8.Write a program to find a given word in a file if it exist and also show the location of
that word in a file.
C++ Program
Q9. Define the structure called student having properties like stud_id, stud_name,
stud_branch, and email_add. Write a program which takes the details of 5 student and
write the details to one file having name Stud_Records.txt.
Q10. Write a program which takes two n*n matrices where n will be specified by the
user. Write a method which does summation of both matrices and store the result in
third matrix also display the resultant matrix.
Q11. Write a program which takes two integer n1 and n2 from user where n1<n2.
Create functions that calculate the sum of all the integers ranging from n1 and n2, sum
of all the odd numbers ranging from n1 and n2, sum of all the even numbers ranging
from n1 and n2. Display an error message if n1>n2.
Q12. Create a structure called Employee having member fields like name, gender and
salary. Write a program that accepts the details of employees. Display the employee
details who has highest salary. Display all employees in sorted order according to their
name
Q13. Create a structure ComplexNumber having real and imaginary part as properties.
Write functions to add and subtract two complex numbers. Call them from the main
program.
Q14. Write a program to remove all the comments ( single line and multiple line ) from a
C program file.
Semester V LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 05 5: : D DI IG GI IT TA AL L C CO OM MM MU UN NI IC CA AT TI IO ON N
Module
No.
Contents
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction:
Digital communication system (description of different modules of the block
diagram), Complex baseband representation of signals, Gram-Schmidt
orthogonalization procedure, bi-orthogonal signals, simplex signal waveforms.
Pulse shape design for channels with ISI: Nyquist pulse, Partial response
signaling (duobinary and modified duobinary pulses).
Concept of Probability:
Random variable, Statistical averages, Correlation, Some important
distribution functions & their statistical properties, Sum of random variables,
Central limit theorem, Random process, Classification of Random Processes,
Power spectral density, Multiple random processes.
15
II
Modulation:
Pulse amplitude modulation (binary and M-ary, QAM), Pulse position
modulation (binary and M-ary), Carrier modulation (M-ary ASK, PSK, FSK,
DPSK), Continuous phase modulation (QPSK and variants, MSK, GMSK).
Receiver in additive white Gaussian noise channels:
Coherent and noncoherent demodulation: Matched filter, Correlator
demodulator, square-law, and envelope detector, Bit-error-rate, symbol error
rate for coherent and noncoherent schemes.
14
III
Information Theory and Coding:
Measure of information, Source encoding, Error free communication over a
noisy channel , Channel capacity of discrete and continuous memory less
channel
Error Correcting codes: Hamming sphere, Hamming distance and Hamming
bound, Relation between minimum distance and error detecting and correcting
capability, Linear block codes, Encoding & syndrome decoding, Cyclic codes,
Systematic cycle codes,convolution codes, code tree & Trellis diagram,
Viterbi and sequential decoding, burst error correction, Turbo codes.
12
References:
1. B.P. Lathi & Zhi Ding, Modern Digital and Analog Communication System, 4
th
editin,
Oxford University Press,2010.
2. J. G. Proakis and M. Salehi, Fundamentals of Communication Systems,
Pearson Education, 2005.
3. S. Haykins, Communication Systems, 5th ed., John wiley, 2008.
4. M. K. Simon, S. M. Hinedi and W. C. Lindsey, Digital Communication Techniques:
Signaling and detection, Prentice Hall India, N. Delhi, 1995.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester VI
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 06 6: : M MI IC CR RO OW WA AV VE E E EN NG GI IN NE EE ER RI IN NG G
Module
No.
Contents
Teaching
Hours
I
Rectangular Wave Guide: Propagation of waves, Field distribution of TE,
TM Modes, Dominant and degenerate modes, Phase & group velocities, Wave
impedances, Power transmission, Power losses in waveguide.
Circular Waveguides: TE & TM modes, Cut-off frequencies and guide
wavelength.
Cavity Resonators- Rectangular & circular cavities, coupling to Cavities,
Quality factors of cavities.
Introduction to Striplines, Microstrip lines and MMICs.
14
II
Microwave Components: Scattering matrix, Microwave T-Junctions: E-
plane, H-plane and Hybrid Tees, Rat-Race junction, Directional couplers.
Attenuators, Phase shifters, Microwave bends, corners and Twists, Irises.
Microwave propagation in ferrites, Faraday rotation, Isolators, Circulators.
Solid State Microwave Devices: PIN diode, Schottky barrier diode, Tunnel
diode, Transferred electron devices (Gunn diode), Avalanche Transit time
devices: IMPATT Diode, TRAPATT Diode.
14
III
Microwave Tubes: Limitation of conventional active devices at microwave
frequency, Two cavity klystron, Reflex klystron, Magnetron, Traveling wave
tube, Backward wave oscillators: Principle of operation, Performance
characteristic and their applications.
Microwave Measurements: General set up of a microwave test bench,
Slotted line carriage, VSWR meter, Microwave power measurements
techniques, Measurement of frequency and wavelength, Impedance and losses.
Measurement of S-parameters
14
References:
1. Samuel Y. Liao, Microwave Devices and Circuits, 3rd Ed, Pearson Education.
2. A. Das and S. K. Das, Microwave Engineering, 2
nd
Edition,TMH.
3. R.E Collin, Foundation for Microwave Engineering , 2nd Ed., John Wiley India.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester VI
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 30 07 7: : V VL LS SI I T TE EC CH HN NO OL LO OG GY Y & & D DE ES SI IG GN N
Module
No.
Contents
Teaching
Hours
I
Crystal Growth and Wafer Preparation: Introduction, Electronic-Grade
Silicon, Czochralski Growing, Silicon shaping.
MOSFET Fabrication: Overview of VLSI Design Methodologies, VLSI
Design Flow, Design Hierarchy, Concepts of Regularity, Modularity and
Locality, Fabrication process flow, NMOS and CMOS- n-well, P-well, twin
tub.
13
II
MOS Transistor : MOS Structure, Operation of MOSFET, MOSFET -
Current /Voltage Characteristics, Scaling and Small geometry effects and
capacitances
MOS Inverters: Introduction, Resistive Load Inverter, Inverters with n-type
MOSFET load-Depletion load inverter, Enhancement load, CMOS Inverter.
14
III
MOS Inverters - Switching Characteristics: Introduction, Delay Time
Definitions, Calculation of Delay Times
Combinational MOS Logic Circuits: Introduction, MOS logic circuits with
depletion NMOS Loads, CMOS logic circuits, complex logic circuits, CMOS
transmission gates (pass gates)
Layout design rules, stick diagram and mask layout design.
Dynamic logic circuits: Introduction, basic principle of pass transistor
circuits, synchronous dynamic circuit techniques, dynamic CMOS circuit
techniques, Domino CMOS logic.
12
References:
1. Sung-Mo Kang & Yosuf Leblebici, CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits: Analysis & Design,
TMH, 3rd Edition.
2. D. A. Pucknell and K. Eshraghian, Basic VLSI Design: Systems and Circuits, PHI, 3rd Ed.,
1994.
3. W.Wolf, Modern VLSI Design: System on Chip, Third Edition, Pearson, 2002.
4. S.M.Sze, VLSI Technology , Tata McGraw-Hill, Second Edition -2003.
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester VI
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
C CS SE E 3 37 71 1: : C CO OM MP PU UT TE ER R A AR RC CH HI IT TE EC CT TU UR RE E A AN ND D A AP PP PL LI IC CA AT TI IO ON N
Module
No.
Contents
Teaching
Hours
I
Introduction to Design Methodology: System design, System
representation, Design process, Gate level components, Register level
components and PLD (revision), Register level design.
The Processor Level: Processor level components, Processor level design.
13
II
Processor basics: CPU fundamental organization, Additional features, Data
representation, Basic formats, Fixed point numbers, Floating point numbers.
Instruction sets formats, Types, Programming considerations
Data path Design: Fixed point arithmetic addition and subtraction,
Multiplication and division, Floating point arithmetic,
Pipelining: Introduction, Pipeline control, Instruction pipelines, Pipeline
performance.
14
III
Control Design: Basic introductory concepts, Hardwired control, Micro
programmed control introduction, Multiplier control unit, CPU control unit,
Memory organization: Multi level memories, Address translation, Memory
allocation, Caches Main features, Address mapping, structure vs.
performance,
System Organization: Basic communication methods, Bus control and
design.
12
References:
John P Hayes Computer Architecture and Organization McGraw Hill 3rd Edition.
M.J. Quinn, M Morris Mano, Computer System Architecture PHI 3rd Edition
Credits: 04 LTP: 310 Semester VI
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 84 4: : D DI IG GI IT TA AL L C CO OM MM MU UN NI IC CA AT TI IO ON N L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. To study and realization of sample & hold circuit.
2. To study and realization of pulse code modulator and demodulator.
3. To study coding and decoding of NRZ-L, NRZ-M data format.
4. To study coding and decoding of AMI, Manchaster data format.
5. To study and realization of ASK modulator and demodulator.
6. To study and realization of FSK modulator and demodulator.
7. To study and realization of PSK modulator and demodulator.
8. To study and realization of Hamming error detection and correction codes.
9. Simulation of digital communication transmitter.
10. Simulation of digital communication receiver.
Semester VI LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 85 5: : S SI IM MU UL LA AT TI IO ON N L LA AB B
BASED ON PSPICE
1 Perform DC analysis for a given circuit with and without dependent sources.
2 Perform transient analysis for a given circuit with step and pulse input.
3 Perform AC analysis for a given circuit.
4 Draw the forward and reverse bias characteristic curves of PN Junction diode.
5 Draw the input and output characteristic of BJT transistor in common-emitter configuration.
6 Plot the voltage transfer characteristics of BJT inverter and perform transient analysis with step
and pulse input with and without parameters.
7 (a) Transient analysis of NMOS inverter using step and pulse input.
(b) DC analysis (voltage transfer characteristics) of NMOS inverter with and without parameters.
8 (a) Transient analysis of CMOS inverter using step and pulse input with and without parameters.
(b) DC analysis (voltage transfer characteristics) of CMOS inverter with and without parameters.
9 Transient & DC Analysis of CMOS-NOR Gate.
10 Transient & DC Analysis of CMOS-NAND Gate.
Semester VI LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 86 6: : M MI IC CR RO OW WA AV VE E L LA AB B
List of Experiments
1. To study microwave test bench and its components.
2. To study reflex klystron working and determine mode numbers.
3. To study coupling directional coupler and determine its coefficient.
4. To study magic tee and determine its coupling coefficient.
5. To study ferrite circulator and determine its coupling coefficient.
6. To measure VSWR and frequency using slotted line.
7. To study frequency measurement using cavity resonator.
8. To study radiation pattern of Horn antenna and find its beam width.
9. To study characteristics of E-plane and H-plane Tee.
10. To study V-I characteristics of Gunn Diode.
11. To study microstrip technique and realization of various microwave components.
Semester VI LTP: 002 Credits: 01
B.Tech. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) (w.e.f. Session-2012-13)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, Institute of Engineering & Technology
E EC CE E 3 38 87 7: : C CA AD D L LA AB B
List of Experiments
VHDL based Experiments-
Synthesis and simulation of Full Adder.
Synthesis and Simulation of Full Subtractor.
Synthesis and Simulation of 3 X 8 Decoder.
Synthesis and Simulation of 8 X 1 Multiplexer.
Synthesis and simulation of priority encoder.
Synthesis and simulation of 2 bit comparator.
Synthesis and Simulation of 9 bit odd parity generator.
Synthesis and Simulation of Flip Flop (D, and T).
Synthesis and simulation of MOD 10 counter.
Synthesis and simulation of Johnson counter.
Semester VI LTP: 002 Credits: 01
You might also like
- Electronics and Computer Science EngineeringDocument147 pagesElectronics and Computer Science EngineeringAniket ShuklaNo ratings yet
- B767 ATA 24 Student BookDocument73 pagesB767 ATA 24 Student BookElijah Paul Merto100% (6)
- Circuit BreakerDocument12 pagesCircuit BreakerHarshalPanchal100% (1)
- Tabela Com Codigos e Caracteristicas de Capacitores de TantaloDocument51 pagesTabela Com Codigos e Caracteristicas de Capacitores de TantaloArialdo FurlaniNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics SyllabusDocument77 pagesMechatronics SyllabussivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- Probability and Random Processes: With Applications to Signal Processing and CommunicationsFrom EverandProbability and Random Processes: With Applications to Signal Processing and CommunicationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsFrom EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsNo ratings yet
- TR-UP - X-Band REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE OF MAGNETRON PDFDocument8 pagesTR-UP - X-Band REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE OF MAGNETRON PDF2by2 BlueNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Instrumentation EngineeringDocument137 pagesElectronics & Instrumentation EngineeringCooldude69No ratings yet
- B.tech Ece Syllabus 2008-09Document102 pagesB.tech Ece Syllabus 2008-09hetkar12345No ratings yet
- Autonomous SylabusDocument190 pagesAutonomous Sylabussatheesh sNo ratings yet
- CourseStrucSyllabi 5yrDualWCN2012Document86 pagesCourseStrucSyllabi 5yrDualWCN2012surabhidivyaNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Telecommunication EngineeringDocument136 pagesElectronics & Telecommunication Engineeringneelguitar13No ratings yet
- Anna Univ Reg-2008-SyllabusDocument118 pagesAnna Univ Reg-2008-SyllabusAnsi_Matt13No ratings yet
- ABET SRM University SyllabusDocument102 pagesABET SRM University SyllabusMohammed RahmathullahNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Eng 07 08 EtDocument86 pagesMechatronics Eng 07 08 EtVenu Madhav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Syl LB Tech Ece 040811Document117 pagesSyl LB Tech Ece 040811Mansi JhambNo ratings yet
- EE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 10.01.14Document67 pagesEE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 10.01.14smrahimNo ratings yet
- 2018 2022 Computer Science EngeeringDocument125 pages2018 2022 Computer Science EngeeringDaksh DevanshNo ratings yet
- Ice Btech FT Syllabus r2007Document92 pagesIce Btech FT Syllabus r2007Aishu1385No ratings yet
- VR17 Ugeee 19-1-2021Document183 pagesVR17 Ugeee 19-1-2021Ravindra VankinaNo ratings yet
- ECE Curriculum EssentialDocument105 pagesECE Curriculum EssentialAkashdeep BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Annexure C-Final Document For BOS With Revised CLOs - by CRC - 21-09-2021 (1) - Rev-2Document61 pagesAnnexure C-Final Document For BOS With Revised CLOs - by CRC - 21-09-2021 (1) - Rev-2Usman ZahidNo ratings yet
- B.Tech EEEE AY 2019 2020Document170 pagesB.Tech EEEE AY 2019 2020دليكى مردووNo ratings yet
- Syllabus B.techDocument34 pagesSyllabus B.techdharmpalbangarwaNo ratings yet
- Srmuniv - Ac.in Sites Default Files Files Btech Syll Elec-Instru r2013-14Document176 pagesSrmuniv - Ac.in Sites Default Files Files Btech Syll Elec-Instru r2013-14GaacksonNo ratings yet
- M.tech .Electronics071011Document49 pagesM.tech .Electronics071011John WilliamNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Electronics and Communication Engineering: CreditsDocument4 pagesB.Tech Electronics and Communication Engineering: CreditsNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- EE Final Upto 3rd Year Syllabus 13.07.12Document32 pagesEE Final Upto 3rd Year Syllabus 13.07.12Ishtiaque AnwarNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Computer Engineering: Curriculum & ProgramsDocument6 pagesElectrical and Computer Engineering: Curriculum & ProgramsEric XiaoNo ratings yet
- BEC Curriculum Syllabus 2017-18 2018-19 24-06-2020 NewDocument169 pagesBEC Curriculum Syllabus 2017-18 2018-19 24-06-2020 NewswethaNo ratings yet
- BEC Curriculum Syllabus 2019-20 24-06-2020 NewDocument178 pagesBEC Curriculum Syllabus 2019-20 24-06-2020 NewadityavarmanNo ratings yet
- Beng (Hons) Electrical and Electronic Engineering - E430: Modules CreditsDocument9 pagesBeng (Hons) Electrical and Electronic Engineering - E430: Modules CreditsSalinee BookauramNo ratings yet
- Ece SyllabusDocument24 pagesEce SyllabusKishore GurramNo ratings yet
- Ice PDFDocument112 pagesIce PDFAnirudhan GuruNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communication Engineering Old Syllabus 2Document82 pagesElectronics & Communication Engineering Old Syllabus 2Tashi DendupNo ratings yet
- Ece New SyllabusDocument113 pagesEce New SyllabusRajesh SuwalkaNo ratings yet
- Vit Syllabaus EceDocument101 pagesVit Syllabaus EcePranavateja ChilukuriNo ratings yet
- Ece Syllabus HptuDocument135 pagesEce Syllabus HptuSumit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Syllabusbtechec1 PDFDocument107 pagesSyllabusbtechec1 PDFAmol AmollNo ratings yet
- Auto Ii To ViiiDocument97 pagesAuto Ii To ViiiDhileepan KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- ECE SyllabusDocument144 pagesECE SyllabusVenkata Ganesh GorlaNo ratings yet
- Courses For B. Tech. in Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument38 pagesCourses For B. Tech. in Electronics & Communication EngineeringDinesh ShawNo ratings yet
- Ic3 8Document62 pagesIc3 8Akshay TanotraNo ratings yet
- Mca Lab-Ece-3014-Manual - Ay 2022-23Document49 pagesMca Lab-Ece-3014-Manual - Ay 2022-23bushraarhaan02No ratings yet
- B.Tech Syllabus Wef 2012-13 Admitted Batch PDFDocument159 pagesB.Tech Syllabus Wef 2012-13 Admitted Batch PDFgggtttggg5519No ratings yet
- EE Curriculum SheetDocument2 pagesEE Curriculum SheetEmilie OlssonNo ratings yet
- 6th Mech - BakDocument23 pages6th Mech - Bakshiva shakthyNo ratings yet
- B (1) .Tech Detailed SyllabiDocument159 pagesB (1) .Tech Detailed SyllabiJynt RjNo ratings yet
- Automobile Eng 07 08 EtDocument95 pagesAutomobile Eng 07 08 EtNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ISUTDocument114 pagesSyllabus ISUTWaniBazillaNo ratings yet
- Btech Electronics and Communication Engineering Curriculum SyllabusDocument167 pagesBtech Electronics and Communication Engineering Curriculum SyllabusHimavanthRavindranNo ratings yet
- Be Electronics & CommunicationsDocument120 pagesBe Electronics & CommunicationsMahesh PremaniNo ratings yet
- A Constituent College of Siddhartha Academy of Higher Education, TumakuruDocument42 pagesA Constituent College of Siddhartha Academy of Higher Education, TumakuruRoyal ClashNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Delhi (Nit Delhi) : Scheme of Instruction and SyllabiDocument22 pagesNational Institute of Technology Delhi (Nit Delhi) : Scheme of Instruction and SyllabiBoom BoomNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mechanical Eng - MEDocument20 pages1 - Mechanical Eng - MEakashkbofficialNo ratings yet
- Btech Ece 2012 PDFDocument58 pagesBtech Ece 2012 PDFpriya meenaNo ratings yet
- B.tech Apjktu (2019 Scheme)Document21 pagesB.tech Apjktu (2019 Scheme)Amarnath RajeshNo ratings yet
- Elex SyllabusDocument148 pagesElex SyllabusJitendra Vernekar100% (1)
- Reliability Investigation of LED Devices for Public Light ApplicationsFrom EverandReliability Investigation of LED Devices for Public Light ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Using Artificial Neural Networks for Analog Integrated Circuit Design AutomationFrom EverandUsing Artificial Neural Networks for Analog Integrated Circuit Design AutomationNo ratings yet
- Stretchable ElectronicsFrom EverandStretchable ElectronicsTakao SomeyaNo ratings yet
- TPS54531 5-A, 28-V Input, Step-Down SWIFT™ DC-DC Converter With Eco-Mode™Document33 pagesTPS54531 5-A, 28-V Input, Step-Down SWIFT™ DC-DC Converter With Eco-Mode™hajaNo ratings yet
- Transient Circuit McqsDocument5 pagesTransient Circuit McqsKrupali SurveNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Smart-UPS On-Line SRT Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument37 pagesOperation Manual: Smart-UPS On-Line SRT Uninterruptible Power SupplyKudzaishe MutambaneshiriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ECEDocument3 pagesLesson Plan ECEVenkatesan SwamyNo ratings yet
- Principles of DC MotorsDocument14 pagesPrinciples of DC MotorsAravind Raj PandianNo ratings yet
- EDCh 4 RF IfDocument3 pagesEDCh 4 RF IfsmileyNo ratings yet
- A LED Dice Using A PIC 16F84Document14 pagesA LED Dice Using A PIC 16F84Daryl Jayson ManaloNo ratings yet
- A Finite Difference Numerical Analysis of Galvanic Corrosion For Semi-InfiniteDocument7 pagesA Finite Difference Numerical Analysis of Galvanic Corrosion For Semi-InfiniteThiagoCarvalhoNo ratings yet
- HighvoltageDocument15 pagesHighvoltageCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 1666Document52 pagesGrundfosliterature 1666Ahmed RamadanNo ratings yet
- IEEE Standard For Transient Overvoltage Protection of DC Electrification Systems by Application of DC Surge ArrestersDocument15 pagesIEEE Standard For Transient Overvoltage Protection of DC Electrification Systems by Application of DC Surge ArrestersAbhijeet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- ZOV Series - High Energy Varistors: DescriptionDocument4 pagesZOV Series - High Energy Varistors: DescriptionIgor PNo ratings yet
- EP FA EL 02 ST - Standard - For - Voltage - LevelDocument15 pagesEP FA EL 02 ST - Standard - For - Voltage - Levelmarin cristianNo ratings yet
- Idea ΔΙΑΚΟΠΤΕΣDocument28 pagesIdea ΔΙΑΚΟΠΤΕΣΙΩΑΝΝΗΣ ΔΟΜΙΝΙΚΟΣNo ratings yet
- UDR MANUFACTURE ManufacturesDocument8 pagesUDR MANUFACTURE ManufacturesQuadri Consultancy ServicesNo ratings yet
- Technical Data - HVR International - Resistors For Compact CircuitryDocument2 pagesTechnical Data - HVR International - Resistors For Compact CircuitryNuma LumaNo ratings yet
- Sintecs Signal Integrity and High Speed Methodology TrainingDocument4 pagesSintecs Signal Integrity and High Speed Methodology TrainingmmasoumianNo ratings yet
- CT Ortea 2019 S07 DVS 2enDocument84 pagesCT Ortea 2019 S07 DVS 2enCLAUDE BIRIKUNZIRANo ratings yet
- The Fluorescent Lighting System BY - Frank DurdaDocument97 pagesThe Fluorescent Lighting System BY - Frank Durdawas00266No ratings yet
- Uset 18 Physical Science PaperDocument16 pagesUset 18 Physical Science PaperAayushi VermaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Dr-Id-300 - 23Document1 pageService Manual Dr-Id-300 - 23bilal aloulouNo ratings yet
- Lpt60 Series Power SupplyDocument3 pagesLpt60 Series Power SupplyJairo ManzanedaNo ratings yet
- HP EQUIVWPN-wmDocument16 pagesHP EQUIVWPN-wmstruja2010No ratings yet
- Operation Manual of Aob29 Series Digital Voltmeter&Ammeter: Chapter 1. General InstructionDocument2 pagesOperation Manual of Aob29 Series Digital Voltmeter&Ammeter: Chapter 1. General InstructionTato SierraNo ratings yet
- LEC1Document17 pagesLEC1christophermrequintoNo ratings yet
- A Reaserch Paper On Solar SystemDocument6 pagesA Reaserch Paper On Solar Systemkhan hadidNo ratings yet